Full text
PDF
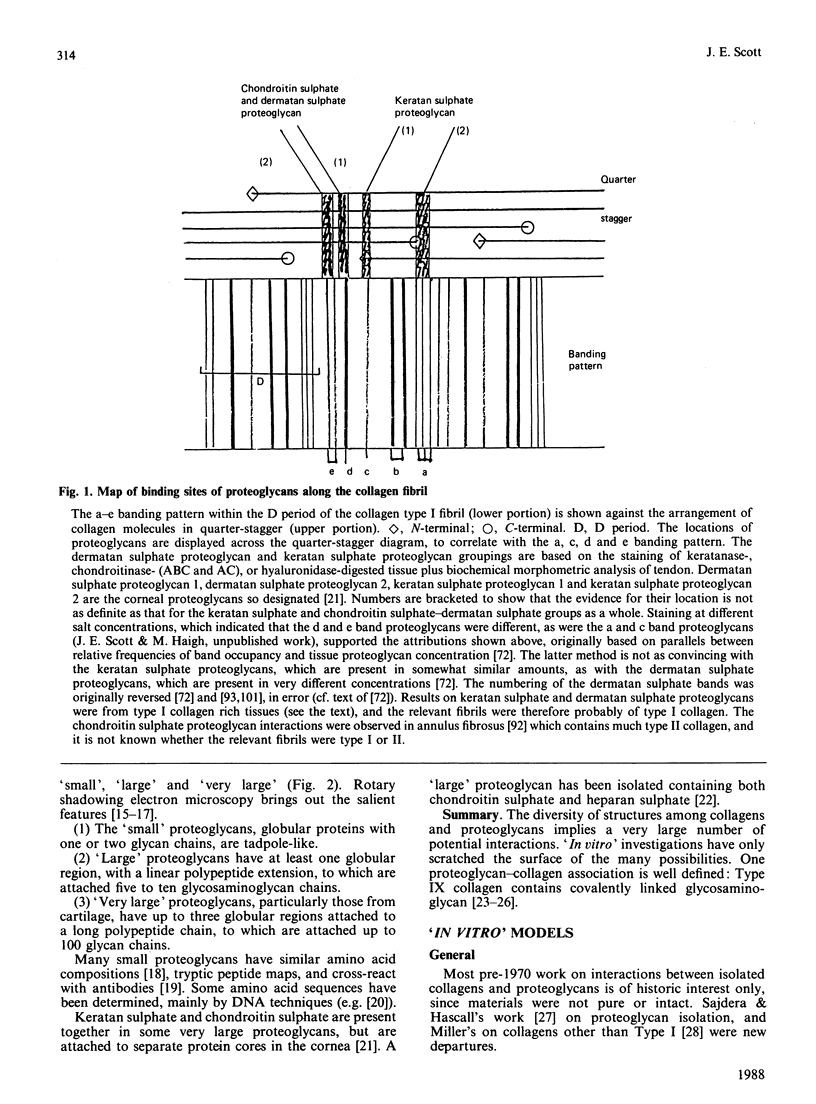









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANSETH A., LAURENT T. C. Studies on corneal polysaccharides. I. Separation. Exp Eye Res. 1961 Sep;1:25–38. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(61)80005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. C. Isolation of a glycoprotein and proteodermatan sulphate from bovine achilles tendon by affinity chromatography on concanavalin A-Sepharose. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 27;379(2):444–455. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUDDECKE E., DRZENIEK R. [Stability constants of the calcium complexes of acid mucopolysaccharides]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1962 May 4;327:49–64. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1962.327.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourdon M. A., Oldberg A., Pierschbacher M., Ruoslahti E. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1321–1325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekhar S., Kleinman H. K., Hassell J. R., Martin G. R., Termine J. D., Trelstad R. L. Regulation of type I collagen fibril assembly by link protein and proteoglycans. Coll Relat Res. 1984 Oct;4(5):323–337. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(84)80001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conochie L. B., Scott J. E., Faulk W. P. A passive agglutination method using collagen-coated tanned sheep erythrocytes to demonstrate collagen-glycosaminoglycan interaction. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Jul;7(4):393–397. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cöster L., Fransson L. A. Isolation and characterization of dermatan sulphate proteoglycans from bovine sclera. Biochem J. 1981 Jan 1;193(1):143–153. doi: 10.1042/bj1930143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damle S. P., Cöster L., Gregory J. D. Proteodermatan sulfate isolated from pig skin. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5523–5527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle B. B., Hukins D. W., Hulmes D. J., Miller A., Woodhead-Galloway J. Collagen polymorphism: its origins in the amino acid sequence. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 5;91(1):79–99. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90373-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H. Z., Chen J. D., Lu P. H., Hao X. G., Li H. T. [Acidic polysaccharides from Holothuria leucospilota (Brandt)]. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 1983 Mar;18(3):203–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H. Z. [A new method for separation and purification of the acidic mucopolysaccharide from Stichopus japonicus]. Zhong Yao Tong Bao. 1982 Jul;7(4):27–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzén A., Heinegård D. Characterization of proteoglycans from the calcified matrix of bovine bone. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 15;224(1):59–66. doi: 10.1042/bj2240059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J., KIRK D. The heat precipitation of collagen from neutral salt solutions: some rate-regulating factors. J Biol Chem. 1958 Aug;233(2):355–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher J. T., Lyon M., Steward W. P. Structure and function of heparan sulphate proteoglycans. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 1;236(2):313–325. doi: 10.1042/bj2360313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald R. A., Schwartz C. E., Cantor J. O. Interaction of cartilage proteoglycans with collagen-substituted agarose gels. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;145(3):601–605. doi: 10.1042/bj1450601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory J. D., Cöster L., Damle S. P. Proteoglycans of rabbit corneal stroma. Isolation and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6965–6970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greyson-Fleg R. T., Scott W. W., Jr, Kuhajda F. P., Magid D., Fishman E. K. Fibrosarcoma in a patient with scleroderma. J Comput Tomogr. 1987 Jul;11(3):318–321. doi: 10.1016/0149-936x(87)90107-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEDBLOM E. E. The role of polysaccharides in corneal swelling. Exp Eye Res. 1961 Sep;1:81–91. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(61)80012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigh M., Scott J. E. A method of processing tissue sections for staining with cu-promeronic blue and other dyes, using CEC techniques, for light and electron microscopy. Basic Appl Histochem. 