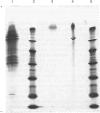
Abstract
The extracellular glucoamylase from certain strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae can be purified from culture medium by a simple chromatographic procedure. The native enzyme is heavily glycosylated and has an Mr of about 250,000, but gel filtration indicates the existence of oligomers of larger size. Dissociation yields a form of Mr about 70,000. The glucoamylase is rich in serine and threonine and in aspartic acid plus asparagine, and has a pI of 4.62 and a pH optimum of 4.5-6.5. The thermostability and resistance to denaturants of the yeast enzyme is compared with those of two other fungal glucoamylases. Kinetic data for the yeast enzyme and a variety of substrates is presented; the enzyme is particularly ineffective in cleaving alpha-(1----6)-glycosidic bonds.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of molecular size and molecular weights of biological compounds by gel filtration. Methods Biochem Anal. 1970;18:1–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEAVEN G. H., HOLIDAY E. R. Ultraviolet absorption spectra of proteins and amino acids. Adv Protein Chem. 1952;7:319–386. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigelow C. C. On the average hydrophobicity of proteins and the relation between it and protein structure. J Theor Biol. 1967 Aug;16(2):187–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(67)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. K., Trimble R. B., Maley F. The effect of carbohydrate depletion on the properties of yeast external invertase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8691–8693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. K., Watorek W., Maley F. Factors affecting the oligomeric structure of yeast external invertase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jun;223(2):543–555. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90619-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonna W. J., Magee P. T. Glycogenolytic enzymes in sporulating yeast. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):844–853. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.844-853.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOFFLER H. Protoplasmic differences between mesophiles and thermophiles. Bacteriol Rev. 1957 Dec;21(4):227–240. doi: 10.1128/br.21.4.227-240.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laluce C., Mattoon J. R. Development of Rapidly Fermenting Strains of Saccharomyces diastaticus for Direct Conversion of Starch and Dextrins to Ethanol. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jul;48(1):17–25. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.1.17-25.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lineback D. R., Russell I. J., Rasmussen C. Two forms of the glucoamylase of Aspergillus niger. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Nov;134(2):539–553. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90316-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazur J. H., Knull H. R., Simpson D. L. Glycoenzymes: a note on the role for the carbohydrate moieties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jul 13;40(1):110–116. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazur J. H., Tominaga Y., Forsberg L. S., Simpson D. L. Glycoenzymes: an unusual type of glycoprotein structure for a glucoamylase. Carbohydr Res. 1980 Sep 8;84(1):103–114. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)85434-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck D. K., Lennarz W. J., Brew K. Primary structural requirements for the enzymatic formation of the N-glycosidic bond in glycoproteins. Studies with alpha-lactalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5786–5794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Inokuchi N., Irie M. Purification and characterization of a glucoamylase from Aspergillus saitoi. J Biochem. 1981 Jan;89(1):125–134. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Tsuchida Y., Irie M. Purification and some properties of three forms of glucoamylase from a Rhizopus species. J Biochem. 1978 Nov;84(5):1183–1194. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Plummer T. H., Jr, Maley F. The release of intact oligosaccharides from specific glycoproteins by endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):818–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita I., Maemura T., Hatano T., Fukui S. Polymorphic extracellular glucoamylase genes and their evolutionary origin in the yeast Saccharomyces diastaticus. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):574–582. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.574-582.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita I., Suzuki K., Fukui S. Nucleotide sequence of the extracellular glucoamylase gene STA1 in the yeast Saccharomyces diastaticus. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):567–573. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.567-573.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]