Abstract
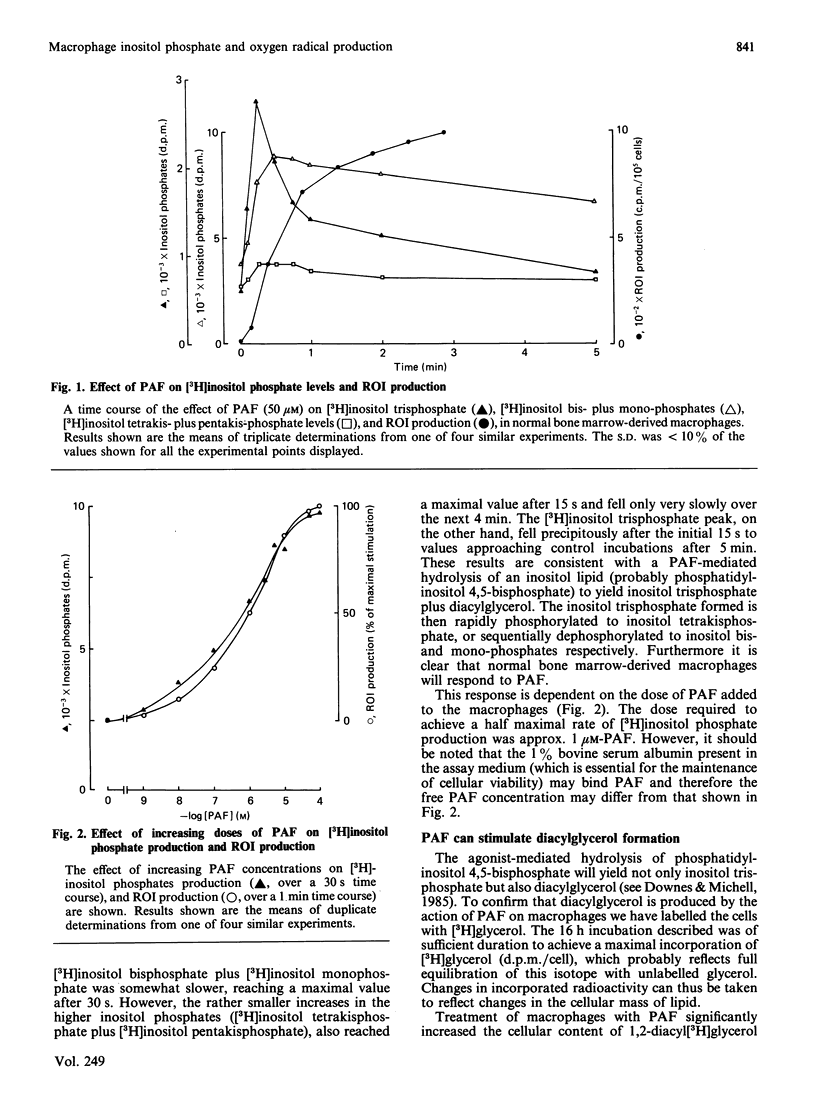
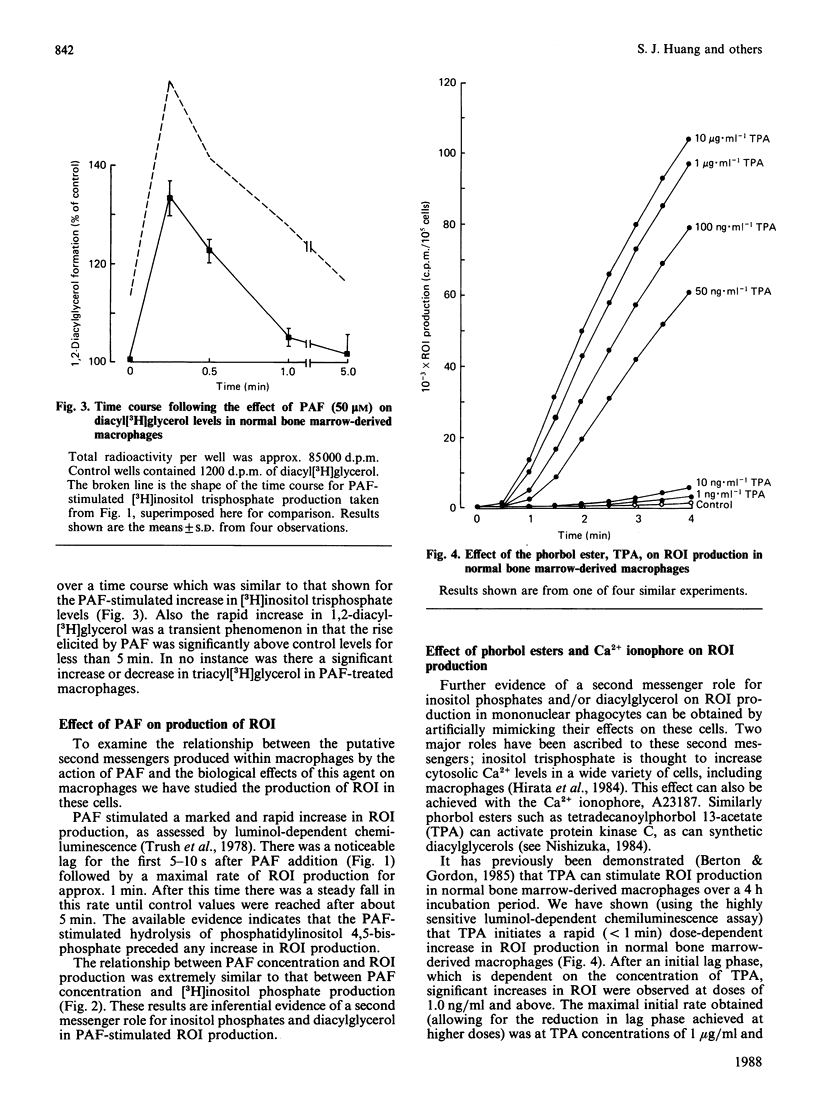
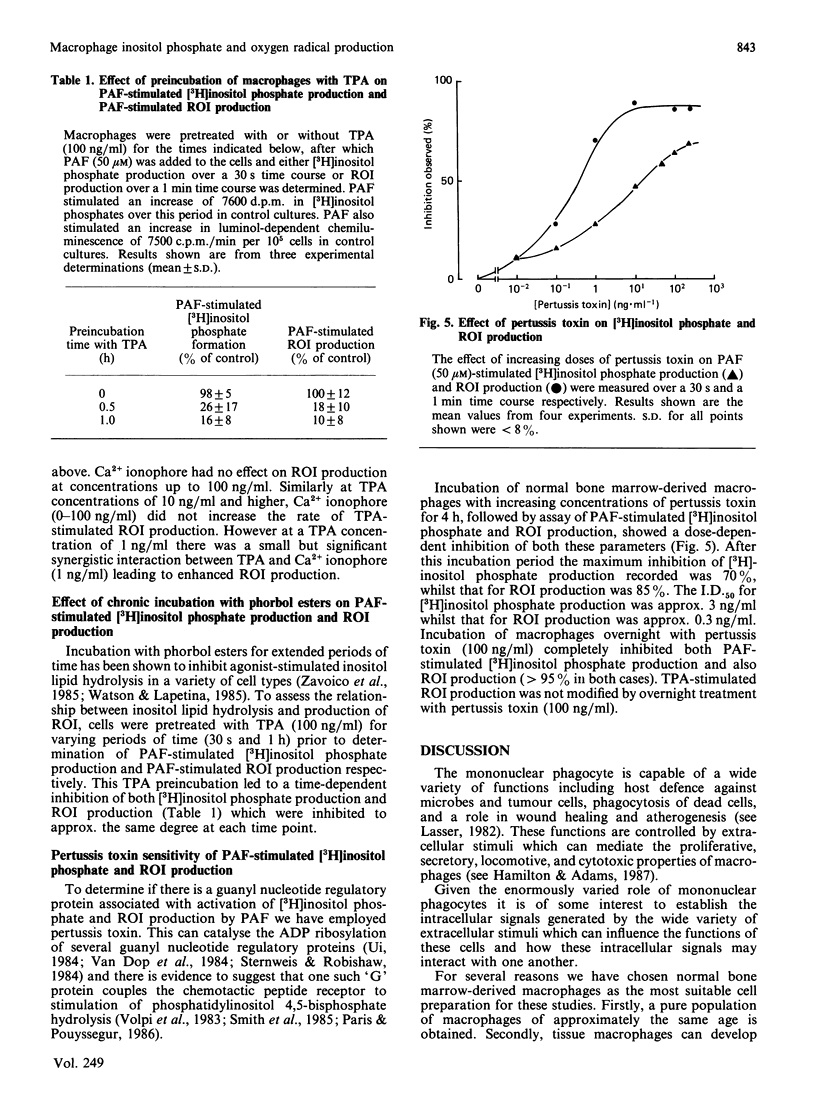
To investigate the relationship between inositol lipid hydrolysis and reactive oxygen-intermediate (ROI) production in macrophages we have examined the effect of platelet-activating factor (PAF) on normal bone marrow-derived macrophages. Addition of PAF to macrophages prelabelled with [3H]inositol caused a marked and rapid increase in [3H]inositol trisphosphate levels. Similarly when PAF was added to [3H]-glycerol prelabelled macrophages there was a rapid increase in 1,2-diacyl[3H]glycerol levels. These events preceded any increase in the rate of PAF-stimulated ROI production by a discernible period of several seconds. Increasing concentrations of PAF led to a markedly similar increase in both ROI production and [3H]inositol lipid hydrolysis suggesting that inositol lipid hydrolysis may lead to the generation of ROI in macrophages. Further evidence that this is the case came from experiments in which pretreatment of macrophages with phorbol esters was shown to inhibit both PAF-stimulated [3H]inositol phosphate production and ROI production to a markedly similar degree. Similarly pertussis toxin inhibited both PAF-stimulated ROI production and [3H]inositol phosphate production. Phorbol esters were shown to activate ROI production in normal bone marrow-derived macrophages whereas the Ca2+ ionophore, A23187, did not. These experiments suggest that PAF stimulates a pertussis toxin-sensitive activation of inositol lipid hydrolysis leading to the formation of inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol. The diacylglycerol formed can then activate protein kinase C leading to the stimulation of ROI production in normal bone marrow-derived macrophages.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O., Hamilton T. A. The cell biology of macrophage activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:283–318. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. Oxidants from phagocytes: agents of defense and destruction. Blood. 1984 Nov;64(5):959–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste J., Henson P. M., Cochrane C. G. Leukocyte-dependent histamine release from rabbit platelets. The role of IgE, basophils, and a platelet-activating factor. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1356–1377. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Gilman A. G. Inhibition of receptor-mediated release of arachidonic acid by pertussis toxin. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. H., Mayer P., Baggiolini M. Stimulation of phagocytosis in bone marrow-derived mouse macrophages by bacterial lipopolysaccharide: correlation with biochemical and functional parameters. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):913–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarnetzki B. Increased monocyte chemotaxis towards leukotriene B4 and platelet activating factor in patients with inflammatory dermatoses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Nov;54(2):486–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty R. W., Godfrey P. P., Hoyle P. C., Putney J. W., Jr, Freer R. J. Secretagogue-induced phosphoinositide metabolism in human leucocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 1;222(2):307–314. doi: 10.1042/bj2220307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Irvine R. F. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and not phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate is the probable precursor of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in agonist-stimulated parotid gland. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):501–506. doi: 10.1042/bj2380501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford-Hutchinson A. W. Neutrophil aggregating properties of PAF-acether and leukotriene B4. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1983;5(1):17–21. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(83)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay J. C., Beckman J. K., Zaboy K. A., Lukens J. N. Modulation of neutrophil oxidative responses to soluble stimuli by platelet-activating factor. Blood. 1986 Apr;67(4):931–936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung H. P. Acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine (platelet-activating factor) mediates heightened metabolic activity in macrophages. Studies on PGE, TXB2 and O2- production, spreading, and the influence of calmodulin-inhibitor W-7. FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 22;160(1-2):209–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80968-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. T., Stephens L., Downes C. P. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands may both result indirectly from receptor-stimulated release of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate from phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):507–516. doi: 10.1042/bj2380507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi H., Kudo I., Inoue K., Onozaki K., Tsushima S., Nomura H., Nojima S. Activation of guinea pig peritoneal macrophages by platelet activating factor (PAF) and its agonists. J Biochem. 