Abstract
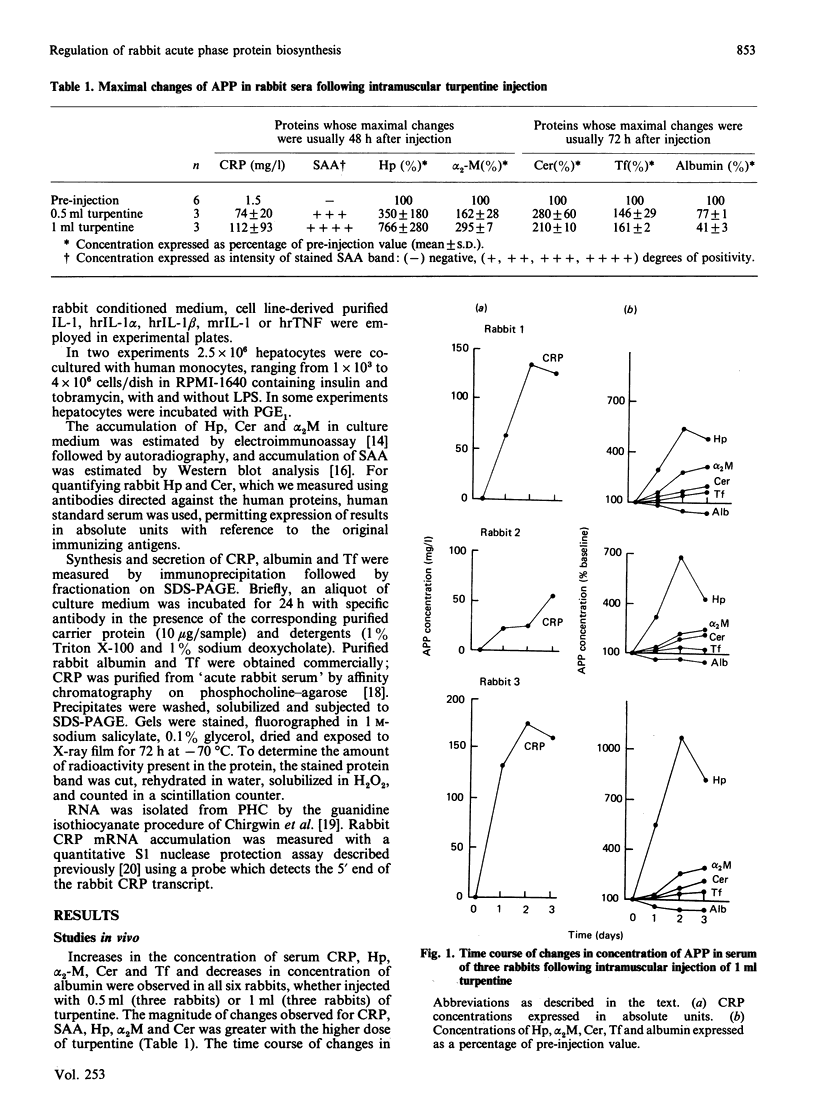
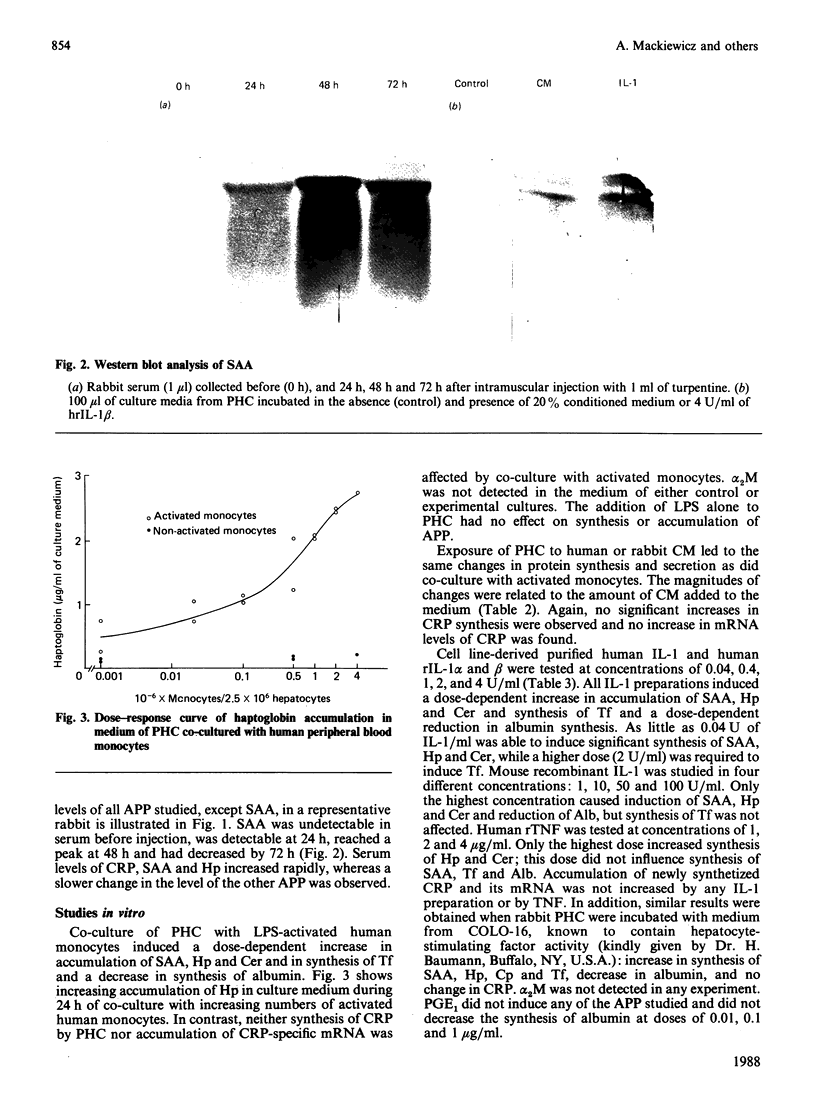
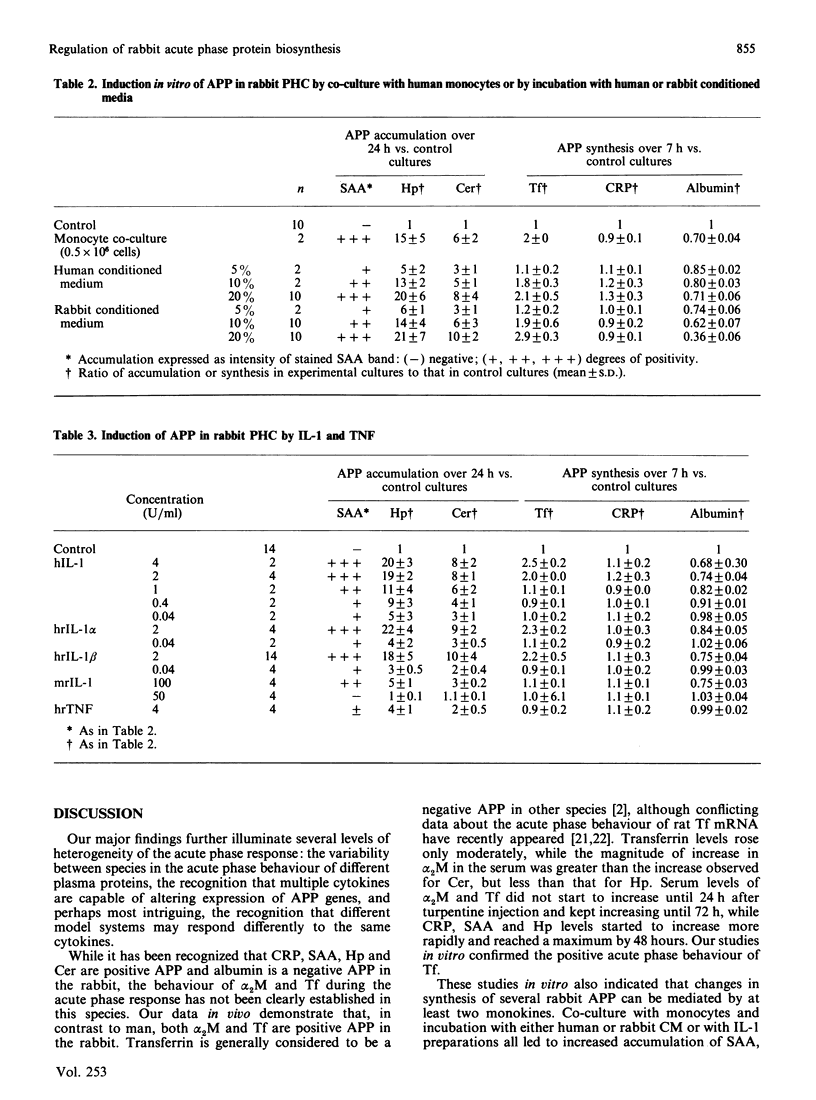
We defined the acute phase behaviour of a number of rabbit plasma proteins in studies (in vivo) and studied the effects of monokine preparations on their synthesis by rabbit primary hepatocyte cultures. Following turpentine injection, increased serum levels of C-reactive protein, serum amyloid A protein, haptoglobin, ceruloplasmin, and decreased concentrations of albumin were observed. In contrast to what is observed in man, concentrations of alpha 2-macroglobulin and transferrin were increased. Co-culture of primary hepatocyte cultures with lipopolysaccharide-activated human peripheral blood monocytes or incubation with conditioned