ABSTRACT
Aim
The aim is to delineate the concept of sleep disturbances in health professional students during the COVID‐19 pandemic.
Design
A concept analysis was conducted.
Methods
A systematic search was conducted for relevant articles published and performed from inception to July 5, 2024. Electronic databases searched included PubMed, Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), Embase and Web of Science. Rodgers' method of evolutionary concept analysis was used.
Results
A total of 50 pertinent articles were included in our analysis. Utilising inductive thematic analysis, this study identified attributes, antecedents and consequences of sleep disturbances. Important attributes included insomnia, disrupted sleep patterns, altered sleep duration/nocturnal sleep duration and poor sleep quality. Antecedents encompassed factors such as gender, age/grade levels, physical activity, screen time of digital production, mental health issues, COVID‐19‐related stressors, financial strain and academic stress. Consequences included both mental and physical health implications. By addressing sleep disturbances and promoting better sleep health among students, we can enhance their learning and performance, which could translate to improved patient care outcomes. Additionally, understanding and mitigating sleep disturbances can contribute to the development of a more resilient and effective health care workforce, capable of providing high‐quality care even during crises like the COVID‐19 pandemic.
Patient or Public Contribution
No patient or public contribution.
Keywords: concept analysis, COVID‐19, health professional students, Rodgers' evolutionary, sleep disturbances
1. Introduction
Sleep disturbances are a well‐documented issue among health professional students and health care professionals (Almojali et al. 2017; O'Byrne, Gavin, and McNicholas 2020). The COVID‐19 pandemic underscored the significant impact of unforeseen global health crises on sleep patterns, particularly in vulnerable populations, including health professional students (Cheung, Fong, and Bressington 2021; Liu et al. 2021; Tull et al. 2020). The pandemic introduced new layers of complexity: Fear of infection, increased workload, rapid changes to remote learning and altered rotation environments (Cao et al. 2020). These unprecedented stressors likely influenced sleep differently than factors explored in previous research (Almojali et al. 2017; Fawzy and Hamed 2017; O'Byrne, Gavin, and McNicholas 2020).
The COVID‐19 pandemic has highlighted the prevalence of sleep problems experienced by health professional students, with 86% reporting disruptions in their sleep patterns and overall well‐being (Son et al. 2020). However, even outside of pandemics, health professional students face unique sleep challenges due to demanding schedules, intensive clinical practice and limited opportunities for emotional support and leisure activities (Almojali et al. 2017). These factors, coupled with the potential for exposure to life‐and‐death situations, can create sleep disturbances (Liu et al. 2021) that significantly impact students' academic performance, clinical competence and long‐term well‐being (Jalali et al. 2020).
Sleep disturbances remain a common issue among health professional students due to a variety of factors, including academic stress, irregular schedules and demanding clinical rotations (Seoane et al. 2020). Given the crucial role of sleep in cognitive functioning, emotional regulation and overall well‐being (Nguyen, Zainal, and Newman 2022), it is essential to have a deeper understanding of sleep disturbances among health professional students to develop effective interventions and support systems.
However, the concept of sleep disturbances has been used inconsistently in the health professional students' context, including ‘difficulty falling asleep’ (Kochuvilayil et al. 2021; Laranjeira et al. 2021), ‘poor/worse sleep’ (Alkalash et al. 2022; da Silva et al. 2021), ‘disturbed sleep pattern’ (Gupta, Jagzape, and Kumar 2021; Singh, Kumar, and Kumari 2024; Soni et al. 2021) and insomnia (Iqbal et al. 2023; Ito et al. 2022; Liao et al. 2022). These varying definitions create confusion and hinder the comparability of research findings. The lack of a clear, unified definition has led to inconsistent measurement and assessment methods in studies on sleep disruption. This inconsistency hinders the comparability of research findings and affects the reliability of research outcomes and the effectiveness of interventions designed for this population.
To address these gaps, Rodgers' evolutionary approach was taken to a concept analysis. This method emphasises that concepts are dynamic and evolve over time with new research findings and practical experiences (Duffy, Browne, and Connolly 2024). The COVID‐19 pandemic significantly impacted students' lifestyles, psychological states and environments, directly impacting their sleep patterns (Li et al. 2024). Using Rodgers' approach allows us to capture the impact and evolution of these changes on the concept of sleep disturbances. Although the study was conducted for only 3 years, this period included significant events (e.g., pandemics) that demonstrably influenced the concept (Hutto, Raynor, and Baliko 2024).
This concept analysis aimed to examine the concept of sleep disturbances in health professional students, with a focus on the COVID‐19 pandemic. Specifically, we aimed to determine the attributes, antecedents and consequences of sleep disturbances in this population and to identify the optimal measures for future studies on interventions. By providing a clear and consistent definition of sleep disturbances among health professional students, we can improve the reliability of research outcomes and the effectiveness of interventions designed for this population. This, in turn, can have significant implications for the academic performance, clinical competence and long‐term well‐being of health professional students.
2. Methods
Rodgers' method of evolutionary concept analysis was used to analyse sleep disturbances in health professional students during COVID‐19 (Rodgers and Knafl 2000). Rodgers' method is a systematic, rigorous and reproducible method that can be used to identify the attributes (features that describe the nature of sleep disturbances), antecedents (factors that precede the existence of sleep disturbances) and consequences (factors that occur as a result of sleep disturbances) of the concept. According to Rodgers and Knafl (2000), a concept analysis consists of six iterative steps: Identifying the concept of interest; choosing the setting and sample; collecting and managing the data; analysing the data; identifying exemplars and interpreting the results and proving implications.
2.1. Identifying the Concept of Interest
The first step is to identify the concept of interest, which is sleep disturbances, and explore related surrogate terms. These surrogate terms, including sleep disorders, insomnia, sleepiness, sleep deprivation, sleep problem, sleep impairment, sleep fragmentation and sleep dysfunction, were incorporated into the literature search to ensure comprehensiveness (Rodgers and Knafl 2000). To avoid missing important studies, we included both the concept of sleep disturbances and its surrogate terms in our search. To avoid disrupting the clarification of this concept, we clearly distinguished between the literature that directly examines ‘sleep disturbances’ and the literature that examines other alternative and related concepts, such as sleep‐related breathing disorders, central disorders of hypersomnolence, circadian rhythm sleep–wake disorders, parasomnias and sleep‐related movement disorders. In our analysis, we focused on those that directly studied ‘sleep disturbances’ to ensure that the definitions and characteristics of the concepts were clarified.
2.2. Setting, Sampling and Data Sources
A systematic search was conducted for relevant articles published and performed from inception to July 5, 2024. Electronic databases searched included PubMed, Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), Embase and Web of Science. The search terms included: (1) ‘covid’, ‘pandemic’ or ‘lockdown’ (title/abstract/keywords); (2) ‘college students’ (title/abstract/keywords); (3) ‘sleep disturbances’, ‘sleep deprivation’, ‘insomnia’, ‘sleep problem*’, ‘sleep impairment’, ‘sleep fragmentation’ OR ‘sleep dysfunction’ (title/abstract/keywords).
Primary studies were considered eligible for the review if they met all of the following inclusion criteria: (1) Participants were health professional students, including medical, nursing, pharmacy students or other related health professional majors, with no restrictions on whether undergraduate or graduate students; (2) the study reported sleep‐related variables, such as sleep parameters, sleep complaints or insomnia symptoms and (3) studies used qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods. The exclusion criteria included: (1) Non‐English publications; (2) conference papers, abstracts, protocols or clinical trials; (3) only reported sleep disorders, such as sleep‐related breathing disorders, central disorders of hypersomnolence, circadian rhythm sleep–wake disorders, parasomnias or sleep‐related movement disorders and (4) animal studies.
The systematic search resulted in the retrieval of 661 records (Figure 1). After removing duplicates, 348 records underwent initial screening. Subsequently, 59 articles were reviewed in full text. Of these, 9 studies were excluded due to not involving health professional students, lacking information on sleep disturbances or being non‐English publications. Finally, 50 studies met the inclusion criteria and were eligible for concept analysis.
FIGURE 1.
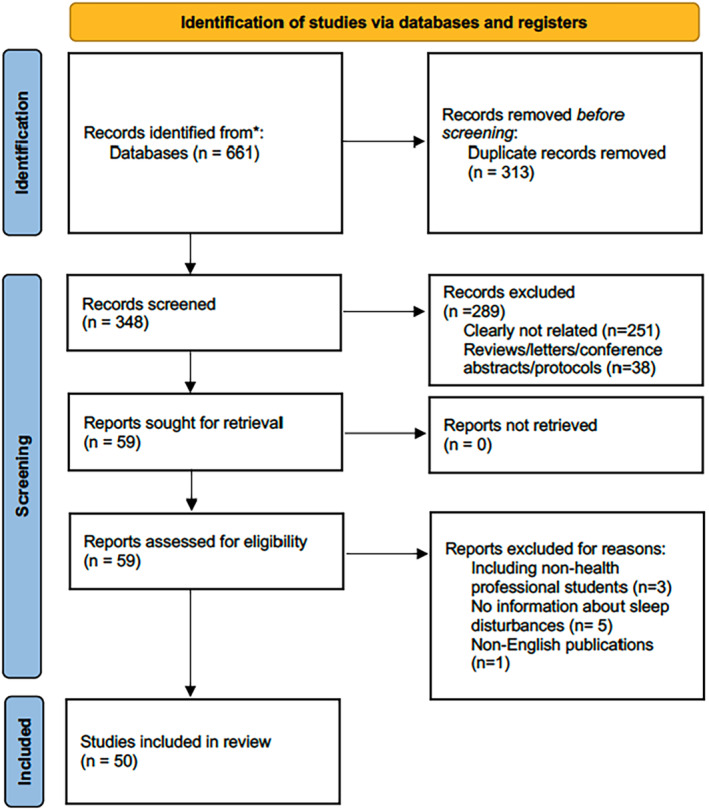
PRISMA flowchart of the study selection process.
