Abstract
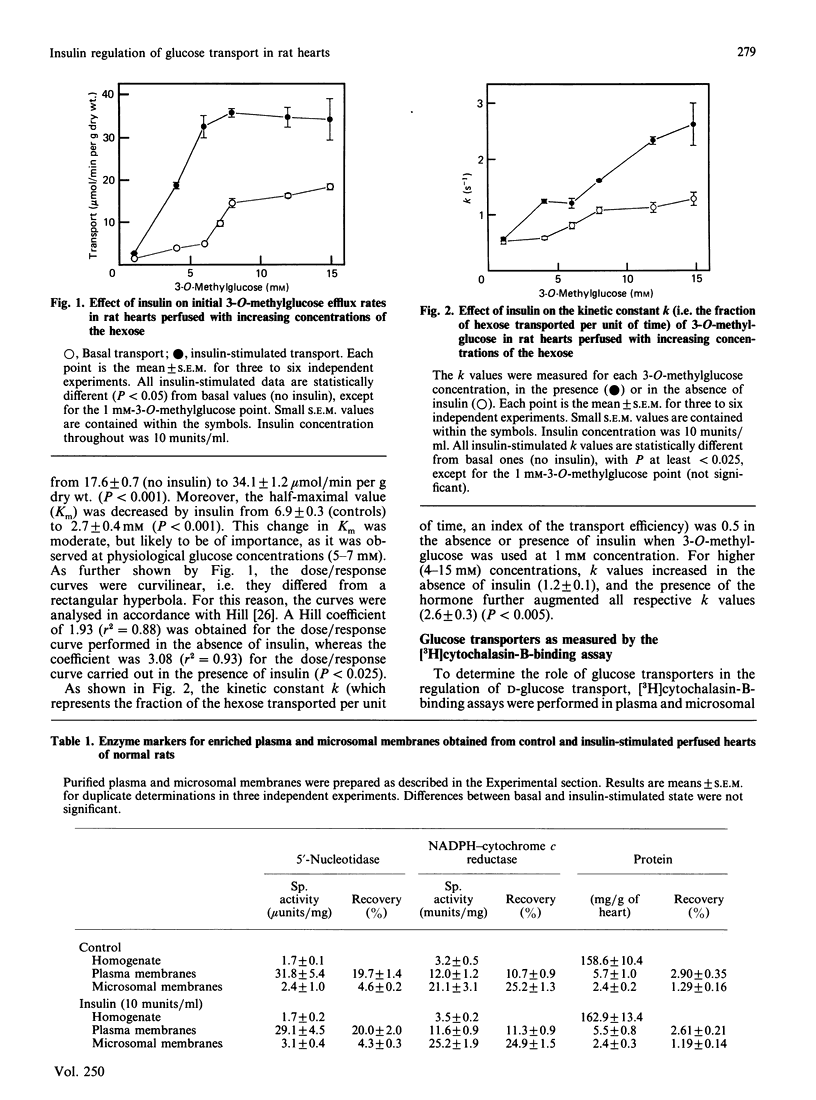
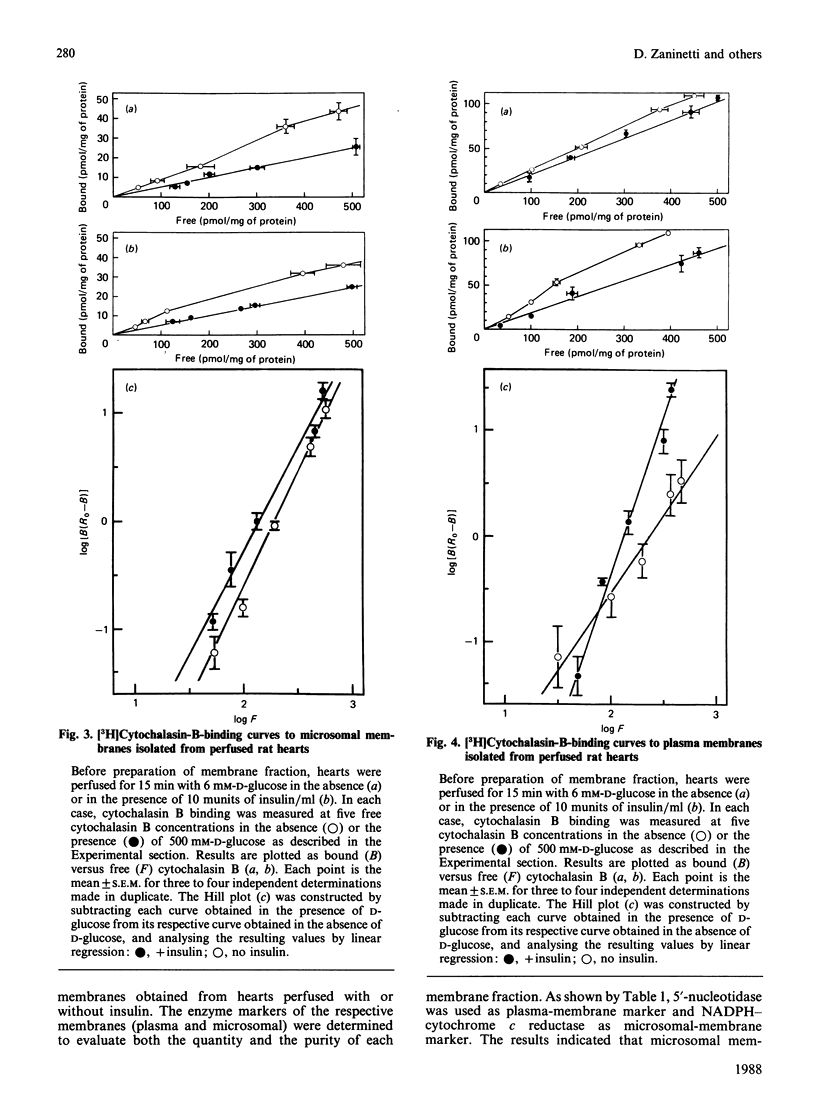
The effect of insulin on glucose transport and glucose transporters was studied in perfused rat heart. Glucose transport was measured by the efflux of labelled 3-O-methylglucose from hearts preloaded with this hexose. Insulin stimulated 3-O-methylglucose transport by: (a) doubling the maximal velocity (Vmax); (b) decreasing the Kd from 6.9 to 2.7 mM; (c) increasing the Hill coefficient toward 3-O-methylglucose from 1.9 to 3.1; (d) increasing the efficiency of the transport process (k constant). Glucose transporters in enriched plasma and microsomal membranes from heart were quantified by the [3H]cytochalasin-B-binding assay. When added to normal hearts, insulin produced the following changes in the glucose transporters: (a) it increased the translocation of transporters from an intracellular pool to the plasma membranes; (b) it increased (from 1.6 to 2.7) the Hill coefficient of the transporters translocated into the plasma membranes toward cytochalasin B, suggesting the existence of a positive co-operativity among the transporters appearing in these membranes; (c) it increased the affinity of the transporters (and hence, possibly, of glucose) for cytochalasin B. The data provide evidence that the stimulatory effect of insulin on glucose transport may be due not to the sole translocation of intracellular glucose transporters to the plasma membrane, but to changes in the functional properties thereof.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avruch J., Wallach D. F. Preparation and properties of plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum fragments from isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 13;233(2):334–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Carruthers A. Insulin regulation of sugar transport in giant muscle fibres of the barnacle. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:397–431. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baly D. L., Horuk R. Dissociation of insulin-stimulated glucose transport from the translocation of glucose carriers in rat adipose cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):21–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudry I. H., Gould M. K. Kinetics of glucose uptake in isolated soleus muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May 6;177(3):527–536. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90315-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung J. Y., Conover C., Regen D. M., Whitfield C. F., Morgan H. E. Effect of insulin on kinetics of sugar transport in heart muscle. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jan;234(1):E70–E78. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.1.E70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crettaz M., Prentki M., Zaninetti D., Jeanrenaud B. Insulin resistance in soleus muscle from obese Zucker rats. Involvement of several defective sites. Biochem J. 1980 Feb 15;186(2):525–534. doi: 10.1042/bj1860525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Wardzala L. J. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4758–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Love E. R., Pratt O. E. Insulin-stimulated entry of glucose into muscle in vivo as a major factor in the regulation of blood glucose. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(2):273–288. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckel J., Wirdeier A., Herberg L., Reinauer H. Insulin resistance in the heart: studies on isolated cardiocytes of genetically obese Zucker rats. Endocrinology. 1985 Apr;116(4):1529–1534. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-4-1529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greco-Perotto R., Assimacopoulos-Jeannet F., Jeanrenaud B. Insulin modifies the properties of glucose transporters in rat brown adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):63–68. doi: 10.1042/bj2470063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greco-Perotto R., Zaninetti D., Assimacopoulos-Jeannet F., Bobbioni E., Jeanrenaud B. Stimulatory effect of cold adaptation on glucose utilization by brown adipose tissue. Relationship with changes in the glucose transporter system. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7732–7736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. V. A new mathematical treatment of changes of ionic concentration in muscle and nerve under the action of electric currents, with a theory as to their mode of excitation. J Physiol. 1910 May 11;40(3):190–224. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1910.sp001366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman G. D., Rees W. D. Side-specific analogues for the rat adipocyte sugar transport system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Feb 8;685(1):78–86. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horuk R., Matthaei S., Olefsky J. M., Baly D. L., Cushman S. W., Simpson I. A. Biochemical and functional heterogeneity of rat adipocyte glucose transporters. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1823–1828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthaei S., Garvey W. T., Horuk R., Hueckstaedt T. P., Olefsky J. M. Human adipocyte glucose transport system. Biochemical and functional heterogeneity of hexose carriers. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):703–709. doi: 10.1172/JCI112874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NARAHARA H. T., OZAND P. Studies of tissue permeability. IX. The effect of insulin on the penetration of 3-methylglucose-H3 in frog muscle. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:40–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORMAN D., MENOZZI P., REID D., LESTER G., HECHTER O. Action of insulin on sugar permeability in rat diaphragm muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1959 Jul 20;42(6):1277–1299. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.6.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neely J. R., Liebermeister H., Battersby E. J., Morgan H. E. Effect of pressure development on oxygen consumption by isolated rat heart. Am J Physiol. 1967 Apr;212(4):804–814. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.4.