Abstract
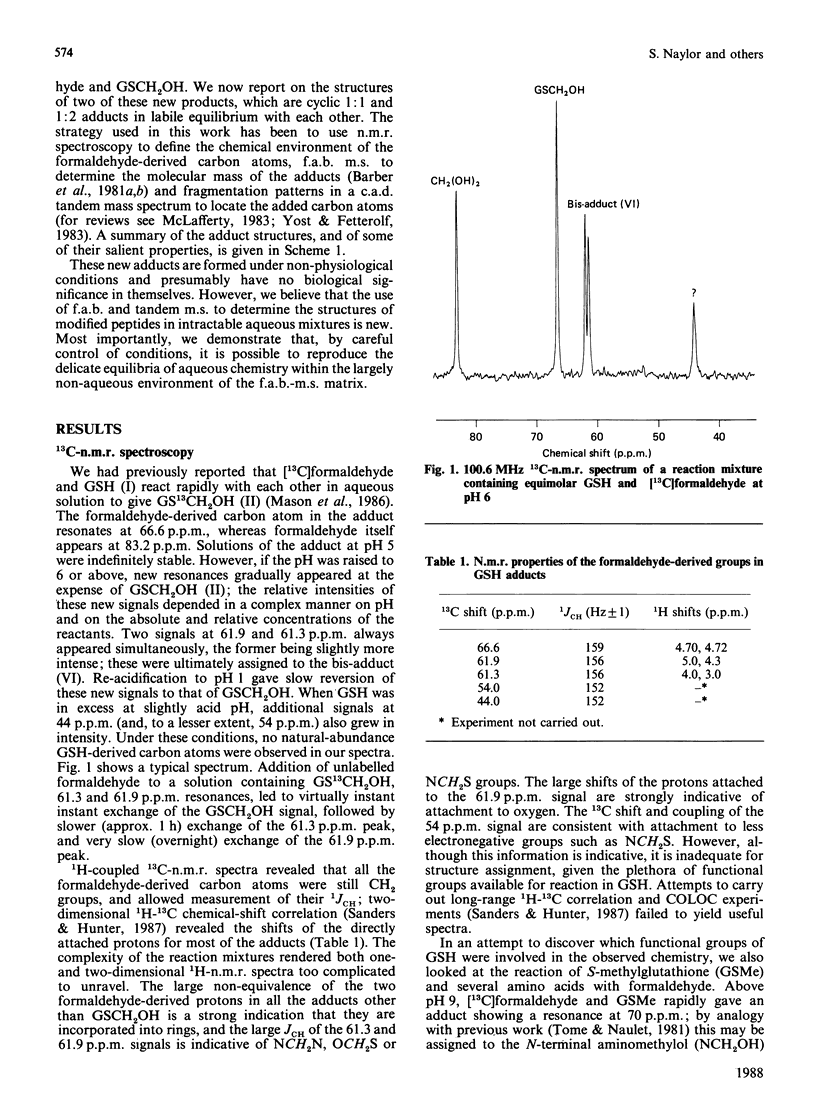
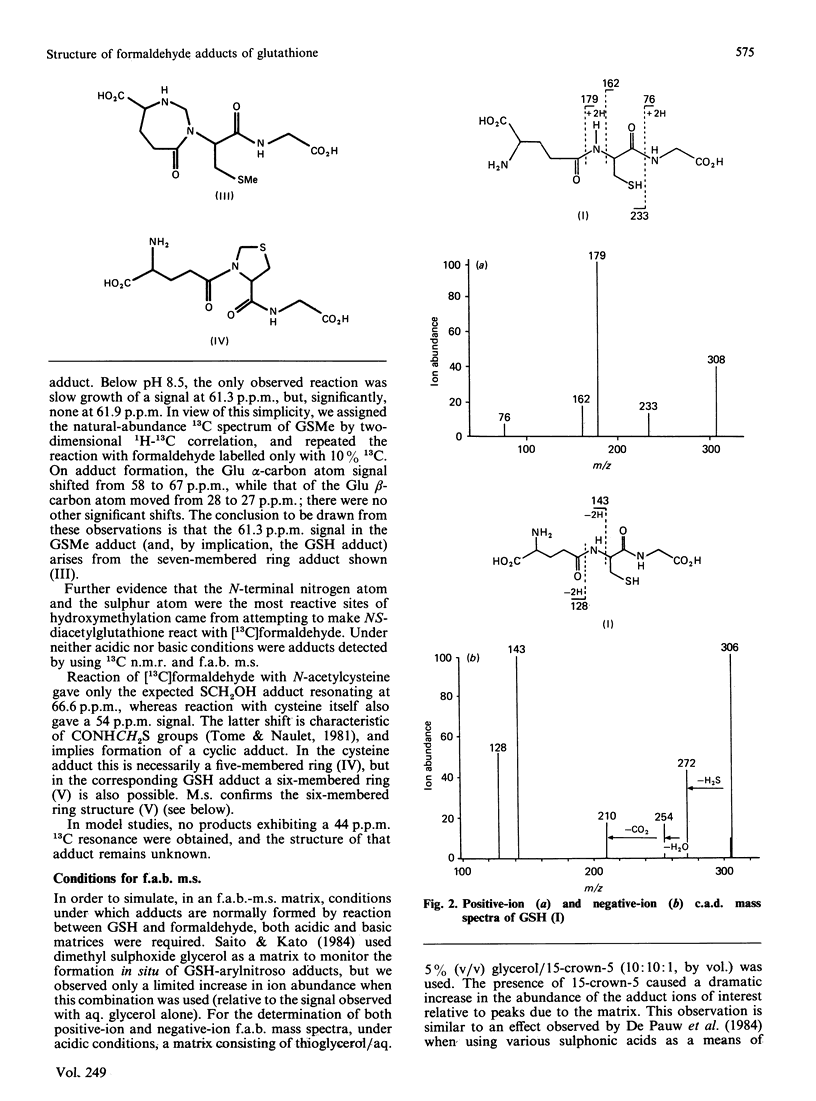
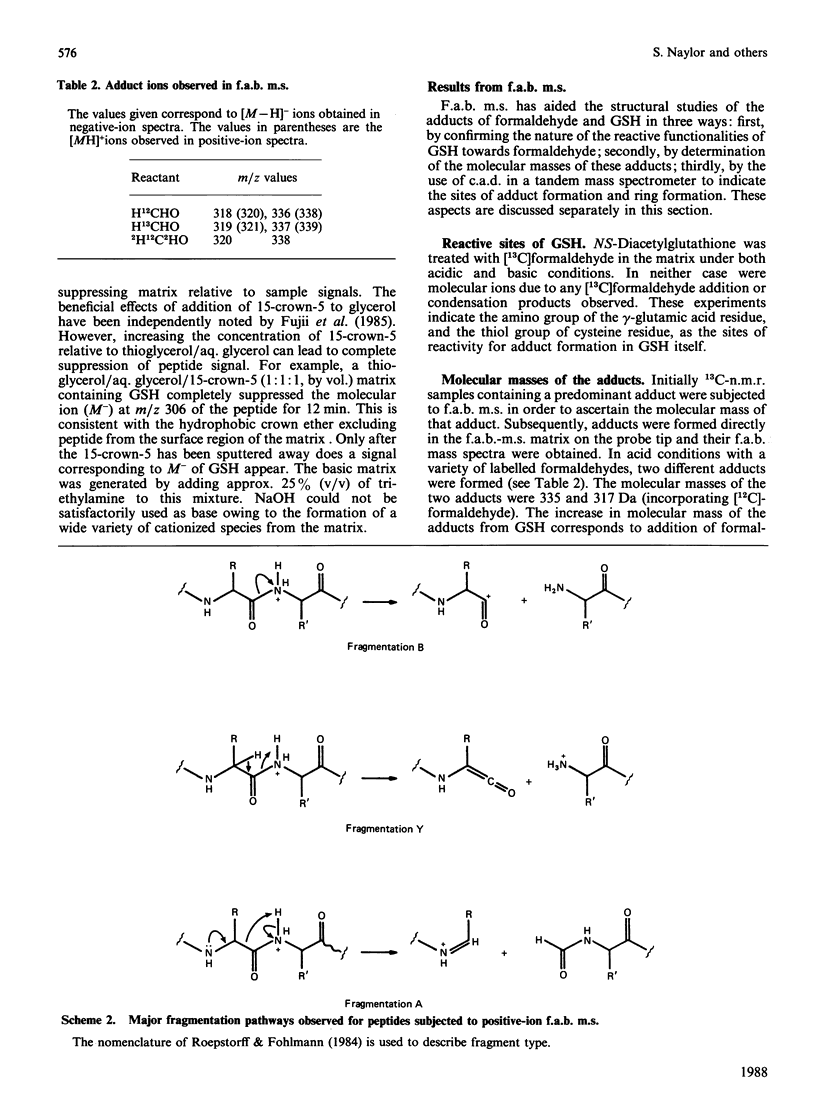
Aqueous mixtures of formaldehyde and glutathione react to form a variety of cyclized adducts in addition to S-hydroxymethylglutathione. The adducts are in labile equilibrium with each other and are not readily separated. The structures of two of the other major adducts were determined by concerted application of 13C-1H two-dimensional chemical-shift correlation, fast-atom-bombardment mass spectrometry and tandem mass spectrometry to the adduct mixtures in aqueous solution.
