Abstract
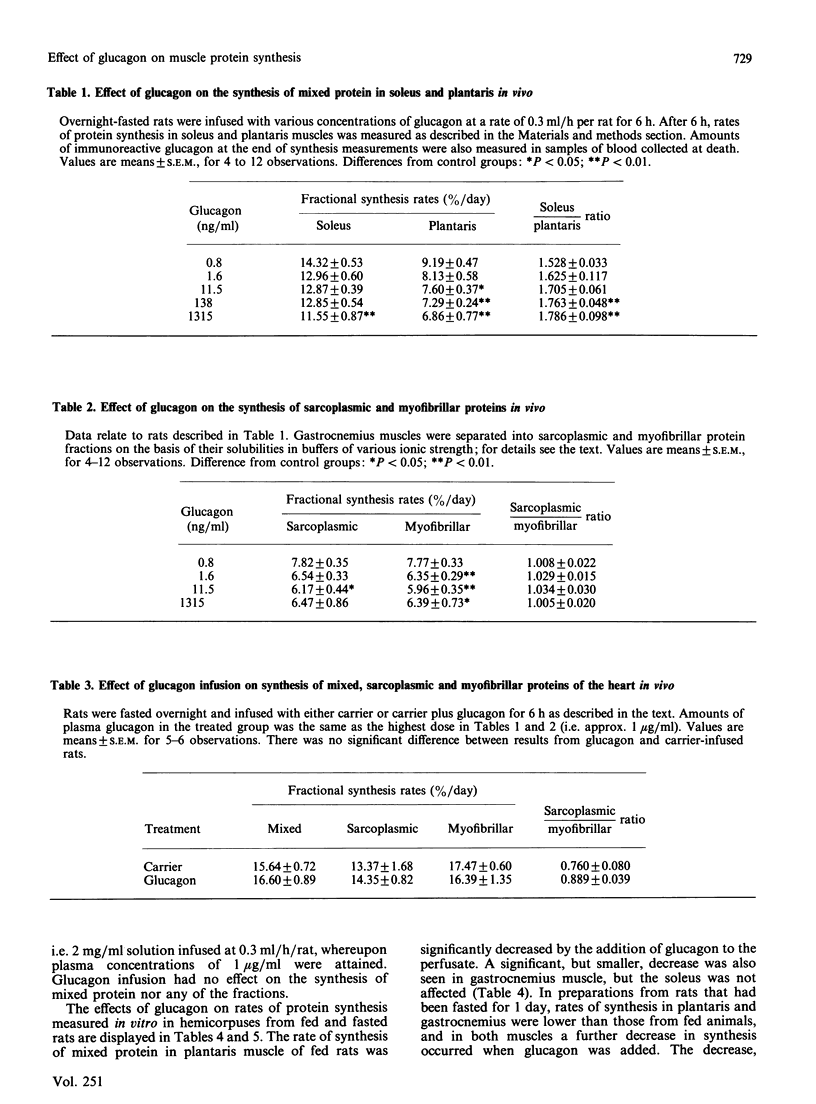
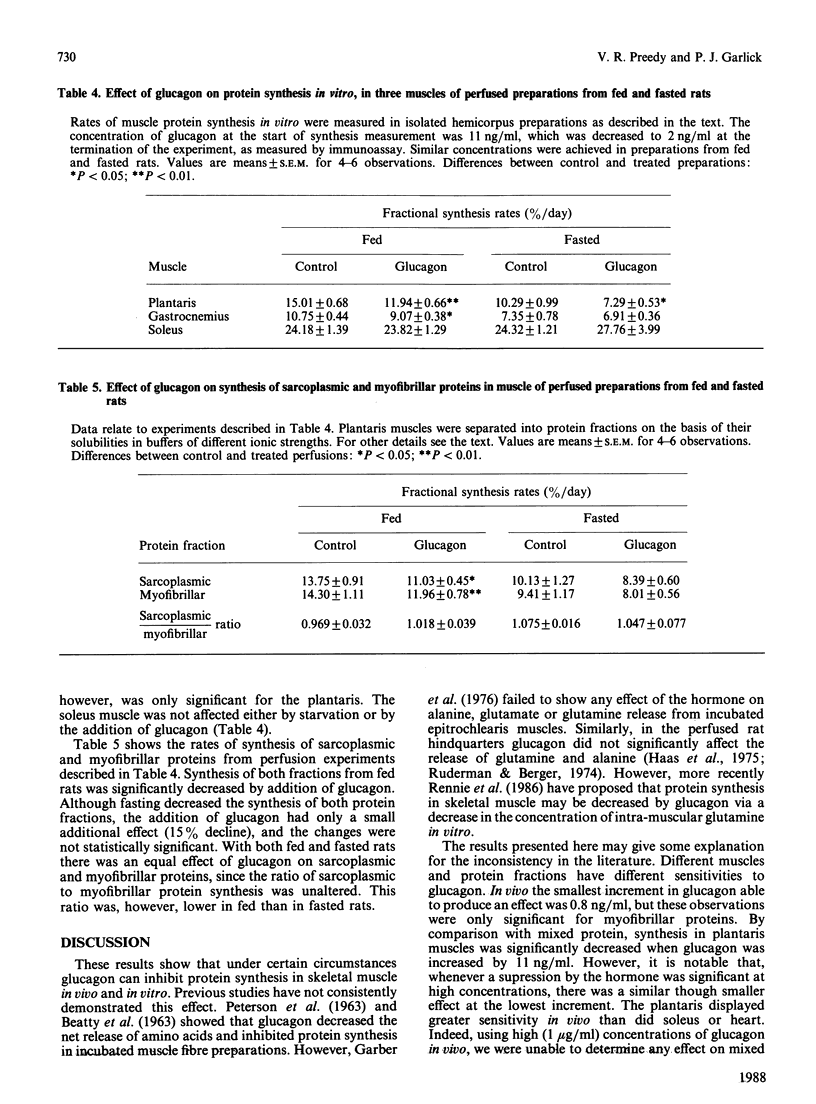
The effect of glucagon on the rate of muscle protein synthesis was examined in vivo and in the isolated perfused rat hemicorpus. An inhibition of protein synthesis in skeletal muscles from overnight-fasted rats at various plasma concentrations of glucagon was demonstrated in vivo. The plantaris muscle (Type II, fibre-rich) was more sensitive than the soleus (Type I, fibre-rich). Myofibrillar and sarcoplasmic proteins were equally sensitive in vivo. However, protein synthesis in mixed protein and in sarcoplasmic and myofibrillar fractions of the heart was unresponsive to glucagon in vivo. In isolated perfused muscle preparations from fed animals, the addition of glucagon also decreased the synthesis of mixed muscle proteins in gastrocnemius (Type I and II fibres) and plantaris, but not in the soleus. The sarcoplasmic and myofibrillar fractions of the plantaris were also equally affected in vitro. Similar results were observed in vitro with 1-day-starved rats, but the changes were less marked.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adibi S. A., Morse E. L., Mirsky I. A. Dietary regulation of liver and muscle transport of amino acid. Am J Physiol. 1976 Feb;230(2):245–250. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alford F. P., Bloodm S. R., Nabarro J. D. Glucagon levels in normal and diabetic subjects: use of a specific immunoabsorbent for glucagon radioimmunoassay. Diabetologia. 1977 Jan;13(1):1–6. doi: 10.1007/BF00996319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alford F. P., Chisholm D. J. Glucagon--new concepts about and "old" hormone. Aust N Z J Med. 1979 Dec;9(6):733–743. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1979.tb04210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariano M. A., Armstrong R. B., Edgerton V. R. Hindlimb muscle fiber populations of five mammals. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Jan;21(1):51–55. doi: 10.1177/21.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEATTY C. H., PETERSON R. D., BOCEK R. M., CRAIG N. C., WELEBER R. EFFECT OF GLUCAGON ON INCORPORATION OF GLYCINE-C14 INTO PROTEIN OF VOLUNTARY SKELETAL MUSCLE. Endocrinology. 1963 Dec;73:721–726. doi: 10.1210/endo-73-6-721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Pratt O. E., Spargo E. The mechanism by which glucagon induces the release of amino acids from muscle and its relevance to fasting. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Mar 18;196(1124):347–365. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaim K. E., Copenhaver M. E., Jefferson L. S. Effects of diabetes on protein synthesis in fast- and slow-twitch rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jul;239(1):E88–E95. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.239.1.E88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. J., Fern M., Preedy V. R. The effect of insulin infusion and food intake on muscle protein synthesis in postabsorptive rats. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 15;210(3):669–676. doi: 10.1042/bj2100669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. J., McNurlan M. A., Preedy V. R. A rapid and convenient technique for measuring the rate of protein synthesis in tissues by injection of [3H]phenylalanine. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):719–723. doi: 10.1042/bj1920719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELANDER E. A. Influence of exercise and restricted activity on the protein composition of skeletal muscle. Biochem J. 1961 Mar;78:478–482. doi: 10.1042/bj0780478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson L. S. A technique for perfusion of an isolated preparation of rat hemicorpus. Methods Enzymol. 1975;39:73–82. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)39011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson L. S. Lilly Lecture 1979: role of insulin in the regulation of protein synthesis. Diabetes. 1980 Jun;29(6):487–496. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.6.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karl I. E., Garber A. J., Kipnis D. M. Alanine and glutamine synthesis and release from skeletal muscle. III. Dietary and hormonal regulation. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 10;251(3):844–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsilambros N., Rahman Y. A., Hinz M., Fussgänger R., Schröder K. E., Straub K., Pfeiffer E. F. Action of streptozotocin on insulin and glucagon responses of rat islets. Horm Metab Res. 1970 Sep;2(5):268–270. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1095056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. B., Goldberg A. L. Effects of food deprivation on protein synthesis and degradation in rat skeletal muscles. Am J Physiol. 1976 Aug;231(2):441–448. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.2.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNurlan M. A., Tomkins A. M., Garlick P. J. The effect of starvation on the rate of protein synthesis in rat liver and small intestine. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 15;178(2):373–379. doi: 10.1042/bj1780373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendlowitz M. The climate of opinion. Clin Res. 1975 Jan;23(1):1–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millward D. J. Protein deficiency, starvation and protein metabolism. Proc Nutr Soc. 1979 May 1;38(1):77–88. doi: 10.1079/pns19790011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. A., Faloona G. R., Unger R. H. Hyperglucagonemia in diabetic ketoacidosis. Its prevalence and significance. Am J Med. 1973 Jan;54(1):52–57. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair K. S., Halliday D., Matthews D. E., Welle S. L. Hyperglucagonemia during insulin deficiency accelerates protein catabolism. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 1):E208–E213. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.253.2.E208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERSON R. D., BEATTY C. H., BOCEK R. M. Effects of insulin and glucagon on carbohydrate and protein metabolism of adductor muscle and diaphragm. Endocrinology. 1963 Jan;72:71–77. doi: 10.1210/endo-72-1-71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrilla R., Goodman M. N., Toews C. J. Effect of glucagon: insulin ratios on hepatic metabolism. Diabetes. 1974 Sep;23(9):725–731. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.9.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Bear C. Two glucagon transducing systems. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):18–18. doi: 10.1038/323018a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preedy V. R., Garlick P. J. Protein synthesis in skeletal muscle of the perfused rat hemicorpus compared with rates in the intact animal. