Abstract
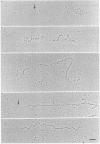
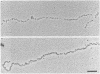
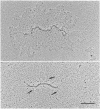
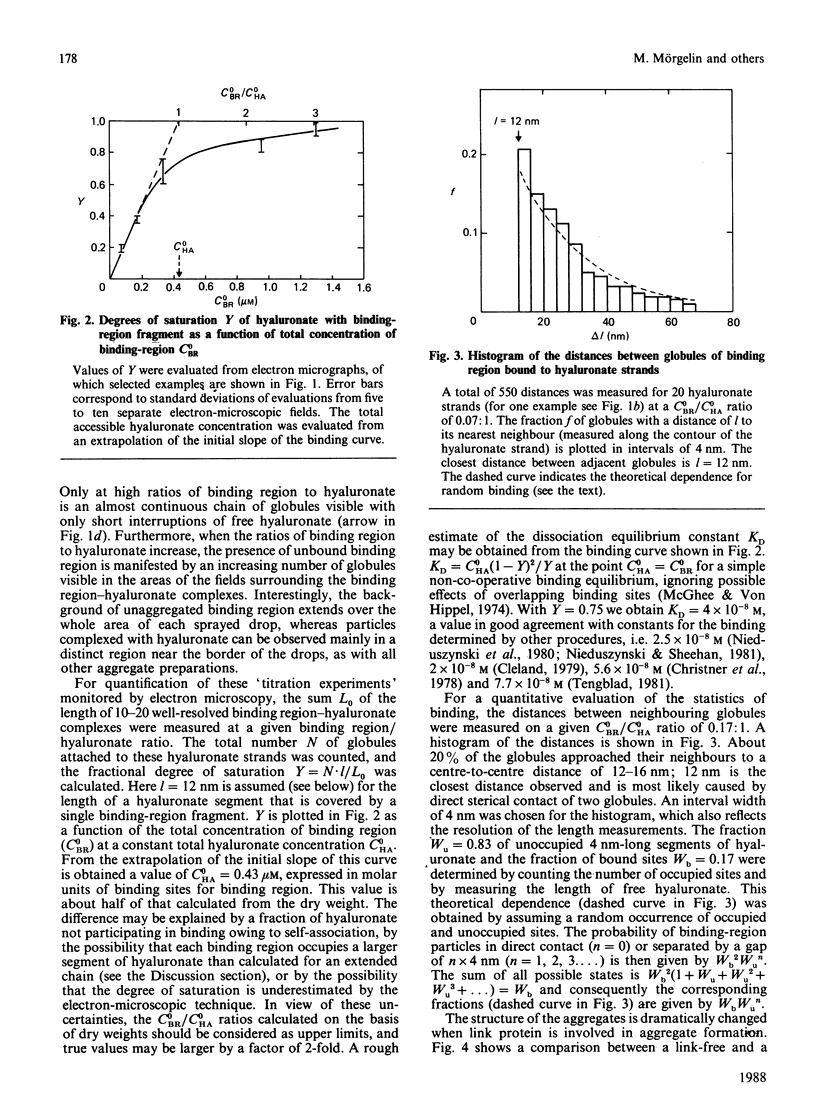
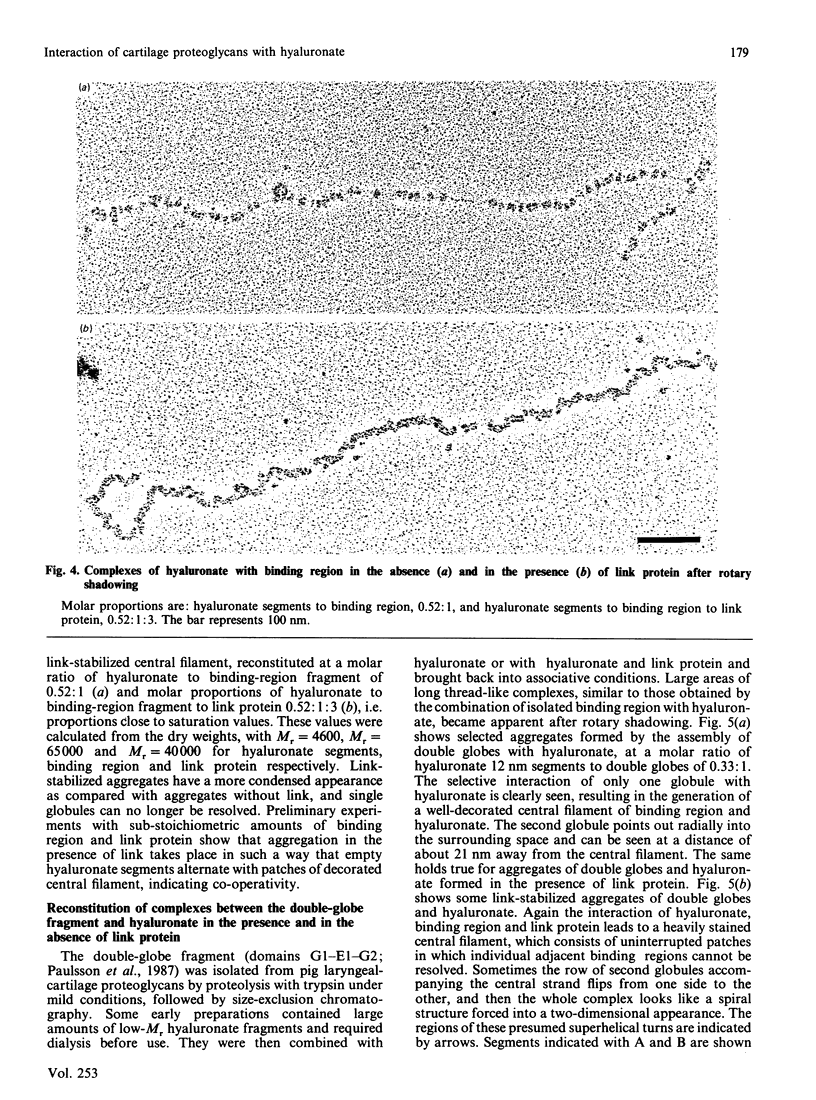
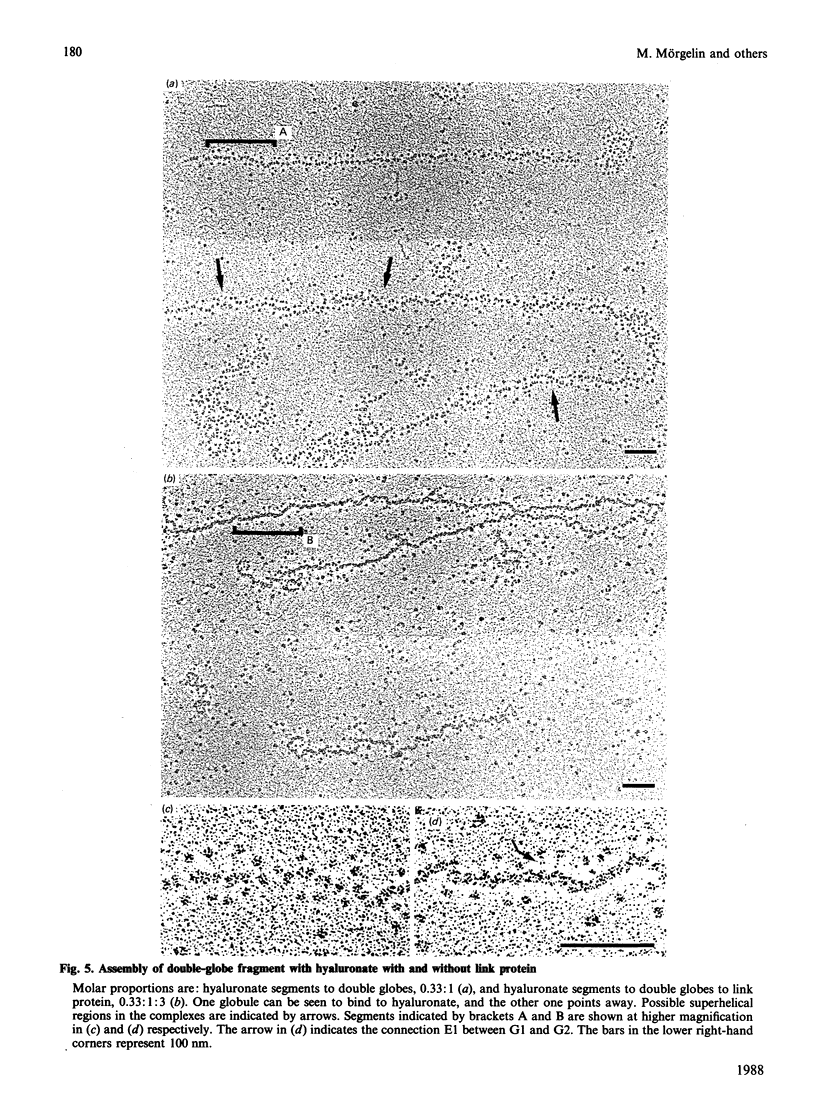
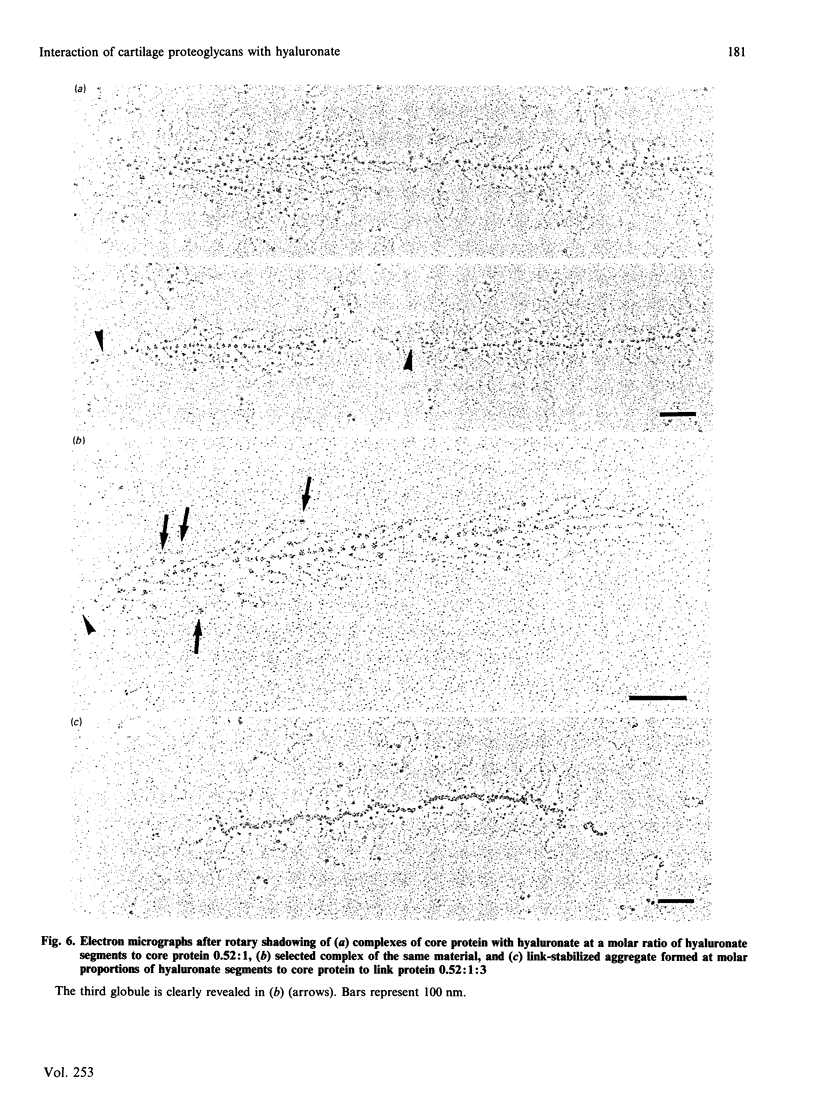
Aggregates formed by the interaction of cartilage proteoglycan monomers and fragments thereof with hyaluronate were studied by electron microscopy by use of rotary shadowing [Wiedemann, Paulsson, Timpl, Engel & Heinegård (1984) Biochem. J. 224, 331-333]. The differences in shape and packing of the proteins bound along the hyaluronate strand in aggregates formed in the presence and in the absence of link protein were examined in detail. The high resolution of the method allowed examination of the involvement in hyaluronate binding of the globular core-protein domains G1, G2 and G3 [Wiedemann, Paulsson, Timpl, Engel & Heinegård (1984) Biochem. J. 224, 331-333; Paulsson, Mörgelin, Wiedemann, Beardmore-Gray, Dunham, Hardingham, Heinegård, Timpl & Engel (1987) Biochem. J. 245, 763-772]. Fragments comprising the globular hyaluronate-binding region G1 form complexes with hyaluronate with an appearance of necklace-like structures, statistically interspaced by free hyaluronate strands. The closest centre-to-centre distance found between adjacent G1 domains was 12 nm. Another fragment comprising the binding region G1 and the adjacent second globular domain G2 attaches to hyaluronate only by one globule. Also, the core protein obtained by chondroitinase digestion of proteoglycan monomer binds only by domain G1, with domain G3 furthest removed from the hyaluronate. Globule G1 shows a statistical distribution along the hyaluronate strands. In contrast, when link protein is added, binding is no longer random, but instead uninterrupted densely packed aggregates are formed.