Full text
PDF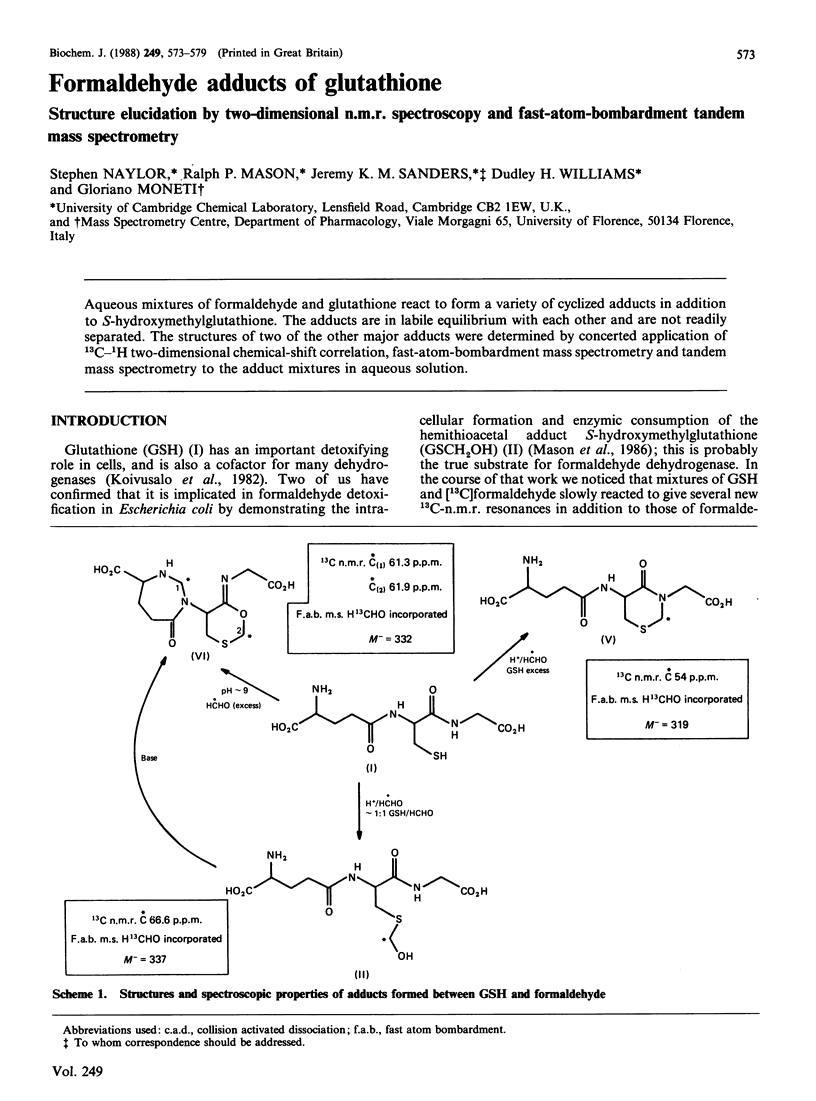


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- De Pauw E., Pelzer G., Dao Viet D., Marien J. On the influence of hydrophobicity in the SIMS spectra of amino acids in glycerol matrix. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 30;123(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90375-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. P., Sanders J. K., Crawford A., Hunter B. K. Formaldehyde metabolism by Escherichia coli. Detection by in vivo 13C NMR spectroscopy of S-(hydroxymethyl)glutathione as a transient intracellular intermediate. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 12;25(16):4504–4507. doi: 10.1021/bi00364a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roepstorff P., Fohlman J. Proposal for a common nomenclature for sequence ions in mass spectra of peptides. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1984 Nov;11(11):601–601. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200111109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito K., Kato R. Glutathione conjugation of arylnitroso compound: detection and monitoring labile intermediates in situ inside a fast atom bombardment mass spectrometer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 15;124(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90907-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tome D., Naulet N. Carbon 13 nuclear magnetic resonance studies on formaldehyde reactions with polyfunctional amino-acids. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1981 Apr;17(4):501–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1981.tb02020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



