Abstract
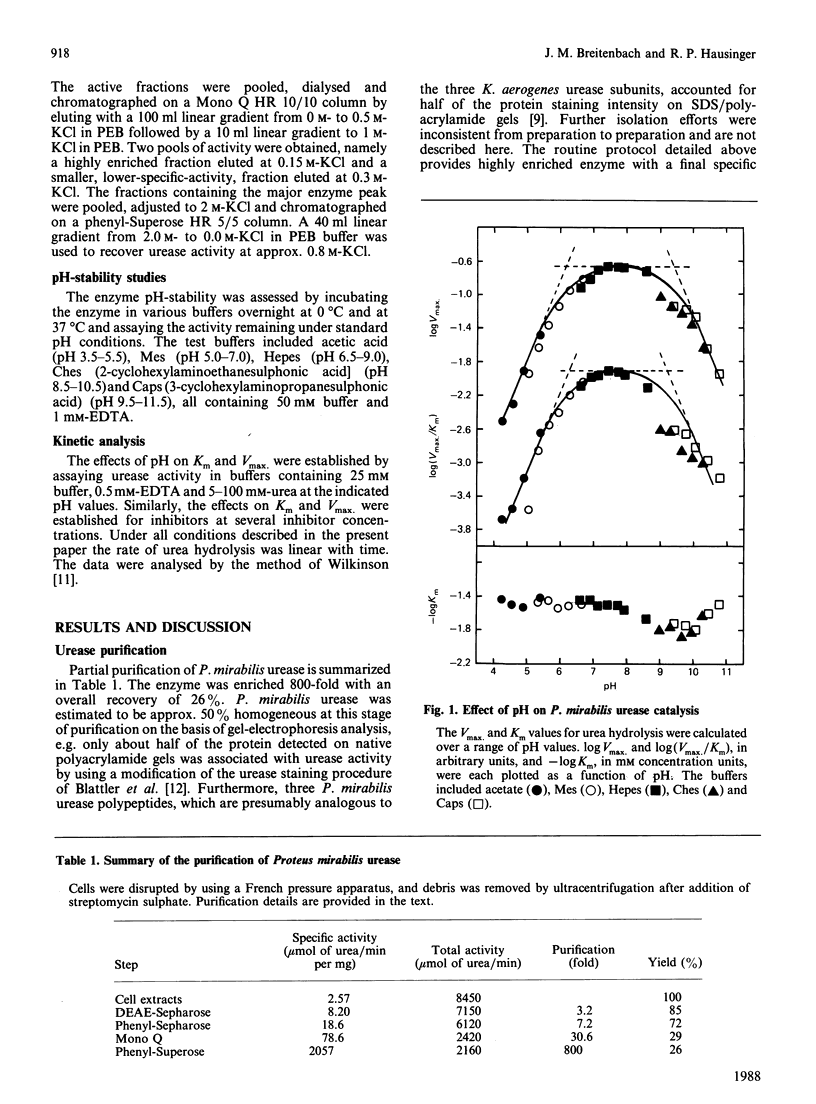
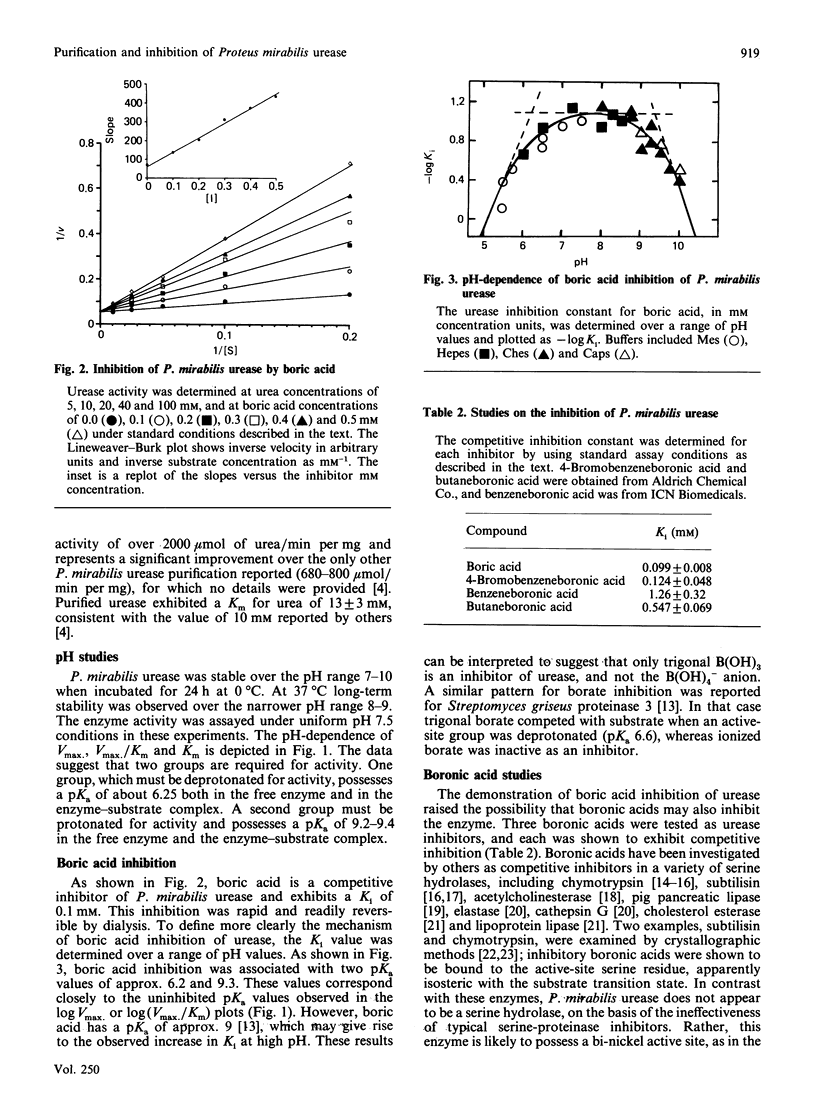
Urease was purified 800-fold and partially characterized from Proteus mirabilis, the predominant microorganism associated with urinary stones. Boric acid is a rapid reversible competitive inhibitor of urease. The pH-dependence of inhibition exhibited pKa values of 6.25 and 9.3, where the latter value is probably due to the inherent pKa of boric acid. Three boronic acids also were shown to inhibit urease competitively.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews R. K., Blakeley R. L., Zerner B. Urea and urease. Adv Inorg Biochem. 1984;6:245–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonov V. K., Ivanina T. V., Berezin I. V., Martinek K. n-Alkylboronic acids as bifunctional reversible inhibitors of alpha-chymotrypsin. FEBS Lett. 1970 Mar 16;7(1):23–25. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80607-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. O., Wilkes S. H., Bayliss M. E., Prescott J. M. Hydroxamates and aliphatic boronic acids: marker inhibitors for aminopeptidase. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2098–2103. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer C. A., Pettersson G. Effect of boric acid on the catalytic activity of Streptomyces griseus protease 3. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 15;45(2):473–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattler D. P., Contaxis C. C., Reithel F. J. Dissociation of urease by glycol and glycerol. Nature. 1967 Oct 21;216(5112):274–275. doi: 10.1038/216274b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner C. W. Boronic acid inhibitors of porcine pancreatic lipase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5064–5068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith D. P., Musher D. M., Itin C. Urease. The primary cause of infection-induced urinary stones. Invest Urol. 1976 Mar;13(5):346–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith D. P., Musher D. M. Prevention of infected urinary stones by urease inhibition. Invest Urol. 1973 Nov;11(3):228–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausinger R. P. Nickel utilization by microorganisms. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):22–42. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.22-42.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausinger R. P. Purification of a nickel-containing urease from the rumen anaerobe Selenomonas ruminantium. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7866–7870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C. A., Shenvi A. B. Inhibition of the serine proteases leukocyte elastase, pancreatic elastase, cathepsin G, and chymotrypsin by peptide boronic acids. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15106–15114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehler K. A., Hess G. P. [A new, specific and reversible bifunctional alkylborinic acid inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase]. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 17;13(26):5345–5350. doi: 10.1021/bi00723a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehler K. A., Lienhard G. E. 2-phenylethaneboronic acid, a possible transition-state analog for chymotrypsin. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2477–2483. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist R. N., Terry C. Inhibition of subtilisin by boronic acids, potential analogs of tetrahedral reaction intermediates. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jan;160(1):135–144. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(74)80018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. A., Alden R. A., Birktoft J. J., Freer S. T., Kraut J. X-ray crystallographic study of boronic acid adducts with subtilisin BPN' (Novo). A model for the catalytic transition state. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7120–7126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millner O. E., Jr, Andersen J. A., Appler M. E., Benjamin C. E., Edwards J. G., Humphrey D. T., Shearer E. M. Flurofamide: a potent inhibitor of bacterial urease with potential clinical utility in the treatment of infection induced urinary stones. J Urol. 1982 Feb;127(2):346–350. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)53779-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipp M., Bender M. L. Inhibition of serine proteases by arylboronic acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):478–480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstein I. J., Hamilton-Miller J. M. Inhibitors of urease as chemotherapeutic agents. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1984;11(1):1–12. doi: 10.3109/10408418409105901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton L. D., Stout J. S., Hosie L., Spencer P. S., Quinn D. M. Phenyl-n-butylborinic acid is a potent transition state analog inhibitor of lipolytic enzymes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 14;134(1):386–392. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90575-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd M. J., Hausinger R. P. Purification and characterization of the nickel-containing multicomponent urease from Klebsiella aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):5963–5967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulinsky A., Mavridis I., Mann R. F. Expression of functionality of alpha-chymotrypsin. An alternate binding mode in the substrate specificity site. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1074–1078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