2.3. Collecting and Managing the Data
During the data collection and management process, the primary sources were reviewed to identify the use of surrogate terms and related concepts. The main objective of concept analysis is to identify the attributes of the concept of interest. In some cases, studies may not provide a clear definition of the concept, but statements that highlight its characteristics can be used as attributes. Additionally, it is crucial to identify the contextual basis of the concept, including its antecedents and consequences. To ensure efficient and reliable abstraction of relevant information, a table matrix was utilised. Two reviewers (PC and YC) developed the matrix and reviewed the primary sources. Two reviewers (PC and YC) extracted relevant information, which was then checked by the other reviewer (WT). The information extracted included study characteristics, sentences describing the concept attributes and antecedents and consequences, which were tabulated into the matrix.
2.4. Analysing the Data
Following Rodgers' evolutionary approach, a standard procedure of thematic analysis was performed until a cohesive and comprehensive consensus was reached. The data were initially coded and analysed by two reviewers (PC and YC), who identified recurring themes for attributes, antecedents and consequences of the concept. The identified themes were then reviewed and refined by a third reviewer (WT), and appropriate ‘labels’ were developed to describe each theme. The final pool of themes was examined to ensure that all aspects of the concept were adequately captured. Using this process, a conceptual definition of sleep disturbances in medical students during the COVID‐19 pandemic was developed by the review team. This involved synthesising the themes and producing a clear and concise description of the concept that accurately reflected its attributes, antecedents and consequences.
2.5. Identifying Exemplars
Exemplars, or real‐world examples of the concept, were identified to further clarify the meaning of sleep disturbances in health professional students during COVID‐19. These exemplars provided concrete illustrations of the concept and its various manifestations.
2.6. Interpreting the Results and Proving Implications
The final step involved interpreting the results of the concept analysis and drawing implications for future research and practice, particularly in the context of public health crises such as the COVID‐19 pandemic. We identified gaps in the current understanding of sleep disturbances among health professional students during such crises and suggested directions for future research to address these gaps. Furthermore, we provided practical implications for improving the sleep health of this population during and beyond the pandemic, including recommendations for interventions, support strategies and policy changes.
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
The studies included in this concept analysis were conducted between 2020 and 2024, reflecting the recent emergence of sleep disturbances among health professional students during the COVID‐19 pandemic. The majority of the studies (47 out of 50) employed quantitative cross‐sectional designs, providing a snapshot of sleep patterns and associated factors among this population. One study was an intervention (Dwivedi et al. 2023), one used mixed‐methods study design (Gupta, Jagzape, and Kumar 2021) and one was a qualitative design (Velarde‐García et al. 2022). Sample sizes of the quantitative studies varied considerably, ranging from 10 to 3412, indicating the diversity of study populations and broad attention to this issue. The geographical distribution of the studies revealed a global reach, with studies conducted in 17 countries. However, a notable concentration of research emerged from India (20 studies, accounting for 40% of the total research), China (four studies, accounting for 8% of the total research) and Brazil (four studies, accounting for 8% of the total research). This suggests that sleep disturbances among health professional students may be particularly prevalent in these regions, possibly due to unique cultural factors, health care systems, duration of quarantine or pandemic‐related stressors. The details of the included articles are shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1.
Study characteristics (n = 50).
| Author (year) | Country | Design | Sample | Age (year) | Female | Population | Outcome measurement | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Al Maqbali et al. (2023) | United Arab Emirates | Cross‐sectional | 918 | 18 years and above | 787 (85.7) | Undergraduate nursing students | Insomnia severity index (ISI) |
| 2 | Alhamed (2023) | Saudi Arabia | Cross‐sectional | 94 | 21.3 (3.1) | 55 (59.1) | Health science students | Pittsburgh sleep quality index (PSQI) |
| 3 | Alkalash et al. (2022) | KSA | Cross‐sectional | 198 | — | 81 (40.9) | Medical students | PSQI |
| 4 | Alrashed et al. (2021) | Saudi Arabia | Cross‐sectional | 453 | 18 years and above | 207 (44.7) | 3rd to 5th year Medical students and interns | Insomnia severity index |
| 5 | Beltrame et al. (2022) | Brazil | Cross‐sectional | 200 | 22–41 | 121 (60.5) | Medical students | Portuguese—Epworth sleepiness scale (ESS‐BR) PSQI‐BR |
| 6 | Bhosale, Mathew, and Hegde (2024) | India | Cross‐sectional | 87 | — | — | Final year dental undergraduate students | Google form ‘has this lockdown period affect your sleep pattern?’ |
| 7 | Calderaro et al. (2023) | Brazil | Cross‐sectional | 684 | 23.15 ± 3.16 | 429 (63%) | Undergraduate medical students | Online surveys |
| 8 | Chhakchhuak et al. (2023) | India | Cross‐sectional | 363 | 18–25 | 135 (37.2) | Undergraduate medical students | Self‐reported sleep disturbances |
| 9 | Coppi et al. (2022) | Italy | Cross‐sectional | 810 | 19–24 | 490 (60.5) | DentistryNursing Dental Hygiene | Number of hours sleeping and changes in the actual time of going to sleep subjective perception of sleeping well or changes in quality |
| 10 | da Silva et al. (2021) | Brazil | Cross‐sectional | 161 | 18–40 | 140 (86.96) | Undergraduate students in speech‐language pathology of both genders | PSQI two items from the World Health Organization Quality of Life–Brief Version (WHOQOL‐BREF) |
| 11 | Daniel et al. (2022) | USA | Cross‐sectional | 496 | — | — | Health service Psychology graduate students | Epidemic‐pandemic impacts inventory |
| 12 | Dwivedi et al. (2023) | India | Interventional study | 549 | 19.56 (0.6) | 203 (36.08) | Undergraduate medical students | PSQI |
| 13 | Elsalem et al. (2020) | Jordan | Cross‐sectional | 1019 | — | 668 (65.6) | Medicine Dentistry Pharmacy Nursing Applied Medical Sciences | Self‐reported sleeping hours |
| 14 | François Isnaldo et al. (2023) | Brazil | Cross‐sectional | 100 | 21–40 | 74 (74) | Dental students | PSQI |
| 15 | Gupta et al. (2022) | India | Cross‐sectional | 419 | — | — | Medical students | Online semi‐structured questionnaire: Lack of proper sleep |
| 16 | Gupta, Jagzape, and Kumar (2021) | India | Mixed‐methods | 10 for qualitative, 88 for quantitative | — | — | 1st‐year Medical students | Online survey and telephonic interview |
| 17 | Haskett et al. (2022) | USA | Cross‐sectional | 195 | 24.9 (3.7) | 116 (63) | Medical students | Self‐reported survey |
| 18 | Hisato et al. (2023) | Poland | Cross‐sectional | 461 | 18 years and above | 319 (69.2) | Health professional students | Self‐reported |
| 19 | Ionescu, Chendea, and Licu (2023) | Romania | Cross‐sectional | 463 | 19 years and above | 285 (71.4) | Undergraduate medical students | ISI |
| 20 | Iqbal et al. (2023) | Malaysia | Cross‐sectional | 472 | 18 years and above | 385 (81.6) | Undergraduate medical students | ISI |
| 21 | Ito et al. (2022) | Japan | Cross‐sectional | 1197 | — | 1126 (94.1) | First‐ to fourth‐year Nursing students | Online survey‐based insomnia severity index‐7 |
| 22 | Joseph et al. (2022) | Jordan | Cross‐sectional | 207 | 18 years and above | 199 (96.1) | Nursing | Self‐reported quality of sleep: Quality of sleep (5‐point Likert): 1–slept poorly to 5–sSlept well |
| 23 | Kara (2021) | Turkey | Cross‐sectional | 402 | 18–39 | 300 (74.6) | Health professional students | Self‐reported sleep duration per night (‘1: ≤ 6 h’; ‘2: 7–8 h’; ‘3: ≥ 9 h’) the presence of sleep problems (yes or no) |
| 24 | Kochuvilayil et al. (2021) | Australia | Cross‐sectional | 212 | 18–23 | 191 (90) | Nursing students | Self‐reported |
| 25 | Kondo et al. (2021) | USA | Cross‐sectional | 557 | 20.4 (1.7) | 535 (96.1) | Undergraduate nursing students | Self‐reported sleeping hours per day |
| 26 | Kothiwale and Padhye (2023) | India | Cross‐sectional | 488 | — | — | Undergratuate dental students | Self‐reported |
| 27 | Laranjeira et al. (2021) | Portugal | Cross‐sectional | 1705 | 21.7 (4.44) | 994 (58.2) | Undergraduate nursing students | Self‐reported |