1986;30(4):479–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Björne-Persson A., Cöster L., Franzén A., Gardell S., Malmström A., Paulsson M., Sandfalk R., Vogel K. The core proteins of large and small interstitial proteoglycans from various connective tissues form distinct subgroups. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 15;230(1):181–194. doi: 10.1042/bj2300181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Sommarin Y., Hedbom E., Wieslander J., Larsson B. Assay of proteoglycan populations using agarose-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1985 Nov 15;151(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkel W., Rauterberg J., Glanville R. W. Isolation of crosslinked peptides from insoluble human leiomyoma. The involvement of the N-terminal, non-helical region of type III collagen in intermolecular crosslinking. Eur J Biochem. 1979 May 15;96(2):249–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13035.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulmes D. J., Miller A., Parry D. A., Piez K. A., Woodhead-Galloway J. Analysis of the primary structure of collagen for the origins of molecular packing. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 5;79(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90275-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junqueira L. C., Montes G. S. Biology of collagen-proteoglycan interaction. Arch Histol Jpn. 1983 Dec;46(5):589–629. doi: 10.1679/aohc.46.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor R., Bornstein P., Sage E. H. Type VIII collagen from bovine Descemet's membrane: structural characterization of a triple-helical domain. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3930–3937. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato M., Koike Y., Ito Y., Suzuki S., Kimata K. Multiple forms of heparan sulfate proteoglycans in the Engelbreth-Holm-Swarm mouse tumor. The occurrence of high density forms bearing both heparan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate side chains. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7180–7188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koda J. E., Bernfield M. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans from mouse mammary epithelial cells. Basal extracellular proteoglycan binds specifically to native type I collagen fibrils. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11763–11770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijer R., van de Stadt R. J., de Koning M. H., van der Korst J. K. Influence of constituents of proteoglycans on type II collagen fibrillogenesis. Coll Relat Res. 1985 Nov;5(5):379–391. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(85)80026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURENT T. C., SCOTT J. E. MOLECULAR WEIGHT FRACTIONATION OF POLYANIONS BY CETYLPYRIDINIUM CHLORIDE IN SALT SOLUTIONS. Nature. 1964 May 16;202:661–662. doi: 10.1038/202661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent T. C., Fraser J. R. The properties and turnover of hyaluronan. Ciba Found Symp. 1986;124:9–29. doi: 10.1002/9780470513385.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie G. W., Bing J. T., Kleinman H. K., Hassell J. R., Aumailley M., Martin G. R., Feldmann R. J. Localization of binding sites for laminin, heparan sulfate proteoglycan and fibronectin on basement membrane (type IV) collagen. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):205–216. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90391-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longas M. O., Fleischmajer R. Immunoelectron microscopy of proteodermatan sulfate in human mid-dermis. Connect Tissue Res. 1985;13(2):117–125. doi: 10.3109/03008208509152390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowther D. A., Natarajan M. The influence of glycoprotein on collagen fibril formation in the presence of chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan. Biochem J. 1972 Apr;127(3):607–608. doi: 10.1042/bj1270607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAURICE D. M. The structure and transparency of the cornea. J Physiol. 1957 Apr 30;136(2):263–286. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek K. M., Elliott G. F., Nave C. A synchrotron X-ray diffraction study of bovine cornea stained with cupromeronic blue. Coll Relat Res. 1986 Jun;6(2):203–218. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(86)80026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek K. M., Scott J. E., Nave C. An X-ray diffraction analysis of rat tail tendons treated with Cupromeronic Blue. J Microsc. 1985 Aug;139(Pt 2):205–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1985.tb02637.