Abstract
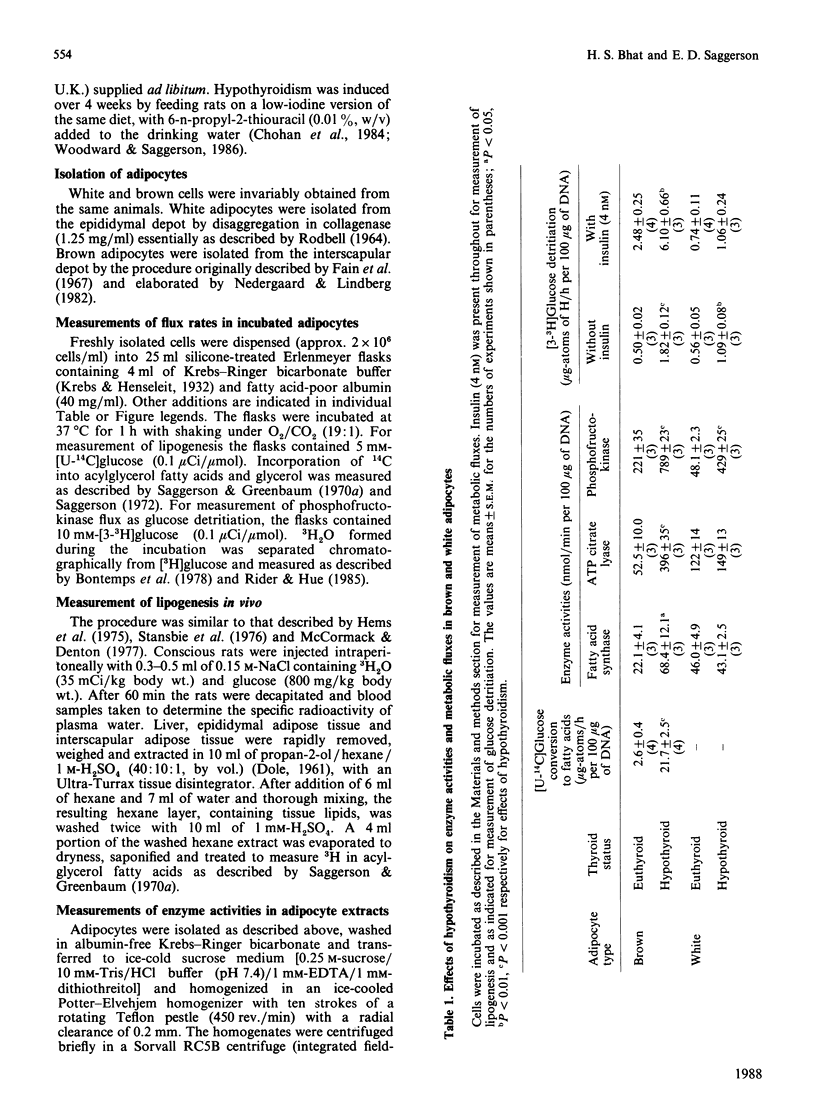
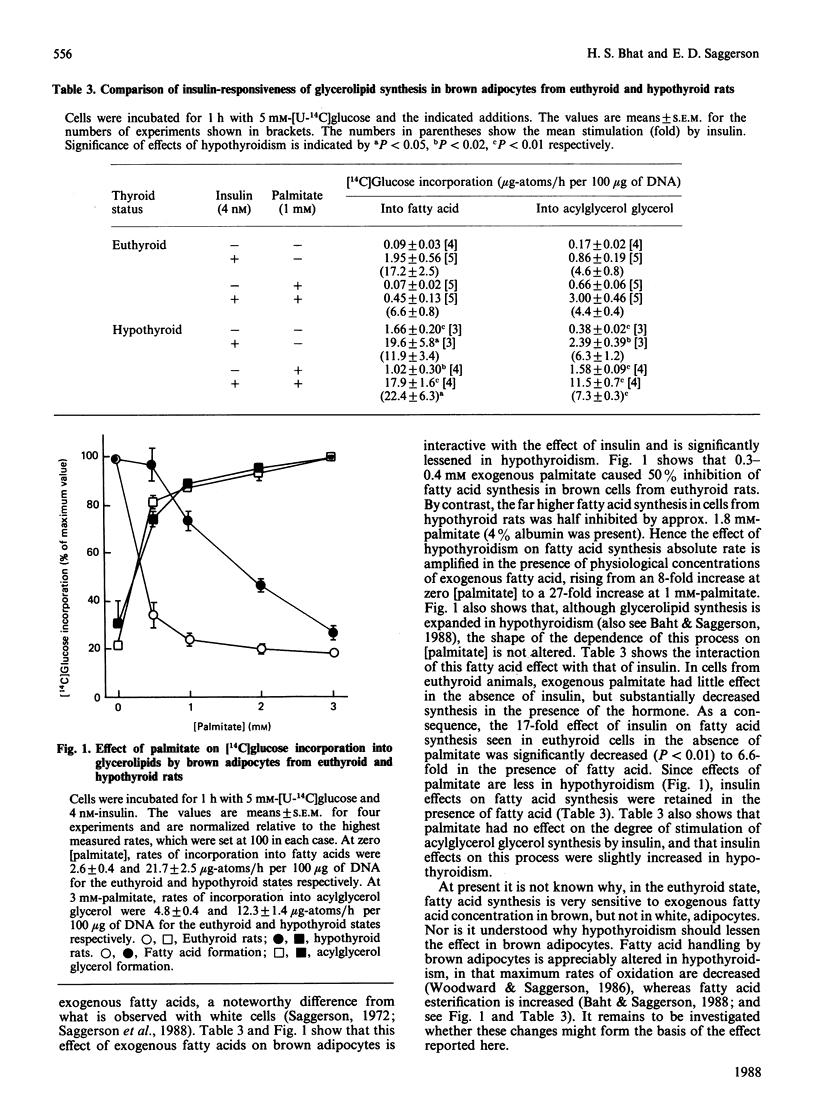
1. Rats were made hypothyroid by feeding them with propylthiouracil together with a low-iodine diet for 4 weeks. 2. [U-14C]Glucose conversion into fatty acids was substantially enhanced in brown adipocytes isolated from hypothyroid rats. Incorporation of 3H2O into fatty acids in vivo was enhanced in hypothyroidism in interscapular brown fat, but not in epididymal white fat or in liver. Hypothyroidism increased the activities of fatty acid synthase and ATP citrate lyase in brown, but not in white, adipocytes. 3. Glycolytic flux in brown adipocytes, quantified by [3-3H]glucose detritiation, was increased by hypothyroidism. This change was accompanied by increased maximum activity of phosphofructokinase. In white adipocytes a large increase in phosphofructokinase maximum activity was observed in hypothyroidism, but this change was accompanied by only small increases in the rate of glucose detritiation by incubated cells. It is suggested that in the brown adipocyte the overall conversion of glucose into fatty acids is enhanced in thyroid deficiency, but that this change is muted in the white adipocyte, possibly because of limitation of glucose transport. 4. Fatty acid synthesis in brown adipocytes from hypothyroid animals was considerably less sensitive to inhibition by exogenous fatty acids than is the process in cells from euthyroid animals. Consequently, the effect of hypothyroidism to enhance lipogenesis is amplified in the presence of physiological concentrations of fatty acid.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baht H. S., Saggerson E. D. Comparison of triacylglycerol synthesis in rat brown and white adipocytes. Effects of hypothyroidism and streptozotocin-diabetes on enzyme activities and metabolic fluxes. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 1;250(2):325–333. doi: 10.1042/bj2500325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baquer N. Z., Cascales M., McLean P., Greenbaum A. L. Effects of thyroid hormone deficiency on the distribution of hepatic metabolites and control of pathways of carbohydrate metabolism in liver and adipose tissue of the rat. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep 15;68(2):403–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bontemps F., Hue L., Hers H. G. Phosphorylation of glucose in isolated rat hepatocytes. Sigmoidal kinetics explained by the activity of glucokinase alone. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):603–611. doi: 10.1042/bj1740603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chohan P., Carpenter C., Saggerson E. D. Changes in the anti-lipolytic action and binding to plasma membranes of N6-L-phenylisopropyladenosine in adipocytes from starved and hypothyroid rats. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 1;223(1):53–59. doi: 10.1042/bj2230053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P. Effect of nucleic acid metabolites on lipolysis in adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1961 Dec;236:3125–3130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamant S., Gorin E., Shafrir E. Enzyme activities related to fatty-acid synthesis in liver and adipose tissue of rats treated with triiodothyronine. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Apr 24;26(4):553–559. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., Reed N., Saperstein R. The isolation and metabolism of brown fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1887–1894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnoni G. V., Landriscina C., Quagliariello E. Fatty acid biosynthesis in adipose tissue and lung subcellular fractions of thyrotoxic rats. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 15;122(1):37–40. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80396-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualberto A., Molinero P., Sobrino F. The effect of experimental hypothyroidism on phosphofructokinase activity and fructose 2,6-bisphosphate concentrations in rat heart. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):137–142. doi: 10.1042/bj2440137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hems D. A., Rath E. A., Verrinder T. R. Fatty acid synthesis in liver and adipose tissue of normal and genetically obese (ob/ob) mice during the 24-hour cycle. Biochem J. 1975 Aug;150(2):167–173. doi: 10.1042/bj1500167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isler D., Hill H. P., Meier M. K. Glucose metabolism in isolated brown adipocytes under beta-adrenergic stimulation. Quantitative contribution of glucose to total thermogenesis. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):789–793. doi: 10.1042/bj2450789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma S. W., Foster D. O. Uptake of glucose and release of fatty acids and glycerol by rat brown adipose tissue in vivo. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1986 May;64(5):609–614. doi: 10.1139/y86-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. R., Denton R. M. The intracellular localization of enzymes in white-adipose-tissue fat-cells and permeability properties of fat-cell mitochondria. Transfer of acetyl units and reducing power between mitochondria and cytoplasm. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(5):861–877. doi: 10.1042/bj1170861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. G., Denton R. M. Evidence that fatty acid synthesis in the interscapular brown adipose tissue of cold-adapted rats is increased in vivo by insulin by mechanisms involving parallel activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase and acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase. Biochem J. 1977 Sep 15;166(3):627–630. doi: 10.1042/bj1660627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Spiegel A. M., Unson C. G., Saggerson E. D. Chemically induced hypothyroidism produces elevated amounts of the alpha subunit of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide binding protein (Gi) and the beta subunit common to all G-proteins. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):223–227. doi: 10.1042/bj2470223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedergaard J., Lindberg O. The brown fat cell. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;74:187–286. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61173-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rider M. H., Hue L. Regulation of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate concentration in white adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1985 Jan 15;225(2):421–428. doi: 10.1042/bj2250421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roncari D. A., Murthy V. K. Effects of thyroid hormones on enzymes involved in fatty acid and glycerolipid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4134–4138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggerson E. D., Greenbaum A. L. The regulation of triglyceride synthesis and fatty acid synthesis in rat epididymal adipose tissue. Effects of altered dietary and hormonal conditions. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(2):221–242. doi: 10.1042/bj1190221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggerson E. D., Greenbaum A. L. The regulation of triglyceride synthesis and fatty acid synthesis in rat epididymal adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1970 Sep;119(2):193–219. doi: 10.1042/bj1190193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggerson E. D. Sensitivity of adipocyte lipolysis to stimulatory and inhibitory agonists in hypothyroidism and starvation. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):387–394. doi: 10.1042/bj2380387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggerson E. D. The regulation of glyceride synthesis in isolated white-fat cells. The effects of palmitate and lipolytic agents. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;128(5):1057–1067. doi: 10.1042/bj1281057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stansbie D., Brownsey R. W., Crettaz M., Denton R. M. Acute effects in vivo of anti-insulin serum on rates of fatty acid synthesis and activities of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase and pyruvate dehydrogenase in liver and epididymal adipose tissue of fed rats. Biochem J. 1976 Nov 15;160(2):413–416. doi: 10.1042/bj1600413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden M. C., Steare S. E., Watts D. I., Palmer T. N. Interactions between insulin and thyroid hormone in the control of lipogenesis. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 15;210(3):937–944. doi: 10.1042/bj2100937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden M. C., Watts D. I., Marshall C. E. Regulation of hepatic lipogenesis in starved and diabetic animals by thyroid hormone. Biosci Rep. 1981 Oct;1(10):757–764. doi: 10.1007/BF01114797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer B. R., Summer G. K. A modified fluorometric micromethod for DNA. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Apr;32(2):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90333-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. J., Marasa J. C. Hormonal regulation of fatty acid synthetase, acetyl-CoA carboxylase and fatty acid synthesis in mammalian adipose tissue and liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 24;380(3):454–472. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward J. A., Saggerson E. D. Effect of adenosine deaminase, N6-phenylisopropyladenosine and hypothyroidism on the responsiveness of rat brown adipocytes to noradrenaline. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):395–403. doi: 10.1042/bj2380395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