| 28 | Liao et al. (2022) | China | Cross‐sectional | 863 | 20.62 (1.45) | 532 (61.65) | Medicine Medical Technology Nursing | ISI |
| 29 | Medina‐Ramirez et al. (2022) | Peru | Cross‐sectional | 310 | 21.6 (3.0) | 193 (62.3) | Medical students | PSQI |
| 30 | Mishra et al. (2022) | India | Cross‐sectional | 267 | 18 years and above | 169 (59.5) | Undergraduate medical students | PSQI |
| 31 | Moses et al. (2023) | India | Cross‐sectional | 288 | — | 197 (68.4%) | Medical students | PSQI |
| 32 | Ranjan, Gupta, and Garg (2023) | India | Cross‐sectional | 432 | 17–25 | 190 (44) | Undergraduate medical students | Self‐reported |
| 33 | Romero‐Blanco et al. (2020 journal of clinical and diagnostic research) | Spain | Cross‐sectional | 207 | 20.57 (4.62) | 81.6 (169) | Nursing students | PSQI |
| 34 | Saraswathi et al. (2020) | India | Cross‐sectional | 217 | 20 (1.6) | 139 (64.1) | Undergraduate medical students | PSQI |
| 35 | Sasirekha et al. (2020) | India | Cross‐sectional | 200 | — | 112 (56) | Undergraduate medical and dental students | Self‐reported sleep duration |
| 36 | Sawant et al. (2023) | India | Cross‐sectional | 346 | 20.5 (2.5) | 138 (39.9) | Undergraduate medical students | Self‐reported |
| 37 | Sebastian, Tojo, and Fathima (2023) | India | Cross‐sectional | 171 | — | — | Medical students | PSQI |
| 38 | Shrestha et al. (2021) | Nepal | Cross‐sectional | 200 | 21.57 (1.52) | 60 (35.71) | Medical students | PSQI self‐reported sleep duration self‐reported sleep latency |
| 39 | Singh et al. (2021) | India | Cross‐sectional | 2225 | — | 1378 (61.9) | Medical students Nursing students | Self‐reported sleep disturbances |
| 40 | Singh, Kumar, and Kumari (2024) | India | Cross‐sectional | 145 | 18–25 | 61 (42.1) | Undergraduate medical students | Self‐reported |
| 41 | Singla, Chatterjee, and Mithra (2023) | India | Cross‐sectional | 319 | 19–22 | 192 (60.2) | Medical students | Self‐reported |
| 42 | Soni et al. (2021) | India | Cross‐sectional | 145 | 21.7 (6.56) | 61 (42.1) | Undergraduate medical students | Self‐reported disturbed sleep pattern |
| 43 | Sundarasamy, Thamizharasan, and Lalan (2020) | India | Cross‐sectional | 470 | — | 256 (54.5) | Medical students | Self‐reported sleep pattern change |
| 44 | Sweety et al. (2023) | India | Cross‐sectional | 390 | 19.6 (2.4) | 208 (53.3) | Medical students | Self‐reported |
| 45 | Swetha and Sumitra (2023) | India | Cross‐sectional | 100 | 19–23 | — | Medical students | Questionnaire |
| 46 | Velarde‐García et al. (2022) | Spain | Qualitative study | 18 | 21–31 | 17 (94.4) | Undergraduate nursing students | Self‐reported |
| 47 | Wang et al. (2023) | China | Cross‐sectional | 3412 | 18 years and above | 2345 (68.7%) | Undergraduate medical students | ESS |
| 48 | Wu et al. (2022) | China | Cross‐sectional | 1336 | 18 years and above | 700 (52.4) | Medical students | PSQI |
| 49 | Xu et al. (2022) | China | Cross‐sectional | 402 | — | 297 (73.88) | Medical students | Self‐reported insomnia |
| 50 | Yadav et al. (2021) | Nepal | Cross‐sectional | 409 | 18–37 | 340 (83.1) | Health science students | Self‐reported sleep during the day |
3.2. Attributes
Attributes are the defining characteristics of a concept and provide context for its meaning (Rodgers and Knafl 2000). Based on the descriptions of sleep disturbances in the primary sources, four key attributes emerged: (1) Insomnia; (2) altered circadian patterns; (3) changed sleep duration/nocturnal sleep duration and (4) poor sleep quality. All the sleep‐related outcomes were self‐reported. Among these studies, 21 used the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) or Insomnia Severity Index (ISI) as their outcome measurements. The use of these validated sleep assessment tools provides some degree of consistency and comparability across the findings.
3.2.1. Insomnia
The first attribute identified in relation to sleep disturbances in health professional students is insomnia. The AASM International Classification of Sleep Disorders—Third Edition, Text Revision (ICSD‐3‐TR; AASM 2023) defines insomnia as a persistent difficulty with sleep initiation, duration or consolidation that occurs despite adequate opportunity and circumstances for sleep and results in concern, dissatisfaction or perceived daytime impairment. The ICSD‐3‐TR identifies three distinct types of insomnia: Short‐term insomnia disorder, chronic insomnia disorder and other insomnia disorders (AASM 2023). Complications of persistent insomnia increase risks for new onset or recurrence of depressive and other psychiatric disorders, as well as suicidality (AASM 2023).
The prevalence of insomnia in health professional students ranges from 18% to 73.2% in six studies (Al Maqbali et al. 2023; Alrashed et al. 2021; Ionescu, Chendea, and Licu 2023; Iqbal et al. 2023; Ito et al. 2022; Liao et al. 2022). All these six studies used the ISI to assess insomnia, which consists of seven items on a 5‐point Likert scale (Bastien, Vallières, and Morin 2001) and measures the severity of difficulty falling asleep, the severity of difficulty staying asleep, early morning awakening, satisfaction with current sleep, interference with daily functioning, noticeability of impairment attributed to insomnia and duration of insomnia.
3.2.2. Altered Circadian Patterns
The second attribute identified is an altered circadian pattern, reflecting disruptions in the normal sleep–wake cycle. Ten articles reported distributed sleep patterns (Beltrame et al. 2022; Bhosale, Mathew, and Hegde 2024; Calderaro et al. 2023; Gupta et al. 2022; Gupta, Jagzape, and Kumar 2021; Kothiwale and Padhye 2023; Ranjan, Gupta, and Garg 2023; Singh, Kumar, and Kumari 2024; Soni et al. 2021; Sundarasamy, Thamizharasan, and Lalan 2020). One study observed ‘irregular sleep habits with the participants going to bed later (66.5%) and getting up later (66.0%) than before the pandemic’ (Beltrame et al. 2022). In a qualitative study, students reported alteration in their sleep cycles, sleeping at odd times in the night and waking up only because of their classes to attend. They expressed their concern: ‘This is not healthy’, ‘It has affected my sleep‐wake cycle’ and ‘I sleep late after checking my social media and the first thing I do in the morning is to check my account’ (Guo et al. 2022). The prevalence rates of altered circadian patterns ranged from 26.0% to 58.5% (Guo et al. 2022; Soni et al. 2021; Sundarasamy, Thamizharasan, and Lalan 2020), indicating that a significant proportion of the population has been affected.
3.2.3. Changed Sleep Duration/Nocturnal Sleep Duration
The third attribute encompasses alterations in sleep duration, involving both increases and decreases (Beltrame et al. 2022; Coppi et al. 2022; Elsalem et al. 2020; Kara 2021; Kondo et al. 2021; Kothiwale and Padhye 2023; Sasirekha et al. 2020). Among the reviewed studies, four studies used nocturnal sleep duration as a metric to evaluate changes in sleep patterns (Beltrame et al. 2022; Coppi et al. 2022; Elsalem et al. 2020; Kara 2021). Conversely, the other five referenced daily sleep duration, which could encompass nighttime sleep as well as daytime napping (Gupta, Jagzape, and Kumar 2021; Kondo et al. 2021; Kothiwale and Padhye 2023; Sasirekha et al. 2020; Yadav et al. 2021).
Phrases such as ‘sleep less than normal’, ‘insufficient sleep time’ and ‘reduction in sleep duration’ were employed to describe diminished sleep duration or nocturnal sleep duration. Optimal continuous sleep time for feeling rested was typically 8 h, but health professional students reported median nighttime sleep durations ranging from 6.7 to 7 h, indicating a significant decrease compared to pre‐pandemic periods (Beltrame et al. 2022). In this study, students reported sleeping less than usual, both on weekdays and weekends, with 44.0% (88 out of 200) and 54.5% (109 out of 200) sleeping less than usual, respectively (Beltrame et al. 2022). These differences were statistically significant (p < 0.001) when compared to the pre‐pandemic period (Beltrame et al. 2022). Coppi et al. (2022) found that 68.6% of 500 students had reduced sleeping duration but did not provide further details on the extent of this decrease. Another study also reported that students were oversleeping or reducing sleeping (Kothiwale and Padhye 2023). Similarly, Elsalem et al. (2020) reported that 44.2% of 1019 participants experienced a reduction in sleep hours, without providing additional information. In contrast, Gupta, Jagzape, and Kumar (2021) reported an increase in average sleep duration from 6.68 h before lockdown to 8.10 h during lockdown after using social media. In the study by Sasirekha et al. (2020), 41.5% of 200 students felt their sleep quota was insufficient. Finally, in the research of Yadav et al. (2021), 11.0% of 409 students reported sleeping less than 6 h per day.