medium prepared from lipopolysaccharide-activated human or rabbit monocytes resulted in dose-dependent induction of serum amyloid A, haptoglobin, ceruloplasmin and transferrin and depression of albumin synthesis, while C-reactive protein synthesis and mRNA levels remained unchanged. A variety of interleukin-1 preparations induced dose-dependent increases in the synthesis and secretion of serum amyloid A, haptoglobin, ceruloplasmin and transferrin and decreased albumin synthesis. Human recombinant tumour necrosis factor (cachectin) induced a dose-dependent increase in synthesis of haptoglobin and ceruloplasmin. In general, human interleukin-1 was more potent than mouse interleukin-1 and tumour necrosis factor. None of the monokines we studied had an effect on C-reactive protein synthesis or mRNA levels. These data confirm that C-reactive protein, serum amyloid A, haptoglobin and ceruloplasmin display acute phase behaviour in the rabbit, and demonstrate that, in contrast to their behaviour in man, alpha 2M and transferrin are positive acute phase proteins in this species. While both interleukin-1 and tumour necrosis factor regulate biosynthesis of a number of these acute phase proteins in rabbit primary hepatocyte cultures, neither of these monokines induced C-reactive protein synthesis. Comparison of these findings with those in human hepatoma cell lines, in which interleukin-1 does not induce serum amyloid A synthesis, suggests that the effect of interleukin-1 on serum amyloid A synthesis may be indirect.
