Abstract
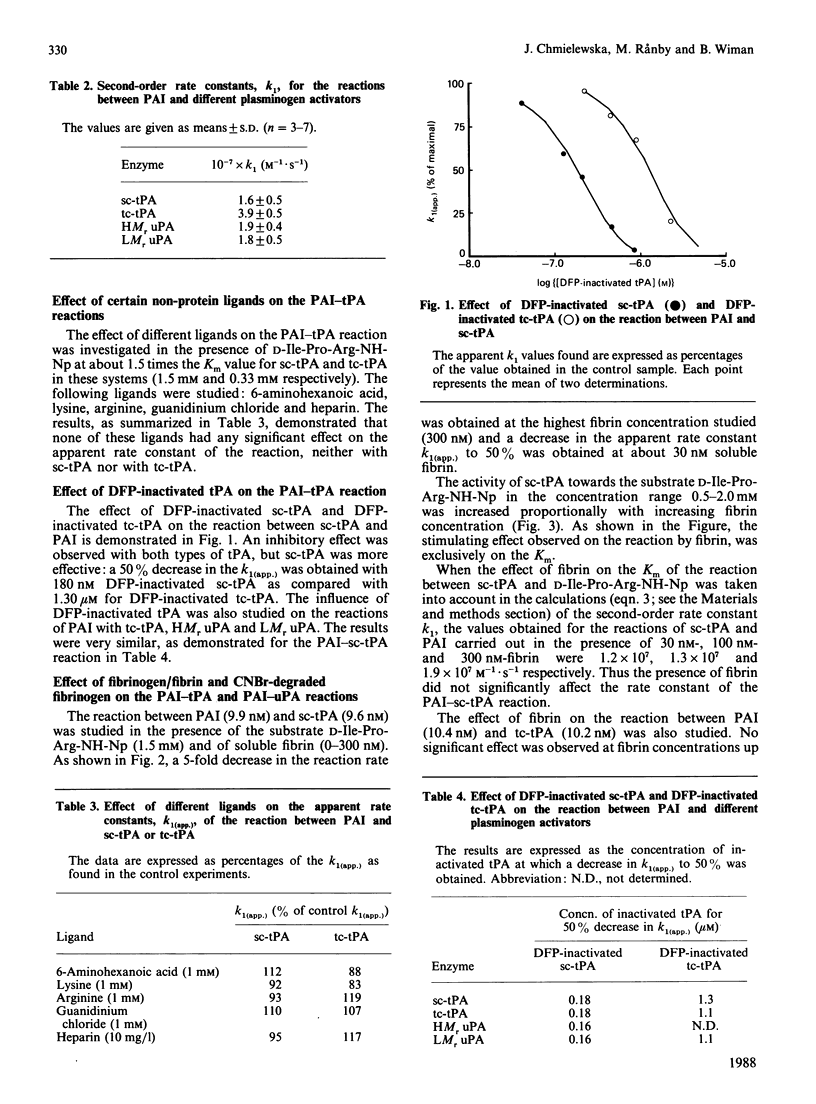
The reactions between plasminogen-activator inhibitor (PAI) and different plasminogen activators were studied in the presence of chromogenic peptide substrates for the enzymes. Our findings suggest that the rate constants for the reactions of PAI with single-chain tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), two-chain tPA, high-Mr urokinase and low-Mr urokinase are high and quite similar (1.6 X 10(7)-3.9 X 10(7) M-1.s-1). A free active site in the enzymes seems to be necessary for their reaction with PAI. Amino acids with antifibrinolytic properties did not interfere with the reactions. However, di-isopropyl phosphorofluoridate-inactivated tPA inhibited the reaction between PAI and all plasminogen activators in a similar way. These findings clearly demonstrated that a 'second-site' interaction, in addition to that between the enzyme active site and the inhibitor 'bait' peptide bond, is of importance for the high reaction rate. The reaction rate between PAI and single-chain tPA in the presence of an activator substrate (D-Ile-Pro-Arg p-nitroanilide) was decreased in the presence of fibrin. Fibrin caused a decrease in the Km for the single-chain tPA-substrate reaction. As a consequence, the 'free' concentration of single-chain tPA in the system decreased in the presence of fibrin, affecting the reaction rate between PAI and single-chain tPA. The phenomenon might be of physiological relevance, in the sense that single-chain tPA bound to fibrin in the presence of plasminogen would be protected against inactivation by PAI.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chmielewska J., Wiman B. Determination of tissue plasminogen activator and its "fast" inhibitor in plasma. Clin Chem. 1986 Mar;32(3):482–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colucci M., Paramo J. A., Collen D. Inhibition of one-chain and two-chain forms of human tissue-type plasminogen activator by the fast-acting inhibitor of plasminogen activator in vitro and in vivo. J Lab Clin Med. 1986 Jul;108(1):53–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekman C. M., Loskutoff D. J. Endothelial cells produce a latent inhibitor of plasminogen activators that can be activated by denaturants. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11581–11587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoylaerts M., Rijken D. C., Lijnen H. R., Collen D. Kinetics of the activation of plasminogen by human tissue plasminogen activator. Role of fibrin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2912–2919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruithof E. K., Tran-Thang C., Bachmann F. Studies on the release of a plasminogen activator inhibitor by human platelets. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Apr 30;55(2):201–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruithof E. K., Tran-Thang C., Ransijn A., Bachmann F. Demonstration of a fast-acting inhibitor of plasminogen activators in human plasma. Blood. 1984 Oct;64(4):907–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G. Quantitation and properties of the active and latent plasminogen activator inhibitors in cultures of human endothelial cells. Blood. 1986 May;67(5):1309–1313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ny T., Sawdey M., Lawrence D., Millan J. L., Loskutoff D. J. Cloning and sequence of a cDNA coding for the human beta-migrating endothelial-cell-type plasminogen activator inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6776–6780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannekoek H., Veerman H., Lambers H., Diergaarde P., Verweij C. L., van Zonneveld A. J., van Mourik J. A. Endothelial plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI): a new member of the Serpin gene family. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2539–2544. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04532.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rånby M. Studies on the kinetics of plasminogen activation by tissue plasminogen activator. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 24;704(3):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengers E. D., van Hinsbergh V. W., Jansen B. G. The active and the inactive plasminogen activator inhibitor from human endothelial cell conditioned medium are immunologically and functionally related to each other. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Sep 4;883(2):233–241. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90313-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffens G. J., Günzler W. A., Otting F., Frankus E., Flohé L. The complete amino acid sequence of low molecular mass urokinase from human urine. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1982 Sep;363(9):1043–1058. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1982.363.2.1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urdén G., Hamsten A., Wiman B. Comparison of plasminogen activator inhibitor activity and antigen in plasma samples. Clin Chim Acta. 1987 Nov 16;169(2-3):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(87)90319-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen J. H., Mullaart E., Chang G. T., Kluft C., Wijngaards G. A simple, sensitive spectrophotometric assay for extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator applicable to measurements in plasma. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Dec 27;48(3):266–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner O. F., Vetterlein M., Binder B. R. Purification of an active plasminogen activator inhibitor immunologically related to the endothelial type plasminogen activator inhibitor from the conditioned media of a human melanoma cell line. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14474–14481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Chmielewska J., Rånby M. Inactivation of tissue plasminogen activator in plasma. Demonstration of a complex with a new rapid inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3644–3647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Collen D. On the kinetics of the reaction between human antiplasmin and plasmin. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar 15;84(2):573–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