3.2.4. Poor Sleep Quality
The fourth attribute of sleep disturbances is poor sleep quality, which was mentioned in 18 studies. Thirteen studies used the PSQI to measure sleep quality (Alkalash et al. 2022; Beltrame et al. 2022; da Silva et al. 2021; Dias Caldeira et al. 2023; Dwivedi et al. 2023; Medina‐Ramirez et al. 2022; Mishra et al. 2022; Moses et al. 2023; Romero‐Blanco et al. 2020; Saraswathi et al. 2020; Sebastian, Tojo, and Fathima 2023; Shrestha et al. 2021; Wu et al. 2022), while five studies used self‐reported assessments of good or poor sleep quality (Coppi et al. 2022; Joseph et al. 2022; Singla, Chatterjee, and Mithra 2023; Sundarasamy, Thamizharasan, and Lalan 2020; Swetha and Sumitra 2023). Global PSQI scores range from 1 to 21, and higher scores indicate poor sleep quality (Buysse et al. 1989). Studies reported percentages of poor sleep quality ranging from 9.4% to 78.5% (Alkalash et al. 2022; Mishra et al. 2022; Romero‐Blanco et al. 2020; Sebastian, Tojo, and Fathima 2023; Shrestha et al. 2021; Singla, Chatterjee, and Mithra 2023; Wu et al. 2022), with variations in cutoff values for distinguishing good and poor sleep quality. Beltrame et al. (2022) assessed self‐perceived sleep quality using a 10‐point Likert scale, comparing sleep before and during the pandemic. They found a statistically significant decrease (p < 0.001) from 8 to 6 h. Among the health professional students experiencing sleep deprivation, 76.5% reported poor sleep quality, with 40.0% having drowsiness, especially prominent among women (p < 0.05). These individuals also had lower quality of life and more adverse psychological and physical outcomes than men (p < 0.05). da Silva et al. (2021) reported a median global PSQI score of 9, indicating overall poor sleep quality in this population. Mishra et al. (2022) found a mean global PSQI score of 5.8 points overall (SD = 3.3), 5.7 points for males (SD = 3.2) and 5.9 points for females (SD = 3.4); individuals who exercised for less than 3 days per week, spent at least 8 h per day using screens, had anxiety symptoms and were not satisfied with themselves were more likely to report poor sleep quality. Moses et al. (2023) reported a global PSQI of 6.33 ± 2.13, with 78.6% of 226 health professional students experiencing poor sleep quality, whereas 21.5% of 62 had good sleep quality. Saraswathi et al. (2020) found that 34.6% of students exhibited poor sleep quality. Shrestha et al. (2021) reported that around 30.0% (n = 51) of students had poor sleep quality (PSQI total score of > 5), with an average PSQI score of 4.24 ± 2.19. Sebastian, Tojo, and Fathima (2023) reported that 9.4% had bad sleep quality during lockdown, which reduced to 4.7% post‐lockdown. It is noteworthy that the literature using the PSQI employs varying cut‐off values to distinguish between good and poor sleep quality. This inconsistency in scoring can potentially affect the comparability of findings across studies. Some studies used a PSQI score greater than 7 as a threshold for poor sleep quality, while others used a lower cutoff of 5. This variability in scoring practices underscores the need for standardised guidelines and consistent application of sleep assessment tools to facilitate meaningful comparisons and aggregation of results.
3.3. Antecedents
Antecedents are events or factors that precede the existence of sleep disturbances and may contribute to the development of a concept (Rodgers and Knafl 2000). Several factors have been identified as antecedents of sleep disturbances in health professional students, which include the following.
3.3.1. Demographic Factors
Research indicates that sleep disturbances among health professional students are notably linked to specific demographics.
3.3.1.1. Gender
Four scholarly articles identified gender as a significant factor in sleep disturbance, particularly highlighting the increased risk faced by women (Beltrame et al. 2022; Shrestha et al. 2021; Wang et al. 2023). According to the articles, women are approximately 1.67 to 2.25 times more likely to experience sleep disturbances than are men (Beltrame et al. 2022; Shrestha et al. 2021). However, one study pointed out that the female gender was a protective factor for the risk of insomnia (Al Maqbali et al. 2023).
3.3.1.2. Age/Grade Level
Studies by Alrashed et al. (2021), Al Maqbali et al. (2023), Shrestha et al. (2021) and Wu et al. (2022) have shown a higher prevalence of sleep disturbances among older students and those in more advanced academic years. Additionally, interns exhibited a threefold higher risk of experiencing sleep disturbances compared to other medical students within the health professional cohort (Alrashed et al. 2021). Meanwhile, students from the classes of 2019/2020 or later had nearly double the risk of sleep disturbances compared to students of the class of 2018 or prior (Shrestha et al. 2021; Wu et al. 2022).
3.3.2. Lifestyle Factors
3.3.2.1. Physical Activity
Insufficient physical activity is associated with an increased risk of poor sleep quality (Mishra et al. 2022). This study examined the association between physical activity levels and sleep quality using the PSQI among health professional students. They demonstrated that health professional students who exercised for fewer than 3 days per week had a higher risk of poor sleep quality, with an odds ratio (OR) of 1.81 (95% CI: 1.01–3.23).
3.3.2.2. Screen Time of Digital Production
Students spending longer than 8 h of screen time per day were more likely to report poor sleep quality (OR = 2.02; 95% CI, 1.12–3.66; Mishra et al. 2022). About 41.5% of health professional students felt that their sleep disturbances were a result of mobile phone use (Sasirekha et al. 2020).
3.3.3. Psychosocial Factors
3.3.3.1. Mental Health Issues
Anxiety, depression and stress are strongly associated with the increasing risk of sleep disturbances among health professional students (Alhamed 2023; Haskett et al. 2022; Saraswathi et al. 2020; Singh et al. 2021). One study mentioned that sleep disturbances were suggested as a partial mediator between academic stress and depressive symptoms (Alhamed 2023). Haskett et al. (2022) reported that students with a lower resilience score reported higher sleep disturbances. Notably, Saraswathi et al. (2020) found a bidirectional association between poor sleep quality and mental health. In that study, students with higher depression, anxiety and stress scores during the COVID‐19 pandemic were found to be more likely to have poor sleep quality. Meanwhile, poor sleep quality was found to be significantly associated with an increase in depression, anxiety and stress. A study by Singh et al. (2021) demonstrated that anxiety was a strong predictor (Wald's coefficient = 13.53) of sleep disturbances.
3.3.3.2. COVID‐19‐Related Factors
A study of final‐year dental undergraduate students reported that 62.1% experienced changes in their sleeping patterns during the lockdown period (Bhosale, Mathew, and Hegde 2024). Fear of COVID‐19 and exposure to COVID‐19 patients have been linked to sleep disturbances in health professional students (da Silva et al. 2021; Ito et al. 2022). Health professional students who visited any clinic during COVID‐19 had a higher risk of sleep disturbances compared to those who did not visit any clinic (OR = 2.32: 95% CI, 0.79–6.75; Alrashed et al. 2021). Students with a higher fear of COVID‐19 had a higher risk of sleep disturbances compared to those with lower fear (OR = 1.05: 95% CI, 1.01–1.08; Ito et al. 2022). Additionally, Al Maqbali et al. (2023) reported that the higher fear of COVID‐19 had a relationship with the total score of ISI (OR = 0.199). They used the Fear of COVID‐19 Scale (FCV‐19S) to measure the fear of COVID‐19 (Ahorsu et al. 2022). Total scores ranged from 7 to 35, with a higher score representing greater fear of COVID‐19.
3.3.3.3. Financial Strain
Financial strain is associated with sleep disturbances. Students who reported worsened financial situations were at higher risk of sleep disturbances (OR = 1.44; 95% CI, 1.01–2.05) than participants whose financial situation had not changed (Ito et al. 2022).
3.3.4. Academic Factors
3.3.4.1. Exam or Study Stress
Remote exams, online learning and long class duration were some of the factors that contributed to sleep disturbances among health professional students. One study reported that 50.6% of students had academic stress, mostly stressed about academic overload (31% to 34%), taking tests (28% to 29%), deadlines (27%) and too many changes at the same time (19% to 22%; Alhamed 2023). Another study reported a significant negative correlation between online learning satisfaction and insomnia (r = −0.25; p < 0.001; Ionescu, Chendea, and Licu 2023). Moreover, students who complained that the duration of online class was longer than 4 h per day had a higher risk of sleep disturbances (β = 23.33, p < 0.001; Singh et al. 2021).
