Abstract
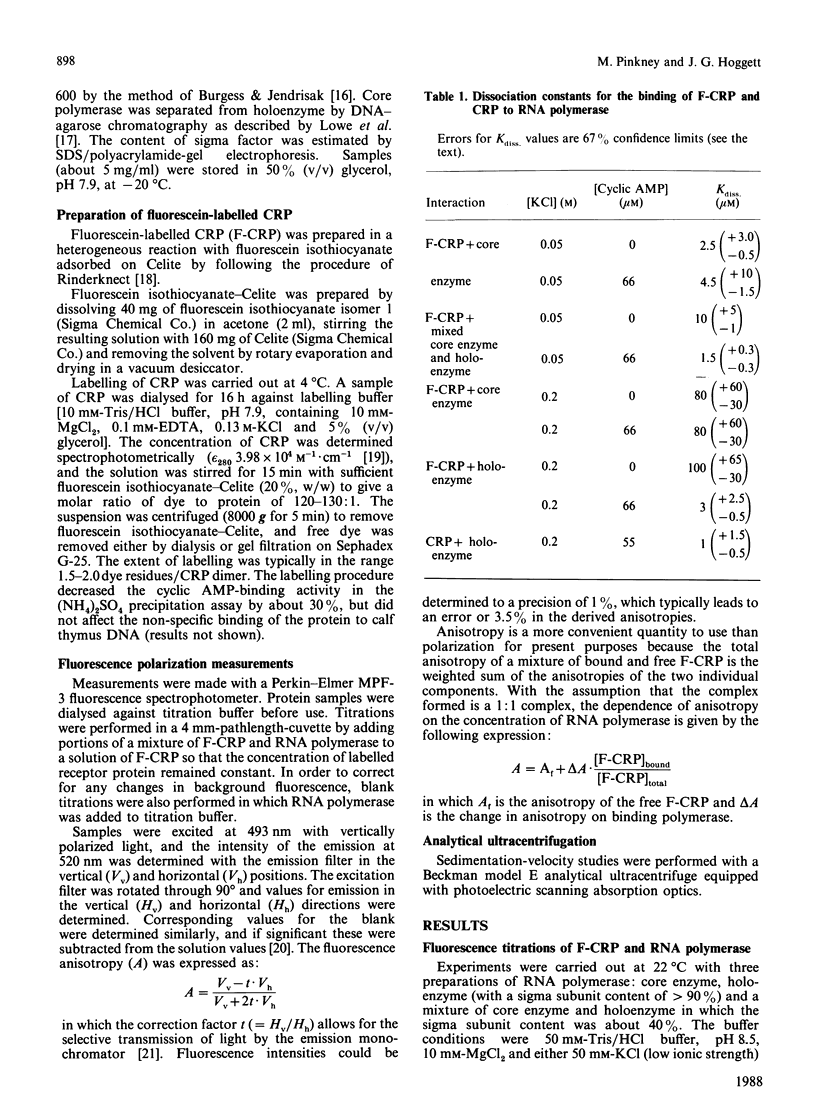
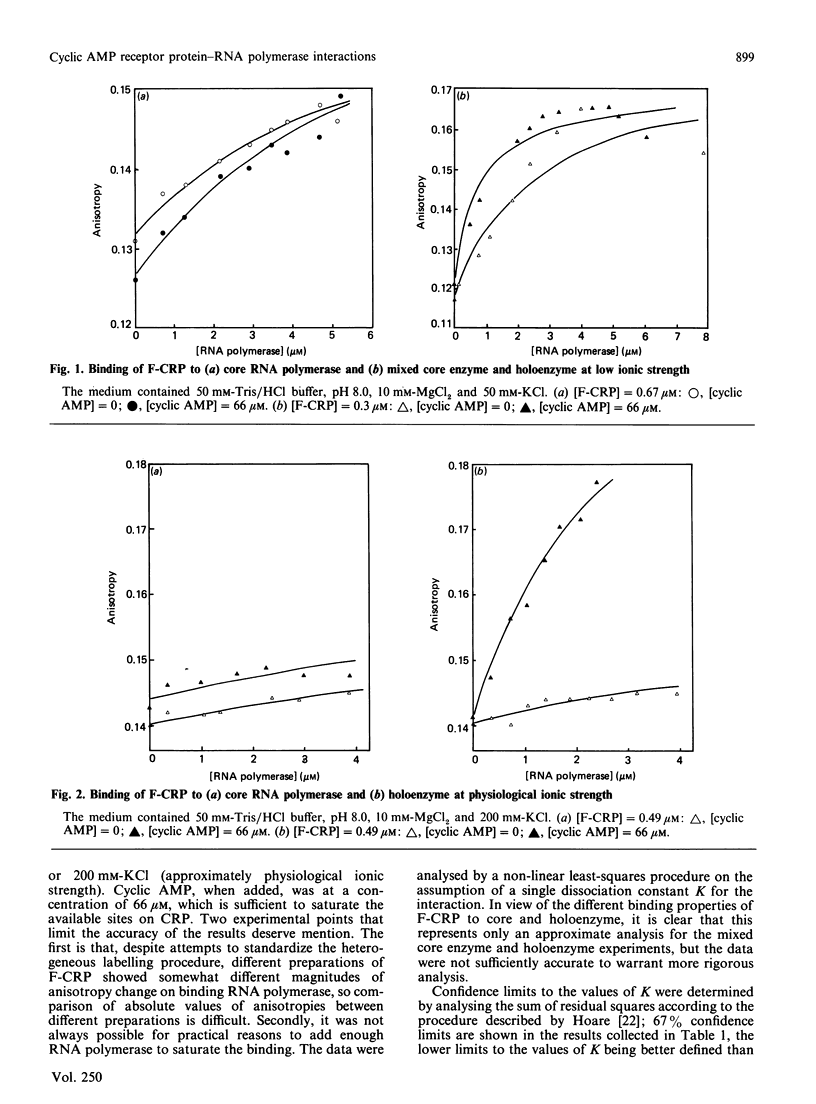
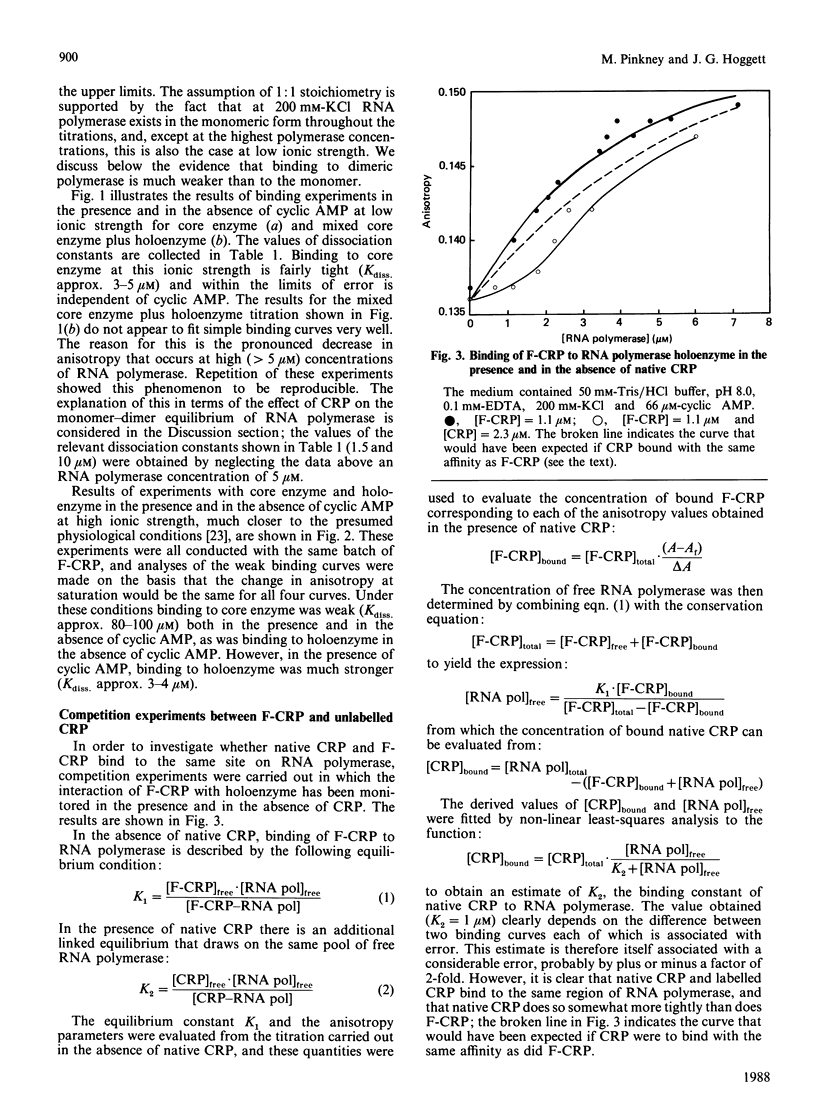
Fluorescence polarization studies were used to study the interaction of a fluorescein-labelled conjugate of the Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein (F-CRP) and RNA polymerase. Under conditions of physiological ionic strength, F-CRP binds to RNA polymerase holoenzyme in a cyclic AMP-dependent manner; the dissociation constant was about 3 microM in the presence of cyclic AMP and about 100 microM in its absence. Binding to core RNA polymerase under the same conditions was weak (Kdiss. approx. 80-100 microM) and independent of cyclic AMP. Competition experiments established that native CRP and F-CRP compete for the same binding site on RNA polymerase holoenzyme and that the native protein binds about 3 times more strongly than does F-CRP. Analytical ultracentrifuge studies showed that CRP binds predominantly to the monomeric rather than the dimeric form of RNA polymerase.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blazy B., Takahashi M., Baudras A. Binding of CRP to DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from E. coli: modulation by cAMP of the interactions with free and DNA-bound holo and core enzyme. Mol Biol Rep. 1980 Mar 31;6(1):39–43. doi: 10.1007/BF00775753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone T., Wilcox G. A rapid high-yield purification procedure for the cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate receptor protein from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 17;541(4):528–534. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANDLIKER W. B., SCHAPIRO H. C., MEDUSKI J. W., ALONSO R., FEIGEN G. A., HAMRICK J. R., Jr APPLICATION OF FLUORESCENCE POLARIZATION TO THE ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY REACTION. THEORY AND EXPERIMENTAL METHOD. Immunochemistry. 1964 Oct;1:165–191. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(64)90041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilen E., Pampeno C., Krakow J. S. Production and properties of the alpha core derived from the cyclic adenosine monophosphate receptor protein of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2469–2473. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoare D. G. A curve-fitting procedure utilizing a small computer for equations containing three or four unknown constants. Anal Biochem. 1972 Apr;46(2):604–615. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90332-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschild A., Irwin N., Ptashne M. Repressor structure and the mechanism of positive control. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90451-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao-Huang Y., Revzin A., Butler A. P., O'Conner P., Noble D. W., von Hippel P. H. Nonspecific DNA binding of genome-regulating proteins as a biological control mechanism: measurement of DNA-bound Escherichia coli lac repressor in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4228–4232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. M., Nicholson B. H. Physical studies on Escherichia coli B RNA polymerase and its subunits. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 14;62(2):303–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Buc H. Is DNA unwound by the cyclic AMP receptor protein? Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):473–485. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Johnson H. N., Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. The DNA binding domain and bending angle of E. coli CAP protein. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):995–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90814-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe P. A., Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Purification and properties of the sigma subunit of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1344–1352. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J. Specific binding of CAP factor to lac promoter DNA. Nature. 1975 Aug 21;256(5519):672–674. doi: 10.1038/256672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malan T. P., Kolb A., Buc H., McClure W. R. Mechanism of CRP-cAMP activation of lac operon transcription initiation activation of the P1 promoter. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):881–909. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissley P., Anderson W. B., Gallo M., Pastan I., Perlman R. L. The binding of cyclic adenosine monophosphate receptor to deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 10;247(13):4264–4269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxe S. A., Revzin A. Cooperative binding to DNA of catabolite activator protein of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 23;18(2):255–263. doi: 10.1021/bi00569a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spassky A., Busby S., Buc H. On the action of the cyclic AMP-cyclic AMP receptor protein complex at the Escherichia coli lactose and galactose promoter regions. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):43–50. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01759.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stender W. Cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate receptor protein: interaction with E. coli RNA polymerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 16;96(1):320–325. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91217-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger B., Clore G. M., Gronenborn A. M., Hillen W. Specific DNA binding of the cAMP receptor protein within the lac operon stabilizes double-stranded DNA in the presence of cAMP. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):289–293. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01419.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiel J., Hershey J. W. Fluorescence polarization studies of the interaction of Escherichia coli protein synthesis initiation factor 3 with 30S ribosomal subunits. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 29;20(20):5859–5865. doi: 10.1021/bi00523a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiel J., Hershey J. W. The binding of fluorescein-labeled protein synthesis initiation factor 2 to Escherichia coli 30 S ribosomal subunits determined by fluorescence polarization. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1215–1220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu F. Y., Nath K., Wu C. W. Conformational transitions of cyclic adenosine monophosphate receptor protein of Escherichia coli. A fluorescent probe study. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2567–2572. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubay G. The isolation and properties of CAP, the catabolite gene activator. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):856–877. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



