Abstract
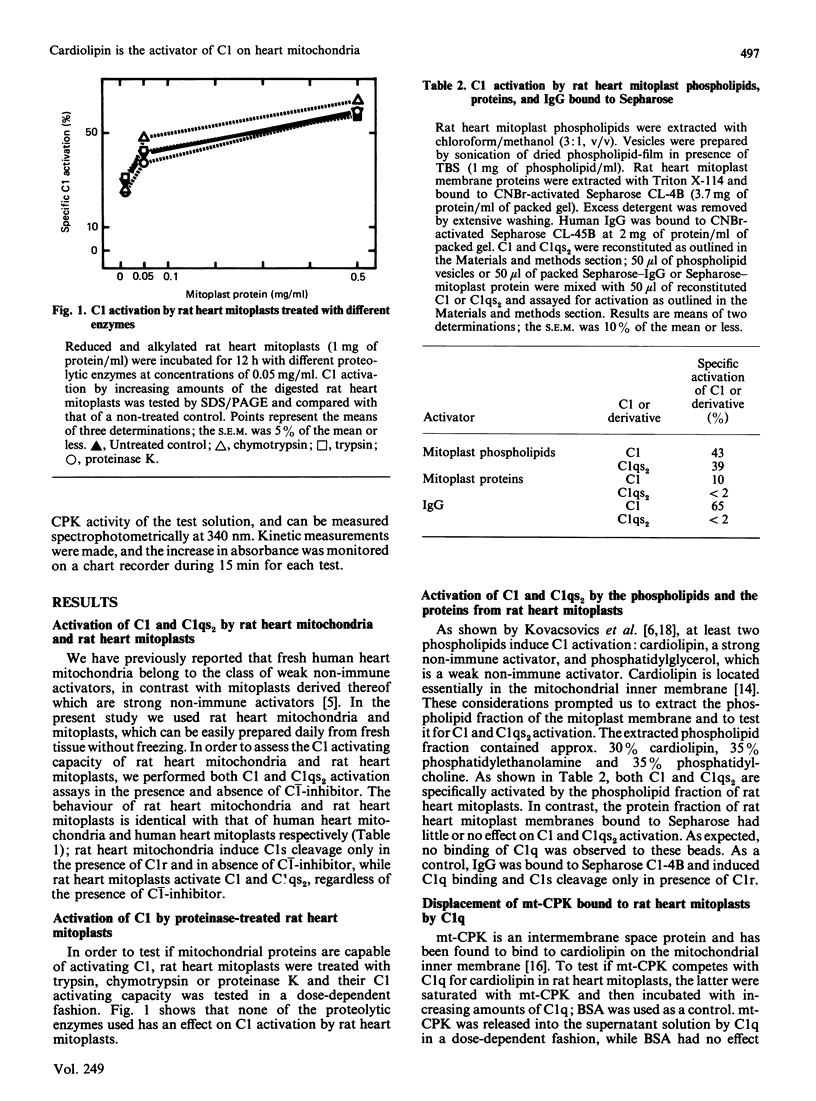
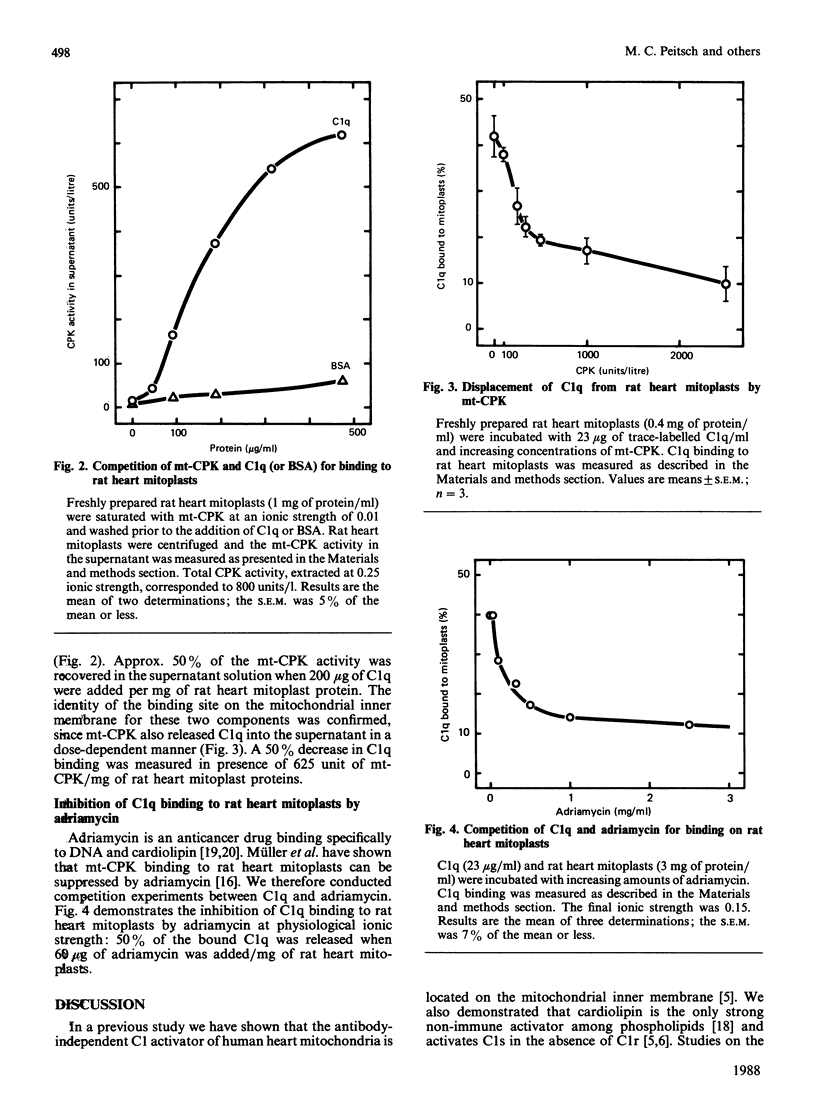
Non-immune activation of the first component of complement (C1) by the heart mitochondrial inner membrane has been investigated. Cardiolipin, the only strong activator of C1 among phospholipids, is present in large amounts in the heart mitochondrial inner membrane. We therefore studied its contribution to C1 activation by mitochondria. The proteins of the mitochondrial inner membrane were found to activate C1 only weakly, in contrast with the phospholipid fraction which induces strong C1 activation. Furthermore, the digestion of mitochondrial inner membranes with proteolytic enzymes did not affect C1 activation. Additional support in favour of cardiolipin being the responsible activator came from competition experiments with mitochondrial creatine kinase (mt-CPK) and adriamycin, known to bind to cardiolipin. Both mt-CPK and adriamycin displaced C1q from the mitochondrial inner membrane. In addition, C1q displaced mt-CPK bound to mitoplasts.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blum H. E., Deus B., Gerok W. Mitochondrial creatine kinase from human heart muscle: purification and characterization of the crystallized isoenzyme. J Biochem. 1983 Oct;94(4):1247–1257. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheneval D., Müller M., Carafoli E. The mitochondrial phosphate carrier reconstituted in liposomes is inhibited by doxorubicin. FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 8;159(1-2):123–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper N. R., Morrison D. C. Binding and activation of the first component of human complement by the lipid A region of lipopolysaccharides. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):1862–1868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daum G. Lipids of mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 12;822(1):1–42. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds A. W., Sim R. B., Porter R. R., Kerr M. A. Activation of the first component of human complement (C1) by antibody-antigen aggregates. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 1;175(2):383–390. doi: 10.1042/bj1750383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Font B., Vial C., Goldschmidt D., Eichenberger D., Gautheron D. C. Heart mitochondrial creatine kinase solubilization. Effect of mitochondrial swelling and SH group reagents. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Nov;212(1):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90359-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goormaghtigh E., Chatelain P., Caspers J., Ruysschaert J. M. Evidence of a specific complex between adriamycin and negatively-charged phospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 27;597(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90145-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goppelt M., Resch K. Densitometric quantitation of individual phospholipids from natural sources separated by one-dimensional thin-layer chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jul;140(1):152–156. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai T., Takase S., Arai M., Fujita T. Serial changes of complement titers in the acute phase of myocardial infarction. Jpn Circ J. 1983 Mar;47(3):289–293. doi: 10.1253/jcj.47.