1985 Jun;97(6):1737–1745. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata M., Suematsu E., Hashimoto T., Hamachi T., Koga T. Release of Ca2+ from a non-mitochondrial store site in peritoneal macrophages treated with saponin by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):229–236. doi: 10.1042/bj2230229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. B., Lee C. S., Cheah M. J., Shen T. Y. Specific receptor sites for 1-O-alkyl-2-O-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (platelet activating factor) on rabbit platelet and guinea pig smooth muscle membranes. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 27;22(20):4756–4763. doi: 10.1021/bi00289a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Torres B. A. Mechanism of calcium ionophore A23187-induced priming of bone marrow-derived macrophages for tumor cell killing: relationship to priming by interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5959–5962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasser A. The mononuclear phagocytic system: a review. Hum Pathol. 1983 Feb;14(2):108–126. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(83)80239-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Katada T., Ui M. Coupling of the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein to chemotactic peptide receptors in neutrophil membranes and its uncoupling by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. A possible role of the toxin substrate in Ca2+-mobilizing receptor-mediated signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6761–6768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris S., Pouysségur J. Pertussis toxin inhibits thrombin-induced activation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis and Na+/H+ exchange in hamster fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):55–60. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04177.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosoff P. M., Stein L. F., Cantley L. C. Phorbol esters induce differentiation in a pre-B-lymphocyte cell line by enhancing Na+/H+ exchange. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7056–7060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharps E. S., McCarl R. L. A high-performance liquid chromatographic method to measure 32P incorporation into phosphorylated metabolites in cultured cells. Anal Biochem. 1982 Aug;124(2):421–424. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Lane B. C., Kusaka I., Verghese M. W., Snyderman R. Chemoattractant receptor-induced hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in human polymorphonuclear leukocyte membranes. Requirement for a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5875–5878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. R., Guilbert L. J., Tushinski R. J., Bartelmez S. H. CSF-1--a mononuclear phagocyte lineage-specific hemopoietic growth factor. J Cell Biochem. 1983;21(2):151–159. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240210206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber A. I. Protein kinase C and the activation of the human neutrophil NADPH-oxidase. Blood. 1987 Mar;69(3):711–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dop C., Yamanaka G., Steinberg F., Sekura R. D., Manclark C. R., Stryer L., Bourne H. R. ADP-ribosylation of transducin by pertussis toxin blocks the light-stimulated hydrolysis of GTP and cGMP in retinal photoreceptors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):23–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpi M., Yassin R., Naccache P. H., Sha'afi R. I. Chemotactic factor causes rapid decreases in phosphatidylinositol,4,5-bisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4-monophosphate in rabbit neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 May 16;112(3):957–964. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91711-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Lapetina E. G. 1,2-Diacylglycerol and phorbol ester inhibit agonist-induced formation of inositol phosphates in human platelets: possible implications for negative feedback regulation of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2623–2626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetton A. D., Monk P. N., Consalvey S. D., Downes C. P. The haemopoietic growth factors interleukin 3 and colony stimulating factor-1 stimulate proliferation but do not induce inositol lipid breakdown in murine bone-marrow-derived macrophages. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3281–3286. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04640.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano K., Nakashima S., Nozawa Y. Coupling of polyphosphoinositide breakdown with calcium efflux in formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-stimulated rabbit neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 1983 Sep 19;161(2):296–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavoico G. B., Halenda S. P., Sha'afi R. I., Feinstein M. B. Phorbol myristate acetate inhibits thrombin-stimulated Ca2+ mobilization and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3859–3862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


