Abstract
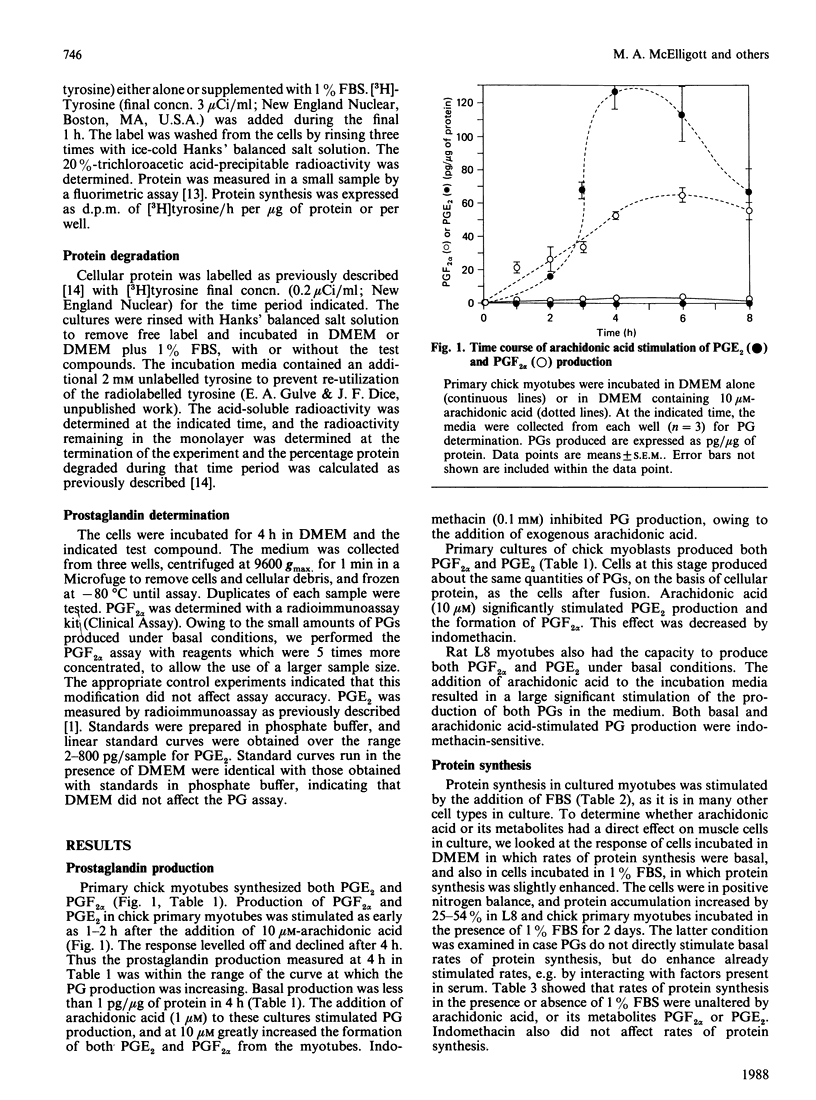
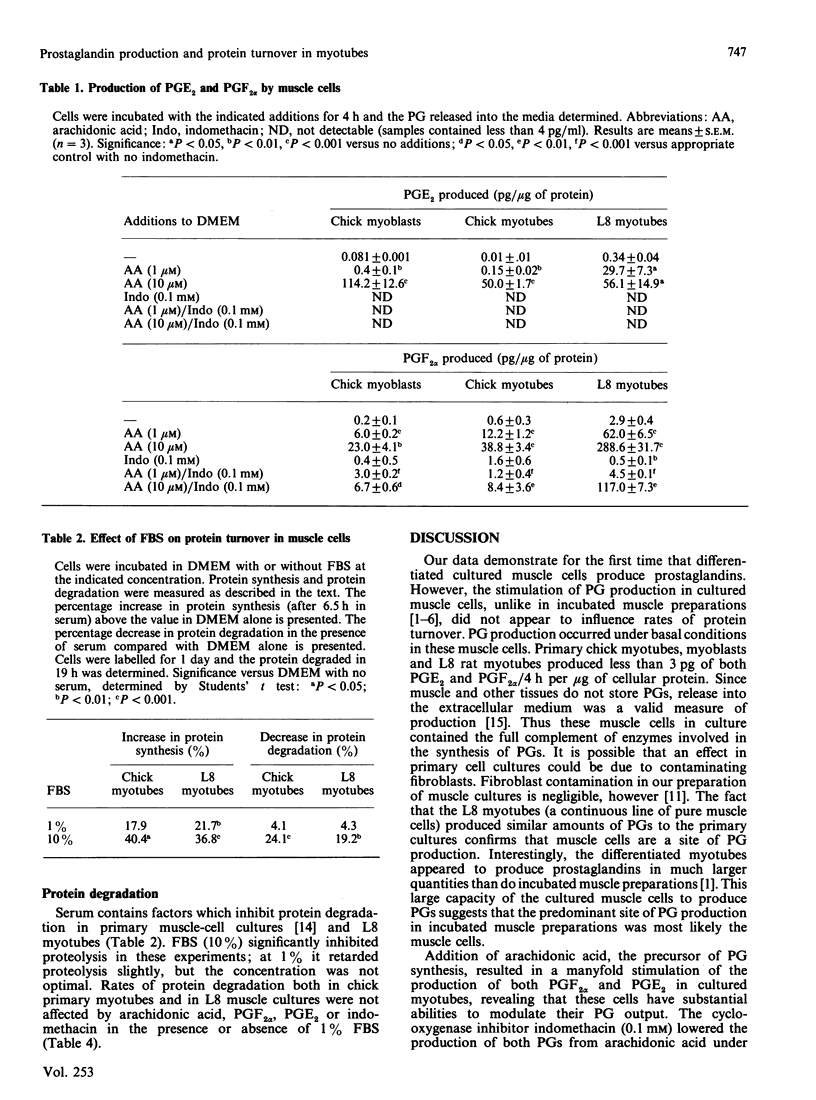
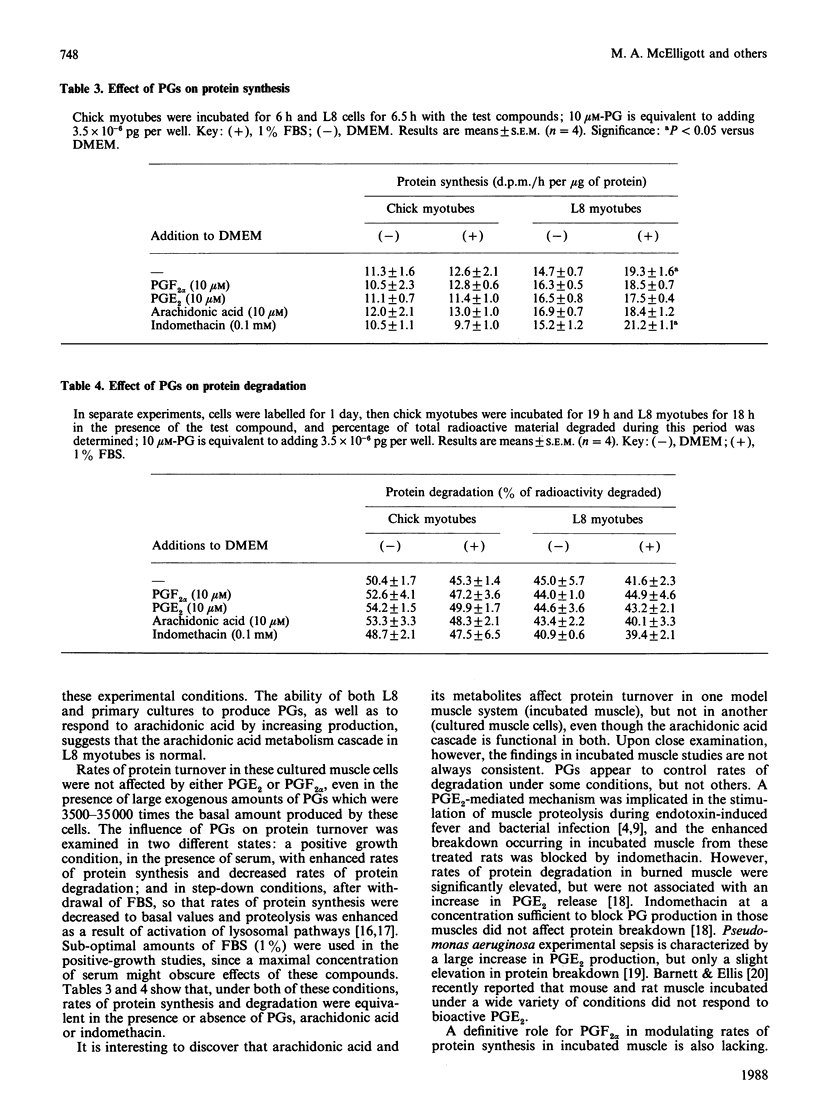
The production of prostaglandins (PG) E2 and F2 alpha and their possible role in regulation of protein turnover in cultured skeletal-muscle cells were examined. Primary chick myoblasts and myotubes, and L8 myotubes, produced PGE2 and PGF2 alpha from endogenous arachidonic acid. PG production by all three cell types was increased manyfold by the addition of exogenous arachidonic acid. Arachidonate-stimulated PG production was inhibited by the addition of indomethacin (0.1 mM). When L8 and chick myotubes were treated with PGE2, PGF2 alpha, arachidonic acid (0.01 mM) or indomethacin (0.1 mM), no significant alterations in rates of protein synthesis or degradation were observed. Rates of protein synthesis and degradation in these cells were responsive to the addition of 10% fetal-bovine serum under identical experimental conditions. Thus, in contrast with incubated adult skeletal muscle, it appears that the production of prostaglandin metabolites from arachidonic acid is unrelated to regulation of protein turnover in cultured muscle cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baracos V., Rodemann H. P., Dinarello C. A., Goldberg A. L. Stimulation of muscle protein degradation and prostaglandin E2 release by leukocytic pyrogen (interleukin-1). A mechanism for the increased degradation of muscle proteins during fever. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 10;308(10):553–558. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303103081002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett J. G., Ellis S. Prostaglandin E2 and the regulation of protein degradation in skeletal muscle. Muscle Nerve. 1987 Jul-Aug;10(6):556–559. doi: 10.1002/mus.880100611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Stein S., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. Fluorometric assay of proteins in the nanogram range. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;155(1):213–220. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(73)80023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENESCO M., PUDDY D. INCREASE IN THE NUMBER OF NUCLEI AND WEIGHT IN SKELETAL MUSCLE OF RATS OF VARIOUS AGES. Am J Anat. 1964 Mar;114:235–244. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001140204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., Baracos V., Rodemann P., Waxman L., Dinarello C. Control of protein degradation in muscle by prostaglandins, Ca2+, and leukocytic pyrogen (interleukin 1). Fed Proc. 1984 Apr;43(5):1301–1306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeczko R. A., Carriere R. M., Etlinger J. D. Endocytosis, proteolysis, and exocytosis of exogenous proteins by cultured myotubes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7051–7058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElligott M. A., Dice J. F. Erythrocyte-mediated microinjection, a technique to study protein degradation in muscle cells. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):559–566. doi: 10.1042/bj2160559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElligott M. A., Dice J. F. Intracellular protein degradation in cultures of dystrophic muscle cells and fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Feb;150(2):442–451. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90588-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElligott M. A., Miao P., Dice J. F. Lysosomal degradation of ribonuclease A and ribonuclease S-protein microinjected into the cytosol of human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11986–11993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElligott M. A., Roisen F. J., Keaton K. S., Triemer D. F., Li Q. S., St John A. C., Yorke G., Bird J. W. Properties of the lysosomal apparatus during differentiation of cultured striated muscle cells. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1981;40(10-11):1333–1347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak J., Bohman S. O., Alster P., Berlin T., Cronestrand R., Sonnenfeld T. Biosynthesis of prostaglandins in microsomes of human skeletal muscle and kidney. Prostaglandins Leukot Med. 1983 Jul;11(3):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0262-1746(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odessey R. Effect of inhibitors of proteolysis and arachidonic acid metabolism on burn-induced protein breakdown. Metabolism. 1985 Jul;34(7):616–620. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(85)90087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Reeds P. J., Atkinson T., Smith R. H. The influence of changes in tension on protein synthesis and prostaglandin release in isolated rabbit muscles. Biochem J. 1983 Sep 15;214(3):1011–1014. doi: 10.1042/bj2141011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeds P. J., Hay