3.4. Consequences of Sleep Disturbances in Health Professional Students
Sleep disturbances in health professional college students can have a significant impact on their academic performance (Alkalash et al. 2022; Medina‐Ramirez et al. 2022), physical health and mental health. One study reported that 91.0% of students who got GPAs 2–2.5 were having poor sleep quality (Alkalash et al. 2022). Another study reported that sleep quality was related to academic satisfaction (Medina‐Ramirez et al. 2022). Sleep disturbances can also lead to physical health issues; one study reported that sleep disturbances were associated with an increased risk of headache in health professional students (β = 32.88, p < 0.001; Singh et al. 2021). Moreover, students with poor sleep quality had greater neuroticism scores on the self‐reported Neuroticism, Extraversion and Openness Personality Inventory (NEO‐PI), a measure of personality traits (1 = strong disagreement and 5 = strong agreement; Moses et al. 2023).
Among the mental health variables, well‐being, depression, anxiety and stress were commonly observed (Chhakchhuak et al. 2023; Saraswathi et al. 2020; Soni et al. 2021; Velarde‐García et al. 2022; Xu et al. 2022; Yadav et al. 2021). These mental health issues were assessed using validated measures such as the Depression Anxiety Stress Scale (DASS), Perceived Stress Scale (PSS) and Impact of Event Scale‐Revised (IES‐R). A study by Saraswathi et al. showed a bidirectional association between sleep disturbances and depression, anxiety and stress (Saraswathi et al. 2020). In this study, 34.6% of the population suffered from poor sleep quality, which was found to be a significant independent predictor of depression (OR = 1.34, 95% CI = 1.19, 1.50), anxiety (OR = 1.23, 95% CI = 1.11, 1.36) and stress (OR = 1.37, 95% CI =1.21, 1.56) during COVID‐19 (Saraswathi et al. 2020). Chhakchhuak et al. (2023)reported that sleep disturbances were a predictor of anxiety (OR = 0.46). Soni et al. reported that 5.5% of students reported that they spend more time sleeping, which also causes stress reduction (Soni et al. 2021). In a qualitative study, a student said, ‘I had trouble sleeping, I would lie in bed, I couldn't breathe, I thought I had caught the coronavirus, then I realized it was a little bit of anxiety’ (Velarde‐García et al. 2022). Another study also reported that sleep less than average (≤ 6 h) compared to normal (7–8 h) increased the risk of anxiety (OR = 2.65; Yadav et al. 2021). A study by Xu et al. (2022) reported that students who had insomnia often had lower well‐being scores compared to those who had no insomnia.
The consequences of sleep disturbances in this population may manifest as detrimental effects on academic performance, mental health and physical health. Sleep disturbances have been associated with decreased academic performance, compromised mental health outcomes, heightened stress levels, exacerbation of existing medical conditions and reduced overall well‐being among health professional students. These findings underscore the importance of addressing sleep disturbances in health professional students to promote their overall well‐being and prevent the development of mental and physical health problems.
3.5. Conceptual Definition
Based on the attributes, antecedents and consequences identified above, we propose the following definition of sleep disturbances in health professional students during COVID‐19:
Sleep disturbances are a multifaceted condition encompassing various manifestations, including insomnia, altered circadian patterns, changed sleep duration/nocturnal sleep duration, and poor sleep quality. Insomnia represents difficulties initiating or maintaining sleep, leading to sleep fragmentation and daytime impairment. Altered circadian patterns manifest as disruptions in the normal sleep‐wake cycle, including irregularities in sleep timing and duration. Changed sleep duration/nocturnal sleep duration refers to deviations from regular sleep patterns, either in increased or decreased sleep duration, impacting restorative sleep quality. Poor sleep quality encompasses subjective experiences of unsatisfactory sleep, often linked to sleep fragmentation, non‐restorative sleep, and daytime dysfunction.
Sleep disturbances among health professional students can stem from various antecedents, including higher age/grades, gender, academic stressors such as study or upcoming exams, psychological factors including depression, anxiety, and stress, heightened fears related to COVID‐19, increased screen time involving digital devices, reduced physical activity, and financial stressors. The consequences of sleep disturbances included worse academic performance, compromised mental health outcomes, heightened stress levels, exacerbation of existing medical conditions, and reduced overall well‐being among health professional students.
This proposed conceptual definition provides a comprehensive understanding of sleep disturbances specifically tailored to the context of health professional students during the COVID‐19 pandemic and similar emerging issues.
3.6. Providing Exemplar
The next step is identifying an exemplar. In Rodgers and Knafl (2000) approach, an exemplar is an actual practical demonstration of the concept in a relevant real‐life example of how the concept may be identified. The exemplar case model shown in Table 2 describes sleep disturbances in health professional students.
TABLE 2.
Exemplar demonstrating the empirical use of sleep disturbance in health professional students during COVID‐19.
| Participant characteristics | Attributes reflected | Antecedents reflected | Consequences reflected |
|---|---|---|---|
|
A nursing student in their third year of their studies is required to be a clinical intern during COVID‐19 Sleep: difficult to fall asleep at night due to worry about COVID‐19 and the exam results. Whenever they thought of the exam, they could not breathe and thought they had anxiety. They woke up several times during sleep, and the sleep duration decreased. The student felt a headache after sleeping from time to time and had poor sleep quality |
Altered circadian patterns Changed sleep duration Poor sleep quality |
COVID‐19 related factor (the fear of COVID‐19) Academic stress |
Physical health issue (headache) Mental health issue (anxiety) |
4. Discussion
This concept analysis of sleep disturbances among health professional students during the COVID‐19 pandemic revealed differences in antecedents, attributes and consequences, indicating the complexity of this concept. Various factors, including fear of COVID‐19 exposure and actual contact with infected patients, emerged as significant contributors to sleep disturbances (Alrashed et al. 2021; Bhosale, Mathew, and Hegde 2024). Specifically, health professional students who visited clinics during the pandemic experienced a markedly higher risk of sleep disturbances (OR = 2.32: 95% CI, 0.76–6.75) compared to those who did not (Alrashed et al. 2021). Fear of COVID‐19 was also linked to an increased risk of sleep disturbances (OR = 1.05: 95% CI, 1.01–1.08; Ito et al. 2022).
We also identified the attributes of this concept of sleep disturbances, which include insomnia, altered circadian patterns, changed sleep duration/nocturnal sleep duration and poor sleep quality. First, the high prevalence of insomnia reflects that insomnia is a common problem among health professional students, who often face intense academic pressure and irregular work schedules (Alrashed et al. 2021). Second, altered circadian patterns indicate a disruption of the normal sleep–wake cycle, manifested in different sleep and wake times than before the pandemic (Kothiwale and Padhye 2023). Additionally, changes in sleep duration include both increases and decreases in sleep time. Most studies indicated an overall decrease in sleep duration during the pandemic (Beltrame et al. 2022; Coppi et al. 2022; Yadav et al. 2021). Poor sleep quality was another major issue faced by health students during the pandemic (Medina‐Ramirez et al. 2022). Despite variations in the PSQI scale used in different studies, the overall trend showed a significant decrease in sleep quality among students during the pandemic.
Sleep disturbances not only affect health professional students' academic performance but also have a profound impact on their mental and physical health. Theoretical implications from this analysis resonate with the previous diathesis–stress model. This model emphasises the interaction between predisposing factors (diathesis) and stressful events (Healey et al. 1981). In the context of sleep, it can suggest that biological vulnerabilities or predispositions interact with stressful life events, contributing to the onset or exacerbation of sleep disturbances or disorders. Although the identified attributes of sleep disturbances in health professional students might not align precisely with established models, they still provide a foundational understanding of the term ‘sleep disturbance’ in this context. Future research should strive for clarity and consistency in defining and operationalising terms related to sleep disturbances.
The antecedents identified in our study include factors such as academic stress, emotional distress and lifestyle changes. These antecedents are critical for understanding the multifaceted nature of sleep disturbances. By recognising these conditions, we can better guide the development of preventive strategies aimed at reducing the risk of sleep disturbances among health professional students, especially during a pandemic. First, schools should provide psychological counselling and support services to help students manage stress and anxiety, thereby improving sleep (Zhou et al. 2023). Second, reasonable curriculum and study plans should be developed to reduce academic stress and encourage students to develop good work and rest habits (Arkan and Bostanlı 2024; Rettinger et al. 2024). Additionally, sleep health education should be provided to raise awareness of the importance of sleep and help students develop healthy sleep habits (Guo et al. 2022). Through these measures, we can help health professional students recover and maintain good sleep habits and enhance their overall health and academic performance. This will not only contribute to their personal development but also help produce healthier and more productive future health care professionals. Thus, understanding these antecedents is essential for improving the overall well‐being of health professional students during a pandemic such as COVID‐19.