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. Isolation and characterization of a collagen from chick cartilage containing three identical alpha chains. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 27;10(9):1652–1659. doi: 10.1021/bi00785a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. The structure of fibril-forming collagens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;460:1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb51152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers D. B. Electron microscopic autoradiography of 35SO4-labelled material closely associated with collagen fibrils in mammalian synovium and ear cartilage. Histochem J. 1976 Mar;8(2):191–199. doi: 10.1007/BF01007168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao K., Bashey R. I. Fine structure of collagen fibrils as revealed by ruthenium red. Exp Mol Pathol. 1972 Aug;17(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(72)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noro A., Kimata K., Oike Y., Shinomura T., Maeda N., Yano S., Takahashi N., Suzuki S. Isolation and characterization of a third proteoglycan (PG-Lt) from chick embryo cartilage which contains disulfide-bonded collagenous polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9323–9331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrink B. A study of the interactions between monomeric tropocollagen and glycosaminoglycans. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Mar 1;33(2):387–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02695.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrink B., Laurent T. C., Carlsson B. The binding of chondroitin sulphate to collagen. FEBS Lett. 1975 Aug 1;56(1):166–169. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80133-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrink B. Non-aggregated tropocollagen at physiological pH and ionic strength. A chemical and physico-chemical characterization of tropocollagen isolated from the skin of lathyritic rats. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Feb;25(3):563–572. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01729.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrink B., Sundelöf L. O. Light scattering in the study of associating macromolecules. The binding of glycosaminoglycans to collagen. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Aug 17;37(2):226–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02979.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrink B. The influence of glycosaminoglycans on the formation of fibers from monomeric tropocollagen in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):129–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrink B., Wasteson A. Nature of the interaction of chondroitin 4-sulphate and chondroitin sulphate-proteoglycan with collagen. Biochem J. 1971 Jan;121(2):227–233. doi: 10.1042/bj1210227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Laidlaw J., Hascall V. C., Dziewiatkowski D. D. The effect of proteoglycans on the formation of fibrils from collagen solutions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Oct;170(2):698–709. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90167-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldberg A., Ruoslahti E. Interactions between chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan, fibronectin, and collagen. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4859–4863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orford C. R., Gardner D. L. Proteoglycan association with collagen d band in hyaline articular cartilage. Connect Tissue Res. 1984;12(3-4):345–348. doi: 10.3109/03008208409013696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. A., Flint M. H., Gillard G. C., Craig A. S. A role for glycosaminoglycans in the development of collagen fibrils. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 22;149(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson M., Mörgelin M., Wiedemann H., Beardmore-Gray M., Dunham D., Hardingham T., Heinegård D., Timpl R., Engel J. Extended and globular protein domains in cartilage proteoglycans. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):763–772. doi: 10.1042/bj2450763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson C. H., Gibson G. J. Proteoglycans of bovine periodontal ligament and skin. Occurrence of different hybrid-sulphated galactosaminoglycans in distinct proteoglycans. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 1;201(1):27–37. doi: 10.1042/bj2010027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole A. R. Proteoglycans in health and disease: structures and functions. Biochem J. 1986 May 15;236(1):1–14. doi: 10.1042/bj2360001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronzière M. C., Berthet-Colominas C., Herbage D. Low-angle X-ray diffraction analysis of the collagen-proteoglycan interactions in articular cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Oct 17;842(2-3):170–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L. C., Choi H. U., Tang L. H., Johnson T. L., Pal S., Webber C., Reiner A., Poole A. R. Isolation of dermatan sulfate proteoglycans from mature bovine articular cartilages. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6304–6313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri A., Dell'orbo C., Quacci D. Electron microscopic visualization of proteoglycans with Alcian Blue. Histochem J. 1975 Mar;7(2):187–197. doi: 10.1007/BF01004562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajdera S. W., Hascall V. C. Proteinpolysaccharide complex from bovine nasal cartilage. A comparison of low and high shear extraction procedures. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 10;244(1):77–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer J., Stejskal E. O., Brewer C. F., Keiser H. D., Sternlicht H. Cross-polarization 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of collagen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Oct;190(2):657–661. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90323-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield B. H., Williams B. R., Doty S. B. Alcian Blue staining of cartilage for electron microscopy. Application of the critical electrolyte concentation principle. Histochem J. 1975 Mar;7(2):139–149. doi: 10.1007/BF01004558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. E. Collagen--proteoglycan interactions. Localization of proteoglycans in tendon by electron microscopy. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 1;187(3):887–891. doi: 10.1042/bj1870887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. E., Haigh M. 'Small'-proteoglycan:collagen interactions: keratan sulphate proteoglycan associates with rabbit corneal collagen fibrils at the 'a' and 'c' bands. Biosci Rep. 1985 Sep;5(9):765–774. doi: 10.1007/BF01119875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. E., Haigh M., Neo G. E., Gibson S. The effect of muscle paralysis on the radial growth of collagen fibrils in developing tendon. Clin Sci (Lond) 1987 Mar;72(3):359–363. doi: 10.1042/cs0720359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. E., Haigh M. Proteoglycan-collagen interactions in intervertebral disc. A chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan associates with collagen fibrils in rabbit annulus fibrosus at the d-e bands. Biosci Rep. 1986 Oct;6(10):879–888. doi: 10.1007/BF01116241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. E., Haigh M. Proteoglycan-type I collagen fibril interactions in bone and non-calcifying connective tissues. Biosci Rep. 1985 Jan;5(1):71–81. doi: 10.1007/BF01117443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. E., Heatley F., Jones M. N., Wilkinson A., Olavesen A. H. Secondary structure of chondroitin sulphate in dimethyl sulphoxide. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;130(3):491–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. E., Hughes E. W. Proteoglycan-collagen relationships in developing chick and bovine tendons. Influence of the physiological environment. Connect Tissue Res. 1986;14(4):267–278. doi: 10.3109/03008208609017470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. E., Kyffin T. W. Demineralization in organic solvents by alkylammonium salts of ethylenediaminetetra-acetic acid. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 1;169(3):697–701. doi: 10.1042/bj1690697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. E., Orford C. R. Dermatan sulphate-rich proteoglycan associates with rat tail-tendon collagen at the d band in the gap region. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 1;197(1):213–216. doi: 10.1042/bj1970213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. E., Orford C. R., Hughes E. W. Proteoglycan-collagen arrangements in developing rat tail tendon. An electron microscopical and biochemical investigation. Biochem J. 1981 Jun 1;195(3):573–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1950573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. E. Proteoglycan histochemistry--a valuable tool for connective tissue biochemists. Coll Relat Res. 1985 Dec;5(6):541–575. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(85)80008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. E. Proteoglycan-collagen interactions. Ciba Found Symp. 1986;124:104–124. doi: 10.1002/9780470513385.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. E. The periphery of the developing collagen fibril. Quantitative relationships with dermatan sulphate and other surface-associated species. Biochem J. 1984 Feb 15;218(1):229–233. doi: 10.1042/bj2180229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P. G., Winterbottom N., Dodd C. M., Edwards E., Pearson C. H. A role for disulphide bridges in the protein core in the interaction of proteodermatan sulphate and collagen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 14;138(3):1348–1354. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80431-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. N., Jr, Williams J. M., Brandt K. D. Interaction of proteoglycans with the pericellular (1 alpha, 2 alpha, 3 alpha) collagens of cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10761–10767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Frame J. Observations on the collagen and proteinpolysaccharide complex of rabbit cornea stroma. J Cell Sci. 1969 Mar;4(2):421–436. doi: 10.1242/jcs.4.2.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speziale P., Bardoni A., Balduini C. Interactions between bovine cornea proteoglycans and collagen. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 1;187(3):655–659. doi: 10.1042/bj1870655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanescu V., Stanescu R., Maroteaux P. Répartition différente du collagene de type I et du collagène de type II dans la zone superficielle et dans la zone intermédiaire du cartilage articulaire. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1976 Jul 19;283(3):279–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole B. P. Binding and precipitation of soluble collagens by chick embryo cartilage proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 10;251(3):895–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole B. P. Developmental role of hyaluronate. Connect Tissue Res. 1982;10(1):93–100. doi: 10.3109/03008208209034409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole B. P., Lowther D. A. Dermatan sulfate-protein: isolation from and interaction with collagen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Dec;128(3):567–578. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valli M., Tira M. E., Balduini C. Isolation and characterization of two proteoglycans from bovine tendon. Ital J Biochem. 1982 May-Jun;31(3):183–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan L., Winterhalter K. H., Bruckner P. Proteoglycan Lt from chicken embryo sternum identified as type IX collagen. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4758–4763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel K. G., Heinegård D. Characterization of proteoglycans from adult bovine tendon. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9298–9306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel K. G., Paulsson M., Heinegård D. Specific inhibition of type I and type II collagen fibrillogenesis by the small proteoglycan of tendon. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 1;223(3):587–597. doi: 10.1042/bj2230587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD G. C., KEECH M. K. The formation of fibrils from collagen solutions. 1. The effect of experimental conditions: kinetic and electron-microscope studies. Biochem J. 1960 Jun;75:588–598. doi: 10.1042/bj0750588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward N. P., Scott J. E., Cöster L. Dermatan sulphate proteoglycans from sclera examined by rotary shadowing and electron microscopy. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 15;242(3):761–766. doi: 10.1042/bj2420761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann H., Paulsson M., Timpl R., Engel J., Heinegård D. Domain structure of cartilage proteoglycans revealed by rotary shadowing of intact and fragmented molecules. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 15;224(1):331–333. doi: 10.1042/bj2240331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. D. The ultrastructural organization of proteoglycans and collagen in human and rabbit scleral matrix. J Cell Sci. 1985 Mar;74:95–104. doi: 10.1242/jcs.74.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Rest M., Mayne R., Ninomiya Y., Seidah N. G., Chretien M., Olsen B. R. The structure of type IX collagen. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):220–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





