Abstract
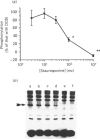
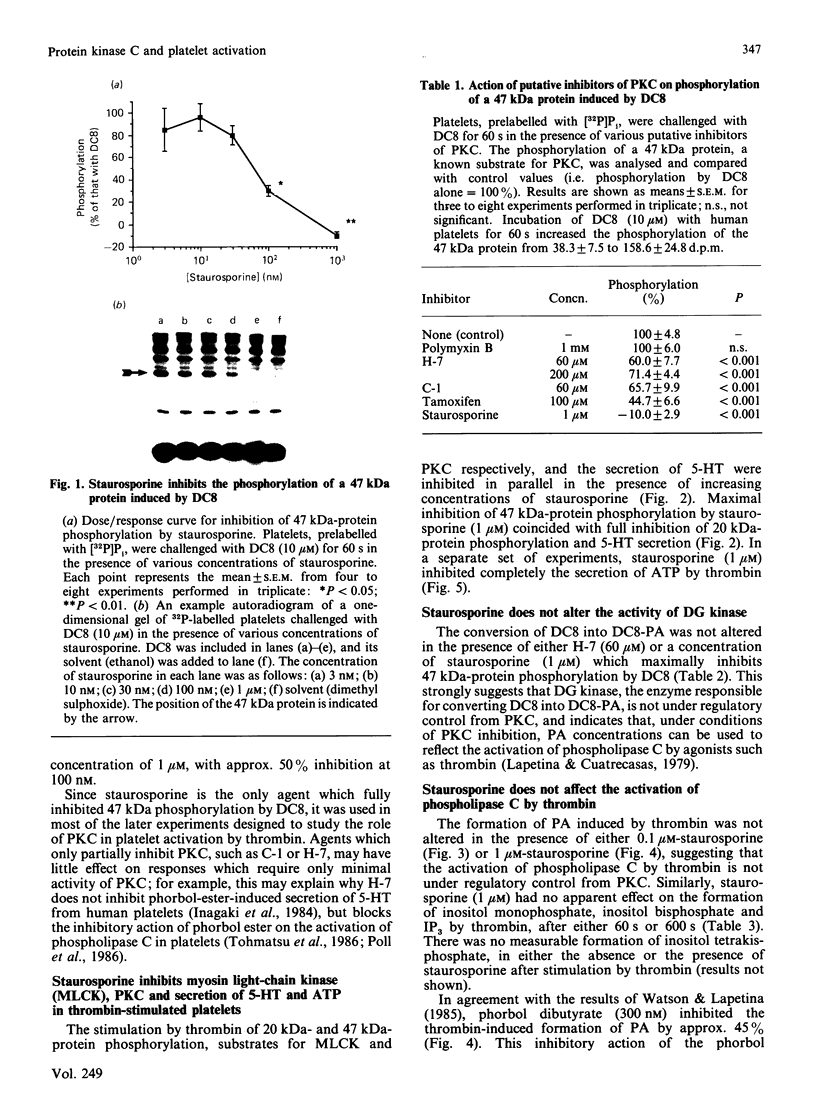
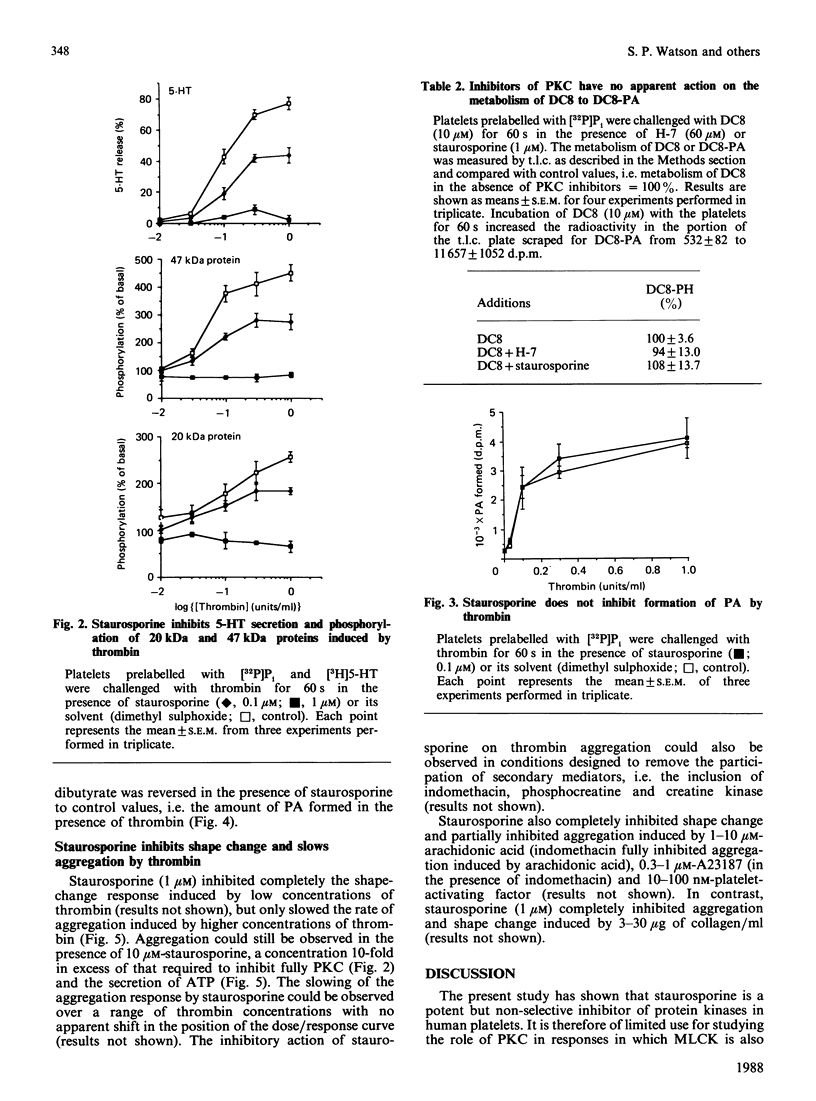
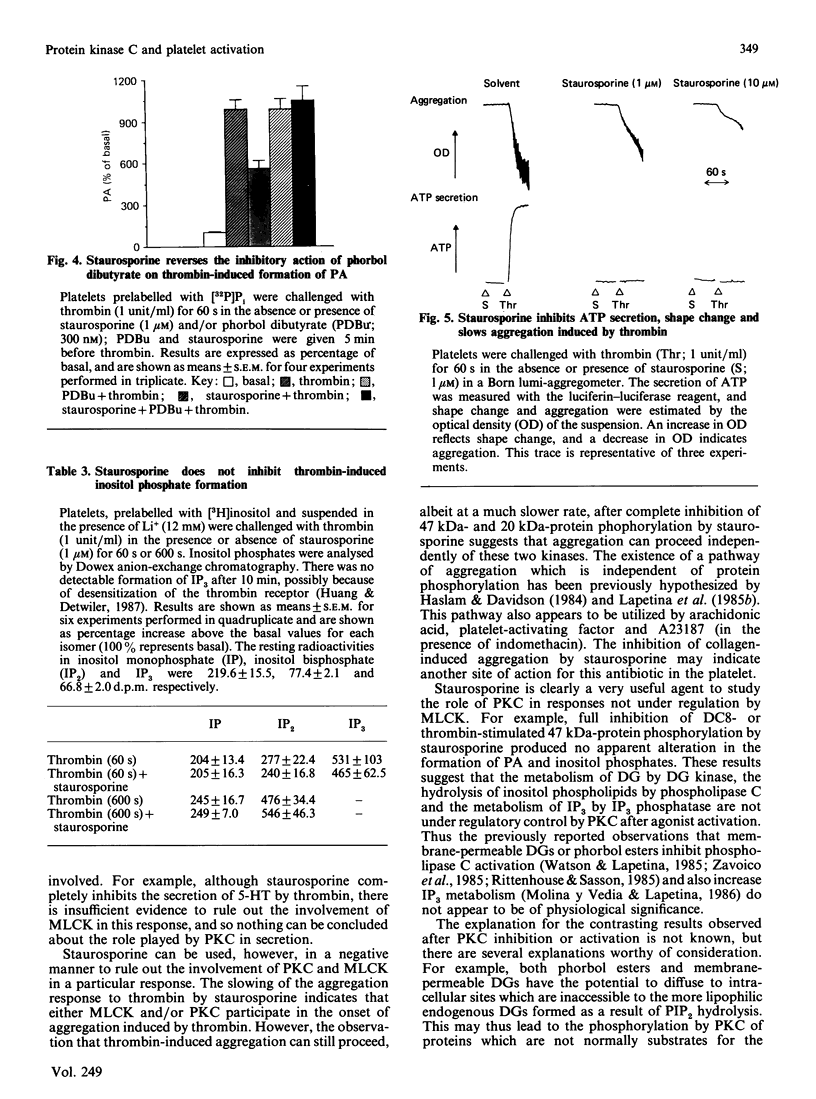
The ability of several putative inhibitors of protein kinase C (PKC) to block dioctanoylglycerol (DC8)-induced phosphorylation of a 47 kDa protein (a recognized substrate for PKC) in human platelets was investigated. Staurosporine (1 microM) caused complete inhibition of phosphorylation, whereas the other reagents were either inactive (polymyxin B) or gave only partial inhibition (C-1, H-7, tamoxifen). Staurosporine (1 microM) fully inhibited the phosphorylation of the 47 kDa protein in platelets challenged with thrombin, but also inhibited the phosphorylation of a 20 kDa protein which is a substrate for myosin light-chain kinase. The inhibition of both kinases by staurosporine was associated with the inhibition of thrombin-induced secretion of ATP and 5-hydroxytryptamine and a slowing of the aggregation response; staurosporine, however, had no effect on the formation of phosphatidic acid and inositol phosphates induced by thrombin. Staurosporine also reversed the inhibitory action of phorbol esters on thrombin-induced formation of phosphatidic acid. These data are consistent with a role for these two kinases in secretion and aggregation (although there must be additional control signals, since aggregation was only slowed, not inhibited), but suggest that neither kinase is involved in the regulation of phosphoinositide metabolism. This latter conclusion contradicts previous observations that the activation of PKC by phorbol esters or membrane-permeable diacylglycerols alters the apparent activity of both phospholipase C and inositol trisphosphatase. Possible explanations for this discrepancy are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Downes C. P., Hanley M. R. Lithium amplifies agonist-dependent phosphatidylinositol responses in brain and salivary glands. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):587–595. doi: 10.1042/bj2060587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Joseph S. K. A role for inositol triphosphate in intracellular Ca2+ mobilization and granule secretion in platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15172–15179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly T. M., Lawing W. J., Jr, Majerus P. W. Protein kinase C phosphorylates human platelet inositol trisphosphate 5'-phosphomonoesterase, increasing the phosphatase activity. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):951–958. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90077-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Parker P. J., Rhee L., Yang-Feng T. L., Chen E., Waterfield M. D., Francke U., Ullrich A. Multiple, distinct forms of bovine and human protein kinase C suggest diversity in cellular signaling pathways. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):859–866. doi: 10.1126/science.3755548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Davidson M. M. Potentiation by thrombin of the secretion of serotonin from permeabilized platelets equilibrated with Ca2+ buffers. Relationship to protein phosphorylation and diacylglycerol formation. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 1;222(2):351–361. doi: 10.1042/bj2220351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horgan K., Cooke E., Hallett M. B., Mansel R. E. Inhibition of protein kinase C mediated signal transduction by tamoxifen. Importance for antitumour activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Dec 15;35(24):4463–4465. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90764-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. M., Detwiler T. C. Thrombin-induced phosphoinositide hydrolysis in platelets. Receptor occupancy and desensitization. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 15;242(1):11–18. doi: 10.1042/bj2420011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaoka T., Lynham J. A., Haslam R. J. Purification and characterization of the 47,000-dalton protein phosphorylated during degranulation of human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11404–11414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Hidaka H. Serotonin secretion from human platelets may be modified by Ca2+-activated, phospholipid-dependent myosin phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14321–14323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Sawamura M., Hoshijima M., Fujikura T., Nishizuka Y. Synergistic functions of protein phosphorylation and calcium mobilization in platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6701–6704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto S., Hidaka H. 1-(5-Isoquinolinesulfonyl)-2-methylpiperazine (H-7) is a selective inhibitor of protein kinase C in rabbit platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 30;125(1):258–264. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80362-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthi S., Joseph S., Kakkar V. V. Synergistic potentiation of 5-hydroxytryptamine secretion by platelet agonists and phorbol myristate acetate despite inhibition of agonist-induced arachidonate/thromboxane and beta-thromboglobulin release and Ca2+ mobilization by phorbol myristate acetate. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 15;238(1):193–199. doi: 10.1042/bj2380193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Cuatrecasas P. Stimulation of phosphatidic acid production in platelets precedes the formation of arachidonate and parallels the release of serotonin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 25;573(2):394–402. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Reep B., Ganong B. R., Bell R. M. Exogenous sn-1,2-diacylglycerols containing saturated fatty acids function as bioregulators of protein kinase C in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1358–1361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Silió J., Ruggiero M. Thrombin induces serotonin secretion and aggregation independently of inositol phospholipids hydrolysis and protein phosphorylation in human platelets permeabilized with saponin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7078–7083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre D. E., Bushfield M., Shaw A. M. Regulation of platelet cytosolic free calcium by cyclic nucleotides and protein kinase C. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 2;188(2):383–388. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80407-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina y Vedia L. M., Lapetina E. G. Phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate and 1-oleyl-2-acetyldiacylglycerol stimulate inositol trisphosphate dephosphorylation in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10493–10495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Molski M. M., Sha'afi R. I. Polymyxin B inhibits phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, but not chemotactic factor, induced effects in rabbit neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 1985 Dec 2;193(2):227–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn D. L., Watson S. P. A diacylglycerol kinase inhibitor, R59022, potentiates secretion by and aggregation of thrombin-stimulated human platelets. Biochem J. 1987 May 1;243(3):809–813. doi: 10.1042/bj2430809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke F. A., Halenda S. P., Zavoico G. B., Feinstein M. B. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate releases Ca2+ from a Ca2+-transporting membrane vesicle fraction derived from human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):956–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Kawasaki H., Imajoh S., Suzuki K., Inagaki M., Yokokura H., Sakoh T., Hidaka H. Tissue-specific expression of three distinct types of rabbit protein kinase C. Nature. 