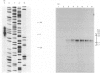
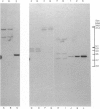
Abstract
The sequence of a gene encoding convicilin, a seed storage protein in pea (Pisum sativum L.), is reported. This gene, designated cvcA, is one of a sub-family of two active genes. The transcription start of cvcA was mapped. Convicilin genes are expressed in developing pea seed cotyledons, with maximum levels of the corresponding mRNA species present at 16-18 days after flowering. The gene sequence shows that convicilin is similar to vicilin, but differs by the insertion of a 121-amino-acid sequence near the N-terminus of the protein. This inserted sequence is very hydrophilic and has a high proportion of charged and acidic residues; it is of a similar amino acid composition to the sequences found near the C-terminal of the alpha-subunit in pea legumin genes, but is not directly homologous with them. Comparison of this sequence with the 'inserted' sequence in soya-bean (Glycine max) conglycinin (a homologous vicilin-type protein) suggests that the two insertions were independent events. The 5' flanking sequence of the gene contains several putative regulatory elements, besides a consensus promoter sequence.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bach R., Friedland P., Brutlag D. L., Kedes L. MAXAMIZE. A DNA sequencing strategy advisor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):295–304. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey R., Domoney C., Stanley J. Convicilin mRNA from pea (Pisum sativum L.) has sequence homology with other legume 7S storage protein mRNA species. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 1;224(2):661–666. doi: 10.1042/bj2240661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. L., Schuler M. A., Beachy R. N. Functional analysis of regulatory elements in a plant embryo-specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8560–8564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croy R. R., Gatehouse J. A., Tyler M., Boulter D. The purification and characterization of a third storage protein (convicilin) from the seeds of pea (Pisum sativum L.). Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):509–516. doi: 10.1042/bj1910509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domoney C., Casey R. Measurement of gene number for seed storage proteins in Pisum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):687–699. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle J. J., Schuler M. A., Godette W. D., Zenger V., Beachy R. N., Slightom J. L. The glycosylated seed storage proteins of Glycine max and Phaseolus vulgaris. Structural homologies of genes and proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9228–9238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatehouse J. A., Bown D., Gilroy J., Levasseur M., Castleton J., Ellis T. H. Two genes encoding 'minor' legumin polypeptides in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Characterization and complete sequence of the LegJ gene. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 15;250(1):15–24. doi: 10.1042/bj2500015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatehouse J. A., Evans I. M., Bown D., Croy R. R., Boulter D. Control of storage-protein synthesis during seed development in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Biochem J. 1982 Oct 15;208(1):119–127. doi: 10.1042/bj2080119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatehouse J. A., Lycett G. W., Croy R. R., Boulter D. The post-translational proteolysis of the subunits of vicilin from pea (Pisum sativum L.). Biochem J. 1982 Dec 1;207(3):629–632. doi: 10.1042/bj2070629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph T., Higgins V., Spencer D. Precursor Forms of Pea Vicilin Subunits: MODIFICATION BY MICROSOMAL MEMBRANES DURING CELL-FREE TRANSLATION. Plant Physiol. 1981 Feb;67(2):205–211. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.2.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn S., Fritz H. J., Starlinger P. Close vicinity of IS1 integration sites in the leader sequence of the gal operon of E. coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 2;167(3):235–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00267414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycett G. W., Croy R. R., Shirsat A. H., Boulter D. The complete nucleotide sequence of a legumin gene from pea (Pisum sativum L.). Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4493–4506. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycett G. W., Croy R. R., Shirsat A. H., Richards D. M., Boulter D. The 5'-flanking regions of three pea legumin genes: comparison of the DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6733–6743. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycett G. W., Delauney A. J., Gatehouse J. A., Gilroy J., Croy R. R., Boulter D. The vicilin gene family of pea (Pisum sativum L.): a complete cDNA coding sequence for preprovicilin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2367–2380. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Sun S. M., Hall T. C. Complete nucleotide sequence of a French bean storage protein gene: Phaseolin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1897–1901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]