Abstract
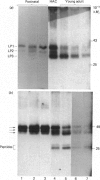
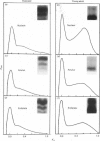
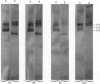
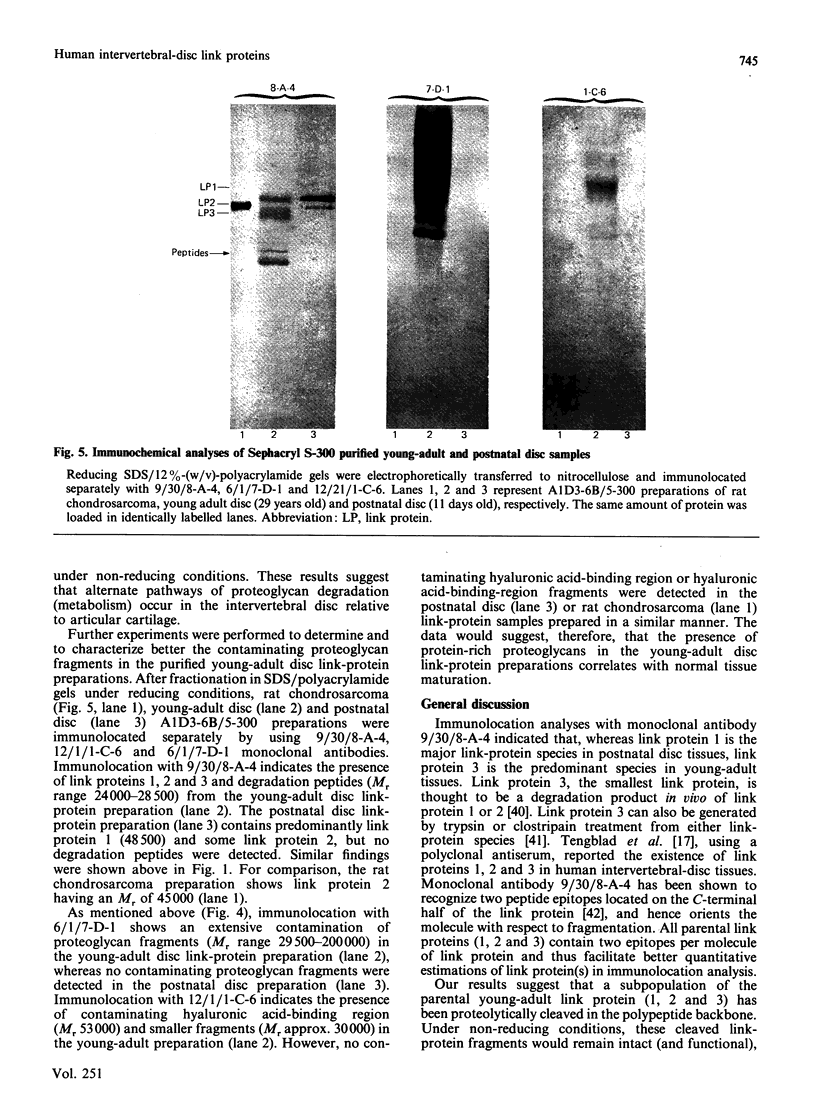
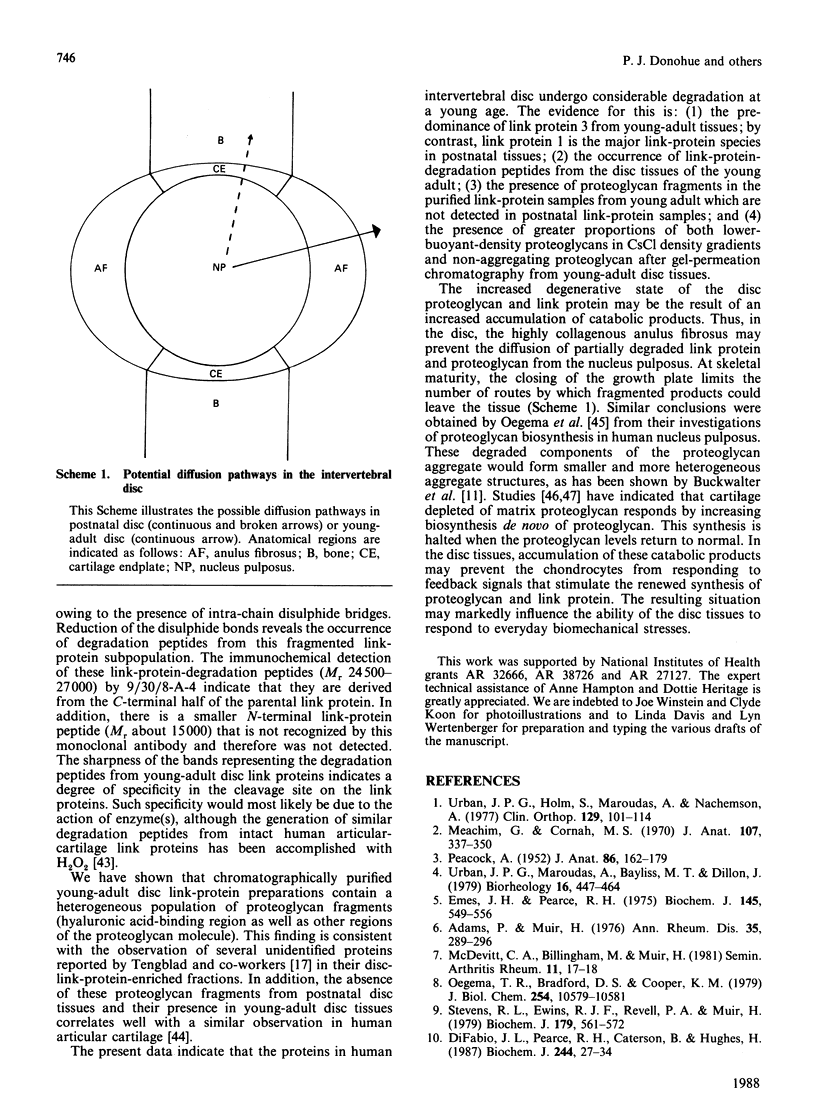
Proteoglycan aggregates (A1) were prepared from the anulus fibrosus, nucleus pulposus and cartilage-endplate tissues of postnatal (0-6-month-old)-and young-adult (20-30-year-old)-human intervertebral discs. The A1 fractions from young-adult disc contained a greater proportion of non-aggregating proteoglycans than did postnatal tissues. After dissociative CsCl-density-gradient fractionation of the A1, more than 90% of the uronic acid was found in the postnatal A1D1, whereas only 60-80% of the hexuronate was present in the A1D1 isolated from young-adult disc tissues. These results indicated that more lower-buoyant-density proteoglycans occur in the young-adult disc. Link-protein-rich fractions (A1D3) were subjected to SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis and immunolocation analyses using monoclonal antibodies specific for epitopes on link protein or proteoglycan. Under non-reducing conditions, the major link protein present in postnatal disc tissues was link protein 1. By contrast, all three link proteins (1, 2 and 3) were detected in young-adult tissues, with the smaller link protein 3 predominating. Analyses of the A1D3 fractions under reducing conditions also indicated the presence of link-protein-degradation peptides (Mr approx. 26,000) from young-adult disc tissues, but not from postnatal tissues. Sequential Sepharose CL-6B and Sephacryl S-300 chromatography in 4 M-guanidinium chloride was employed to separate the link proteins of the A1D3 fraction from protein-rich proteoglycan. Immunolocation analyses indicated that postnatal samples contained no detectable contaminating proteoglycan fragments. However, young-adult link-protein preparations could not be separated from hyaluronic acid-binding region and other proteoglycan fragments by means of these chromatographic procedures. The studies indicate that, compared with hyaline articular cartilage, degraded link protein and proteoglycan accumulate at an early age in young-adult disc tissues. These partially degraded proteoglycan aggregate components may significantly alter the biomechanical properties of disc tissues.
