Abstract
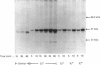
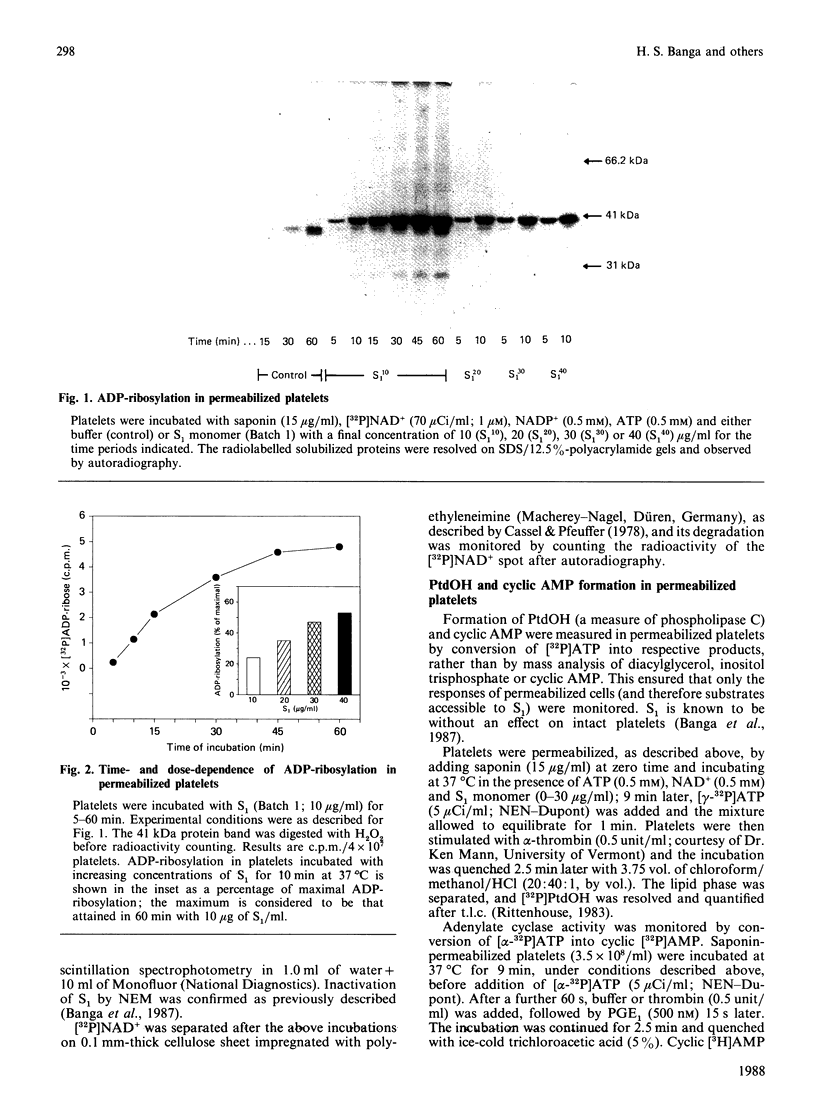
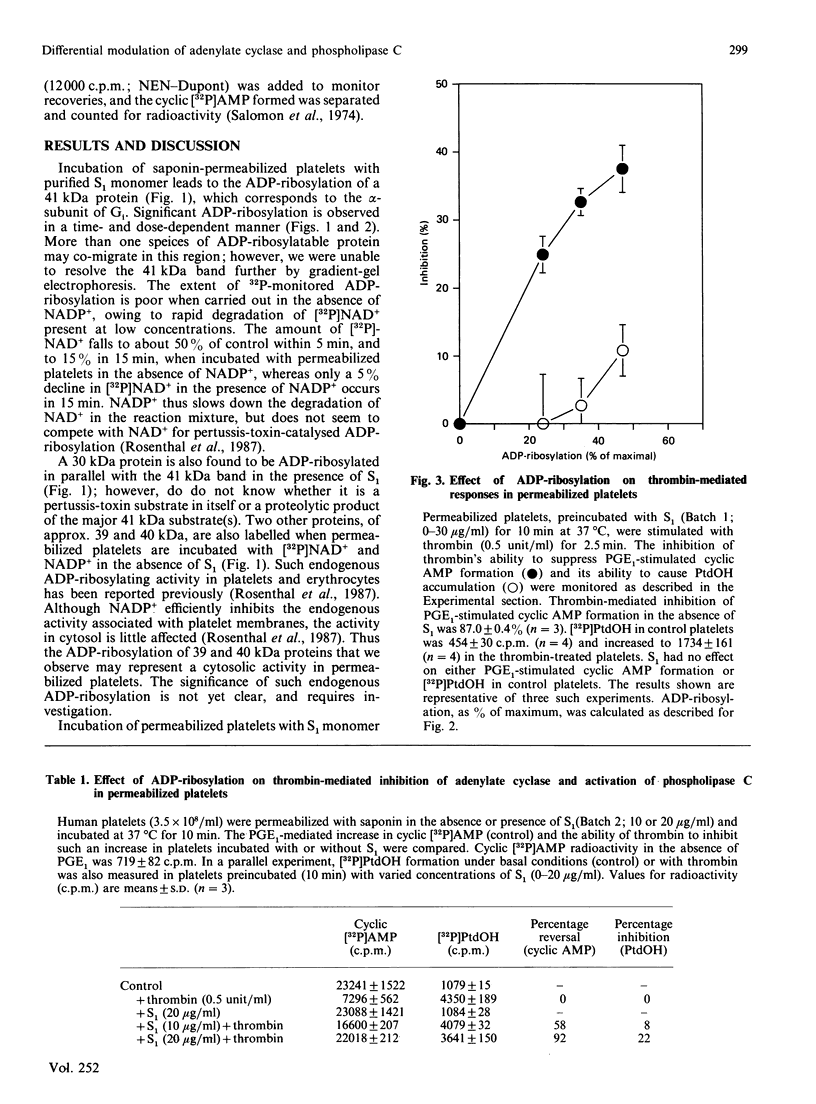
Thrombin stimulates phospholipase C and inhibits adenylate cyclase in human platelets. We have studied the effect of purified S1 monomer, the ADP-ribosylating subunit of pertussis toxin, on these receptor-coupled G-protein-dependent activities. ADP-ribosylation of a 41 kDa protein is associated with a marked decrease in the ability of thrombin to inhibit cyclic AMP formation, but has little effect on phospholipase C. Therefore adenylate cyclase and phospholipase C appear to be modulated by different G-proteins.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aktories K., Jakobs K. H. Ni-mediated inhibition of human platelet adenylate cyclase by thrombin. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 3;145(2):333–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banga H. S., Simons E. R., Brass L. F., Rittenhouse S. E. Activation of phospholipases A and C in human platelets exposed to epinephrine: role of glycoproteins IIb/IIIa and dual role of epinephrine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9197–9201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banga H. S., Walker R. K., Winberry L. K., Rittenhouse S. E. Pertussis toxin can activate human platelets. Comparative effects of holotoxin and its ADP-ribosylating S1 subunit. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):14871–14874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Laposata M., Banga H. S., Rittenhouse S. E. Regulation of the phosphoinositide hydrolysis pathway in thrombin-stimulated platelets by a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide-binding protein. Evaluation of its contribution to platelet activation and comparisons with the adenylate cyclase inhibitory protein, Gi. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16838–16847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Shaller C. C., Belmonte E. J. Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate-induced granule secretion in platelets. Evidence that the activation of phospholipase C mediated by platelet thromboxane receptors involves a guanine nucleotide binding protein-dependent mechanism distinct from that of thrombin. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1269–1275. doi: 10.1172/JCI112947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Pfeuffer T. Mechanism of cholera toxin action: covalent modification of the guanyl nucleotide-binding protein of the adenylate cyclase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2669–2673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandt R., Aktories K., Jakobs K. H. Evidence for two GTPases activated by thrombin in membranes of human platelets. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 1;237(3):669–674. doi: 10.1042/bj2370669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Davidson M. M. Receptor-induced diacylglycerol formation in permeabilized platelets; possible role for a GTP-binding protein. J Recept Res. 1984;4(1-6):605–629. doi: 10.3109/10799898409042576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D., Bojanic D., Gawler D., O'Hagan S., Wilson A. Thrombin, unlike vasopressin, appears to stimulate two distinct guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins in human platelets. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 15;238(1):109–113. doi: 10.1042/bj2380109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Bokoch G. M., Northup J. K., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Properties and function of the purified protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3568–3577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G. Effect of pertussis toxin on the phosphodiesteratic cleavage of the polyphosphoinositides by guanosine 5'-O-thiotriphosphate and thrombin in permeabilized human platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 19;884(2):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90166-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee A. I., Gutierrez L., McKay I. A., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Dynamic fatty acylation of p21N-ras. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3353–3357. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02656.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Ui M. Simultaneous inhibitions of inositol phospholipid breakdown, arachidonic acid release, and histamine secretion in mast cells by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. A possible involvement of the toxin-specific substrate in the Ca2+-mobilizing receptor-mediated biosignaling system. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3584–3593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke F., Zavoico G. B., Smith L. H., Jr, Feinstein M. B. Stimulus-response coupling in a cell-free platelet membrane system. GTP-dependent release of Ca2+ by thrombin, and inhibition by pertussis toxin and a monoclonal antibody that blocks calcium release by IP3. FEBS Lett. 1987 Apr 6;214(1):176–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80037-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris S., Pouysségur J. Pertussis toxin inhibits thrombin-induced activation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis and Na+/H+ exchange in hamster fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):55–60. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04177.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S. Production of diglyceride from phosphatidylinositol in activated human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):580–587. doi: 10.1172/JCI109339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse S. E. Human platelets contain phospholipase C that hydrolyzes polyphosphoinositides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5417–5420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse S. E., Sasson J. P. Mass changes in myoinositol trisphosphate in human platelets stimulated by thrombin. Inhibitory effects of phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8657–8660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal W., Binder T., Schultz G. NADP efficiently inhibits endogenous but not pertussis toxin-catalyzed covalent modification of membrane proteins incubated with NAD. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 26;211(2):137–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81424-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosoff P. M., Walker R., Winberry L. Pertussis toxin triggers rapid second messenger production in human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2419–2423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarver A. P., King W. G., Rittenhouse S. E. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,2-cyclic 4,5-trisphosphate are minor components of total mass of inositol trisphosphate in thrombin-stimulated platelets. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17268–17271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verghese M. W., Smith C. D., Snyderman R. Potential role for a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein in chemoattractant receptor mediated polyphosphoinositide metabolism, Ca++ mobilization and cellular responses by leukocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Mar 15;127(2):450–457. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80181-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]