Abstract
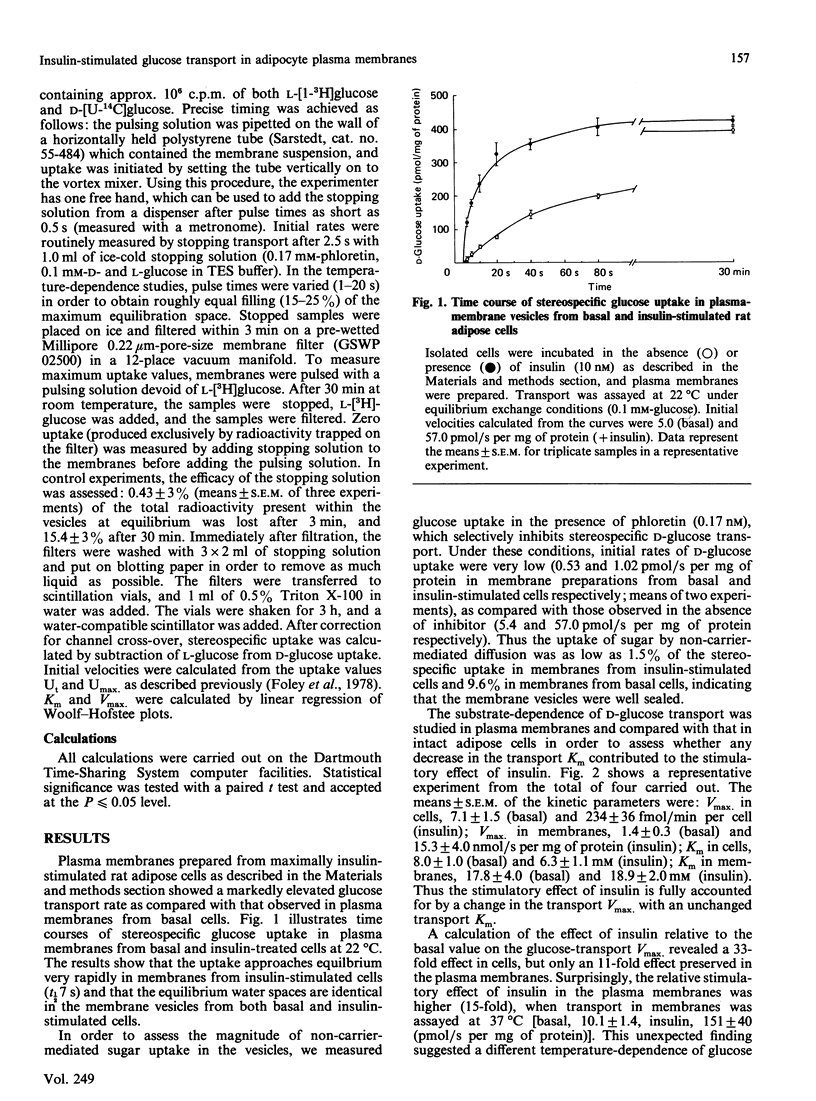
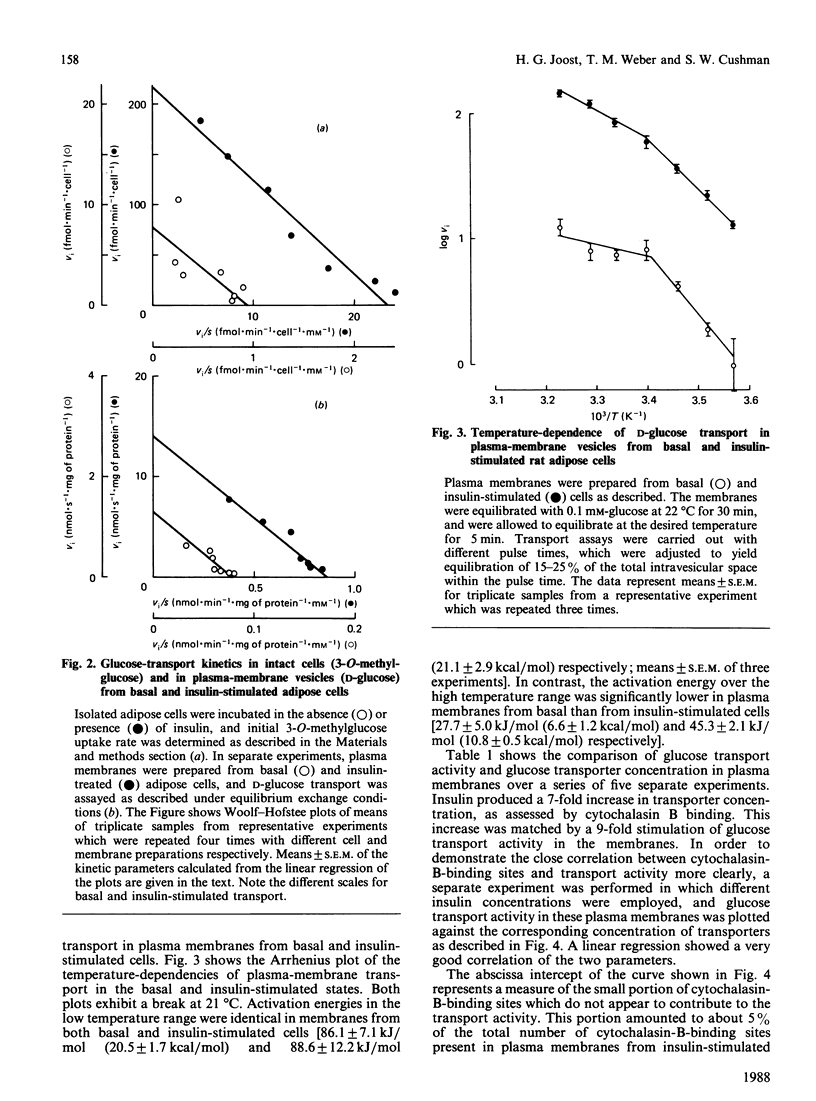
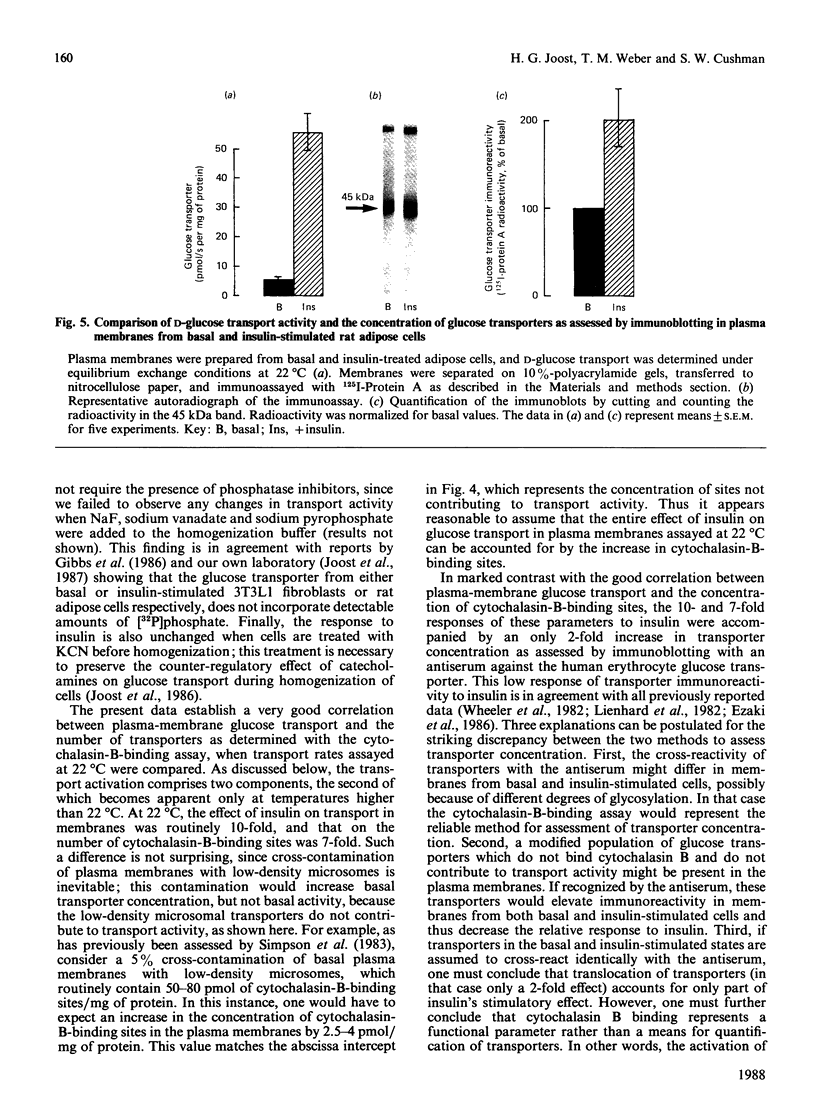
Conditions are described which allow the isolation of rat adipose-cell plasma membranes retaining a large part of the stimulatory effect of insulin in intact cells. In these membranes, the magnitude of glucose-transport stimulation in response to insulin was compared with the concentration of transporters as measured with the cytochalasin-B-binding assay or by immunoblotting with an antiserum against the human erythrocyte glucose transporter. Further, the substrate- and temperature-dependencies of the basal and insulin-stimulated states were compared. Under carefully controlled homogenization conditions, insulin-treated adipose cells yielded plasma membranes with a glucose transport activity 10-15-fold higher than that in membranes from basal cells. Insulin increased the transport Vmax. (from 1,400 +/- 300 to 15,300 +/- 3,400 pmol/s per mg of protein; means +/- S.E.M.; assayed at 22 degrees C) without any significant change in Km (from 17.8 +/- 4.4 to 18.9 +/- 1.4 nM). Arrhenius plots of plasma-membrane transport exhibited a break at 21 degrees C, with a higher activation energy over the lower temperature range. The activation energy over the higher temperature range was significantly lower in membranes from basal than from insulin-stimulated cells [27.7 +/- 5.0 kJ/mol (6.6 +/- 1.2 kcal/mol) and 45.3 +/- 2.1 kJ/mol (10.8 +/- 0.5 kcal/mol) respectively], giving rise to a larger relative response to insulin when transport was assayed at 37 degrees C as compared with 22 degrees C. The stimulation of transport activity at 22 degrees C was fully accounted for by an increase in the concentration of transporters measured by cytochalasin B binding, if a 5% contamination of plasma membranes with low-density microsomes was assumed. However, this 10-fold stimulation of transport activity contrasted with an only 2-fold increase in transporter immunoreactivity in membranes from insulin-stimulated cells. These data suggest that, in addition to stimulating the translocation of glucose transporters to the plasma membrane, insulin appears to induce a structural or conformational change in the transporter, manifested in an altered activation energy for plasma-membrane transport and possibly in an altered immunoreactivity as assessed by Western blotting.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carter-Su C., Czech M. P. Reconstitution of D-glucose transport activity from cytoplasmic membranes. Evidence against recruitment of cytoplasmic membrane transporters into the plasma membrane as the sole action of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10382–10386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Wardzala L. J. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4758–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezaki O., Kasuga M., Akanuma Y., Takata K., Hirano H., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Kasahara M. Recycling of the glucose transporter, the insulin receptor, and insulin in rat adipocytes. Effect of acidtropic agents. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3295–3305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezaki O., Kono T. Effects of temperature on basal and insulin-stimulated glucose transport activities in fat cells. Further support for the translocation hypothesis of insulin action. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14306–14310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foley J. E., Cushman S. W., Salans L. B. Glucose transport in isolated rat adipocytes with measurements of L-arabinose uptake. Am J Physiol. 1978 Feb;234(2):E112–E119. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.2.E112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs E. M., Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E. The glucose transporter in 3T3-L1 adipocytes is phosphorylated in response to phorbol ester but not in response to insulin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16597–16603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honnor R. C., Dhillon G. S., Londos C. cAMP-dependent protein kinase and lipolysis in rat adipocytes. I. Cell preparation, manipulation, and predictability in behavior. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15122–15129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joost H. G., Weber T. M., Cushman S. W., Simpson I. A. Activity and phosphorylation state of glucose transporters in plasma membranes from insulin-, isoproterenol-, and phorbol ester-treated rat adipose cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11261–11267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joost H. G., Weber T. M., Cushman S. W., Simpson I. A. Insulin-stimulated glucose transport in rat adipose cells. Modulation of transporter intrinsic activity by isoproterenol and adenosine. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10033–10036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnieli E., Zarnowski M. J., Hissin P. J., Simpson I. A., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transport systems in the isolated rat adipose cell. Time course, reversal, insulin concentration dependency, and relationship to glucose transport activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4772–4777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lienhard G. E., Kim H. H., Ransome K. J., Gorga J. C. Immunological identification of an insulin-responsive glucose transporter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Apr 14;105(3):1150–1156. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludvigsen C., Jarett L. A comparison of basal and insulin-stimulated glucose transport in rat adipocyte plasma membranes. Diabetes. 