Abstract
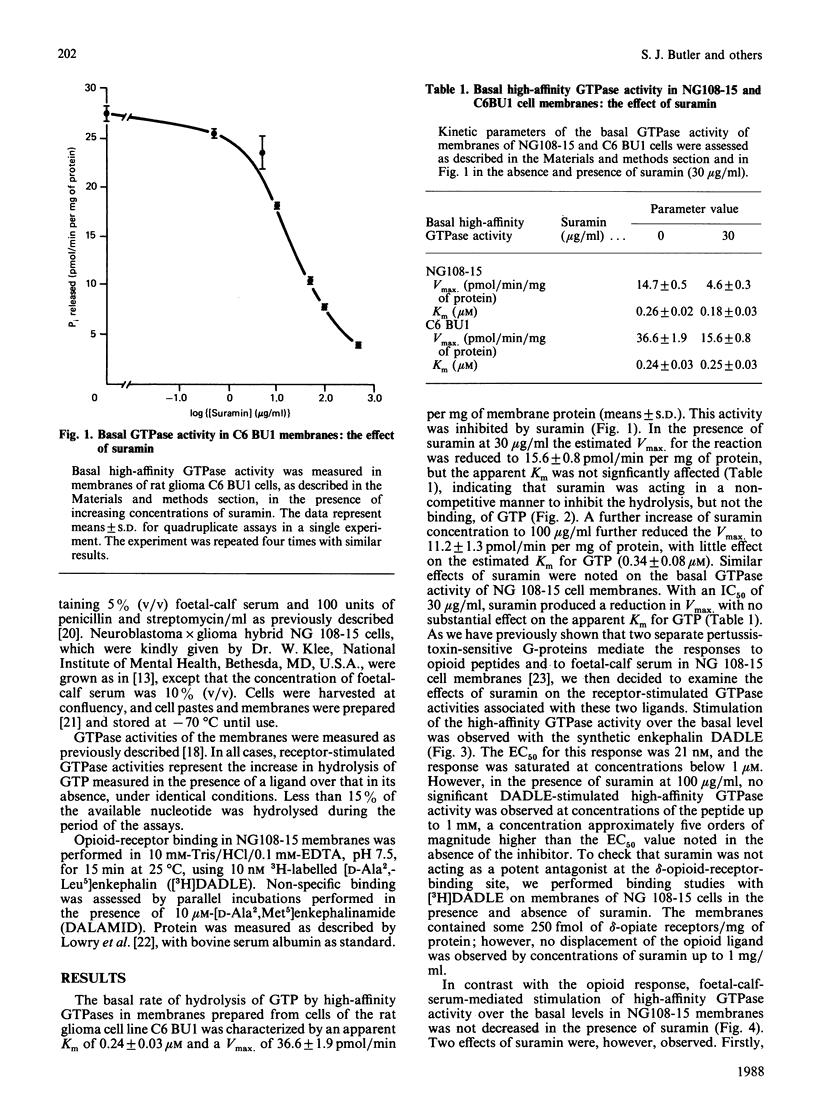
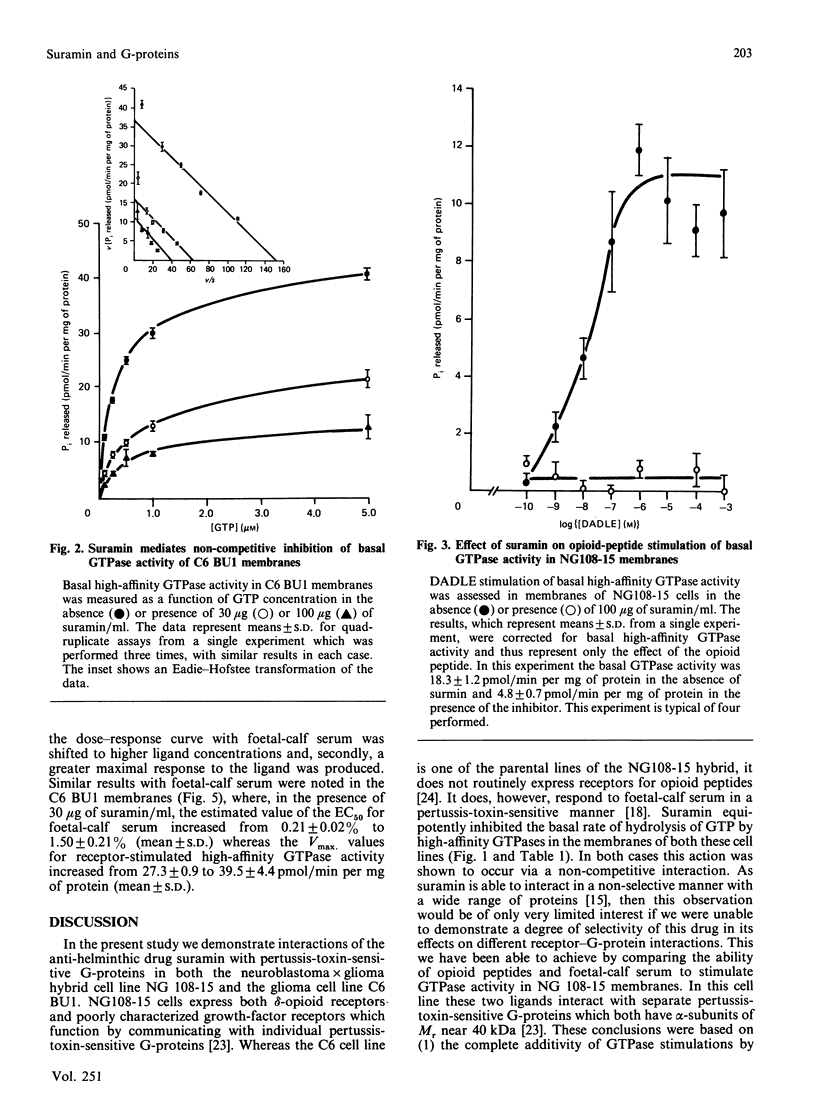
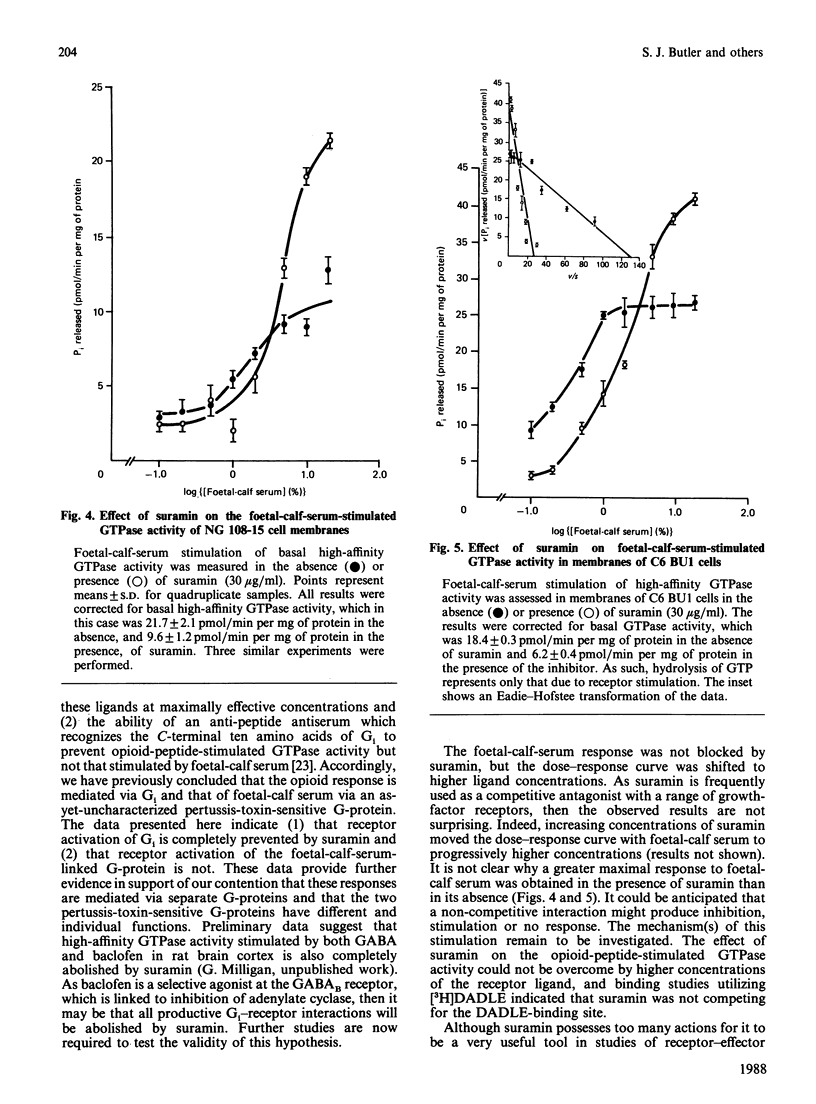
The anti-helminthic drug suramin inhibited the basal high-affinity GTPase activity of both C6 BU1 glioma and NG 108-15 neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid-cell membranes with an IC50 (concentration causing half-maximal inhibition) value close to 30 micrograms/ml. This effect was shown to occur via a non-competitive mechanism in which the binding affinity of the G-proteins for GTP was not altered, but the maximal velocity of the subsequent hydrolysis was reduced. In NG 108-15 membranes, both opioid peptides and foetal-calf serum stimulated high-affinity GTPase activity in a pertussis-toxin-sensitive manner. These effects have previously been shown to be mediated by different G-proteins [McKenzie, Kelly, Unson, Spiegel & Milligan (1988) Biochem. J. 249, 653-659]. Suramin completely prevented the opioid-peptide-stimulated increase in GTP hydrolysis, but did not prevent the opioid peptide from binding to its receptor. Suramin, however, did not block the foetal-calf-serum-stimulated GTPase response. This selective action of suramin provides further evidence for distinct roles for two separate pertussis-toxin-sensitive G-proteins in signal transduction in NG 108-15 membranes and provides the first evidence for a selective effect of a drug on the functions of different G-proteins.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betsholtz C., Johnsson A., Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Efficient reversion of simian sarcoma virus-transformation and inhibition of growth factor-induced mitogenesis by suramin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6440–6444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Masters S. B., Sullivan K. A. Mammalian G proteins: structure and function. Biochem Soc Trans. 