S. M., Glennie R. T., Mackie W. S., Garlick P. J. The effect of indomethacin on the stimulation of protein synthesis by insulin in young post-absorptive rats. Biochem J. 1985 Apr 1;227(1):255–261. doi: 10.1042/bj2270255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeds P. J., Palmer R. M. Changes in prostaglandin release associated with inhibition of muscle protein synthesis by dexamethasone. Biochem J. 1984 May 1;219(3):953–957. doi: 10.1042/bj2190953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeds P. J., Palmer R. M. The possible involvement of prostaglandin F2 alpha in the stimulation of muscle protein synthesis by insulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 15;116(3):1084–1090. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodemann H. P., Goldberg A. L. Arachidonic acid, prostaglandin E2 and F2 alpha influence rates of protein turnover in skeletal and cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1632–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. M., Sugden P. H. Effects of pressure overload and insulin on protein turnover in the perfused rat heart. Prostaglandins are not involved although their synthesis is stimulated by insulin. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 15;243(2):473–479. doi: 10.1042/bj2430473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. H., Palmer R. M., Reeds P. J. Protein synthesis in isolated rabbit forelimb muscles. The possible role of metabolites of arachidonic acid in the response to intermittent stretching. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 15;214(1):153–161. doi: 10.1042/bj2140153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton G. H., Padalino M., Moss R. Influences of inactivity and indomethacin on soleus phosphatidylethanolamine and size. Prostaglandins. 1986 Mar;31(3):545–559. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(86)90116-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turinsky J., Loegering D. J. Prostaglandin E2 and muscle protein turnover in Pseudomonas aeruginosa sepsis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 29;840(1):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen R. G., Schwartz K., Bouveret P., Sell S. M., Gros F. Contractile protein isozymes in muscle development: identification of an embryonic form of myosin heavy chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5197–5201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