The concept of sleep disturbances has been extensively analysed in various patient populations, including those with diabetes (Zhu et al. 2018), heart failure (Zheng 2021), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV; Pujasari and Chung 2022) and surgical patients (Yuan et al. 2024). Comparing our findings with these previous studies highlights both unique and common aspects of sleep disturbances across different groups. In patients with diabetes, sleep disturbances are often linked to glycemic control and diabetes‐related complications (Zhu et al. 2018). For patients with heart failure, sleep disturbances are primarily caused by the physical symptoms of the disease, such as sleep apnea (Zheng 2021). Patients with HIV frequently experience sleep disturbances due to the side effects of antiretroviral therapy (Pujasari and Chung 2022). Sleep disturbances in surgical patients are often acute and related to the perioperative period, including preoperative anxiety and postoperative pain (Yuan et al. 2024). Comparing these different contexts emphasises the multifaceted nature of sleep disturbances and the importance of tailored interventions. Understanding these nuances is crucial for developing effective strategies to improve sleep health in each population. Future research should continue to explore the specific factors contributing to sleep disturbances in diverse patient groups and compare these with findings in health professional students. This holistic approach is essential for improving sleep health and overall well‐being in both patient and student populations.
Clinically, identifying attributes like altered sleep duration or patterns among health professional students during the pandemic holds crucial implications. Interventions focusing on educating students about sleep hygiene, addressing specific stressors and offering support services could significantly improve their sleep quality. Nurses and health care professionals should consider these findings while formulating strategies to support the well‐being of health professional students. Our analysis has provided a foundational understanding of sleep disturbances among health professional students, but it has also highlighted the need for clarity and consistency in defining and operationalising the term ‘sleep disturbance’ in this population.
It is important to note that the antecedents of sleep disturbances can also be related to the consequences (Freeman et al. 2020). For example, psychosocial factors such as mental health issues, anxiety, depression and stress are strongly associated with sleep disturbances among health professional students. These factors can not only precede the development of sleep disturbances but also result from them. Similarly, sleep disturbances can have a significant impact on physical and mental health, including increased risk of developing mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety and stress. Therefore, it is essential to address sleep disturbances among health professional students, not only to improve academic performance and overall well‐being but also to prevent the development of chronic health conditions. Future research should explore the complex relationships between the antecedents and consequences of sleep disturbances to develop more effective interventions and support strategies (Freeman et al. 2020). Further exploration of this link could elucidate the underlying mechanisms, potentially shedding light on stress hormones, irregular sleep schedules or social isolation.
Although an exhaustive search was conducted, the number of qualitative studies remained limited (n = 2). Qualitative studies would provide rich information about this concept. The lack of qualitative studies underscores the early developmental stage of the concept. Analysing areas of consensus and disparity across disciplines in this concept analysis, following Rodgers and Knafl (2000) approach, serves as a crucial step in advancing our understanding. While it is acknowledged that COVID‐19 is no longer a primary public health concern, the persistence of sleep disturbances among health professional students remains pertinent. Continued research is essential to comprehensively understand the multifaceted factors contributing to sleep disturbances in this population. This will facilitate a better exploration of the context and support the development of effective interventions aimed at enhancing sleep health.
5. Conclusions
This concept analysis was undertaken to define the concept of sleep disturbances in health professional students during the COVID‐19 pandemic, fostering its applicability in clinical practice and research. The analysis of sleep disturbances among health professional students during the COVID‐19 pandemic revealed the impact of uncertainties, fears and disruptions associated with this global crisis on sleep patterns. The attributes identified in this analysis—insomnia, altered circadian patterns, changes in sleep duration and poor sleep quality—should be integral to future investigations. These attributes provide a structured understanding of sleep disturbances and their multifaceted impacts. Addressing these specific attributes through targeted interventions can improve sleep quality and overall health outcomes for health professional students. Recognising and addressing these attributes are critical in developing effective strategies to mitigate the adverse effects of sleep disturbances during and beyond the pandemic. Future research is needed to shed more light on the diverse attributes of sleep disturbance, particularly exploring interdisciplinary variations. Future studies aimed at identifying the risk factors and consequences of sleep disturbances will aid in developing a comprehensive theoretical framework essential for enhancing interventions tailored to support the well‐being of health professional students.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Supporting information
Data S1.
Acknowledgements
We thank the authors of the original works cited in this review.
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
- AASM . 2023. International Classification of Sleep Disorders. 3rd ed. Darien, IL: American Academy of Sleep Medicine. [Google Scholar]
- Ahorsu, D. K. , Lin C. Y., Imani V., Saffari M., Griffiths M. D., and Pakpour A. H.. 2022. “The Fear of COVID‐19 Scale: Development and Initial Validation.” International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction 20, no. 3: 1537–1545. 10.1007/s11469-020-00270-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al Maqbali, M. , Alsaraireh M., AlMekkawi M., Melhem O., and Bashayreh I.. 2023. “Fear of COVID‐19, Stress, Anxiety, Depression, and Insomnia Among Undergraduate Nursing Students in Oman.” Nursing Practice Today 10, no. 4: 318–326. 10.18502/npt.v10i4.14078. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Alhamed, A. A. 2023. “The Link Among Academic Stress, Sleep Disturbances, Depressive Symptoms, Academic Performance, and the Moderating Role of Resourcefulness in Health Professions Students During COVID‐19 Pandemic.” Journal of Professional Nursing 46: 83–91. 10.1016/j.profnurs.2023.02.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkalash, S. , Alzubaidi H., Alessi N., Alghanmi A., and Almasoudi A.. 2022. “Sleep Quality Among Al Qunfudhah Medical Students and Its Effects on Their Academic Performance During Covid‐19 Pandemic.” Medical Science 26, no. 120: ms50e2066. 10.54905/disssi/v26i120/ms50e2066. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Almojali, A. I. , Almalki S. A., Alothman A. S., Masuadi E. M., and Alaqeel M. K.. 2017. “The Prevalence and Association of Stress With Sleep Quality Among Medical Students.” Journal of Epidemiology and Global Health 7, no. 3: 169–174. 10.1016/j.jegh.2017.04.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alrashed, F. A. , Sattar K., Ahmad T., Akram A., Karim S. I., and Alsubiheen A. M.. 2021. “Prevalence of Insomnia and Related Psychological Factors With Coping Strategies Among Medical Students in Clinical Years During the COVID‐19 Pandemic.” Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences 28, no. 11: 6508–6514. 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.07.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkan, B. , and Bostanlı A.. 2024. “Teaching Psychiatric Nursing With Films During the COVID‐19 Pandemic: A Qualitative Study.” Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing. Published ahead of print, May 7, 2024. 10.1111/jpm.13059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastien, C. H. , Vallières A., and Morin C. M.. 2001. “Validation of the Insomnia Severity Index as an Outcome Measure for Insomnia Research.” Sleep Medicine 2, no. 4: 297–307. 10.1016/s1389-9457(00)00065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltrame, K. , Trindade‐Suedam I. K., Trindade S. H. K., and Marzano‐Rodrigues M. N.. 2022. “Web Survey During COVID‐19 Pandemic in São Paulo State: How Are Medical Students Sleeping and Living?” Sleep Science 15, no. 4: 374–382. 10.5935/1984-0063.20220066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhosale, T. , Mathew R., and Hegde A. M.. 2024. “Reality Faced by Dental Students During COVID‐19 Pandemic Situation.” Journal of Health and Allied Sciences NU 14, no. 2: 267–272. 10.1055/s-0043-1770961. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Buysse, D. J. , Reynolds C. F. 3rd, Monk T. H., Berman S. R., and Kupfer D. J.. 1989. “The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A New Instrument for Psychiatric Practice and Research.” Psychiatry Research 28, no. 2: 193–213. 10.1016/0165-1781(89)90047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderaro, D. C. , Teodoro M. L. M., Basualto S., et al. 2023. “Participating as a Research Team During the COVID‐19 Pandemic Benefits Mental Health of Undergraduate Medical Students in Brazil.” Psychology, Health & Medicine 28, no. 6: 1441–1449. 10.1080/13548506.2022.2141280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W. , Fang Z., Hou G., et al. 2020. “The Psychological Impact of the COVID‐19 Epidemic on College Students in China.” Psychiatry Research 287: 112934. 