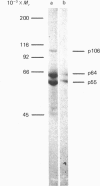
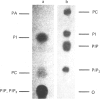
Abstract
The rate of energy-dependent nucleoside triphosphatase (NTPase)-mediated nucleocytoplasmic translocation of poly(A)-containing mRNA [poly(A)+mRNA] across the nuclear envelope is thought to be regulated by poly(A)-sensitive phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of nuclear-envelope protein. Studying the phosphorylation-related inhibition of the NTPase, we found that phosphorylation of one polypeptide of rat liver envelopes by endogenous NI- and NII-like protein kinase was particularly sensitive to poly(A). This polypeptide (106 kDa) was also phosphorylated by nuclear-envelope-bound Ca2+-activated and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase (protein kinase C). Activation of kinase C by tumour-promoting phorbol esters resulted in inhibition of nuclear-envelope NTPase activity and in a concomitant decrease of mRNA (actin) efflux rate from isolated rat liver nuclei. Protein kinase C, but not nuclear envelope NI-like or NII-like protein kinase, was found to be solubilized from the envelope by Triton X-100, whereas the presumable poly(A)-binding site [the 106 kDa polypeptide, representing the putative carrier for poly(A)+mRNA transport] remained bound to this structure. RNA efflux from detergent-treated nuclei lost its susceptibility to phorbol esters. Addition of purified protein kinase C to these nuclei restored the effect of the tumour promoters. Protein kinase C was found to bind also to isolated rat liver nuclear matrices in the absence but not in the presence of ATP. The NII-like nuclear-envelope protein kinase co-purified together with the 106 kDa polypeptide which specifically binds to poly(A) in an ATP-labile linkage.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson R. P., Blobel G. Isolation of nuclear pore complexes in association with a lamina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1007–1011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agranoff B. W., Murthy P., Seguin E. B. Thrombin-induced phosphodiesteratic cleavage of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2076–2078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agutter P. S., Harris J. R., Stevenson I. Ribonucleic acid stimulation of mammalian liver nuclear-envelope nucleoside triphosphatase. A possible enzymic marker for the nuclear envelope. Biochem J. 1977 Mar 15;162(3):671–679. doi: 10.1042/bj1620671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agutter P. S., McArdle H. J., McCaldin B. Evidence for involvement of nuclear envelope nucleoside triphosphatase in nucleocytoplasmic translocation of ribonucleoprotein. Nature. 1976 Sep 9;263(5573):165–167. doi: 10.1038/263165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso S., Minty A., Bourlet Y., Buckingham M. Comparison of three actin-coding sequences in the mouse; evolutionary relationships between the actin genes of warm-blooded vertebrates. J Mol Evol. 1986;23(1):11–22. doi: 10.1007/BF02100994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. L., Gemmell M. A., Coussens P. M., Murao S., Huberman E. Specific protein phosphorylation in human promyelocytic HL-60 leukemia cells susceptible or resistant to induction of cell differentiation by phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate. Cancer Res. 1985 Oct;45(10):4955–4962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann M., Bernd A., Schröder H. C., Zahn R. K., Müller W. E. The role of protein phosphokinase and protein phosphatase during the nuclear envelope nucleoside triphosphatase reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 27;773(2):308–316. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglia F. A., Maul G. G. Nuclear ribonucleoprotein release and nucleoside triphosphatase activity are inhibited by antibodies directed against one nuclear matrix glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2285–2289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. M. Protein kinase C activation by diacylglycerol second messengers. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):631–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90774-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernd A., Schröder H. C., Zahn R. K., Müller W. E. Age-dependence of polyadenylate stimulation of nuclear-envelope nucleoside triphosphatase. Mech Ageing Dev. 1982 Dec;20(4):331–341. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(82)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernd A., Schröder H. C., Zahn R. K., Müller W. E. Modulation of the nuclear-envelope nucleoside triphosphatase by poly(A)-rich mRNA and by microtubule protein. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec;129(1):43–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07018.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Ernst Klenk Lecture, November 1985. Intracellular signalling through inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1986 Jun;367(6):447–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Nuclei from rat liver: isolation method that combines purity with high yield. Science. 1966 Dec 30;154(3757):1662–1665. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3757.1662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. H., Scott D. L., Gordon E. A., LaBelle E. F. Phosphoinositides in mitogenesis: neomycin inhibits thrombin-stimulated phosphoinositide turnover and initiation of cell proliferation. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):479–488. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90105-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clawson G. A., Koplitz M., Moody D. E., Smuckler E. A. Effects of thioacetamide treatment on nuclear envelope nucleoside triphosphatase activity and transport of RNA from rat liver nuclei. Cancer Res. 1980 Jan;40(1):75–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clawson G. A., Smuckler E. A. Increased nucleoside triphosphatase activity of rat liver nuclear matrix following low dose carcinogen intoxication. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Oct 15;108(3):1331–1339. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)92146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clawson G. A., Woo C. H., Button J., Smuckler E. A. Photoaffinity labeling of the major nucleosidetriphosphatase of rat liver nuclear envelope. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 17;23(15):3501–3507. doi: 10.1021/bi00310a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delpech M., Levy-Favatier F., Moisand F., Kruh J. Rat liver nuclear protein kinases NI and NII. Purification, subunit composition, substrate specificity, possible levels of regulation. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 15;160(2):333–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjardins P. R., Lue P. F., Liew C. C., Gornall A. G. Purification and properties of rat liver nuclear protein kinases. Can J Biochem. 1972 Dec;50(12):1249–1259. doi: 10.1139/o72-170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Glenney P. The microvillus 110K cytoskeletal protein is an integral membrane protein. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):743–751. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90410-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Sastre F., Folch-Pi J. Thin-layer chromatography of the phosphoinositides. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jul;9(4):532–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Gibson W., Shaper J. H. Characterization of the major polypeptides of the rat liver nuclear envelope. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2710–2719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindås-Mügge I., Sauermann G. Transport of beta-globin mRNA from nuclei of murine Friend erythroleukemia cells. Reversible inhibition of transport by the oxidizing sulfhydryl reagent o-iodosobenzoate. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 1;148(1):49–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08805.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kljajić Z., Schröder H. C., Rottmann M., Cuperlović M., Movsesian M., Uhlenbruck G., Gasić M., Zahn R. K., Müller W. E. A D-mannose-specific lectin from Gerardia savaglia that inhibits nucleocytoplasmic transport of mRNA. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Nov 16;169(1):97–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13585.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam K. S., Kasper C. B. Selective phosphorylation of a nuclear envelope polypeptide by an endogenous protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 23;18(2):307–311. doi: 10.1021/bi00569a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Connolly T. M., Deckmyn H., Ross T. S., Bross T. E., Ishii H., Bansal V. S., Wilson D. B. The metabolism of phosphoinositide-derived messenger molecules. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1519–1526. doi: 10.1126/science.3024320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. R., Agutter P. S. The relationship between polyribonucleotide binding and the phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of nuclear envelope protein. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 28;116(2):145–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80629-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messer R., Schröder H. C., Breter H. J., Müller W. E. Differential polyadenylation pattern of ovalbumin precursor RNAs during development. Mol Biol Rep. 1986;11(2):81–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00364818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffett R. B., Webb T. E. Regulated transport of messenger ribonucleic acid from isolated liver nuclei by nucleic acid binding proteins. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3253–3262. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murty C. N., Verney E., Sidransky H. The effect of tryptrophan on nucleocytoplasmic translocation of RNA in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 3;474(1):117–128. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90219-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottmann M., Schröder H. C., Gramzow M., Renneisen K., Kurelec B., Dorn A., Friese U., Müller W. E. Specific phosphorylation of proteins in pore complex-laminae from the sponge Geodia cydonium by the homologous aggregation factor and phorbol ester. Role of protein kinase C in the phosphorylation of DNA topoisomerase II. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3939–3944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02735.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUDIER F. W. SEDIMENTATION STUDIES OF THE SIZE AND SHAPE OF DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:373–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Bachmann M., Diehl-Seifert B., Müller W. E. Transport of mRNA from nucleus to cytoplasm. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1987;34:89–142. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60494-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Becker R., Bachmann M., Gramzow M., Seve A. P., Monsigny M., Müller W. E. Differential changes of nuclear-envelope-associated enzyme activities involved in nucleocytoplasmic mRNA transport in the developing rat brain and liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 13;868(2-3):108–118. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(86)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Diehl-Seifert B., Rottmann M., Messer R., Bryson B. A., Agutter P. S., Müller W. E. Functional dissection of nuclear envelope mRNA translocation system: effects of phorbol ester and a monoclonal antibody recognizing cytoskeletal structures. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Mar;261(2):394–404. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90355-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Rottmann M., Bachmann M., Müller W. E., McDonald A. R., Agutter P. S. Proteins from rat liver cytosol which stimulate mRNA transport. Purification and interactions with the nuclear envelope mRNA translocation system. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Aug 15;159(1):51–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09832.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Rottmann M., Bachmann M., Müller W. E. Purification and characterization of the major nucleoside triphosphatase from rat liver nuclear envelopes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):663–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Trölltsch D., Friese U., Bachmann M., Müller W. E. Mature mRNA is selectively released from the nuclear matrix by an ATP/dATP-dependent mechanism sensitive to topoisomerase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8917–8925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Zahn R. K., Dose K., Müller W. E. Purification and characterization of a poly(A)-specific exoribonuclease from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4535–4538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumm D. E., Webb T. E. Insulin-modulated transport of RNA from isolated live nuclei. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Aug;210(1):275–279. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer R. W. Specificity of chemical modification of ribonucleic acid transport by liver carcinogens in the rat. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 9;13(8):1764–1767. doi: 10.1021/bi00705a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoglund U., Andersson K., Björkroth B., Lamb M. M., Daneholt B. Visualization of the formation and transport of a specific hnRNP particle. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):847–855. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90542-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Wells W. W. Phosphorylation of rat liver nuclear envelopes. I. Characterization of in vitro protein phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9360–9367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Wells W. W. Phosphorylation of rat liver nuclear envelopes. II. Characterization of in vitro lipid phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9368–9373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Wells W. W. Solubilization and reconstitution of a nuclear envelope-associated ATPase. Synergistic activation by RNA and polyphosphoinositides. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11890–11894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Kant J. A. Preparation of impermeable ghosts and inside-out vesicles from human erythrocyte membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:172–180. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steer R. C., Goueli S. A., Wilson M. J., Ahmed K. Cobalt-stimulated protein phosphokinase activity of the pore complex-lamina fraction from rat liver nuclear envelope. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Feb 12;92(3):919–925. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90790-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steer R. C., Wilson M. J., Ahmed K. Phosphoprotein phosphatase activity of rat liver nuclear membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 28;89(4):1082–1087. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steer R. C., Wilson M. J., Ahmed K. Protein phosphokinase activity of rat liver nuclear membrane. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Mar 15;119(2):403–406. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90372-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornburg W., Gamo S., O'Malley A. F., Lindell T. J. Properties of rat liver nuclear protein kinases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 9;571(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90222-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiruppathi C., Alpers D. H., Seetharam B. Phase separation of rat intestinal brush border membrane proteins using Triton X-114. Anal Biochem. 1986 Mar;153(2):330–335. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicentini L. M., Villereal M. L. Serum, bradykinin and vasopressin stimulate release of inositol phosphates from human fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 17;123(2):663–670. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90280-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M., Cuatrecasas P., Sahyoun N. Interaction of protein kinase C with membranes is regulated by Ca2+, phorbol esters, and ATP. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15718–15722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M., LeVine H., 3rd, May W. S., Jr, Cuatrecasas P., Sahyoun N. A model for intracellular translocation of protein kinase C involving synergism between Ca2+ and phorbol esters. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):546–549. doi: 10.1038/317546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M., Sahyoun N. Protein kinase C and phosphatidylserine bind to Mr 110,000/115,000 polypeptides enriched in cytoskeletal and postsynaptic density preparations. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13327–13332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yutani Y., Tei Y., Yukioka M., Inoue A. Occurrence of NI and NII type protein kinases in the nuclei from various tissues of the rat. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Oct 15;218(2):409–420. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90362-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]