Abstract
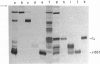
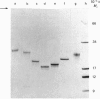
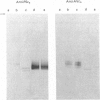
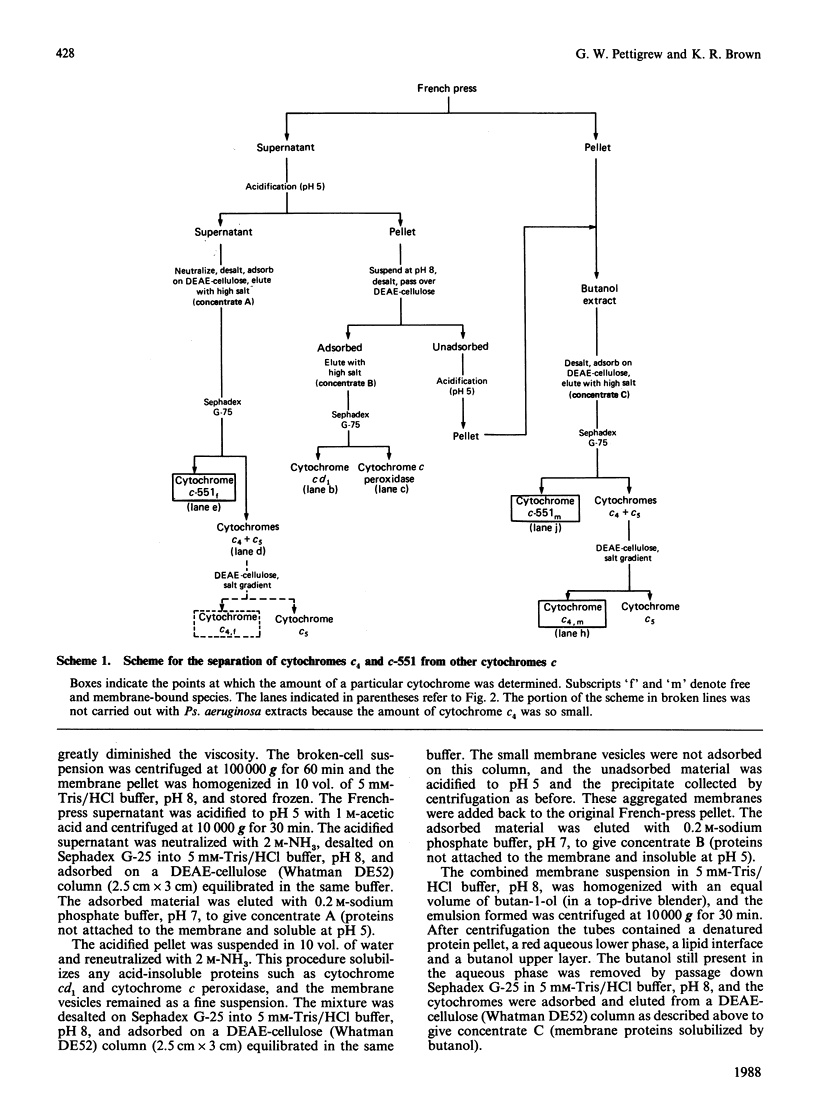
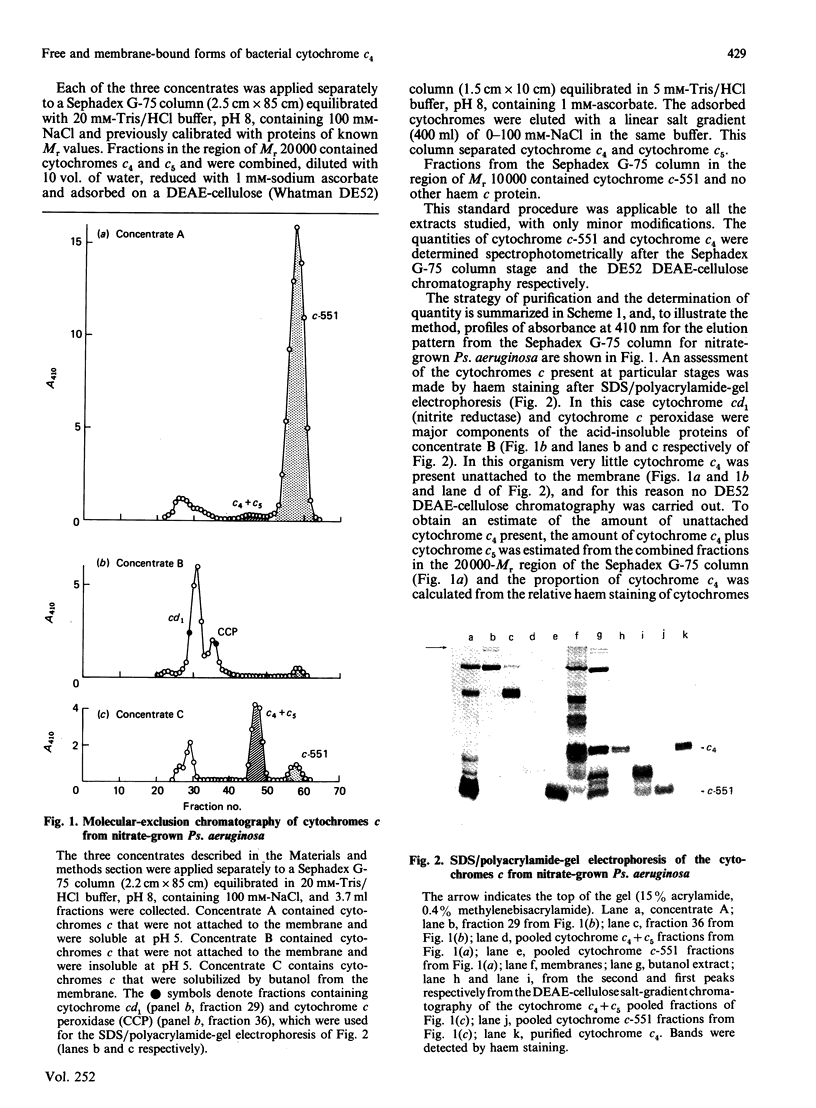
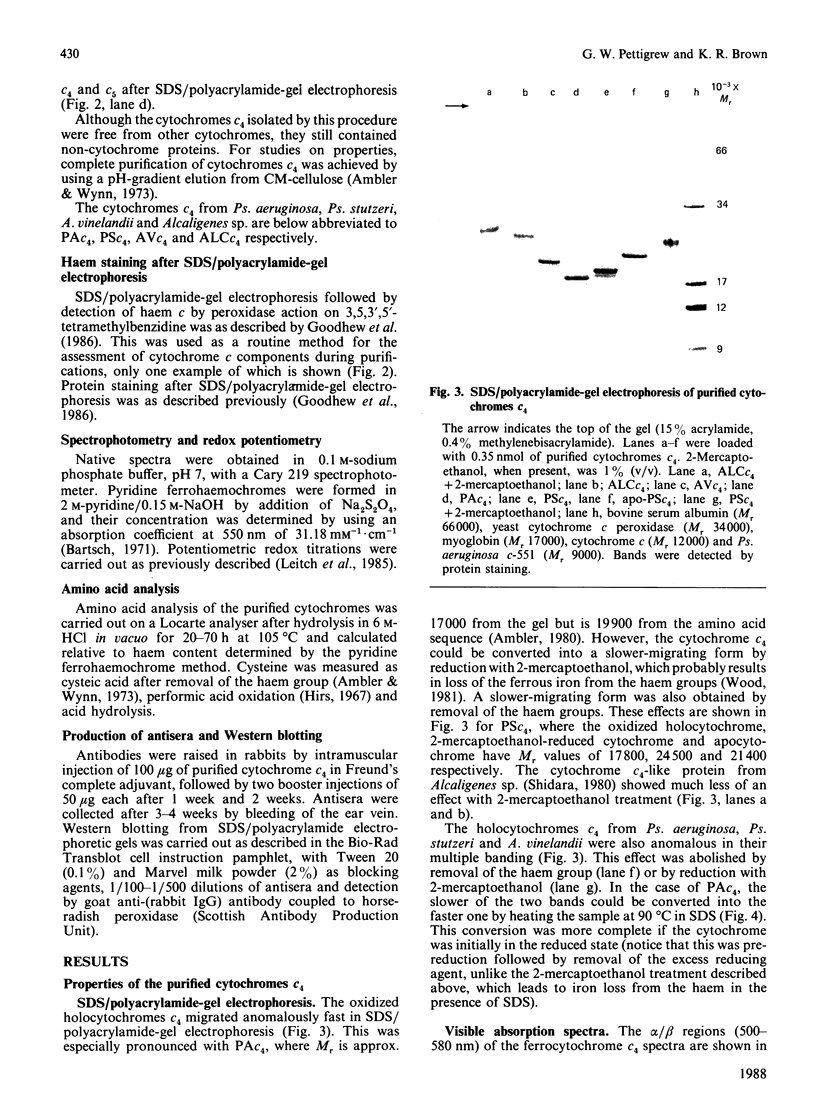
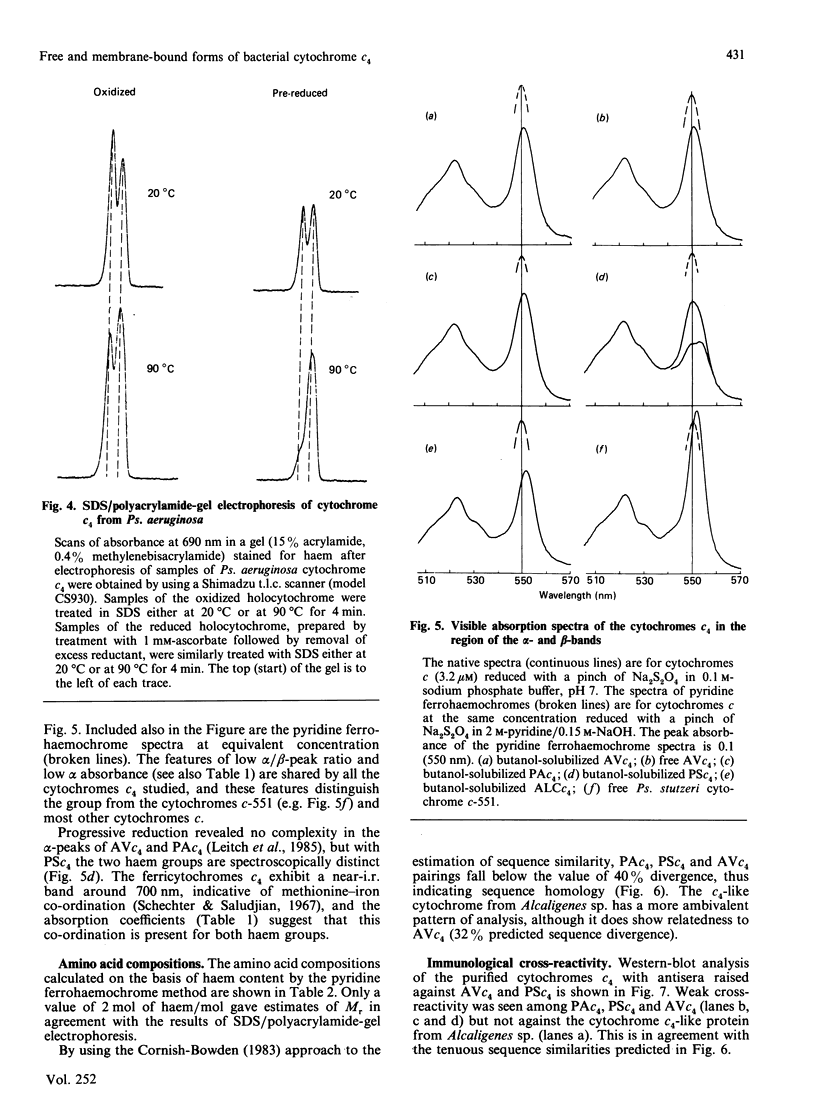
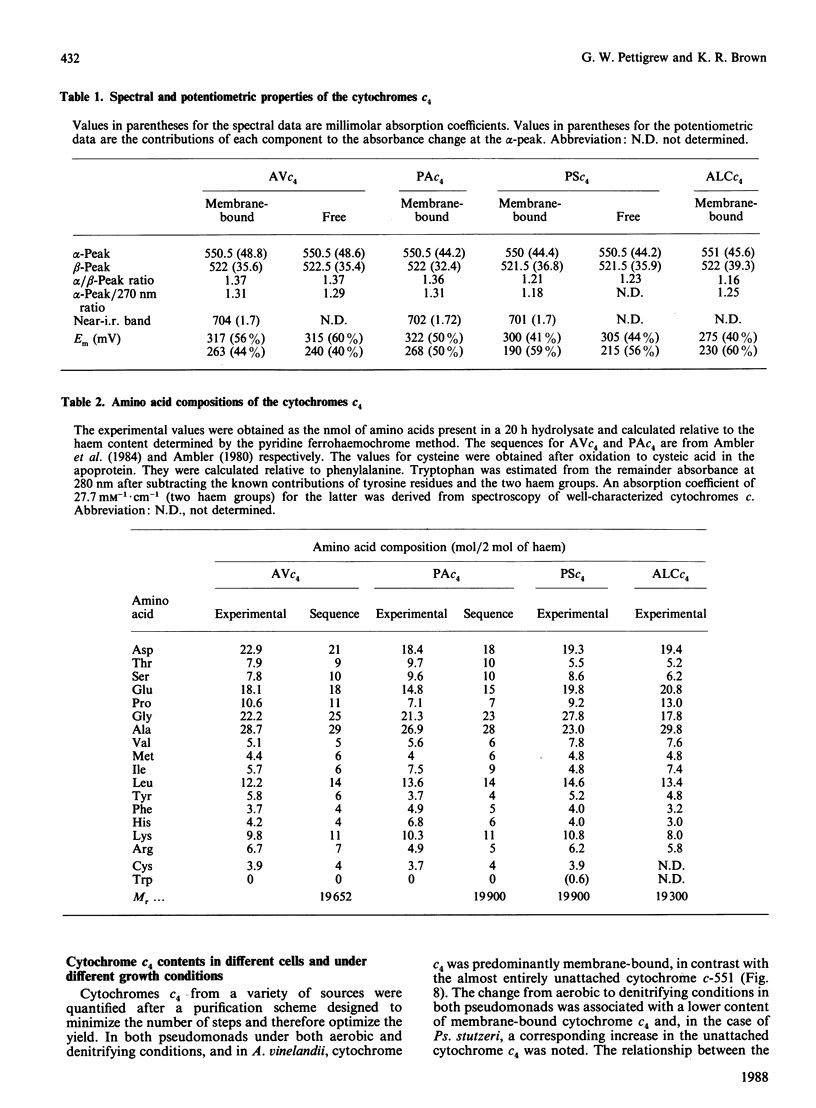
Cytochrome c4 was isolated from cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas stutzeri and Azotobacter vinelandii. The dihaem nature, Mr of approx. 20,000 and ferrohaem spectra in the region of the alpha- and beta-peaks define this family of cytochromes c. The behaviour of the holocytochromes in SDS was atypical, but removal of the haem groups resulted in a normal migration. In all three organisms most of the cytochrome c4 was tightly bound to the membrane, but some free cytochrome was detected. The membrane-attached cytochrome could be extracted with butanol, and this solubilized form was then indistinguishable in properties from the free form. Denitrifying rather than aerobic growth conditions hardly affected the total cytochrome c4 in the two pseudomonads, but there was slightly more free form and less membrane-attached form in denitrifying growth. The nature of the attachment of cytochrome c4 to the membrane is discussed and a model is proposed for the process of solubilization.