Abstract
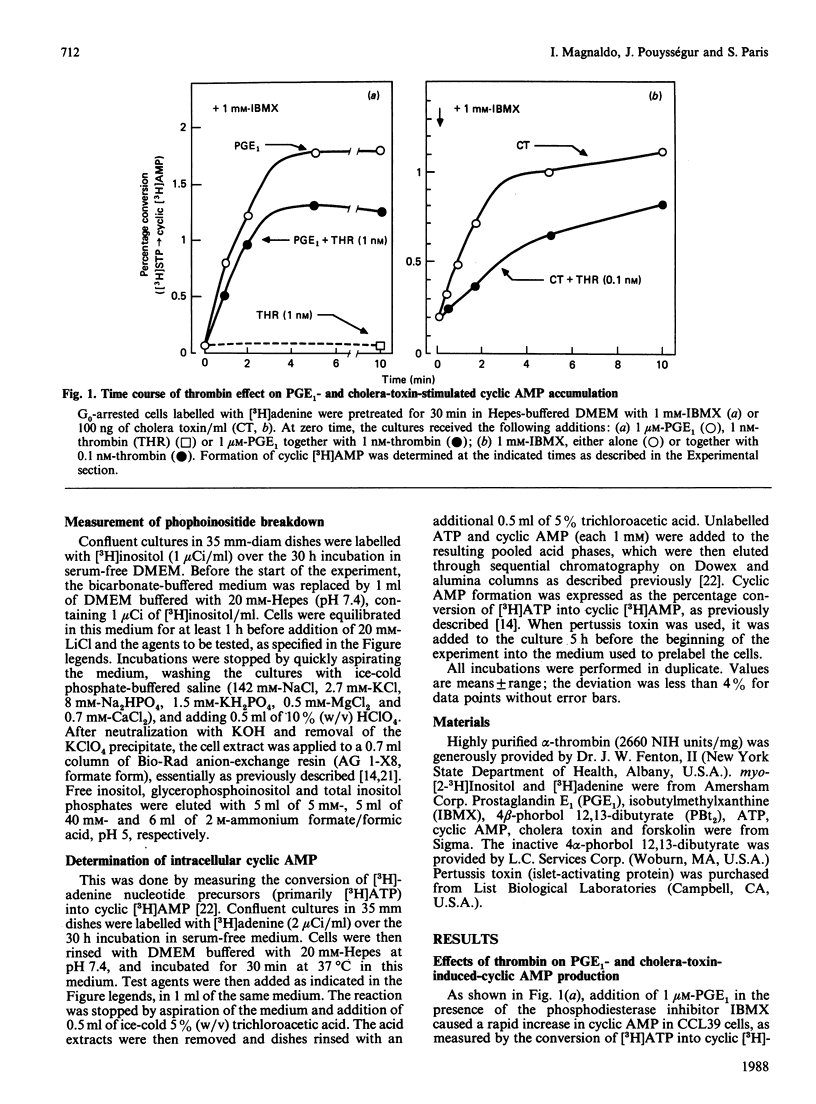
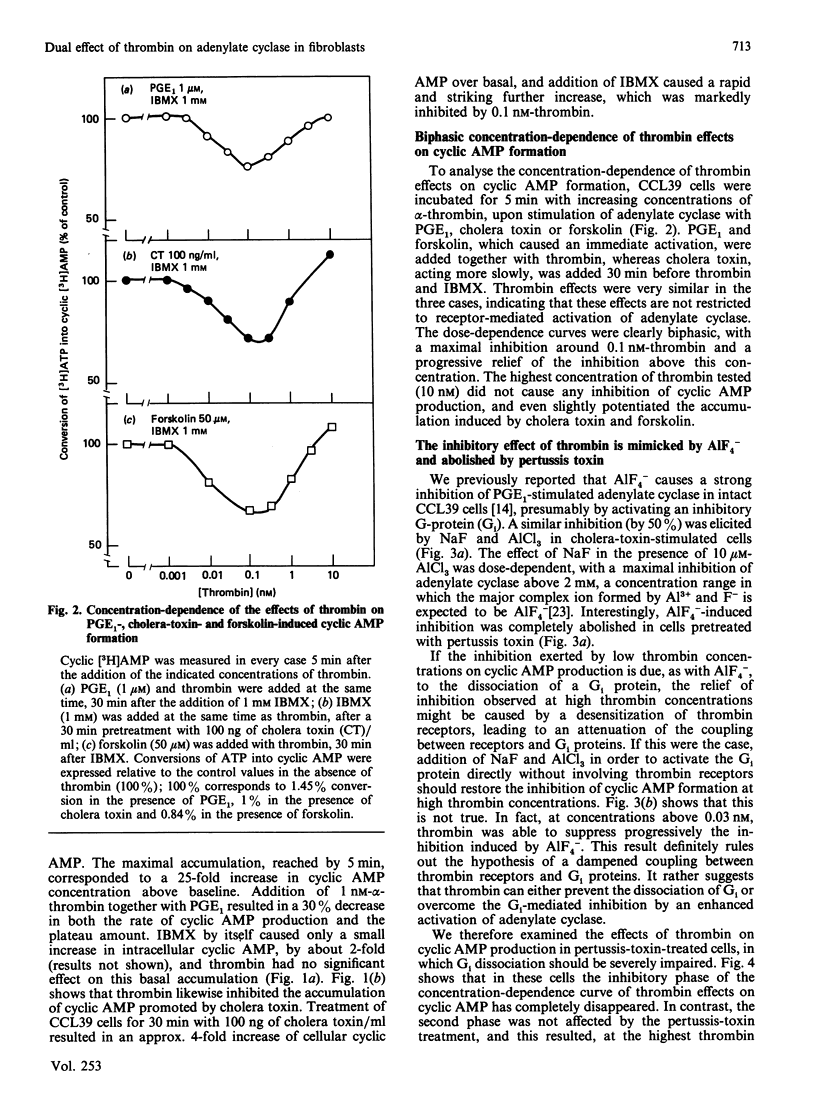
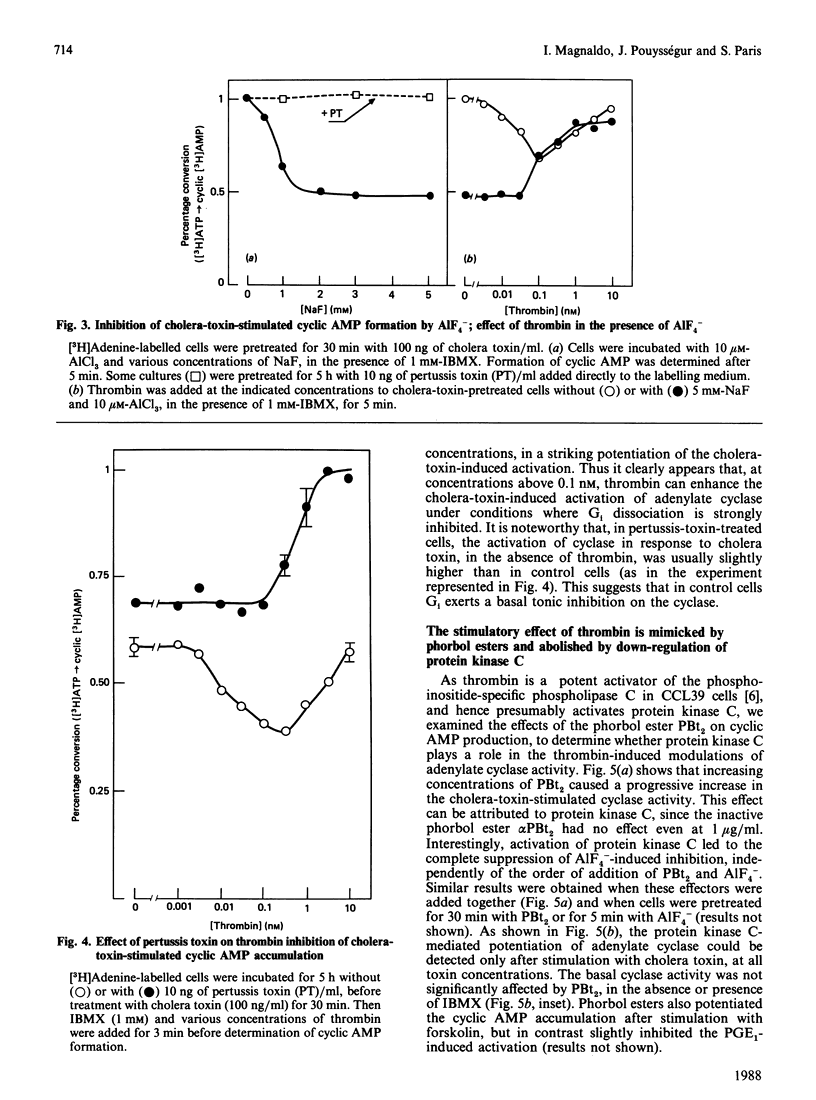
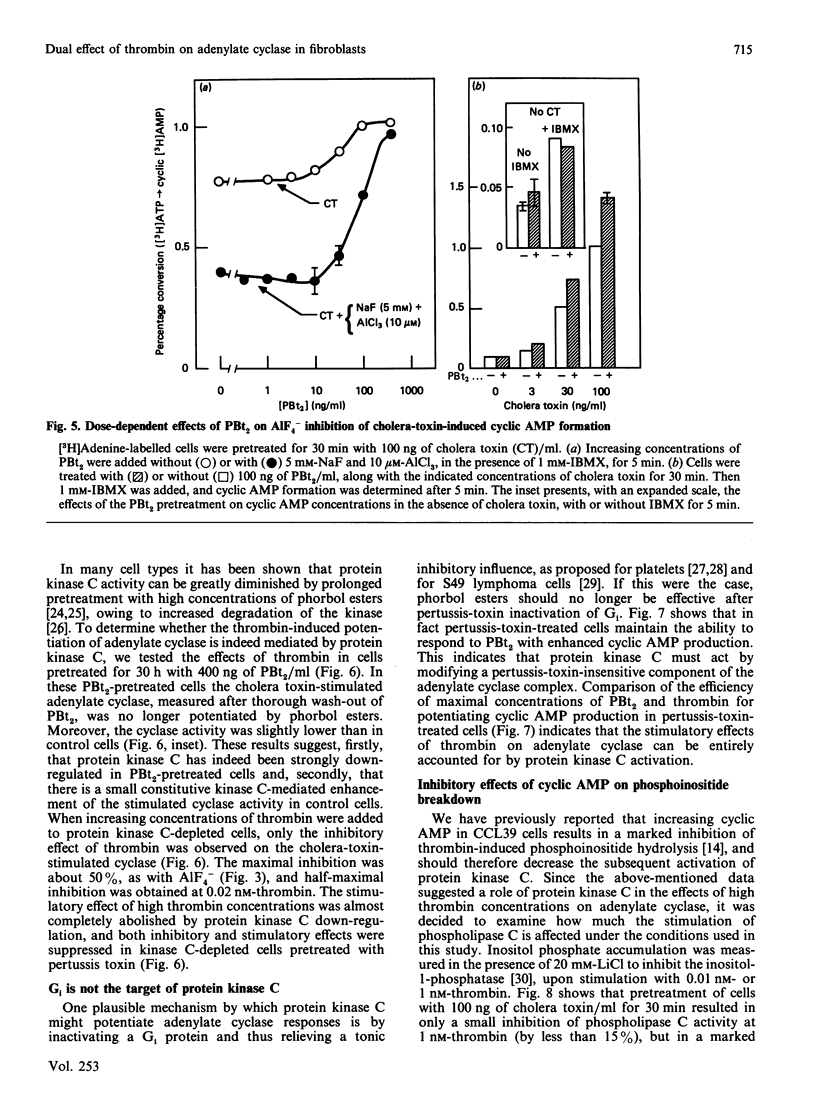
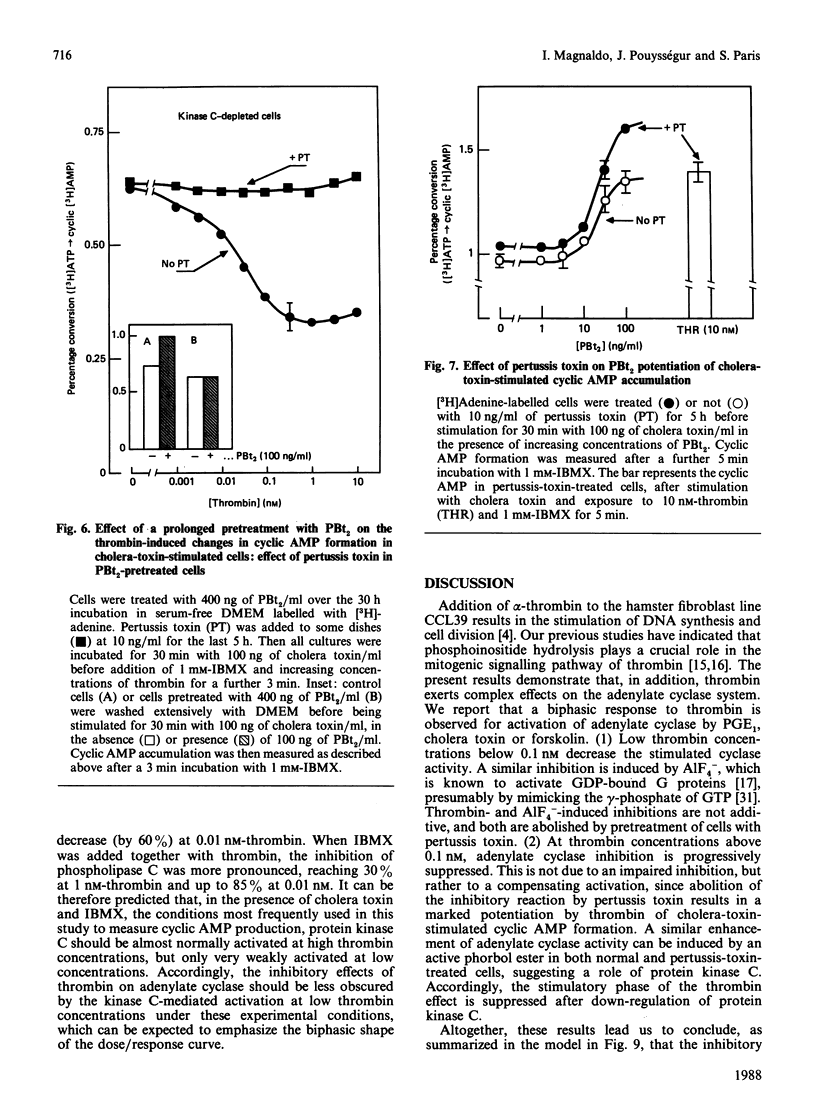
Previous studies in Chinese-hamster fibroblasts (CCL39 line) indicate that an important signalling pathway involved in thrombin's mitogenicity is the activation of a phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C, mediated by a pertussis-toxin-sensitive GTP-binding protein (Gp). The present studies examine the effects of thrombin on the adenylate cyclase system and the interactions between the two signal transduction pathways. We report that thrombin exerts two opposite effects on cyclic AMP accumulation stimulated by cholera toxin, forskolin or prostaglandin E1. (1) Low thrombin concentrations (below 0.1 nM) decrease cyclic AMP formation. A similar inhibition is induced by A1F4-, and both thrombin- and A1F4- -induced inhibitions are abolished by pertussis toxin. (2) Increasing thrombin concentration from 0.1 to 10 nM results in a progressive suppression of adenylate cyclase inhibition and in a marked enhancement of cyclic AMP formation in pertussis-toxin-treated cells. A similar stimulation is induced by an active phorbol ester, and thrombin-induced potentiation of adenylate cyclase is suppressed by down-regulation of protein kinase C. Therefore, we conclude that (1) the inhibitory effect of thrombin on adenylate cyclase is the direct consequence of the activation of a pertussis-toxin-sensitive inhibitory GTP-binding protein (Gi) possibly identical with Gp, and (2) the potentiating effect of thrombin on cyclic AMP formation is due to stimulation of protein kinase C, as an indirect consequence of Gp activation. Our results suggest that the target of protein kinase C is an element of the adenylate cyclase-stimulatory GTP-binding protein (Gs) complex. At low thrombin concentrations, activation of phospholipase C is greatly attenuated by increased cyclic AMP, leading to predominance of the Gi-mediated inhibition.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aktories K., Jakobs K. H. Ni-mediated inhibition of human platelet adenylate cyclase by thrombin. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 3;145(2):333–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballester R., Rosen O. M. Fate of immunoprecipitable protein kinase C in GH3 cells treated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15194–15199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. D., Brunton L. L. Enhancement of adenylate cyclase activity in S49 lymphoma cells by phorbol esters. Withdrawal of GTP-dependent inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12036–12041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. D., Brunton L. L. Multiple effects of phorbol esters on hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity in S49 lymphoma cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jun;252(6 Pt 1):E783–E789. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.252.6.E783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. D., Buxton I. L., Brunton L. L. Enhancement of adenylate cyclase activity in S49 lymphoma cells by phorbol esters. Putative effect of C kinase on alpha s-GTP-catalytic subunit interaction. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2625–2628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigay J., Deterre P., Pfister C., Chabre M. Fluoroaluminates activate transducin-GDP by mimicking the gamma-phosphate of GTP in its binding site. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone E. A., Fretten P., Palmer S., Kirk C. J., Michell R. H. Rapid accumulation of inositol phosphates in isolated rat superior cervical sympathetic ganglia exposed to V1-vasopressin and muscarinic cholinergic stimuli. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 1;221(3):803–811. doi: 10.1042/bj2210803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozou J. C., Amar S., Vincent J. P., Kitabgi P. Neurotensin-mediated inhibition of cyclic AMP formation in neuroblastoma N1E115 cells: involvement of the inhibitory GTP-binding component of adenylate cyclase. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 May;29(5):489–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Laposata M., Banga H. S., Rittenhouse S. E. Regulation of the phosphoinositide hydrolysis pathway in thrombin-stimulated platelets by a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide-binding protein. Evaluation of its contribution to platelet activation and comparisons with the adenylate cyclase inhibitory protein, Gi. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16838–16847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. H., Glenn K. C., Cunningham D. D. Conditions which affect initiation of animal cell division by trypsin and thrombin. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Apr;95(1):13–22. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040950103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney D. H., Scott D. L., Gordon E. A., LaBelle E. F. Phosphoinositides in mitogenesis: neomycin inhibits thrombin-stimulated phosphoinositide turnover and initiation of cell proliferation. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):479–488. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90105-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambard J. C., Paris S., L'Allemain G., Pouysségur J. Two growth factor signalling pathways in fibroblasts distinguished by pertussis toxin. Nature. 1987 Apr 23;326(6115):800–803. doi: 10.1038/326800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. B., Buchanan J. M. Mitogenic activity of blood components. I. Thrombin and prothrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):131–135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Falloon J., Milligan G., Pines M., Gallin J. I., Spiegel A. Immunochemical evidence for a novel pertussis toxin substrate in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):8058–8062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallcher L. M., Sherman W. R. The effects of lithium ion and other agents on the activity of myo-inositol-1-phosphatase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10896–10901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobs K. H., Aktories K., Schultz G. Mechanism of pertussis toxin action on the adenylate cyclase system. Inhibition of the turn-on reaction of the inhibitory regulatory site. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Apr 2;140(1):177–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobs K. H., Bauer S., Watanabe Y. Modulation of adenylate cyclase of human platelets by phorbol ester. Impairment of the hormone-sensitive inhibitory pathway. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):425–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Gilman A. G., Watanabe Y., Bauer S., Jakobs K. H. Protein kinase C phosphorylates the inhibitory guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory component and apparently suppresses its function in hormonal inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):431–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Oinuma M., Kusakabe K., Ui M. A new GTP-binding protein in brain tissues serving as the specific substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. FEBS Lett. 1987 Mar 23;213(2):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81521-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Oinuma M., Ui M. Mechanisms for inhibition of the catalytic activity of adenylate cyclase by the guanine nucleotide-binding proteins serving as the substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5215–5221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in transmembrane signalling. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:149–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Allemain G., Paris S., Magnaldo I., Pouysségur J. Alpha-thrombin-induced inositol phosphate formation in G0-arrested and cycling hamster lung fibroblasts: evidence for a protein kinase C-mediated desensitization response. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Nov;129(2):167–174. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041290207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerea K. M., Glomset J. A. Agents that elevate the concentration of cAMP in platelets inhibit the formation of a NaDodSO4-resistant complex between thrombin and a 40-kDa protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5620–5624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnaldo I., Talwar H., Anderson W. B., Pouysségur J. Evidence for a GTP-binding protein coupling thrombin receptor to PIP2-phospholipase C in membranes of hamster fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 1;210(1):6–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81287-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters S. B., Stroud R. M., Bourne H. R. Family of G protein alpha chains: amphipathic analysis and predicted structure of functional domains. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan E. B., Detwiler T. C. Modified platelet responses to thrombin. Evidence for two types of receptors or coupling mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):739–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Ui M. Phosphatidic acid may stimulate membrane receptors mediating adenylate cyclase inhibition and phospholipid breakdown in 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5522–5529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oinuma M., Katada T., Ui M. A new GTP-binding protein in differentiated human leukemic (HL-60) cells serving as the specific substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8347–8353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris S., Pouysségur J. Further evidence for a phospholipase C-coupled G protein in hamster fibroblasts. Induction of inositol phosphate formation by fluoroaluminate and vanadate and inhibition by pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):1970–1976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris S., Pouysségur J. Pertussis toxin inhibits thrombin-induced activation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis and Na+/H+ exchange in hamster fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):55–60. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04177.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohjanpelto P. Stimulation of DNA synthesis in human fibroblasts by thrombin. J Cell Physiol. 1978 May;95(2):189–194. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040950208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raben D. M., Yasuda K., Cunningham D. D. Modulation of thrombin-stimulated lipid responses in cultured fibroblasts. Evidence for two coupling mechanisms. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2759–2765. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebecchi M. J., Rosen O. M. Stimulation of polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis by thrombin in membranes from human fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 1;245(1):49–57. doi: 10.1042/bj2450049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Pena A., Rozengurt E. Disappearance of Ca2+-sensitive, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase activity in phorbol ester-treated 3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):1053–1059. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Murray M., Zachary I., Collins M. Protein kinase C activation enhances cAMP accumulation in Swiss 3T3 cells: inhibition by pertussis toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2282–2286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel A. M. Signal transduction by guanine nucleotide binding proteins. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Jan;49(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Pouysségur J. Affinity labeling of high-affinity alpha-thrombin binding sites on the surface of hamster fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 12;847(3):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Pérez-Rodríguez R., Franchi A., Chambard J. C., Pouysségur J. Analysis of growth factor "relaxation" in Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts required for tumoral expression. J Cell Physiol. 1983 May;115(2):123–130. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041150204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. A., Murphy W., Haslam R. J. Effects of activation of protein kinase C on the agonist-induced stimulation and inhibition of cyclic AMP formation in intact human platelets. Biochem J. 1987 May 1;243(3):667–678. doi: 10.1042/bj2430667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimasa T., Sibley D. R., Bouvier M., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Cross-talk between cellular signalling pathways suggested by phorbol-ester-induced adenylate cyclase phosphorylation. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):67–70. doi: 10.1038/327067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S., Parker P. J., Ullrich A., Stabel S. Down-regulation of protein kinase C is due to an increased rate of degradation. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 15;244(3):775–779. doi: 10.1042/bj2440775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


