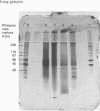
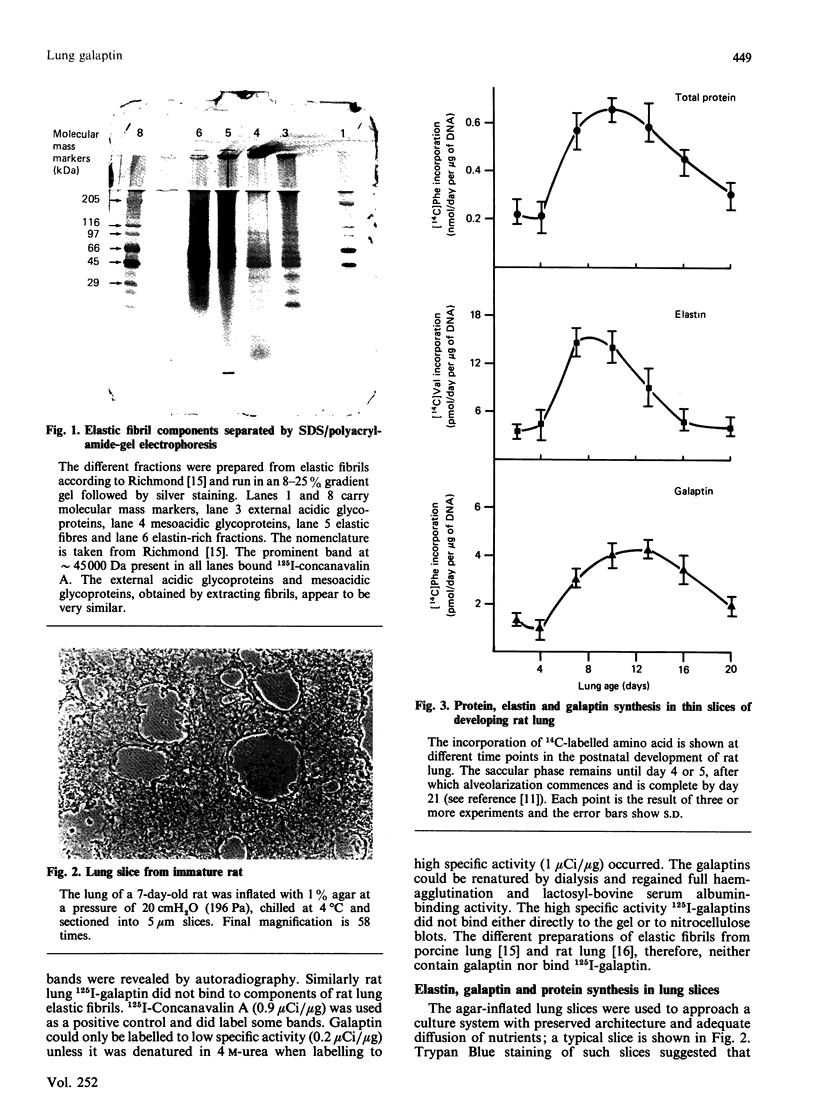
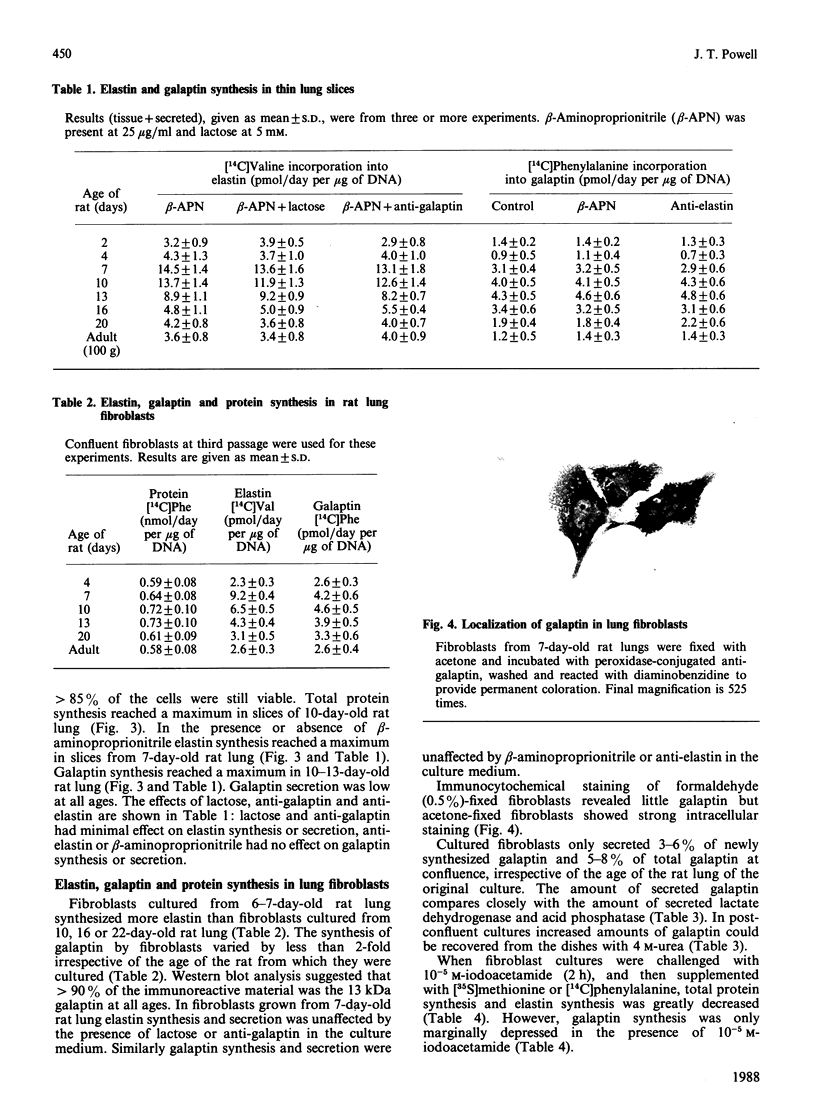
Abstract
Previously it has been suggested that galaptin, an endogenous beta-galactoside-binding lectin, may function in the organization of lung elastic fibres. Galaptin was not present in preparations of rat or porcine lung elastic fibrils, neither did it bind to any of the fibril-associated proteins when these were separated by SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Elastin and galaptin synthesis and secretion were investigated in lung fibroblast cultures and in anatomically preserved slices from developing rat lung. In both systems the synthesis and secretion of elastin was unmodified by the presence of beta-galactosides or antigalaptin in the culture medium. The synthesis of galaptin was unmodified by the presence of anti-elastin or beta-aminoproprionitrile in the culture medium. Cultured fibroblasts secreted elastin but only trivial amounts of galaptin. When cultures were treated with iodoacetamide (10(-5)M) galaptin synthesis was maintained but elastin synthesis ceased. These results argue against galaptin having an important role in the synthesis, secretion or organization of the elastic fibril.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barondes S. H. Soluble lectins: a new class of extracellular proteins. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1259–1264. doi: 10.1126/science.6367039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer E. C., Tokuyasu K. T., Barondes S. H. Localization of an endogenous lectin in chicken liver, intestine, and pancreas. J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;82(2):565–571. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.2.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer E. C., Zweig S. E., Barondes S. H. Two lactose binding lectins from chicken tissues. Purified lectin from intestine is different from those in liver and muscle. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4236–4239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caltabiano M. M., Koestler T. P., Poste G., Greig R. G. Induction of 32- and 34-kDa stress proteins by sodium arsenite, heavy metals, and thiol-reactive agents. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13381–13386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerra R. F., Gitt M. A., Barondes S. H. Three soluble rat beta-galactoside-binding lectins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10474–10477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerra R. F., Haywood-Reid P. L., Barondes S. H. Endogenous mammalian lectin localized extracellularly in lung elastic fibers. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1580–1589. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs R. A., Feizi T. beta-Galactoside-binding muscle lectins of man and monkey show antigenic cross-reactions with those of bovine origin. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 1;183(3):755–758. doi: 10.1042/bj1830755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipman S. D., Faris B., Barone L. M., Pratt C. A., Franzblau C. Processing of soluble elastin in cultured neonatal rat smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12780–12785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerch L. B., Whitney P. L., Massaro D. Rat lung lectin synthesis, degradation and activation. Developmental regulation and modulation by dexamethasone. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):683–690. doi: 10.1042/bj2450683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly D. T., Knight M. B., Harakas N. K., Wittwer A. J., Feder J. Determination of the number of endothelial cells in culture using an acid phosphatase assay. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jan;152(1):136–140. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Mitsui K., Motizuki M., Tsurugi K. The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes. The site and the characteristics of the modification in 28 S ribosomal RNA caused by the toxins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5908–5912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning J. C., Cleary E. G. Identification of glycoproteins associated with elastin-associated microfibrils. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Apr;33(4):287–294. doi: 10.1177/33.4.3980982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitt M. A., Barondes S. H. Evidence that a human soluble beta-galactoside-binding lectin is encoded by a family of genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7603–7607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANSING A. I., ROSENTHAL T. B., ALEX M., DEMPSEY E. W. The structure and chemical characterization of elastic fibers as revealed by elastase and by electron microscopy. Anat Rec. 1952 Dec;114(4):555–575. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091140404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Surface-specific iodination of membrane proteins of viruses and eucaryotic cells using 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3alpha,6alpha-diphenylglycoluril. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4807–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers B., Dubick M., Last J. A., Rucker R. B. Elastin synthesis during perinatal lung development in the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Nov 22;761(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90357-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J. T. Purification and properties of lung lectin. Rat lung and human lung beta-galactoside-binding proteins. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 1;187(1):123–129. doi: 10.1042/bj1870123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J. T., Whitney P. L. Postnatal development of rat lung. Changes in lung lectin, elastin, acetylcholinesterase and other enzymes. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 15;188(1):1–8. doi: 10.1042/bj1880001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond V. L. The microfibrillar components of porcine lung elastic fiber. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 28;669(2):193–205. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90240-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Bornstein P. The elastic fiber. I. The separation and partial characterization of its macromolecular components. J Cell Biol. 1969 Feb;40(2):366–381. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin K., Kjellén L., Obrink B. Intercellular adhesion between juvenile liver cells. A method to measure the formation of stable lateral contacts between cells attached to a collagen gel. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Oct 15;109(2):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow C. P., Leffler H., Barondes S. H. Multiple soluble beta-galactoside-binding lectins from human lung. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7383–7390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vytásek R. A sensitive fluorometric assay for the determination of DNA. Anal Biochem. 1982 Mar 1;120(2):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90342-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney P. L., Powell J. T., Sanford G. L. Oxidation and chemical modification of lung beta-galactoside-specific lectin. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 15;238(3):683–689. doi: 10.1042/bj2380683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney P., Maxwell S., Ryan U., Massaro D. Synthesis and binding of lactose-specific lectin by isolated lung cells. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 1):C258–C264. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.3.C258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Waard A., Hickman S., Kornfeld S. Isolation and properties of beta-galactoside binding lectins of calf heart and lung. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7581–7587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]