Abstract
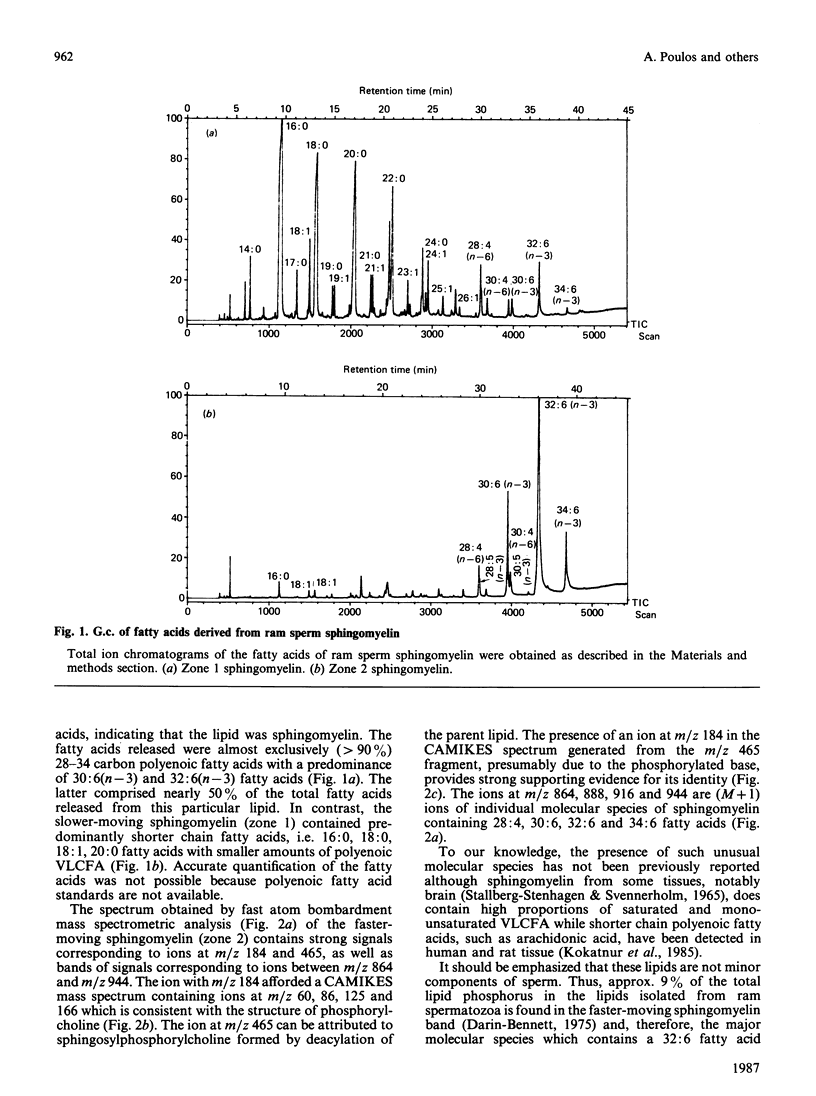
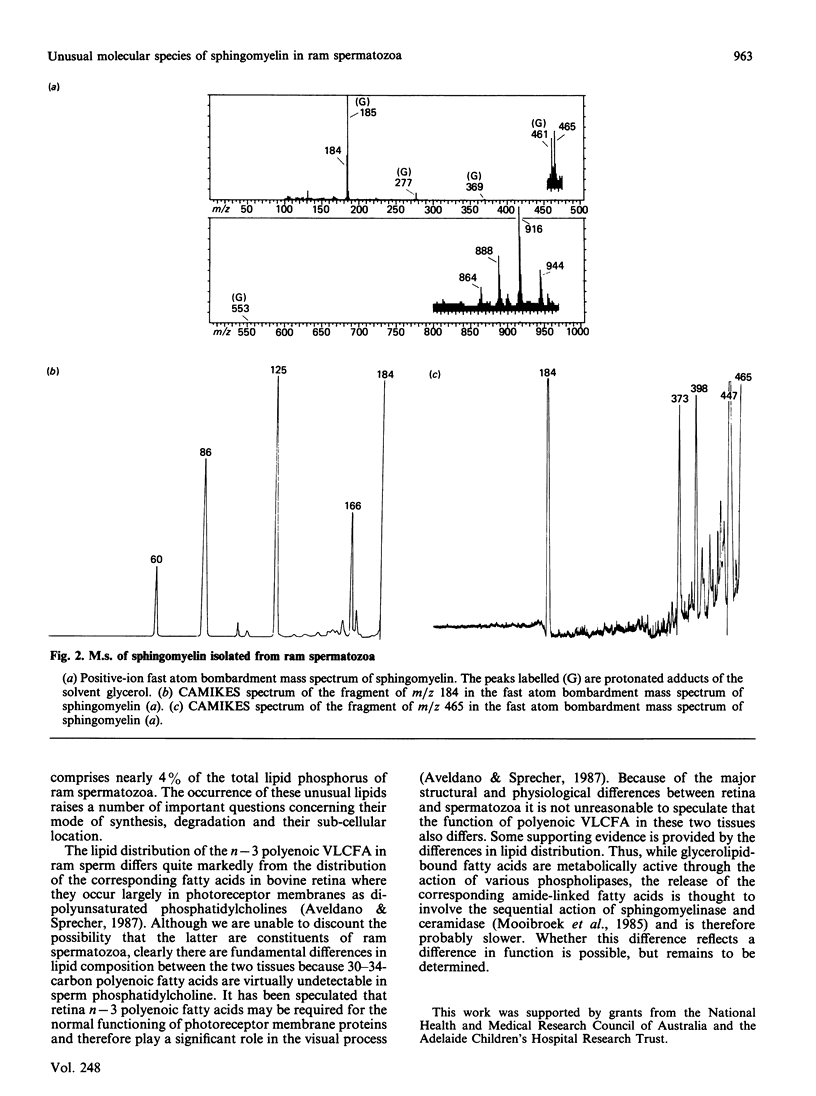
The high levels of very long chain fatty acids found in ram spermatozoa are located almost exclusively in one of two separable species of sphingomyelin. Mass spectral analysis, including fast atom bombardment of the purified sphingomyelin, has shown the fatty acids to have a carbon chain length of between 28 and 34, with between four and six double bonds, and to belong predominantly to the n-3 series.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aveldaño M. I. A novel group of very long chain polyenoic fatty acids in dipolyunsaturated phosphatidylcholines from vertebrate retina. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1172–1179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aveldaño M. I., Sprecher H. Very long chain (C24 to C36) polyenoic fatty acids of the n-3 and n-6 series in dipolyunsaturated phosphatidylcholines from bovine retina. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1180–1186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokatnur M., Brooks V., Plauche W. C. Fatty acids of sphingomyelin from amniotic fluid of normal and diabetic pregnancies. Lipids. 1985 Jul;20(7):449–453. doi: 10.1007/BF02534236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooibroek M. J., Cook H. W., Clarke J. T., Spence M. W. Catabolism of exogenous and endogenous sphingomyelin and phosphatidylcholine by homogenates and subcellular fractions of cultured neuroblastoma cells. Effects of anesthetics. J Neurochem. 1985 May;44(5):1551–1558. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb08794.