Abstract
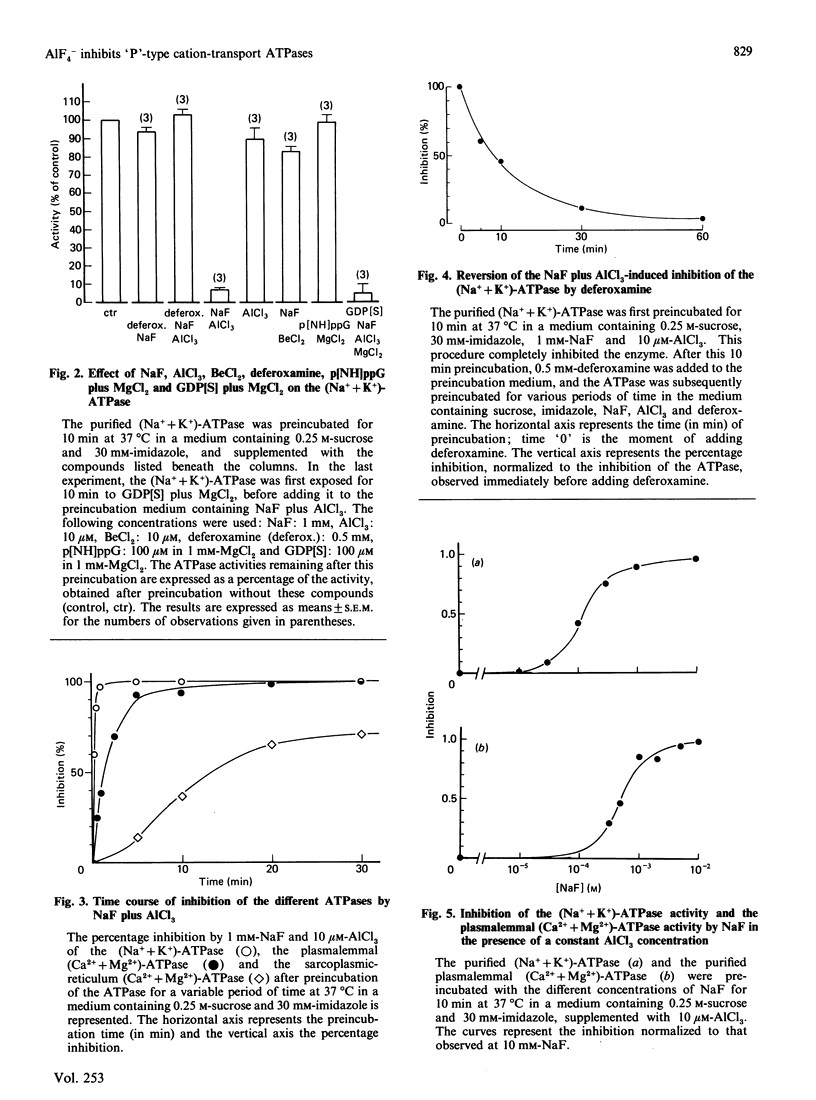
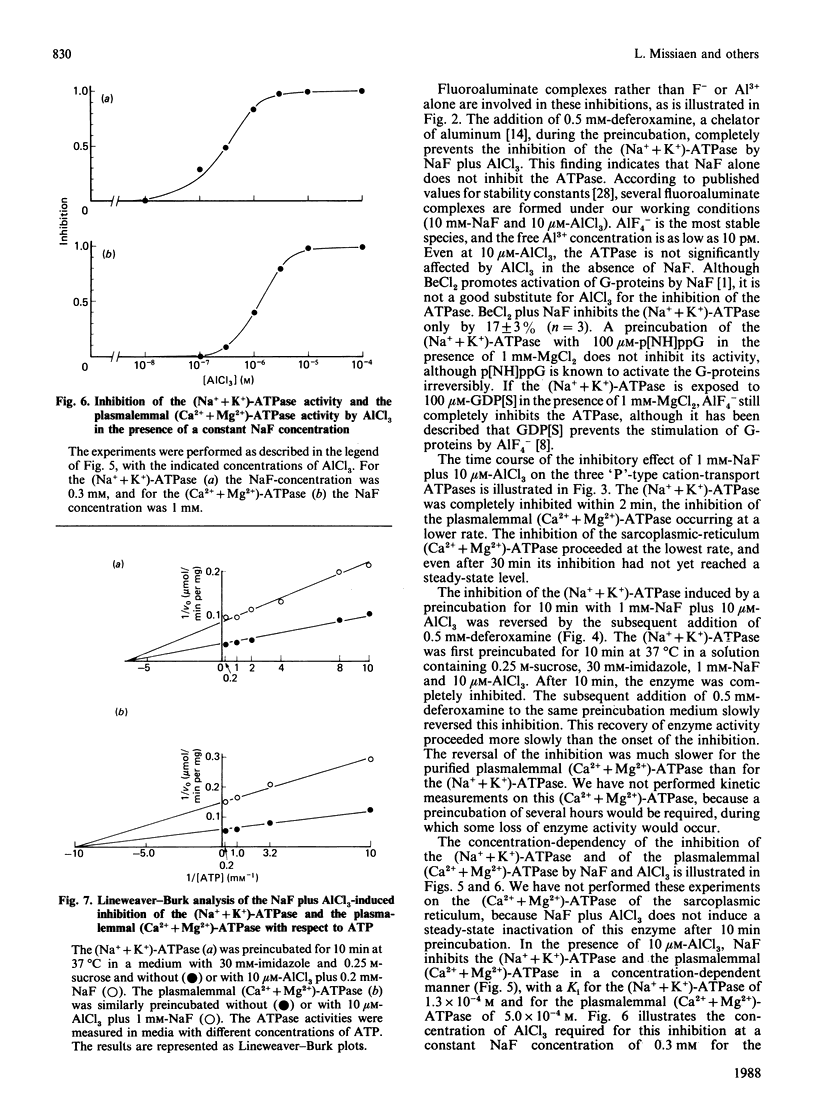
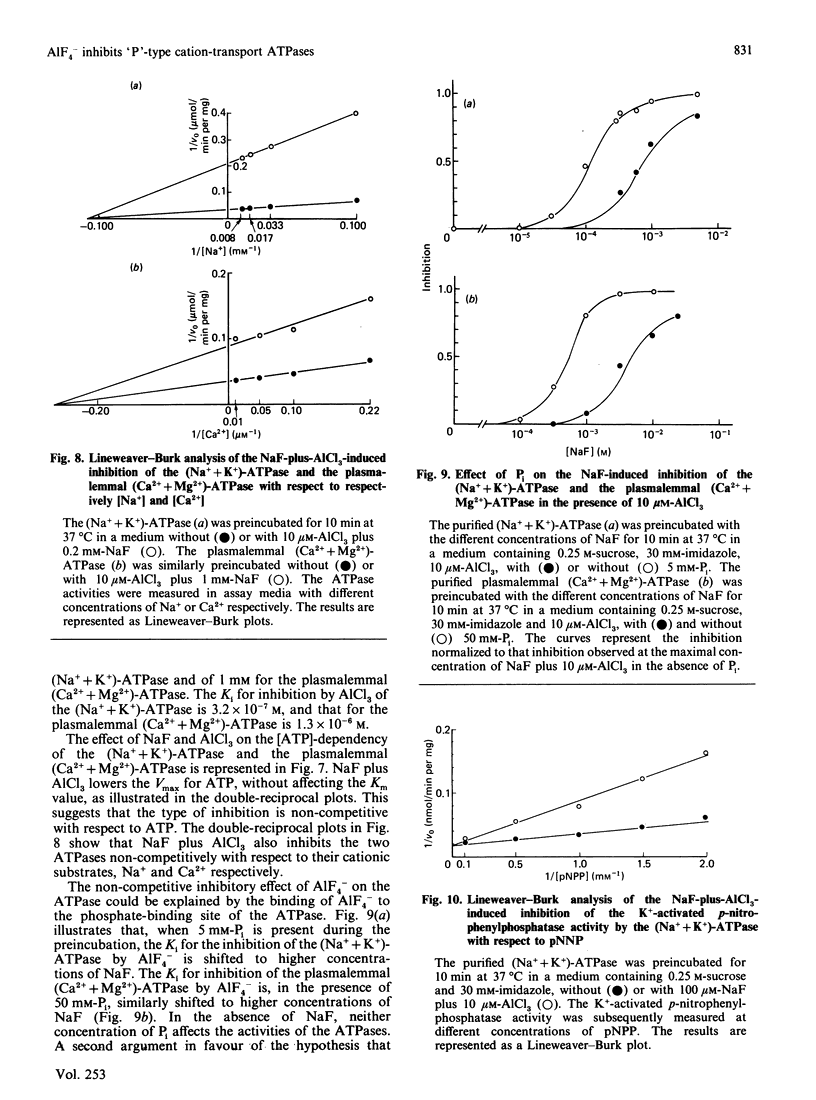
The only known cellular action of AlF4- is to stimulate the G-proteins. The aim of the present work is to demonstrate that AlF4- also inhibits 'P'-type cation-transport ATPases. NaF plus AlCl3 completely and reversibly inhibits the activity of the purified (Na+ + K+)-ATPase (Na+- and K+-activated ATPase) and of the purified plasmalemmal (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase (Ca2+-stimulated and Mg2+-dependent ATPase). It partially inhibits the activity of the sarcoplasmic-reticulum (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase, whereas it does not affect the mitochondrial H+-transporting ATPase. The inhibitory substances are neither F- nor Al3+ but rather fluoroaluminate complexes. Because AlF4- still inhibits the ATPase in the presence of guanosine 5'-[beta-thio]diphosphate, and because guanosine 5'-[beta gamma-imido]triphosphate does not inhibit the ATPase, it is unlikely that the inhibition could be due to the activation of an unknown G-protein. The time course of inhibition and the concentrations of NaF and AlCl3 required for this inhibition differ for the different ATPases. AlF4- inhibits the (Na+ + K+)-ATPase and the plasmalemmal (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase noncompetitively with respect to ATP and to their respective cationic substrates, Na+ and Ca2+. AlF4- probably binds to the phosphate-binding site of the ATPase, as the Ki for inhibition of the (Na+ + K+)-ATPase and of the plasmalemmal (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase is shifted in the presence of respectively 5 and 50 mM-Pi to higher concentrations of NaF. Moreover, AlF4- inhibits the K+-activated p-nitrophenylphosphatase of the (Na+ + K+)-ATPase competitively with respect to p-nitrophenyl phosphate. This AlF4- -induced inhibition of 'P'-type cation-transport ATPases warns us against explaining all the effects of AlF4- on intact cells by an activation of G-proteins.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bigay J., Deterre P., Pfister C., Chabre M. Fluoride complexes of aluminium or beryllium act on G-proteins as reversibly bound analogues of the gamma phosphate of GTP. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2907–2913. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Bocckino S. B., Waynick L. E., Exton J. H. Role of a guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein in the hydrolysis of hepatocyte phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate by calcium-mobilizing hormones and the control of cell calcium. Studies utilizing aluminum fluoride. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14477–14483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Studies on the hepatic calcium-mobilizing activity of aluminum fluoride and glucagon. Modulation by cAMP and phorbol myristate acetate. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11056–11063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Katada T., Northup J. K., Hewlett E. L., Gilman A. G. Identification of the predominant substrate for ADP-ribosylation by islet activating protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2072–2075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt D. R., Ross E. M. Effect of Al3+ plus F- on the catecholamine-stimulated GTPase activity of purified and reconstituted Gs. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):7036–7041. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishna R., Anderson W. B. Ca2+-induced hydrophobic site on calmodulin: application for purification of calmodulin by phenyl-Sepharose affinity chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 29;104(2):830–836. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90712-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillon G., Mouillac B., Balestre M. N. Activation of polyphosphoinositide phospholipase C by fluoride in WRK1 cell membranes. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 18;204(2):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80808-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Harden T. K. Guanine nucleotide-dependent pertussis-toxin-insensitive stimulation of inositol phosphate formation by carbachol in a membrane preparation from human astrocytoma cells. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 1;239(1):141–146. doi: 10.1042/bj2390141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes B. P., Barritt G. J. The stimulation by sodium fluoride of plasma-membrane Ca2+ inflow in isolated hepatocytes. Evidence that a GTP-binding regulatory protein is involved in the hormonal stimulation of Ca2+ inflow. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 1;245(1):41–47. doi: 10.1042/bj2450041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. R., Cala S. E. Biochemical evidence for functional heterogeneity of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11809–11818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaho Y., Moss J., Vaughan M. Mechanism of inhibition of transducin GTPase activity by fluoride and aluminum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11493–11497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Bokoch G. M., Northup J. K., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Properties and function of the purified protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3568–3577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Northup J. K., Bokoch G. M., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Subunit dissociation and guanine nucleotide-dependent hormonal inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3578–3585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I. Guanine nucleotide and NaF stimulation of phospholipase C activity in rat cerebral-cortical membranes. Studies on substrate specificity. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):35–40. doi: 10.1042/bj2440035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Smigel M. D., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. The subunits of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Resolution of the activated 45,000-dalton (alpha) subunit. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11369–11376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray T. K., Forte J. G. Studies on the phosphorylated intermediates of a K+-stimulated ATPase from rabbit gastric mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 7;443(3):451–467. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90465-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. D., Davis R. L., Steinberg M. Fluoride and beryllium interact with the (Na + K)-dependent ATPase as analogs of phosphate. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1986 Dec;18(6):521–531. doi: 10.1007/BF00743148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuurmans Stekhoven F., Bonting S. L. Transport adenosine triphosphatases: properties and functions. Physiol Rev. 1981 Jan;61(1):1–76. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert R., Rosenthal W., Schultz G. Guanine nucleotides stimulate NADPH oxidase in membranes of human neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 1;205(1):161–165. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80886-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Aluminum: a requirement for activation of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by fluoride. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4888–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strnad C. F., Parente J. E., Wong K. Use of fluoride ion as a probe for the guanine nucleotide-binding protein involved in the phosphoinositide-dependent neutrophil transduction pathway. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 29;206(1):20–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81332-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W., Merritt J. E., Putney J. W., Jr, Rubin R. P. A guanine nucleotide-dependent regulatory protein couples substance P receptors to phospholipase C in rat parotid gland. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):362–368. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90919-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbist J., Wuytack F., De Schutter G., Raeymaekers L., Casteels R. Reconstitution of the purified calmodulin-dependent (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase from smooth muscle. Cell Calcium. 1984 Jun;5(3):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(84)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma A. K., Penniston J. T. Two Ca2+-requiring p-nitrophenylphosphatase activities of the highly purified Ca2+-pumping adenosinetriphosphatase of human erythrocyte membranes, one requiring calmodulin and the other ATP. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5010–5015. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuytack F., Casteels R. Demonstration of a (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase activity probably related to Ca2+ transport in the microsomal fraction of porcine coronary artery smooth muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 25;595(2):257–263. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Smedt H., Borghgraef R., Ceuterick F., Heremans K. Pressure effects on lipid-protein interactions in (NA+ + K+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 5;556(3):479–489. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90135-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


