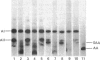
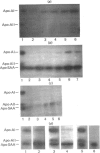
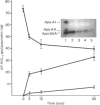
Abstract
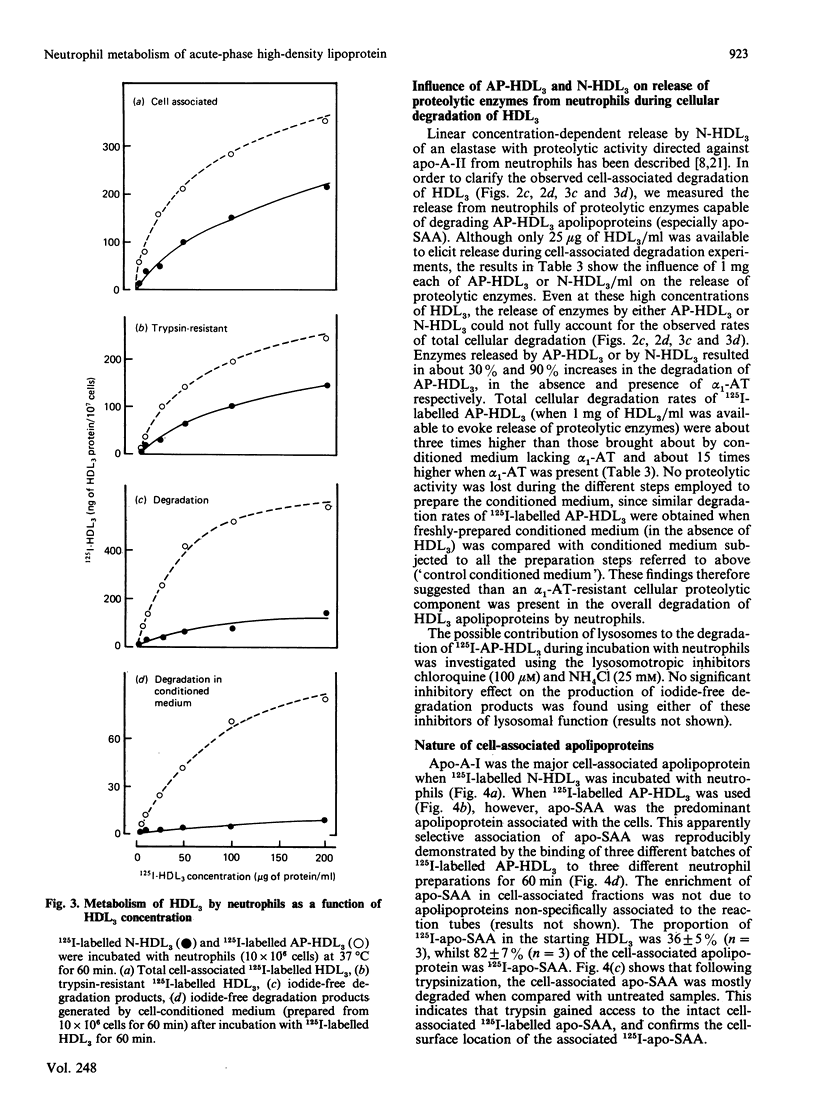
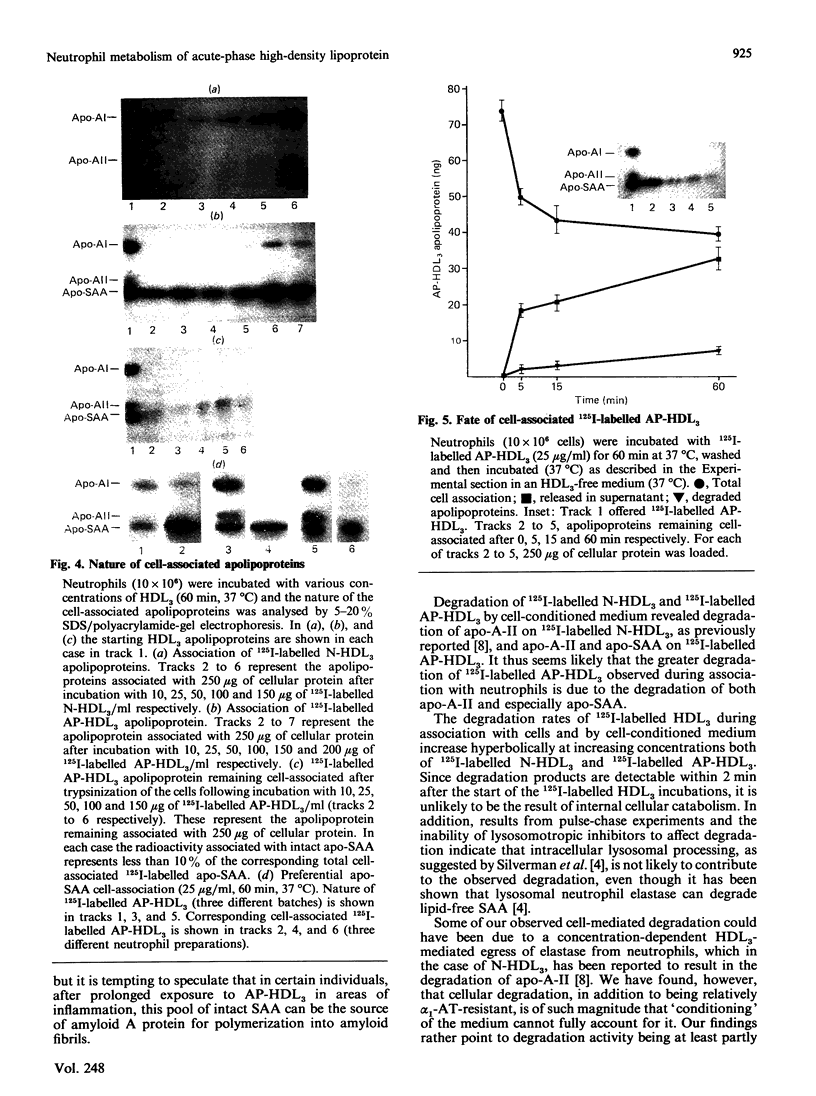
The interaction of normal and acute-phase high-density lipoproteins of the subclass 3 (N-HDL3 and AP-HDL3) with human neutrophils and the accompanying degradation of HDL3 apolipoproteins have been studied in vitro. The chemical composition of normal and acute-phase HDL3 was similar except that serum amyloid A protein (apo-SAA) was a major apolipoprotein in AP-HDL3 (approx. 30% of total apolipoproteins). 125I-labelled AP-HDL3 was degraded 5-10 times faster than 125I-labelled N-HDL3 during incubation with neutrophils or neutrophil-conditioned medium. Apo-SAA, like apolipoprotein A-II (apo-A-II), was more susceptible than apolipoprotein A-I (apo-A-I) to the action of proteases released from the cells. The amounts of cell-associated AP-HDL3 apolipoproteins at saturation were up to 2.8 times greater than N-HDL3 apolipoproteins; while apo-A-I was the major cell-associated apolipoprotein when N-HDL3 was bound, apo-SAA constituted 80% of the apolipoproteins bound in the case of AP-HDL3. The associated intact apo-SAA was mostly surface-bound as it was accessible to the action of exogenous trypsin. alpha 1-Antitrypsin-resistant (alpha 1-AT-resistant) cellular degradation of AP-HDL3 apolipoproteins also occurred; experiments in which pulse-chase labelling was performed or lysosomotropic agents were used indicated that insignificant intracellular degradation occurred which points to the involvement of cell-surface proteases in this degradation.
Full text
PDF


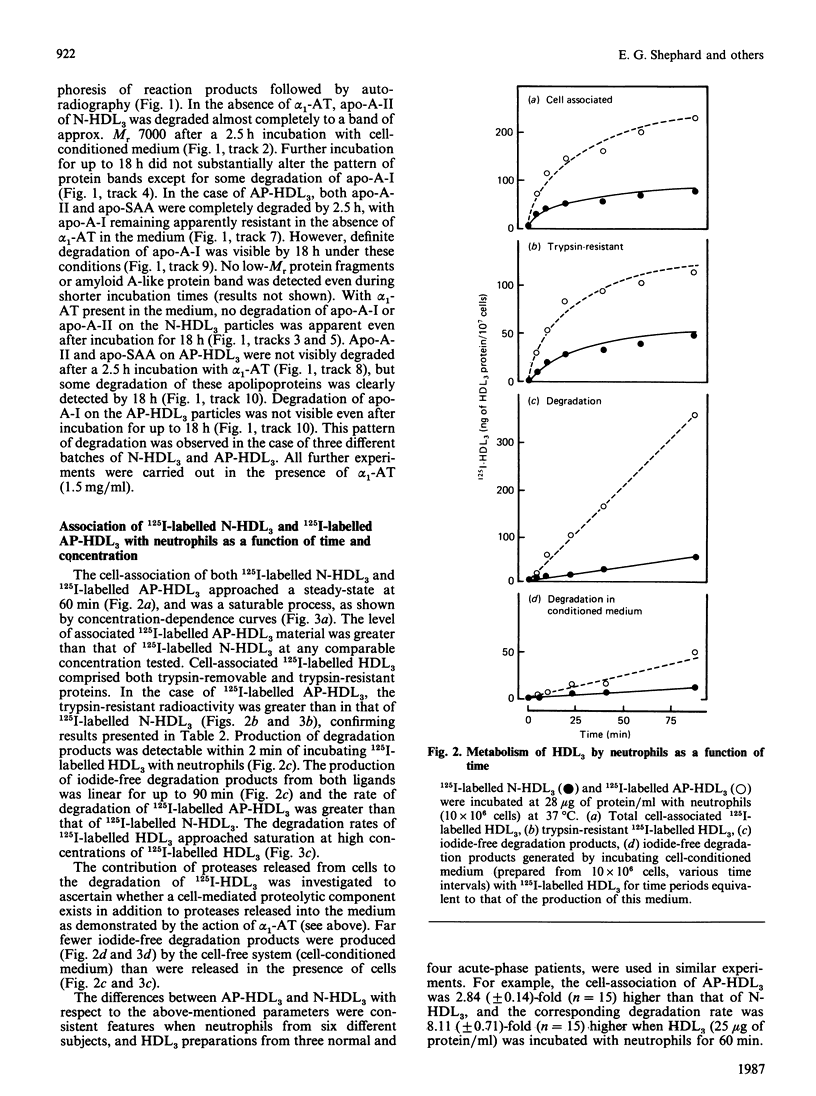


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bausserman L. L., Herbert P. N., Rodger R., Nicolosi R. J. Rapid clearance of serum amyloid A from high-density lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Feb 9;792(2):186–191. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90221-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P., Eriksen N. Amyloid protein SAA is associated with high density lipoprotein from human serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4025–4028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierman E. L., Stein O., Stein Y. Lipoprotein uptake and metabolism by rat aortic smooth muscle cells in tissue culture. Circ Res. 1974 Jul;35(1):136–150. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.1.