Full text
PDF



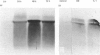
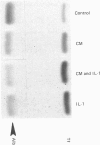
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumann H., Jahreis G. P., Sauder D. N., Koj A. Human keratinocytes and monocytes release factors which regulate the synthesis of major acute phase plasma proteins in hepatic cells from man, rat, and mouse. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7331–7342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch H. E., Schreiber G. Transcriptional regulation of plasma protein synthesis during inflammation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8077–8080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington G. J., Wilson D. R., Lachman L. B. Monocyte-conditioned medium, interleukin-1, and tumor necrosis factor stimulate the acute phase response in human hepatoma cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):787–793. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller G. M., Otto J. M., Woloski B. M., McGary C. T., Adams M. A. The effects of hepatocyte stimulating factor on fibrinogen biosynthesis in hepatocyte monolayers. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1481–1486. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathi M. K., Schultz D., Mackiewicz A., Samols D., Hu S. I., Brabenec A., Macintyre S. S., Kushner I. Heterogeneous nature of the acute phase response. Differential regulation of human serum amyloid A, C-reactive protein, and other acute phase proteins by cytokines in Hep 3B cells. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):564–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman N. D., Liu T. Y. Biosynthesis of human C-reactive protein in cultured hepatoma cells is induced by a monocyte factor(s) other than interleukin-1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2363–2368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. I., Miller S. M., Samols D. Cloning and characterization of the gene for rabbit C-reactive protein. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 2;25(24):7834–7839. doi: 10.1021/bi00372a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koj A., Gauldie J., Sweeney G. D., Regoeczi E., Sauder D. N. A simple bioassay for monocyte-derived hepatocyte stimulating factor: increased synthesis of alpha 2-macroglobulin and reduced synthesis of albumin by cultured rat hepatocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Feb 11;76(2):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90309-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner I., Mackiewicz A. Acute phase proteins as disease markers. Dis Markers. 1987 Mar;5(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner I., Somerville J. A. Estimation of the molecular size of C-reactive protein and CX-reactive protein in serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 28;207(1):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laishes B. A., Williams G. M. Conditions affecting primary cell cultures of functional adult rat hepatocytes. 1. The effect of insulin. In Vitro. 1976 Jul;12(7):521–532. doi: 10.1007/BF02796495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Electroimmuno assay. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:21–37. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le P. T., Mortensen R. F. Induction and regulation by monokines of hepatic synthesis of the mouse serum amyloid P-component (SAP). J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2526–2533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebreton de Vonne T., Mouray H., Gutman N. Les alpha-macroglobulines du lapin au cours de la reection inflammatoire. Clin Chim Acta. 1970 Dec;30(3):603–607. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(70)90251-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macintyre S. S. C-reactive protein. Methods Enzymol. 1988;163:383–399. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)63038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northemann W., Andus T., Gross V., Nagashima M., Schreiber G., Heinrich P. C. Messenger RNA activities of four acute phase proteins during inflammation. FEBS Lett. 1983 Sep 19;161(2):319–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter D. H., Dinarello C. A., Punsal P. I., Colten H. R. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor regulates hepatic acute-phase gene expression. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1349–1354. doi: 10.1172/JCI112721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter D. H., Dinarello C. A., Punsal P. I., Colten H. R. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor regulates hepatic acute-phase gene expression. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1349–1354. doi: 10.1172/JCI112721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter D. H., Goldberger G., Dinarello C. A., Mizel S. B., Colten H. R. Regulation of class III major histocompatibility complex gene products by interleukin-1. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):850–852. doi: 10.1126/science.3010455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramadori G., Sipe J. D., Dinarello C. A., Mizel S. B., Colten H. R. Pretranslational modulation of acute phase hepatic protein synthesis by murine recombinant interleukin 1 (IL-1) and purified human IL-1. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):930–942. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shim B. S. Increase in serum haptoglobin stimulated by prostaglandins. Nature. 1976 Jan 29;259(5541):326–327. doi: 10.1038/259326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voelkel E. F., Levine L., Alper C. A., Tashjian A. H., Jr Acute phase reactants ceruloplasmin and haptoglobin and their relationship to plasma prostaglandins in rabbits bearing the VS2 carcinoma. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1078–1088. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whicher J. T., Martin M. F., Dieppe P. A. Absence of prostaglandin stimulated increase in acute phase proteins in systemic sclerosis. Lancet. 1980 Nov 29;2(8205):1187–1188. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92614-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]