1987 Feb;15(1):35–38. doi: 10.1042/bst0150035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawler D., Milligan G., Spiegel A. M., Unson C. G., Houslay M. D. Abolition of the expression of inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein Gi activity in diabetes. Nature. 1987 May 21;327(6119):229–232. doi: 10.1038/327229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Milligan G., Pines M., Goldsmith P., Codina J., Klee W., Spiegel A. Use of specific antibodies to quantitate the guanine nucleotide-binding protein Go in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Meren R. ADP-ribosylation of membrane proteins catalyzed by cholera toxin: basis of the activation of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3050–3054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Rosenthal W., Trautwein W., Schultz G. The GTP-binding protein, Go, regulates neuronal calcium channels. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):445–447. doi: 10.1038/325445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. Direct modification of the membrane adenylate cyclase system by islet-activating protein due to ADP-ribosylation of a membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3129–3133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski G., Klee W. A. Opiates inhibit adenylate cyclase by stimulating GTP hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4185–4189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters S. B., Stroud R. M., Bourne H. R. Family of G protein alpha chains: amphipathic analysis and predicted structure of functional domains. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie F. R., Kelly E. C., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M., Milligan G. Antibodies which recognize the C-terminus of the inhibitory guanine-nucleotide-binding protein (Gi) demonstrate that opioid peptides and foetal-calf serum stimulate the high-affinity GTPase activity of two separate pertussis-toxin substrates. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 1;249(3):653–659. doi: 10.1042/bj2490653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G. Foetal-calf serum stimulates a pertussis-toxin-sensitive high-affinity GTPase activity in rat glioma C6 BU1 cells. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):501–505. doi: 10.1042/bj2450501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Gierschik P., Spiegel A. M., Klee W. A. The GTP-binding regulatory proteins of neuroblastoma x glioma, NG108-15, and glioma, C6, cells. Immunochemical evidence of a pertussis toxin substrate that is neither Ni nor No. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Gierschik P., Spiegel A. M. The use of specific antibodies to identify and quantify guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. Biochem Soc Trans. 1987 Feb;15(1):42–45. doi: 10.1042/bst0150042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G. Guanine nucleotide regulation of the pertussis and cholera toxin substrates of rat glioma C6 BU1 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 6;929(2):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90176-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Streaty R. A., Gierschik P., Spiegel A. M., Klee W. A. Development of opiate receptors and GTP-binding regulatory proteins in neonatal rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8626–8630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. K., Nirenberg M., Klee W. A. Morphine receptors as regulators of adenylate cyclase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):590–594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel A. M. Signal transduction by guanine nucleotide binding proteins. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Jan;49(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Tremble P. M., Lavin M. F., Sunday M. E. Platelet-derived growth factor receptors form a high affinity state in membrane preparations. Kinetics and affinity cross-linking studies. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5287–5294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