1987 Jan 8;325(7000):161–166. doi: 10.1038/325161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poll C., Kyrle P., Westwick J. Activation of protein kinase C inhibits sodium fluoride-induced elevation of human platelet cytosolic free calcium and thromboxane B2 generation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90922-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock W. K., Sage S. O., Rink T. J. Stimulation of Ca2+ efflux from fura-2-loaded platelets activated by thrombin or phorbol myristate acetate. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 5;210(2):132–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Sanchez A., Hallam T. J. Diacylglycerol and phorbol ester stimulate secretion without raising cytoplasmic free calcium in human platelets. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):317–319. doi: 10.1038/305317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse S. E., Sasson J. P. Mass changes in myoinositol trisphosphate in human platelets stimulated by thrombin. Inhibitory effects of phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8657–8660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su H. D., Mazzei G. J., Vogler W. R., Kuo J. F. Effect of tamoxifen, a nonsteroidal antiestrogen, on phospholipid/calcium-dependent protein kinase and phosphorylation of its endogenous substrate proteins from the rat brain and ovary. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Oct 15;34(20):3649–3653. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tohmatsu T., Hattori H., Nagao S., Ohki K., Nozawa Y. Reversal by protein kinase C inhibitor of suppressive actions of phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate on polyphosphoinositide metabolism and cytosolic Ca2+ mobilization in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):868–875. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80500-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Lapetina E. G. 1,2-Diacylglycerol and phorbol ester inhibit agonist-induced formation of inositol phosphates in human platelets: possible implications for negative feedback regulation of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2623–2626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Reep B., McConnell R. T., Lapetina E. G. Collagen stimulates [3H]inositol trisphosphate formation in indomethacin-treated human platelets. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 15;226(3):831–837. doi: 10.1042/bj2260831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavoico G. B., Halenda S. P., Sha'afi R. I., Feinstein M. B. Phorbol myristate acetate inhibits thrombin-stimulated Ca2+ mobilization and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3859–3862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]