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka Y., Czech M. P. Photoaffinity labeling of insulin-sensitive hexose transporters in intact rat adipocytes. Direct evidence that latent transporters become exposed to the extracellular space in response to insulin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8125–8133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schudt C., Gaertner U., Pette D. Insulin action on glucose transport and calcium fluxes in developing muscle cells in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep;68(1):103–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottocasa G. L., Kuylenstierna B., Ernster L., Bergstrand A. An electron-transport system associated with the outer membrane of liver mitochondria. A biochemical and morphological study. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):415–438. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Kono T. Evidence that insulin causes translocation of glucose transport activity to the plasma membrane from an intracellular storage site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2542–2545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taegtmeyer H., Hems R., Krebs H. A. Utilization of energy-providing substrates in the isolated working rat heart. Biochem J. 1980 Mar 15;186(3):701–711. doi: 10.1042/bj1860701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinten J., Gliemann J., Osterlind K. Exchange of 3-O-methylglucose in isolated fat cells. Concentration dependence and effect of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 10;251(3):794–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardzala L. J., Cushman S. W., Salans L. B. Mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Enhancement of the number of functional transport systems. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8002–8005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardzala L. J., Jeanrenaud B. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat diaphragm. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport units to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7090–7093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Smith M. M., Robinson F. W., Kono T. Insulin action on glucose transport in cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13117–13122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T. J., Hinkle P. C. The glucose transporter of mammalian cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:503–517. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitesell R. R., Abumrad N. A. Increased affinity predominates in insulin stimulation of glucose transport in the adipocyte. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2894–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitesell R. R., Gliemann J. Kinetic parameters of transport of 3-O-methylglucose and glucose in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5276–5283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaninetti D., Crettaz M., Jeanrenaud B. Dysregulation of glucose transport in hearts of genetically obese (fa/fa) rats. Diabetologia. 1983 Dec;25(6):525–529. doi: 10.1007/BF00284464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