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens K. A two-dimensional thin-layer chromatographic procedure for the estimation of plasmalogens. Biochem J. 1966 Aug;100(2):354–361. doi: 10.1042/bj1000354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polito A. J., Akita T., Sweeley C. C. Gas chromatography and mass spectrometry of sphingolipid bases. Characterization of sphinga-4,14-dienine from plasma sphingomyelin. Biochemistry. 1968 Jul;7(7):2609–2614. doi: 10.1021/bi00847a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos A., Sharp P., Johnson D., White I., Fellenberg A. The occurrence of polyenoic fatty acids with greater than 22 carbon atoms in mammalian spermatozoa. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):891–895. doi: 10.1042/bj2400891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos A., Sharp P., Singh H., Johnson D., Fellenberg A., Pollard A. Detection of a homologous series of C26-C38 polyenoic fatty acids in the brain of patients without peroxisomes (Zellweger's syndrome). Biochem J. 1986 Apr 15;235(2):607–610. doi: 10.1042/bj2350607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal M. D., Hill J. R. Human vascular endothelial cells synthesize and release 24- and 26-carbon polyunsaturated fatty acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 12;795(2):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAELLBERG-STENHAGEN S., SVENNERHOLM L. FATTY ACID COMPOSITION OF HUMAN BRAIN SPHINGOMYELINS: NORMAL VARIATION WITH AGE AND CHANGES DURING MYELIN DISORDERS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jan;6:146–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P., Poulos A., Fellenberg A., Johnson D. Structure and lipid distribution of polyenoic very-long-chain fatty acids in the brain of peroxisome-deficient patients (Zellweger syndrome). Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):61–67. doi: 10.1042/bj2480061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