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.112934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, T. , Fong T. K. H., and Bressington D.. 2021. “COVID‐19 Under the SARS Cloud: Mental Health Nursing During the Pandemic in Hong Kong.” Journal of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing 28, no. 2: 115–117. 10.1111/jpm.12639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chhakchhuak, V. , Ray K., Saha S. K., and Basu M.. 2023. “A Cross‐Sectional Study on Anxiety due to COVID‐19 and Its Predictors Among Undergraduate Medical Students in a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital of Kolkata, West Bengal.” Indian Journal of Public Health 67, no. 1: 35–40. 10.4103/ijph.ijph_690_22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppi, F. , Nasi M., Sabatini S., et al. 2022. “Lifestyle Changes During the First and Second Waves of the COVID‐19 Pandemic in Medical College Students: Are There Gender‐Related Differences?” Acta Biomed 93, no. 5: e2022312. 10.23750/abm.v93i5.13694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, K. , Guedes‐Granzotti R. B., Veis Ribeiro V., Dornelas R., Alcântara Cruz P. J., and César C. P. H. A. R.. 2021. “Quality of Life and Sleep Among Brazilian Speech‐Language Pathology Students During the COVID‐19 Pandemic.” Perspectives of the ASHA Special Interest Groups 6, no. 5: 1146–1157. 10.1044/2021_PERSP-20-00251. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, K. E. , Szkody E., Aggarwal P., Peterman A. H., Washburn J. J., and Selby E. A.. 2022. “Characterizing Changes in Mental Health‐Related Outcomes for Health Service Psychology Graduate Students During the First Year of the COVID‐19 Pandemic.” Journal of Clinical Psychology 78, no. 11: 2281–2298. 10.1002/jclp.23392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dias Caldeira, F. I. , Silva Dias I. C., Tribucci Zamariolli J., et al. 2023. “Evaluation of Quality of Life, Sleep, and Sleepiness in Dental Students During Active Learning and Remote Emergency Learning.” Health Sciences Journal/Revista Ciências Em Saúde 13, no. 3: 17–22. 10.21876/rcshci.v13i3.1387. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy, A. , Browne F., and Connolly M.. 2024. “Safeguarding Adults: A Concept Analysis.” Journal of Advanced Nursing. Published ahead of print, June 28, 2024. 10.1111/jan.16306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, D. , Kaur N., Shukla S., and Tripathi S.. 2023. “The Impact of Yogic Practices on Perception of Stress and Sleep Among Medical Students Amid COVID‐19 Pandemic.” National Journal of Physiology, Pharmacy and Pharmacology 13: 1. 10.5455/njppp.2023.13.06293202326062023. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Elsalem, L. , Al‐Azzam N., Jum'ah A. A., Obeidat N., Sindiani A. M., and Kheirallah K. A.. 2020. “Stress and Behavioral Changes With Remote E‐Exams During the Covid‐19 Pandemic: A Cross‐Sectional Study Among Undergraduates of Medical Sciences.” Annals of Medicine and Surgery 60: 271–279. 10.1016/j.amsu.2020.10.058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawzy, M. , and Hamed S. A.. 2017. “Prevalence of Psychological Stress, Depression and Anxiety Among Medical Students in Egypt.” Psychiatry Research 255: 186–194. 10.1016/j.psychres.2017.05.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François Isnaldo, F. , Dias I., Zamariolli J., Gasque K., Teixeira A., and Rodriguez L.. 2023. “Evaluation of Quality of Life, Sleep, and Sleepiness in Dental Students During Active Learning and Remote Emergency Learning.” Revista Ciências em Saúde 13: 17–22. 10.21876/rcshci.v13i3.1387. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, D. , Sheaves B., Waite F., Harvey A. G., and Harrison P. J.. 2020. “Sleep Disturbance and Psychiatric Disorders.” Lancet Psychiatry 7, no. 7: 628–637. 10.1016/s2215-0366(20)30136-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B. , Song Y., Zhao L., et al. 2022. “Sleep Quality and Creativity in Chinese College Student During the COVID‐19 Pandemic: The Mediating Role of Executive Function.” Frontiers in Public Health 10: 987372. 10.3389/fpubh.2022.987372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A. , Haritha D., Ramachandran R., et al. 2022. “Nationwide Impact of COVID‐19 Pandemic on Postgraduate Medical Teaching, Research, and Mental Stress: A Cross‐Sectional Online Questionnaire‐Based Survey.” Journal of Anaesthesiology Clinical Pharmacology 38, no. Suppl 1: S34–s45. 10.4103/joacp.JOACP_673_20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A. , Jagzape A., and Kumar M.. 2021. “Social Media Effects Among Freshman Medical Students During COVID‐19 Lock‐Down: An Online Mixed Research.” Journal of Education Health Promotion 10, no. 1: 55. 10.4103/jehp.jehp_749_20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskett, L. A. , Doster D. L., Athanasiadis D. I., et al. 2022. “Resilience Matters: Student Perceptions of the Impact of COVID‐19 on Medical Education.” American Journal of Surgery 224, no. 1 Pt B: 358–362. 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2022.01.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healey, E. S. , Kales A., Monroe L. J., Bixler E. O., Chamberlin K., and Soldatos C. R.. 1981. “Onset of Insomnia: Role of Life‐Stress Events.” Psychosomatic Medicine 43, no. 5: 439–451. 10.1097/00006842-198110000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisato, T. , Nandy S., Monga E. M., Sytek P., Abouzid M., and Ahmed A. A.. 2023. “Psychological Distress Among Healthcare Students in Poland from COVID‐19 to War on Ukraine: A Cross‐Sectional Exploratory Study.” Frontiers in Public Health 11: 1186442. 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1186442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutto, A. , Raynor P., and Baliko B.. 2024. “Shared Trauma: An Evolutionary Model Concept Analysis in Light of COVID‐19.” International Journal of Mental Health Nursing. Published ahead of print, April 2, 2024. 10.1111/inm.13326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ionescu, C. G. , Chendea A., and Licu M.. 2023. “Is Satisfaction With Online Learning Related to Depression, Anxiety, and Insomnia Symptoms? A Cross‐Sectional Study on Medical Undergraduates in Romania.” European Journal of Investigation in Health Psychology and Education 13, no. 3: 580–594. 10.3390/ejihpe13030045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, R. M. , Effendi N. I. B. R., Alwi S. S. S., Saidi H. I., and Sarchio S. N. E.. 2023. “Insomnia and Depression Levels Among Malaysian Undergraduate Students in the Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences (FMHS), Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM) During Movement Control Order (MCO).” PLoS One 18: e0283098. 10.1371/journal.pone.0283098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito, Y. , Kako J., Kajiwara K., et al. 2022. “Impact of the COVID‐19 Pandemic on the Mental Health of Nursing Students in Japan: A Cross‐Sectional Study.” Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine 27, no. 1: 40. 10.1265/ehpm.22-00128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalali, R. , Khazaei H., Paveh B. K., Hayrani Z., and Menati L.. 2020. “The Effect of Sleep Quality on Students' Academic Achievement.” Advances in Medical Education and Practice 11: 497–502. 10.2147/amep.S261525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, R. A. , Turner T., Lee C., Akers S. W., Whorley E., and Goodrich C.. 2022. “Impact of COVID‐19 on Nursing Students: Factors Associated With PTSD Risk.” Journal of Christian Nursing 39: 250–257. 10.1097/CNJ.0000000000000951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kara, B. 2021. “Determinants of Perceived Stress in Health Professional Students During the COVID‐19 Pandemic.” AIMS Medical Science 8, no. 2: 147–162. 10.3934/medsci.2021014. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kochuvilayil, T. , Fernandez R. S., Moxham L. J., et al. 2021. “COVID‐19: Knowledge, Anxiety, Academic Concerns and Preventative Behaviours Among Australian and Indian Undergraduate Nursing Students: A Cross‐Sectional Study.” Journal of Clinical Nursing 30, no. 5–6: 882–891. 10.1111/jocn.15634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, A. , Abuliezi R., Naruse K., Oki T., Niitsu K., and Ezeonwu M. C.. 2021. “Perceived Control, Preventative Health Behaviors, and the Mental Health of Nursing Students During the COVID‐19 Pandemic: A Cross‐Sectional Study.” Inquiry: A Journal of Medical Care Organization, Provision and Financing 58: 469580211060279. 10.1177/00469580211060279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kothiwale, S. V. , and Padhye V. K.. 2023. “Assessment of Anxiety and Behavior Changes on Digital Education in Undergraduate Dental Students During COVID‐19 Pandemic.” Journal of the Scientific Society 50, no. 2: 168–176. 10.4103/jss.jss_16_22. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Laranjeira, C. , Querido A., Marques G., et al. 2021. “COVID‐19 Pandemic and Its Psychological Impact Among Healthy Portuguese and Spanish Nursing Students.” Health Psychology Research 9, no. 1: 24508. 10.52965/001c.24508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. , Luo C., Liu L., et al. 2024. “Depression, Anxiety, and Insomnia Symptoms Among Chinese College Students: A Network Analysis Across Pandemic Stages.” Journal of Affective Disorders 356: 54–63. 10.1016/j.jad.2024.04.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao, X. , Zhang S., Wang Y., Jiang J., Li Y., and Zhang W.. 2022. “Mental Burden Among Chinese Undergraduate Medical Students: A Prospective Longitudinal Study Before, During, and After the COVID‐19 Outbreak.” Frontiers in Psychiatry 13: 982469. 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.982469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z. , Liu R., Zhang Y., et al. 2021. “Association Between Perceived Stress and Depression Among Medical Students During the Outbreak of COVID‐19: The Mediating Role of Insomnia.” Journal of Affective Disorders 292: 89–94. 