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilheimer D. W., Eisenberg S., Levy R. I. The metabolism of very low density lipoprotein proteins. I. Preliminary in vitro and in vivo observations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 21;260(2):212–221. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne R. E., Polacek D., Gordon J. I., Scanu A. M. The enzyme that cleaves apolipoprotein A-II upon in vitro incubation of human plasma high-density lipoprotein-3 with blood polymorphonuclear cells is an elastase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14537–14543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifton P. M., Mackinnon A. M., Barter P. J. Effects of serum amyloid A protein (SAA) on composition, size, and density of high density lipoproteins in subjects with myocardial infarction. J Lipid Res. 1985 Dec;26(12):1389–1398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coetzee G. A., Strachan A. F., van der Westhuyzen D. R., Hoppe H. C., Jeenah M. S., de Beer F. C. Serum amyloid A-containing human high density lipoprotein 3. Density, size, and apolipoprotein composition. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9644–9651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. High density lipoprotein metabolism. J Lipid Res. 1984 Oct;25(10):1017–1058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen N., Benditt E. P. Trauma, high density lipoproteins, and serum amyloid protein A. Clin Chim Acta. 1984 Jul 16;140(2):139–149. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(84)90338-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godenir N. L., Jeenah M. S., Coetzee G. A., Van der Westhuyzen D. R., Strachan A. F., De Beer F. C. Standardisation of the quantitation of serum amyloid A protein (SAA) in human serum. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Nov 7;83(2):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90243-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. S., Benditt E. P. Changes in high density lipoprotein content following endotoxin administration in the mouse. Formation of serum amyloid protein-rich subfractions. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10510–10517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husebekk A., Skogen B., Husby G., Marhaug G. Transformation of amyloid precursor SAA to protein AA and incorporation in amyloid fibrils in vivo. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Mar;21(3):283–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisilevsky R., Boudreau L., Foster D. Kinetics of amyloid deposition. II. The effects of dimethylsulfoxide and colchicine therapy. Lab Invest. 