Full text
PDF

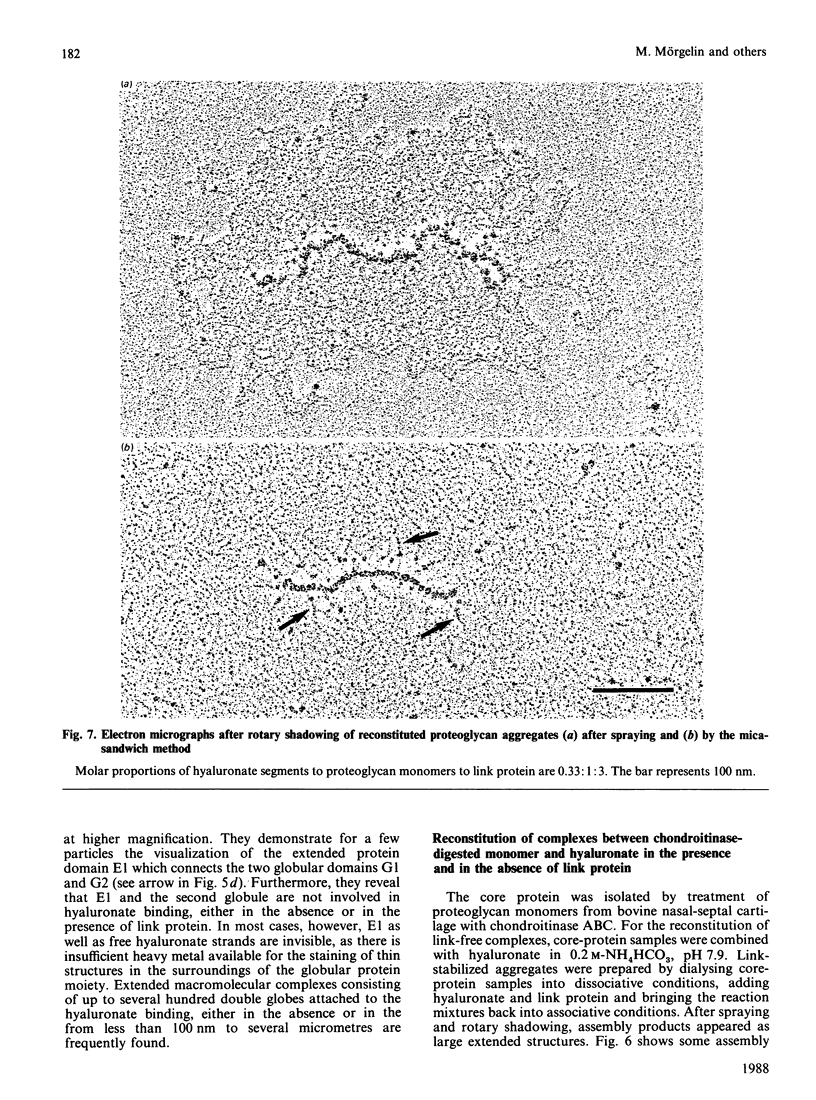



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayliss M. T., Venn M., Maroudas A., Ali S. Y. Structure of proteoglycans from different layers of human articular cartilage. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 1;209(2):387–400. doi: 10.1042/bj2090387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet F., Dunham D. G., Hardingham T. E. Structure and interactions of cartilage proteoglycan binding region and link protein. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):77–85. doi: 10.1042/bj2280077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckwalter J. A., Kuettner K. E., Thonar E. J. Age-related changes in articular cartilage proteoglycans: electron microscopic studies. J Orthop Res. 1985;3(3):251–257. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100030301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christner J. E., Brown M. L., Dziewiatkowski D. D. Affinity binding of the cartilage proteoglycan protein-keratan sulfate core to immobilized hyaluronic acid. Anal Biochem. 1978 Oct 1;90(1):22–32. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland R. L. Binding of hyaluronic acid oligosaccharides by cartilage proteoglycan. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 27;87(4):1140–1145. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(79)80026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doege K., Fernandez P., Hassell J. R., Sasaki M., Yamada Y. Partial cDNA sequence encoding a globular domain at the C terminus of the rat cartilage proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8108–8111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doege K., Sasaki M., Horigan E., Hassell J. R., Yamada Y. Complete primary structure of the rat cartilage proteoglycan core protein deduced from cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17757–17767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J., Furthmayr H. Electron microscopy and other physical methods for the characterization of extracellular matrix components: laminin, fibronectin, collagen IV, collagen VI, and proteoglycans. Methods Enzymol. 1987;145:3–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)45003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faltz L. L., Caputo C. B., Kimura J. H., Schrode J., Hascall V. C. Structure of the complex between hyaluronic acid, the hyaluronic acid-binding region, and the link protein of proteoglycan aggregates from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1381–1387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzén A., Björnsson S., Heinegård D. Cartilage proteoglycan aggregate formation. Role of link protein. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 1;197(3):669–674. doi: 10.1042/bj1970669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Beardmore-Gray M., Dunham D. G., Ratcliffe A. Cartilage proteoglycans. Ciba Found Symp. 1986;124:30–46. doi: 10.1002/9780470513385.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. The specific interaction of hyaluronic acid with cartillage proteoglycans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 15;279(2):401–405. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E. The role of link-protein in the structure of cartilage proteoglycan aggregates. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 1;177(1):237–247. doi: 10.1042/bj1770237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Heinegård D. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. II. Oligosaccharide competitors of the proteoglycan-hyaluronic acid interaction. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4242–4249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Sajdera S. W. Physical properties and polydispersity of proteoglycan from bovine nasal cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):4920–4930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Axelsson I. Distribution of keratan sulfate in cartilage proteoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1971–1979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Franzén A., Hedbom E., Sommarin Y. Common structures of the core proteins of interstitial proteoglycans. Ciba Found Symp. 1986;124:69–88. doi: 10.1002/9780470513385.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Hascall V. C. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. 3. Characteristics of the proteins isolated from trypsin digests of aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4250–4256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Lohmander S., Thyberg J. Cartilage proteoglycan aggregates. Electron-microscopic studies of native and fragmented molecules. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 1;175(3):913–919. doi: 10.1042/bj1750913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Wieslander J., Sheehan J., Paulsson M., Sommarin Y. Separation and characterization of two populations of aggregating proteoglycans from cartilage. Biochem J. 1985 Jan 1;225(1):95–106. doi: 10.1042/bj2250095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEINSCHMIDT A. K., LANG D., JACHERTS D., ZAHN R. K. [Preparation and length measurements of the total desoxyribonucleic acid content of T2 bacteriophages]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 31;61:857–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmander L. S., De Luca S., Nilsson B., Hascall V. C., Caputo C. B., Kimura J. H., Heinegard D. Oligosaccharides on proteoglycans from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6084–6091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., von Hippel P. H. Theoretical aspects of DNA-protein interactions: co-operative and non-co-operative binding of large ligands to a one-dimensional homogeneous lattice. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):469–489. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mould A. P., Holmes D. F., Kadler K. E., Chapman J. A. Mica sandwich technique for preparing macromolecules for rotary shadowing. J Ultrastruct Res. 1985 Apr;91(1):66–76. doi: 10.1016/0889-1605(85)90077-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieduszynski I. A., Sheehan J. K. Equilibrium and kinetic studies of the interaction between cartilage proteoglycan and hyaluronate. Biochem Soc Trans. 1981 Dec;9(6):502–504. doi: 10.1042/bst0090502a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieduszynski I. A., Sheehan J. K., Phelps C. F., Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Equilibrium-binding studies of pig laryngeal cartilage proteoglycans with hyaluronate oligosaccharide fractions. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 1;185(1):107–114. doi: 10.1042/bj1850107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldberg A., Antonsson P., Heinegård D. The partial amino acid sequence of bovine cartilage proteoglycan, deduced from a cDNA clone, contains numerous Ser-Gly sequences arranged in homologous repeats. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):255–259. doi: 10.1042/bj2430255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson M., Mörgelin M., Wiedemann H., Beardmore-Gray M., Dunham D., Hardingham T., Heinegård D., Timpl R., Engel J. Extended and globular protein domains in cartilage proteoglycans. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):763–772. doi: 10.1042/bj2450763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Hellmann W., Kleinschmidt A. K. Electron microscopic studies of proteoglycan aggregates from bovine articular cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1877–1883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Hellmann W., Kleinschmidt A. K. Macromolecular models of proteinpolysaccharides from bovine nasal cartilage based on electron microscopic studies. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 25;245(16):4123–4130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sai S., Tanaka T., Kosher R. A., Tanzer M. L. Cloning and sequence analysis of a partial cDNA for chicken cartilage proteoglycan core protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5081–5085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotton D. M., Burke B. E., Branton D. The molecular structure of human erythrocyte spectrin. Biophysical and electron microscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):303–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tengblad A. A comparative study of the binding of cartilage link protein and the hyaluronate-binding region of the cartilage proteoglycan to hyaluronate-substituted Sepharose gel. Biochem J. 1981 Nov 1;199(2):297–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1990297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P., Wyler T., Buddecke E. Electron microscopic and physico-chemical studies on bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycan. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Jul;353(7):1043–1052. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1972.353.2.1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann H., Paulsson M., Timpl R., Engel J., Heinegård D. Domain structure of cartilage proteoglycans revealed by rotary shadowing of intact and fragmented molecules. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 15;224(1):331–333. doi: 10.1042/bj2240331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]