1980 May;29(5):373–378. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.5.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. B., Carter J. R., Jr Insulin-stimulated glucose uptake by subcellular particles from adipose tissue cells. Science. 1970 Feb 6;167(3919):873–874. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3919.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martz A., Mookerjee B. K., Jung C. Y. Insulin and phorbol esters affect the maximum velocity rather than the half-saturation constant of 3-O-methylglucose transport in rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13606–13609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Yver D. R., Hissin P. J., Wardzala L. J., Karnieli E., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transporters in the isolated rat adipose cells: characterization of subcellular fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 19;763(4):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Kono T. Evidence that insulin causes translocation of glucose transport activity to the plasma membrane from an intracellular storage site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2542–2545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor L. P., Holman G. D. Symmetrical kinetic parameters for 3-O-methyl-D-glucose transport in adipocytes in the presence and in the absence of insulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 6;642(2):325–335. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90449-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda N., Flanagan J. E., Kono T. Reassessment of insulin effects on the Vmax and Km values of hexose transport in isolated rat epididymal adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2737–2745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardzala L. J., Cushman S. W., Salans L. B. Mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Enhancement of the number of functional transport systems. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8002–8005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T. J., Simpson I. A., Sogin D. C., Hinkle P. C., Cushman S. W. Detection of the rat adipose cell glucose transporter with antibody against the human red cell glucose transporter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Mar 15;105(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitesell R. R., Abumrad N. A. Increased affinity predominates in insulin stimulation of glucose transport in the adipocyte. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2894–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitesell R. R., Abumrad N. A. Modulation of basal glucose transporter Km in the adipocyte by insulin and other factors. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15090–15096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]