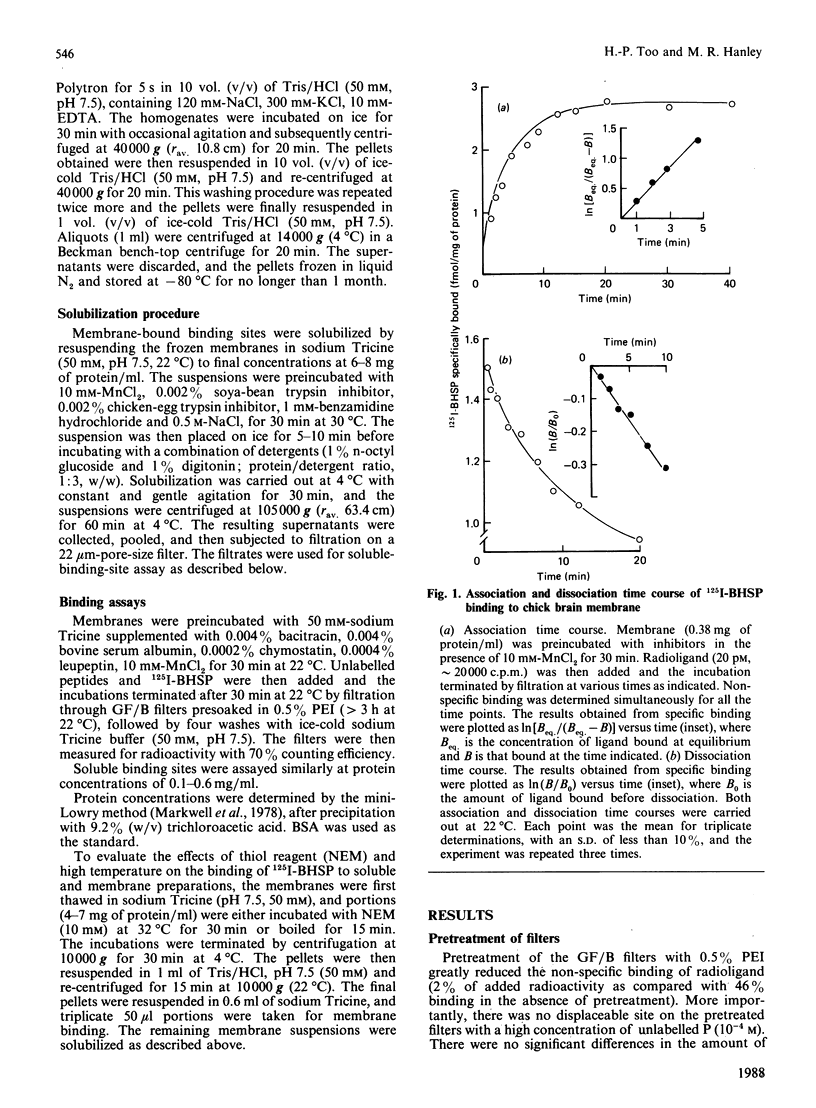
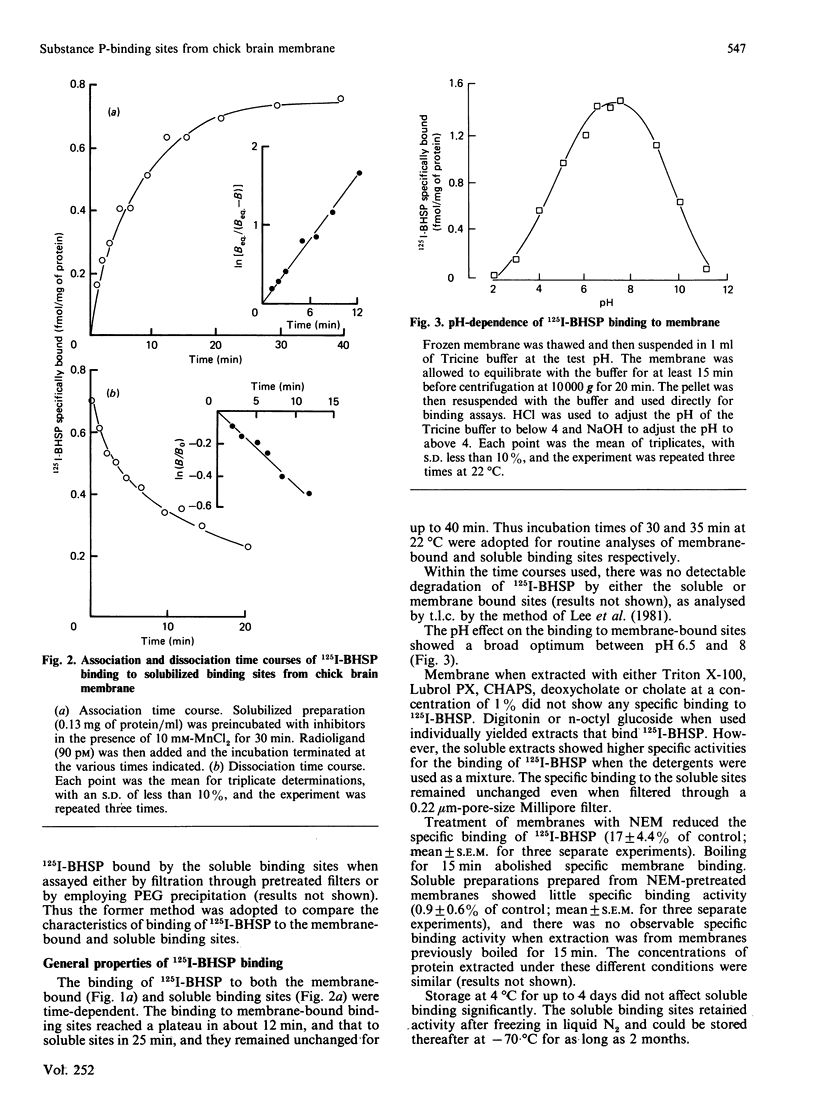
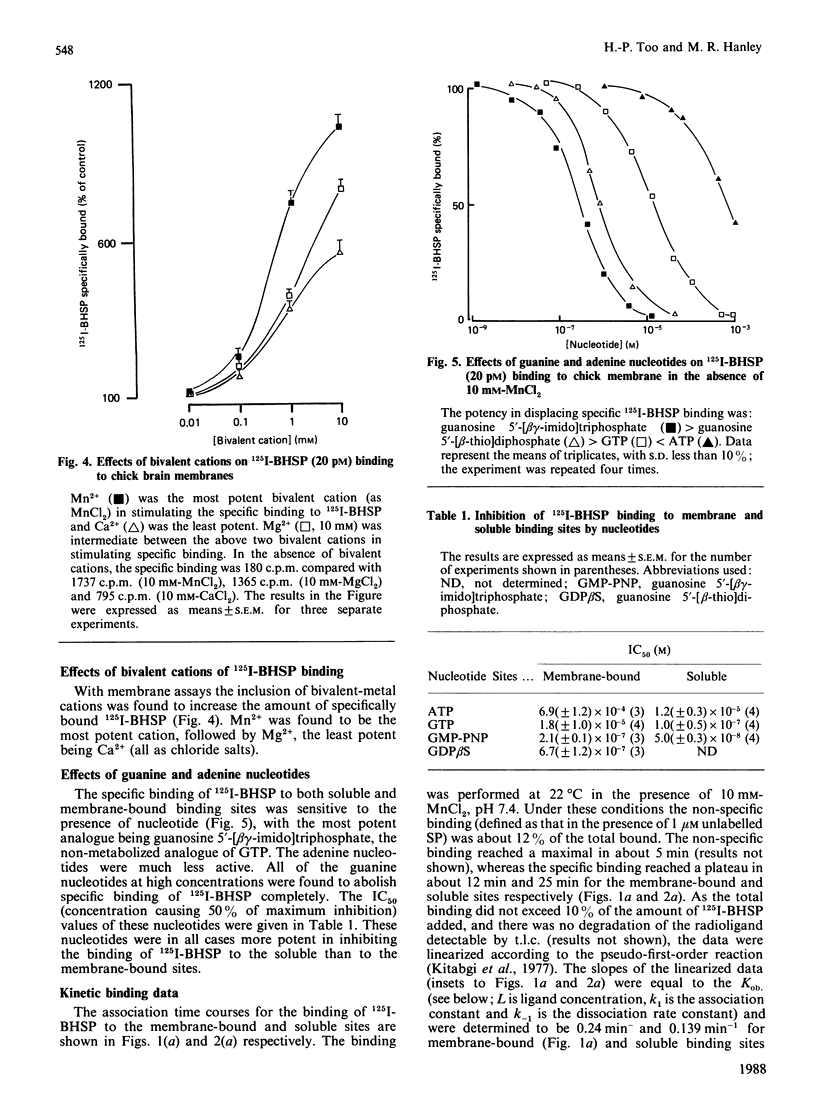
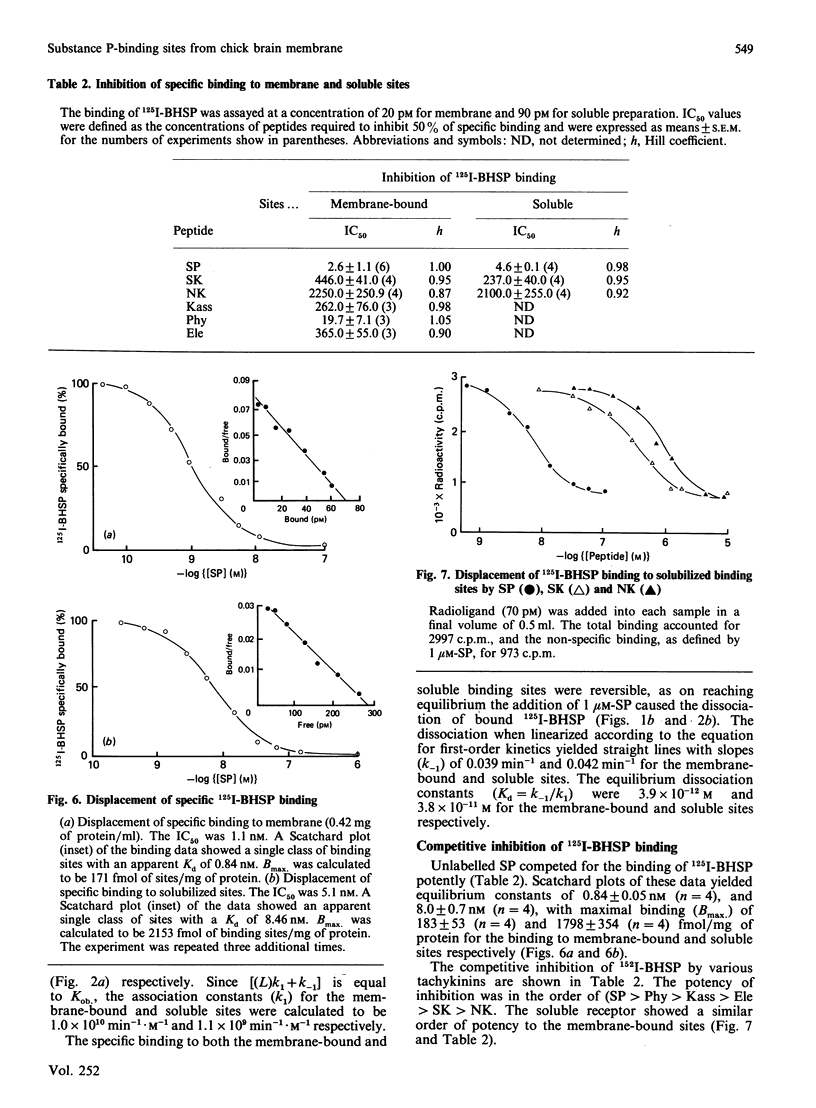
Abstract
Sites binding monoiodinated-Bolton-Hunter-reagent-labelled substance P were solubilized from 1-day-old-chick brain membrane by using non-ionic detergents (1% digitonin/1% n-octyl glucoside) and a high concentration of NaCl (0.5 M). The solubilized preparation retained the pharmacological properties of the high-affinity binding sites found in the native membrane. The high density of specific binding sites (approximately 2 pmol of binding sites/mg of protein) suggests that the chick brain membranes may be a useful source for the purification of the substance P-binding sites.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruns R. F., Lawson-Wendling K., Pugsley T. A. A rapid filtration assay for soluble receptors using polyethylenimine-treated filters. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):74–81. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90427-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burcher E., Buck S. H., Lovenberg W., O'Donohue T. L. Characterization and autoradiographic localization of multiple tachykinin binding sites in gastrointestinal tract and bladder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Mar;236(3):819–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr D. B., Jones K. J., Bergland R. M., Hamilton A., Kasting N. W., Fisher J. E., Martin J. B. Causal links between plasma and CSF endorphin levels in stress: vector-ARMA analysis. Peptides. 1985;6 (Suppl 1):5–10. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cascieri M. A., Chicchi G. G., Liang T. Demonstration of two distinct tachykinin receptors in rat brain cortex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1501–1507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi P., Carraway R., Van Rietschoten J., Granier C., Morgat J. L., Menez A., Leeman S., Freychet P. Neurotensin: specific binding to synaptic membranes from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1846–1850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. M., Campbell N. J., Williams B. J., Iversen L. L. Multiple tachykinin binding sites in peripheral tissues and in brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov 4;130(3):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. M., Iversen L. L., Hanley M. R., Sandberg B. E. The possible existence of multiple receptors for substance P. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Mar;318(4):281–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00501166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. M., Sandberg B. E., Hanley M. R., Iversen L. L. Purification and characterisation of a membrane-bound substance-P-degrading enzyme from human brain. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Feb;114(2):315–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. W., Musacchio J. M. The determination of dissociation constants for substance P and substance P analogues in the guinea pig ileum by pharmacological procedures. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 May;23(3):558–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama M. Selective solubilization of physalaemin-type substance P binding sites from rat brain membranes by glycodeoxycholate and NaCl. Brain Res. 1986 Apr 2;370(1):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91122-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita H., Sugiyama M., Furukawa T. Inhibition by sulfur-containing amino acids and GABA of sympathetic neurotransmission in guinea-pig vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Nov 11;95(1-2):13–19. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90262-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payan D. G., McGillis J. P., Organist M. L. Binding characteristics and affinity labeling of protein constituents of the human IM-9 lymphoblast receptor for substance P. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14321–14329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma P. M., Musacchio J. M. N-ethylmaleimide blocks the modulatory effects of divalent cations and guanine nucleotides on the brain substance P receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun 12;138(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90331-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel A. M. Signal transduction by guanine nucleotide binding proteins. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Jan;49(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Too H. P., Unger W. G., Hanley M. R. Evidence for multiple tachykinin receptor subtypes on the rabbit iris sphincter muscle. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Jan;33(1):64–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrens Y., Beaujouan J. C., Glowinski J. Pharmacological characterisation of two tachykinin binding sites in the rat cerebral cortex. Neuropeptides. 1985 Mar;6(1):59–70. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(85)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrens Y., Beaujouan J. C., Saffroy M., Daguet de Montety M. C., Bergström L., Glowinski J. Substance P receptors in primary cultures of cortical astrocytes from the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9216–9220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