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 15;214(2):433–442. doi: 10.1042/bj2140433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preedy V. R., Garlick P. J. Rates of protein synthesis in skin and bone, and their importance in the assessment of protein degradation in the perfused rat hemicorpus. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 15;194(1):373–376. doi: 10.1042/bj1940373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preedy V. R., Garlick P. J. The effect of glucagon administration on protein synthesis in skeletal muscles, heart and liver in vivo. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 15;228(3):575–581. doi: 10.1042/bj2280575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preedy V. R., Pain V. M., Garlick P. J. Comparison of rates of protein synthesis in skeletal muscle measured in vivo and in the perfused hemicorpus [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1979 Oct;7(5):1040–1042. doi: 10.1042/bst0071040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preedy V. R., Pain V. M., Garlick P. J. The effect of glucagon on muscle protein synthesis in the perfused rat hemicorpus [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Jun;8(3):367–368. doi: 10.1042/bst0080367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preedy V. R., Pain V. M., Garlick P. J. The metabolic state of muscle in the isolated perfused rat hemicorpus in relation to rates of protein synthesis. Biochem J. 1984 Mar 1;218(2):429–440. doi: 10.1042/bj2180429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL T. W., SUTHERLAND E. W. Formation of a cyclic adenine ribonucleotide by tissue particles. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jun;232(2):1065–1076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDLE P. J. The effect of glucagon preparations on the uptake of glucose by isolated rat diaphragm. J Endocrinol. 1958 Nov;17(4):396–400. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0170396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie M. J., Hundal H. S., Babij P., MacLennan P., Taylor P. M., Watt P. W., Jepson M. M., Millward D. J. Characteristics of a glutamine carrier in skeletal muscle have important consequences for nitrogen loss in injury, infection, and chronic disease. Lancet. 1986 Nov 1;2(8514):1008–1012. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92617-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Berger M. The formation of glutamine and alanine in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5500–5506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Houghton C. R., Hems R. Evaluation of the isolated perfused rat hindquarter for the study of muscle metabolism. Biochem J. 1971 Sep;124(3):639–651. doi: 10.1042/bj1240639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stearns S. B., Benzo C. A. Glucagon and insulin relationships in genetically diabetic (db/db) and in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Horm Metab Res. 1978 Jan;10(1):20–23. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland E. W., Robison G. A. The role of cyclic AMP in the control of carbohydrate metabolism. Diabetes. 1969 Dec;18(12):797–819. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.12.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Murphy G. J., Hruby V. J., Houslay M. D. Activation of two signal-transduction systems in hepatocytes by glucagon. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):68–71. doi: 10.1038/323068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