10.1016/j.jad.2021.05.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medina‐Ramirez, S. A. , Rojas‐Humpire R., Canaza J. F., Hernandez F., and Huancahuire‐Vega S.. 2022. “Online Academic Satisfaction During the COVID‐19 Pandemic in Medical Students: Role of Sleep, Emotions, College Adjustment, and Digital Skills.” F1000Research 11: 241. 10.12688/f1000research.76127.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, J. , Panigrahi A., Samanta P., Dash K., Mahapatra P., and Behera M. R.. 2022. “Sleep Quality and Associated Factors Among Undergraduate Medical Students During Covid‐19 Confinement.” Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health 15: 101004. 10.1016/j.cegh.2022.101004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses, I. C. , Vaithiyalingam M. A., Kumar N. K., Musthafa S. M., Gunasekaran S., and Periasamy P.. 2023. “Medical Students' Sleep Quality Following the COVID‐19 Pandemic Lockdown in Erode, Tamil Nadu: A Cross‐Sectional Study.” International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research 15, no. 7: 695–701. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V. V. , Zainal N. H., and Newman M. G.. 2022. “Why Sleep Is Key: Poor Sleep Quality Is a Mechanism for the Bidirectional Relationship Between Major Depressive Disorder and Generalized Anxiety Disorder Across 18 Years.” Journal of Anxiety Disorders 90: 102601. 10.1016/j.janxdis.2022.102601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Byrne, L. , Gavin B., and McNicholas F.. 2020. “Medical Students and COVID‐19: The Need for Pandemic Preparedness.” Journal of Medical Ethics 46, no. 9: 623–626. 10.1136/medethics-2020-106353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pujasari, H. , and Chung M. H.. 2022. “Sleep Disturbance in the Context of HIV: A Concept Analysis.” SAGE Open Nursing 8: 23779608221094541. 10.1177/23779608221094541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranjan, R. , Gupta C. K., and Garg M.. 2023. “Perceived Stress Levels and Relieving Strategies Among Medical Students During Three Waves of COVID Pandemic.” International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research 15, no. 7: 373–376. [Google Scholar]
- Rettinger, L. , Putz P., Aichinger L., et al. 2024. “Telehealth Education in Allied Health Care and Nursing: Web‐Based Cross‐Sectional Survey of Students' Perceived Knowledge, Skills, Attitudes, and Experience.” JMIR Medical Education 10: e51112. 10.2196/51112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers, B. , and Knafl K.. 2000. “Concept Analysis and Evolutionary View.” In Concept Development in Nursing: Foundations, Techniques and Applications, edited by Rodgers B., and Knafl K.. 2nd ed., 77–102. Philadelphia, PA: Saunder. [Google Scholar]
- Romero‐Blanco, C. , Rodríguez‐Almagro J., Onieva‐Zafra M. D., Parra‐Fernández M. L., Prado‐Laguna M. D. C., and Hernández‐Martínez A.. 2020. “Sleep Pattern Changes in Nursing Students During the COVID‐19 Lockdown.” International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 14: 5222. 10.3390/ijerph17145222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraswathi, I. , Saikarthik J., Kumar K. S., Srinivasan K. M., Ardhanaari M., and Gunapriya R.. 2020. “Impact of COVID‐19 Outbreak on the Mental Health Status of Undergraduate Medical Students in a COVID‐19 Treating Medical College: A Prospective Longitudinal Study.” PeerJ 8: e10164. 10.7717/peerj.10164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasirekha, M. , Mahima Sophia M., Vaijayanthimala P., and Leonoline Ebenezer J.. 2020. “Study of Mobile Phone Usage in Undergraduate Medical and Dental Students During Covid‐19 Lockdown.” Indian Journal of Public Health Research and Development 11, no. 7: 813–825. [Google Scholar]
- Sawant, N. S. , Vinchurkar P., Kolwankar S., Patil T., Rathi K., and Urkude J.. 2023. “Online Teaching, Learning, and Health Outcomes: Impact on Medical Undergraduate Students.” Industrial Psychiatry Journal 32, no. 1: 59–64. 10.4103/ipj.ipj_52_22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian, L. , Tojo J., and Fathima F.. 2023. “Sleep Quality of Undergraduate Medical Students During and Post‐Lockdown: A Cross‐Sectional Research.” Indian Journal of Community Medicine 48, no. 4: 609–611. 10.4103/ijcm.ijcm_571_22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seoane, H. A. , Moschetto L., Orliacq F., et al. 2020. “Sleep Disruption in Medicine Students and Its Relationship With Impaired Academic Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis.” Sleep Medicine Reviews 53: 101333. 10.1016/j.smrv.2020.101333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, D. , Adhikari S. P., Rawal N., et al. 2021. “Sleep Quality Among Undergraduate Students of a Medical College in Nepal During COVID‐19 Pandemic: An Online Survey.” F1000Research 10: 505. 10.12688/f1000research.53904.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh, H. K. , Joshi A., Malepati R. N., et al. 2021. “A Survey of E‐Learning Methods in Nursing and Medical Education During COVID‐19 Pandemic in India.” Nurse Education Today 99: 104796. 10.1016/j.nedt.2021.104796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R. K. , Kumar M., and Kumari S.. 2024. “Study of Stress in Medical Undergraduate Student During COVID Pandemic in Darbhanga Medical College, Laheriasarai, Bihar.” International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research 16, no. 1: 1347–1351. [Google Scholar]
- Singla, R. , Chatterjee P., and Mithra P.. 2023. “Impact of COVID‐19 on Academic and Psychological Aspects in Students of Medicine: A Cross‐Sectional Study.” Cureus Journal of Medical Science 15, no. 11: e48259. 10.7759/cureus.48259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Son, C. , Hegde S., Smith A., Wang X., and Sasangohar F.. 2020. “Effects of COVID‐19 on College Students' Mental Health in the United States: Interview Survey Study.” Journal of Medical Internet Research 22, no. 9: e21279. 10.2196/21279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soni, A. , Solanki S., Choudhary R., and Randa V.. 2021. “A Cross Sectional Study on Relationship Between Perceived Stress, Copingbehaviour and Lifestyle Changesduring COVID‐19 Pandemic Era Among Medical Undergraduates.” Journal of Cardiovascular Disease Research 12, no. 6: 1146–1153. 10.31838/jcdr.2021.12.06.158. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sundarasamy, V. G. , Thamizharasan R., and Lalan R. H.. 2020. “Psychological Impact of COVID‐19 on Medical College Students.” European Journal of Molecular and Clinical Medicine 7, no. 10: 435–443. [Google Scholar]
- Swetha, M. , and Sumitra L. K.. 2023. “The Impact of COVID‐19 Pandemic on Medical Students: A Cross‐Sectional Study.” National Journal of Physiology, Pharmacy and Pharmacology 13, no. 5: 1006–1010. 10.5455/njppp.2023.13.083932022023102022. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sweety, L. M. , ShaLini S., and Chitra C. B.. 2023. “Comparison of Stress Levels with Online and Offline Mode of Teaching in Medical Undergraduate Students during COVID‐19 Pandemic: A Cross‐sectional Study.” Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research 17, no. 6: CC07–CC10. [Google Scholar]
- Tull, M. T. , Edmonds K. A., Scamaldo K. M., Richmond J. R., Rose J. P., and Gratz K. L.. 2020. “Psychological Outcomes Associated With Stay‐At‐Home Orders and the Perceived Impact of COVID‐19 on Daily Life.” Psychiatry Research 289: 113098. 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velarde‐García, J. F. , González‐Hervías R., Álvarez‐Embarba B., et al. 2022. “Under‐Graduate Nursing Students Working During the First Outbreak of the COVID‐19 Pandemic: A Qualitative Study of Psychosocial Effects and Coping Strategies.” International Journal of Nursing Practice 28, no. 5: e13065. 10.1111/ijn.13065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. , Peng P., Liu Y. H., et al. 2023. “Gender Differences in Alcohol Abuse/Dependence Among Medical Undergraduates During the Post‐COVID‐19 Pandemic Period (October 20, 2020‐April 5, 2021) in China.” BMC Psychiatry 23, no. 1: 753. 10.1186/s12888-023-05260-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H. , Li H., Li X., et al. 2022. “Psychological Health and Sleep Quality of Medical Graduates During the Second Wave of COVID‐19 Pandemic in Post‐Epidemic Era.” Frontiers in Public Health 10: 876298. 10.3389/fpubh.2022.876298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T. , Sun X. T., Jiang P., Chen M. J., Yue Y., and Dong E. H.. 2022. “Effects of Cell Phone Dependence on Mental Health Among College Students During the Pandemic of COVID‐19: A Cross‐Sectional Survey of a Medical University in Shanghai.” Frontiers in Psychology 13: 920899. 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.920899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, R. K. , Baral S., Khatri E., et al. 2021. “Anxiety and Depression Among Health Sciences Students in Home Quarantine During the COVID‐19 Pandemic in Selected Provinces of Nepal.” Frontiers in Public Health 9: 580561. 10.3389/fpubh.2021.580561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X. , Ju Z., Zhang X., and Yin X.. 2024. “Perioperative Sleep Disturbance in Surgical Patients: A Concept Analysis.” Clinical Nursing Research 33: 493–501. 10.1177/10547738241258509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, T. 2021. “Sleep Disturbance in Heart Failure: A Concept Analysis.” Nursing Forum 56, no. 3: 710–716. 10.1111/nuf.12566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L. , Chankoson T., Wu Y., and Cai E.. 2023. “Thriving Psychological Well‐Being in Undergraduate Nursing Student: A Grounded Theory Study With the Life Grid Approach.” BMC Nursing 22, no. 1: 240. 10.1186/s12912-023-01338-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B. , Vincent C., Kapella M. C., et al. 2018. “Sleep Disturbance in People With Diabetes: A Concept Analysis.” Journal of Clinical Nursing 27, no. 1–2: e50–e60. 10.1111/jocn.14010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data S1.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.