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P., Daniel M., Melis K., Stout C. D. The amino acid sequence of the dihaem cytochrome c4 from the bacterium Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 15;222(1):217–227. doi: 10.1042/bj2220217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P., Wynn M. The amino acid sequences of cytochromes c-551 from three species of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;131(3):485–498. doi: 10.1042/bj1310485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry E. A., Trumpower B. L. Isolation of ubiquinol oxidase from Paracoccus denitrificans and resolution into cytochrome bc1 and cytochrome c-aa3 complexes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2458–2467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma G., Braster M., Stouthamer A. H., van Verseveld H. W. Isolation and characterization of ubiquinol oxidase complexes from Paracoccus denitrificans cells cultured under various limiting growth conditions in the chemostat. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jun 15;165(3):657–663. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11491.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capaldi R. A., Vanderkooi G. The low polarity of many membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):930–932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornish-Bowden A. Relating proteins by amino acid composition. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:60–75. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurtshuk P., Jr, Mueller T. J., Wong T. Y. Isolation and purification of the cytochrome oxidase of Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 14;637(2):374–382. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(81)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T., Shidara S. Components of cytochrome system and purification and some properties of c-type cytochromes of a denitrifying bacterium, Pseudomonas stutzeri. J Biochem. 1969 Mar;65(3):351–360. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitch F. A., Brown K. R., Pettigrew G. W. Complexity in the redox titration of the dihaem cytochrome c4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 17;808(2):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(85)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M. C., Payne W. J., Peck H. D., Jr, LeGall J. Comparison of cytochromes from anaerobically and aerobically grown cells of Pseudomonas perfectomarinus. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):278–286. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.278-286.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M. C., Peck H. D., Jr, Payne W. J., Anderson J. L., Dervartanian D. V., Legall J. Purification and properties of the diheme cytochrome (cytochrome c-552) from Pseudomonas perfectomarinus. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 29;129(1):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80779-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Kamen M. D. New perspectives on c-type cytochromes. Adv Protein Chem. 1982;35:105–212. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60469-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON J. W., WILSON P. W., BURRIS R. H. Direct demonstration of ammonia as an intermediate in nitrogen fixation by Azotobacter. J Biol Chem. 1953 Sep;204(1):445–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter E., Saludjian P. Conformation of ferricytochrome c. IV. Relationship between optical absorption and protein conformation. Biopolymers. 1967;5(8):788–790. doi: 10.1002/bip.1967.360050812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shidara S. Components of the cytochrome system of Alcaligenes sp. N.C.I.B., 11015, with special reference to particulate bound c-type cytochromes. J Biochem. 1980 Apr;87(4):1177–1184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swank R. T., Burris R. H. Purification and properties of cytochromes c of Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Aug 5;180(3):473–489. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(69)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TISSIERES A. Purification, some properties and the specific biological activity of cytochromes c4 and c5 from Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochem J. 1956 Nov;64(3):582–589. doi: 10.1042/bj0640582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. A., Hunter C. N., Jones O. T. Changes in the cytochrome composition of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides grown aerobically, photosynthetically and on dimethyl sulphoxide. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):783–790. doi: 10.1042/bj2120783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. M. Fluorescent gels as a general technique for characterizing bacterial c-type cytochromes. Anal Biochem. 1981 Mar 1;111(2):235–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90559-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. M. Why do c-type cytochromes exist? FEBS Lett. 1983 Dec 12;164(2):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80289-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]