1983 Jan;48(1):60–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavie G., Zucker-Franklin D., Franklin E. C. Elastase-type proteases on the surface of human blood monocytes: possible role in amyloid formation. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):175–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley J. J., Kushner I. Serum C-reactive protein levels in disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:406–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22153.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks J. S., Rudel L. L. Alteration of high density lipoprotein subfraction distribution with induction of serum amyloid A protein (SAA) in the nonhuman primate. J Lipid Res. 1985 Jan;26(1):82–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks J. S., Rudel L. L. Metabolism of the serum amyloid A proteins (SSA) in high-density lipoproteins and chylomicrons of nonhuman primates (vervet monkey). Am J Pathol. 1983 Sep;112(3):243–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polacek D., Byrne R. E., Burrous M., Scanu A. M. Factors controlling the release from human blood polymorphonuclear cells in vitro of a proteolytic activity directed against apolipoprotein A-II. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14531–14536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontremoli S., Melloni E., Michetti M., Sacco O., Sparatore B., Salamino F., Damiani G., Horecker B. L. Cytolytic effects of neutrophils: role for a membrane-bound neutral proteinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1685–1689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramadori G., Sipe J. D., Dinarello C. A., Mizel S. B., Colten H. R. Pretranslational modulation of acute phase hepatic protein synthesis by murine recombinant interleukin 1 (IL-1) and purified human IL-1. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):930–942. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shephard E. G., van Helden P. D., Strauss M., Böhm L., De Beer F. C. Functional effects of CRP binding to nuclei. Immunology. 1986 Jul;58(3):489–494. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman S. L., Cathcart E. S., Skinner M., Cohen A. S. The degradation of serum amyloid A protein by activated polymorphonuclear leucocytes: participation of granulocytic elastase. Immunology. 1982 Aug;46(4):737–744. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]