Full text
PDF

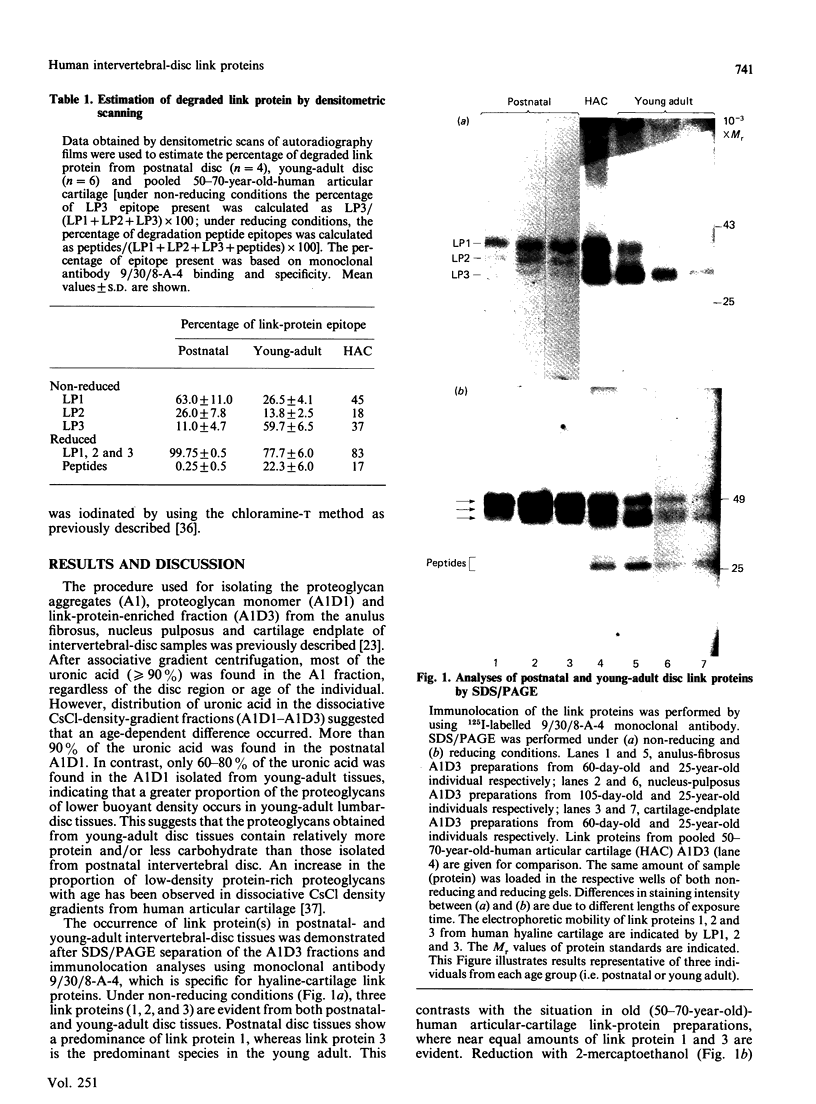
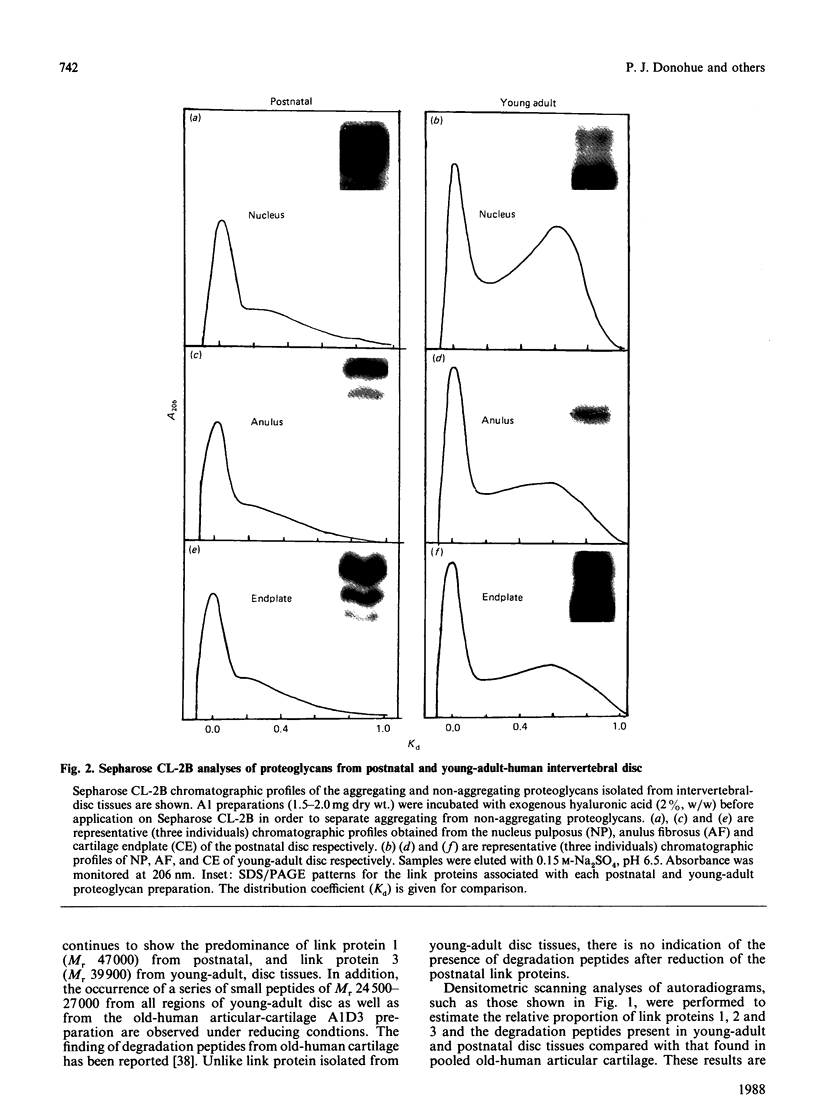
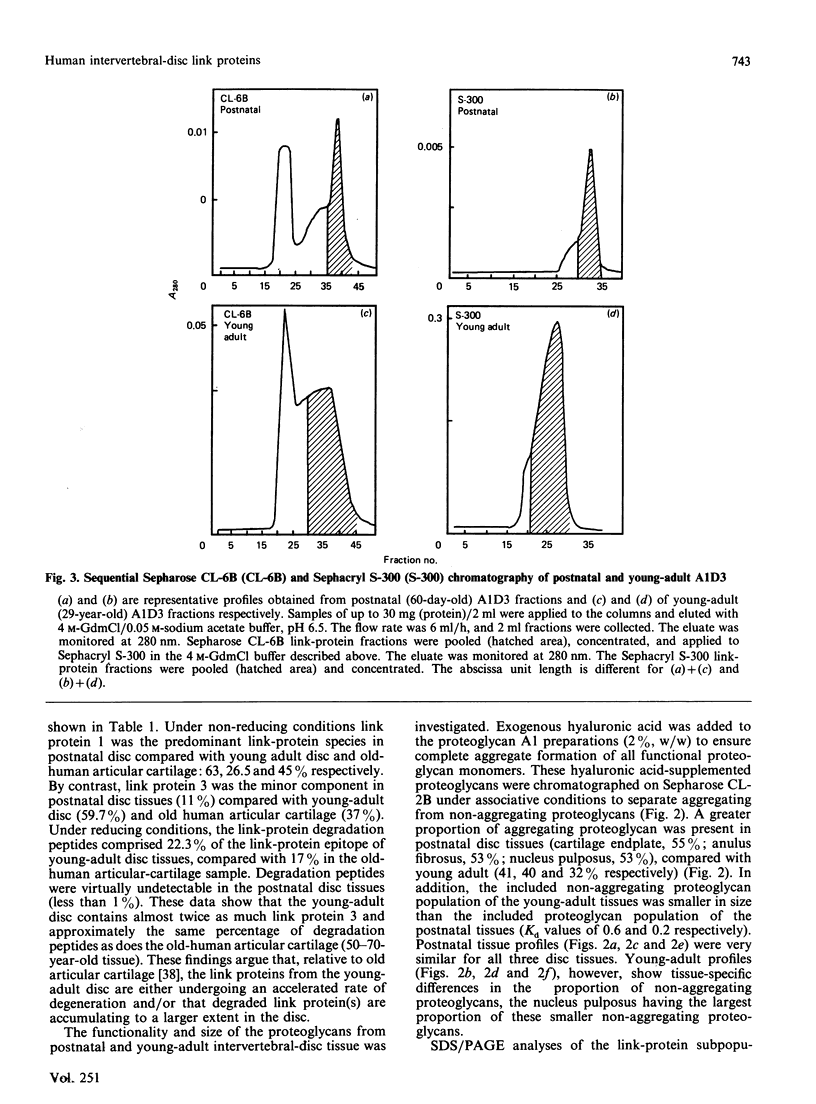
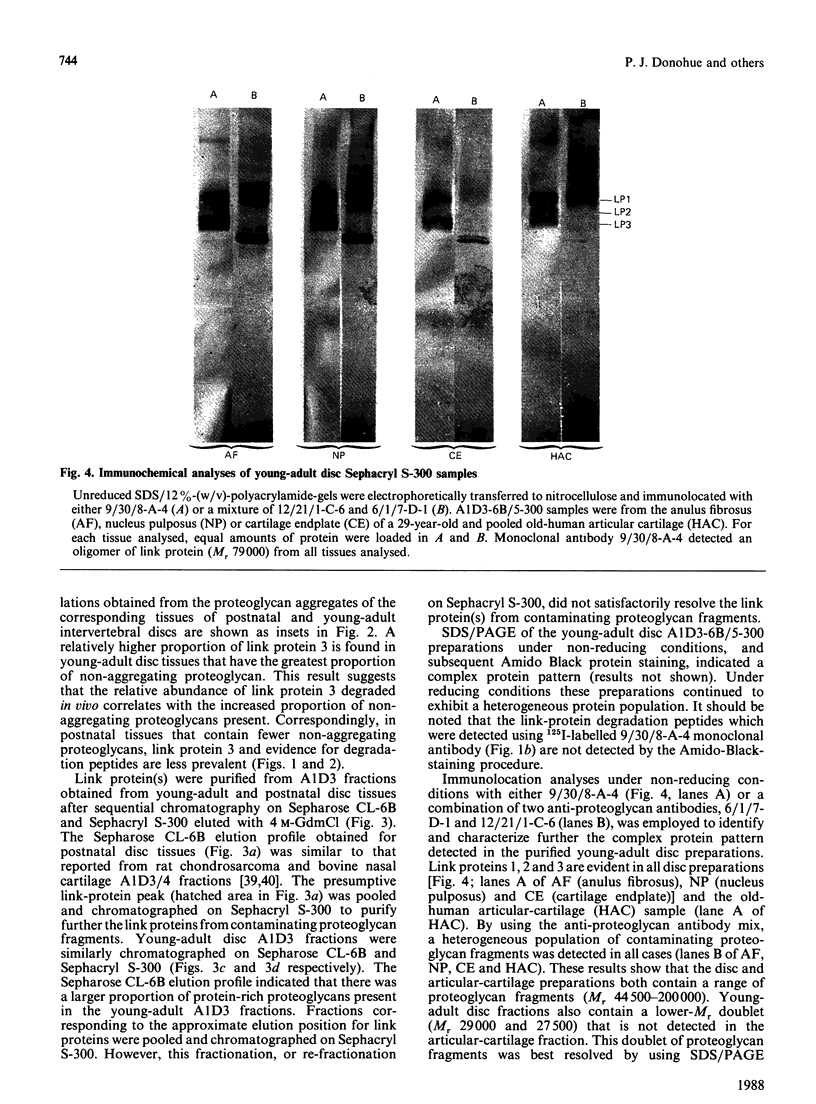

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P., Muir H. Qualitative changes with age of proteoglycans of human lumbar discs. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976 Aug;35(4):289–296. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.4.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BITTER T., MUIR H. M. A modified uronic acid carbazole reaction. Anal Biochem. 1962 Oct;4:330–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(62)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. R., Caterson B. The isolation and characterization of the link proteins from proteoglycan aggregates of bovine nasal cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2387–2393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet F., Dunham D. G., Hardingham T. E. Structure and interactions of cartilage proteoglycan binding region and link protein. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):77–85. doi: 10.1042/bj2280077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckwalter J. A., Pedrini-Mille A., Pedrini V., Tudisco C. Proteoglycans of human infant intervertebral disc. Electron microscopic and biochemical studies. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985 Feb;67(2):284–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterson B., Baker J. R., Christner J. E., Lee Y., Lentz M. Monoclonal antibodies as probes for determining the microheterogeneity of the link proteins of cartilage proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11348–11356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterson B., Baker J. R. The link proteins as specific components of cartilage proteoglycan aggregates in vivo. Associative extraction of proteoglycan aggregate from swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2394–2399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterson B., Christner J. E., Baker J. R., Couchman J. R. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed against connective tissue proteoglycans. Fed Proc. 1985 Feb;44(2):386–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterson B., Christner J. E., Baker J. R. Identification of a monoclonal antibody that specifically recognizes corneal and skeletal keratan sulfate. Monoclonal antibodies to cartilage proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8848–8854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFabio J. L., Pearce R. H., Caterson B., Hughes H. The heterogeneity of the non-aggregating proteoglycans of the human intervertebral disc. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):27–33. doi: 10.1042/bj2440027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emes J. H., Pearce R. H. The proteoglycans of the human intervertebral disc. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;145(3):549–556. doi: 10.1042/bj1450549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzén A., Björnsson S., Heinegård D. Cartilage proteoglycan aggregate formation. Role of link protein. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 1;197(3):669–674. doi: 10.1042/bj1970669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Fitton-Jackson S., Muir H. Replacement of proteoglycans in embryonic chick cartilage in organ culture after treatment with testicular hyaluronidase. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;129(1):101–112. doi: 10.1042/bj1290101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E. The role of link-protein in the structure of cartilage proteoglycan aggregates. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):237–247. doi: 10.1042/bj1770237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Sajdera S. W. Proteinpolysaccharide complex from bovine nasal cartilage. The function of glycoprotein in the formation of aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2384–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Axelsson I., Inerot S. Skeletal keratan sulfate from different tissues. Characterization and alkaline degradation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 23;581(1):122–127. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D. Extraction, fractionation and characterization of proteoglycans from bovine tracheal cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 28;285(1):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90190-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Hascall V. C. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. 3. Characteristics of the proteins isolated from trypsin digests of aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4250–4256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M., Nieduszynski I. A. A study of equilibrium binding of link protein to hyaluronate. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 1;213(2):445–450. doi: 10.1042/bj2130445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meachim G., Cornah M. S. Fine structure of juvenile human nucleus pulposus. J Anat. 1970 Sep;107(Pt 2):337–350. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mort J. S., Caterson B., Poole A. R., Roughley P. J. The origin of human cartilage proteoglycan link-protein heterogeneity and fragmentation during aging. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):805–812. doi: 10.1042/bj2320805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mort J. S., Poole A. R., Roughley P. J. Age-related changes in the structure of proteoglycan link proteins present in normal human articular cartilage. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 15;214(1):269–272. doi: 10.1042/bj2140269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neame P. J., Périn J. P., Bonnet F., Christner J. E., Jollès P., Baker J. R. An amino acid sequence common to both cartilage proteoglycan and link protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12402–12404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Bradford D. S., Cooper K. M. Aggregated proteoglycan synthesis in organ cultures of human nucleus pulposus. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10579–10581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Bradford D. S., Cooper K. M. Aggregated proteoglycan synthesis in organ cultures of human nucleus pulposus. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10579–10581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Hascall V. C., Dziewiatkowski D. D. Isolation and characterization of proteoglycans from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6151–6159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEACOCK A. Observations on the postnatal structure of the intervertebral disc in man. J Anat. 1952 Apr;86(2):162–179. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., White R. J. Age-related changes in the structure of the proteoglycan subunits from human articular cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):217–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., White R. J., Poole A. R. Identification of a hyaluronic acid-binding protein that interferes with the preparation of high-buoyant-density proteoglycan aggregates from adult human articular cartilage. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 1;231(1):129–138. doi: 10.1042/bj2310129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., White R. J., Poole A. R. Identification of a hyaluronic acid-binding protein that interferes with the preparation of high-buoyant-density proteoglycan aggregates from adult human articular cartilage. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 1;231(1):129–138. doi: 10.1042/bj2310129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandy J. D., Brown H. L., Lowther D. A. Control of proteoglycan synthesis. Studies on the activation of synthesis observed during culture of articular cartilages. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 15;188(1):119–130. doi: 10.1042/bj1880119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda S., Schlamowitz M. Studies of 125I trace labeling of immunoglobulin G by chloramine-T. Immunochemistry. 1970 Nov;7(11):885–898. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. W., Oike Y., Handley C., Hascall V. C., Hampton A., Caterson B. Characteristics of the core protein of the aggregating proteoglycan from the Swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Cell Biochem. 1984;26(4):247–259. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240260405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. L., Ewins R. J., Revell P. A., Muir H. Proteoglycans of the intervertebral disc. Homology of structure with laryngeal proteoglycans. Biochem J. 1979 Jun 1;179(3):561–572. doi: 10.1042/bj1790561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tengblad A., Pearce R. H., Grimmer B. J. Demonstration of link protein in proteoglycan aggregates from human intervertebral disc. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 15;222(1):85–92. doi: 10.1042/bj2220085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban J. P., Holm S., Maroudas A., Nachemson A. Nutrition of the intervertebral disk. An in vivo study of solute transport. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1977 Nov-Dec;(129):101–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban J. P., Maroudas A., Bayliss M. T., Dillon J. Swelling pressures of proteoglycans at the concentrations found in cartilaginous tissues. Biorheology. 1979;16(6):447–464. doi: 10.3233/bir-1979-16609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]