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacsovics T. J., Peitsch M. C., Kress A., Isliker H. Antibody-independent activation of C1. I. Differences in the mechanism of C1 activation by nonimmune activators and by immune complexes: C1r-independent activation of C1s by cardiolipin vesicles. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1864–1870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacsovics T., Tschopp J., Kress A., Isliker H. Antibody-independent activation of C1, the first component of complement, by cardiolipin. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2695–2700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEPOW I. H., NAFF G. B., TODD E. W., PENSKY J., HINZ C. F. Chromatographic resolution of the first component of human complement into three activities. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:983–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus L. M., Kolb W. P., Crawford M. H., O'Rourke R. A., Grover F. L., Pinckard R. N. Complement localization in ischemic baboon myocardium. Lab Invest. 1983 Apr;48(4):436–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medicus R. G., Chapuis R. M. The first component of complement. I. Purification and properties of native C1. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):390–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peitsch M. C., Kovacsovics T. J., Tschopp J., Isliker H. Antibody-independent activation of C1. II. Evidence for two classes of nonimmune activators of the classical pathway of complement. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1871–1876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porumb H., Petrescu I. Interaction with mitochondria of the anthracycline cytostatics adriamycin and daunomycin. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1986;48(2):103–125. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(86)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer H., Mathey D., Hugo F., Bhakdi S. Deposition of the terminal C5b-9 complement complex in infarcted areas of human myocardium. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1945–1949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storrs S. B., Kolb W. P., Olson M. S. C1q binding and C1 activation by various isolated cellular membranes. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):416–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner A. J., Lesavre P. H., Cooper N. R. Purification and radiolabeling of human C1q. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):648–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziccardi R. J. A new role for C-1-inhibitor in homeostasis: control of activation of the first component of human complement. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2505–2508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziccardi R. J., Cooper N. R. Activation of C1r by proteolytic cleavage. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):504–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruijff B., Cullis P. R. Cytochrome c specifically induces non-bilayer structures in cardiolipin-containing model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 18;602(3):477–490. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90327-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


