Abstract
Cultured Chinese-hamster ovary cells (CHO cells) were found to produce and secrete a lipase, which was identified as a lipoprotein lipase by the following criteria. Its activity was stimulated by serum and apolipoprotein CII, and was inhibited by high salt concentration. The lipase bound to heparin-agarose and co-eluted with 125I-labelled bovine lipoprotein lipase in a salt gradient. A chicken antiserum to bovine lipoprotein lipase inhibited the activity and precipitated a labelled protein of the same apparent size as bovine lipoprotein lipase from media of CHO cells labelled with [35S]methionine. The lipase activity and secretion were similar in growing cells and in cells that had reached confluency. Hence, lipoprotein lipase appears to be expressed constitutively in CHO cells and is not linked to certain growth conditions, as in pre-adipocyte and macrophage cell lines. At 37 degrees C, but not at 4 degrees C, heparin increased the release of lipase to the medium 2-4-fold. This increased release occurred without depletion of cell-associated lipase activity, suggesting that heparin enhanced release of newly synthesized lipase.
Full text
PDF

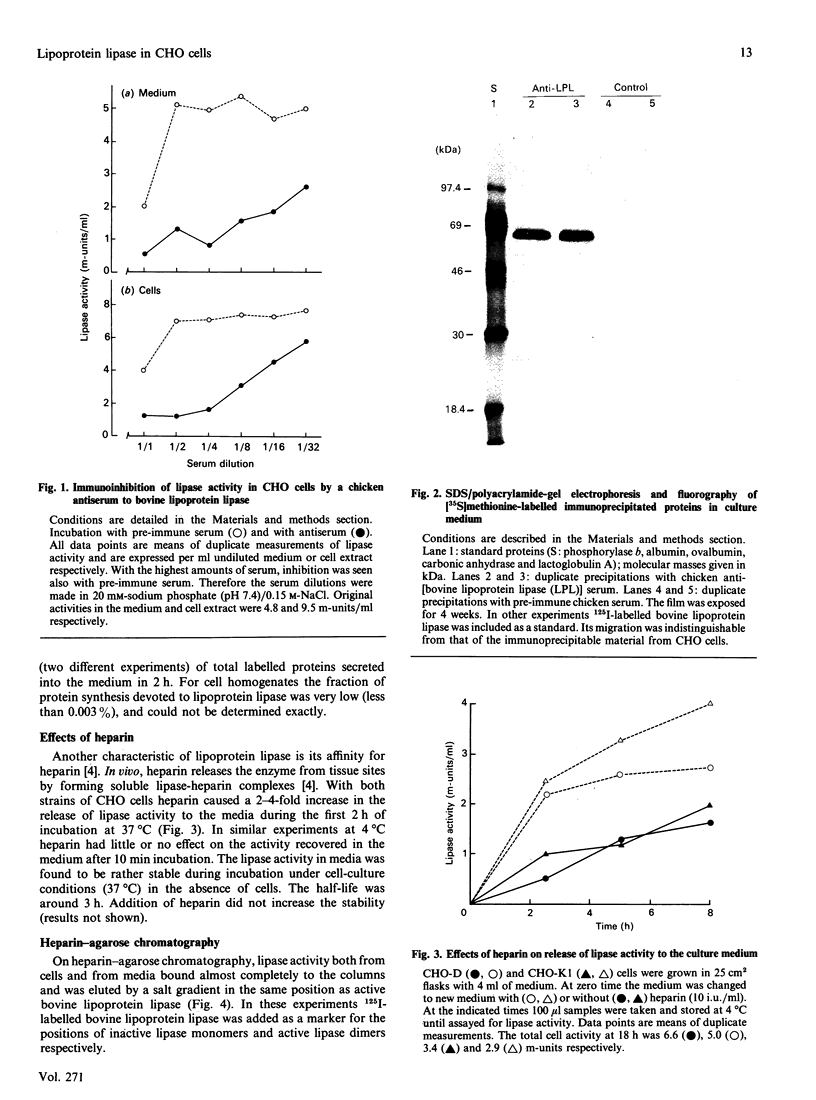

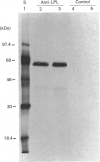
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ailhaud G., Dani C., Amri E. Z., Djian P., Vannier C., Doglio A., Forest C., Gaillard D., Négrel R., Grimaldi P. Coupling growth arrest and adipocyte differentiation. Environ Health Perspect. 1989 Mar;80:17–23. doi: 10.1289/ehp.898017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auwerx J. H., Deeb S., Brunzell J. D., Peng R., Chait A. Transcriptional activation of the lipoprotein lipase and apolipoprotein E genes accompanies differentiation in some human macrophage-like cell lines. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2651–2655. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camps L., Gåfvels M., Reina M., Wallin C., Vilaró S., Olivecrona T. Expression of lipoprotein lipase in ovaries of the guinea pig. Biol Reprod. 1990 May-Jun;42(5-6):917–927. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod42.6.917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar L. A., Hoogewerf A. J., Cupp M., Rapport C. A., Bensadoun A. Secretion and degradation of lipoprotein lipase in cultured adipocytes. Binding of lipoprotein lipase to membrane heparan sulfate proteoglycans is necessary for degradation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1767–1774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. A., Stein J. C., Strieleman P. J., Bensadoun A. Avian adipose lipoprotein lipase: cDNA sequence and reciprocal regulation of mRNA levels in adipose and heart. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jun 1;1008(1):92–101. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90174-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckel R. H. Lipoprotein lipase. A multifunctional enzyme relevant to common metabolic diseases. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 20;320(16):1060–1068. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904203201607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enerbäck S., Semb H., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Carlsson P., Hermansson M. L., Olivecrona T., Bjursell G. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA encoding lipoprotein lipase of guinea pig. Gene. 1987;58(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R., Sopher O. Control of lipoprotein lipase secretion in mouse macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 6;1001(2):120–126. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern P. A., Marshall S., Eckel R. H. Regulation of lipoprotein lipase in primary cultures of isolated human adipocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):199–208. doi: 10.1172/JCI111675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchgessner T. G., Svenson K. L., Lusis A. J., Schotz M. C. The sequence of cDNA encoding lipoprotein lipase. A member of a lipase gene family. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8463–8466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivecrona T., Bengtsson G. Immunochemical properties of lipoprotein lipase. Development of an immunoassay applicable to several mammalian species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jun 16;752(1):38–45. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90230-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivecrona T., Chernick S. S., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Garrison M., Scow R. O. Synthesis and secretion of lipoprotein lipase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Demonstration of inactive forms of lipase in cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10748–10759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne J. C., Jr, Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Lee N. S., Olivecrona T. Studies on inactivation of lipoprotein lipase: role of the dimer to monomer dissociation. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5606–5611. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson B., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Enerbäck S., Olivecrona T., Jörnvall H. Structural features of lipoprotein lipase. Lipase family relationships, binding interactions, non-equivalence of lipase cofactors, vitellogenin similarities and functional subdivision of lipoprotein lipase. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 15;179(1):39–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J., Olivecrona T., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G. Distribution of lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase between plasma and tissues: effect of hypertriglyceridemia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 4;837(3):262–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90049-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semb H., Olivecrona T. Lipoprotein lipase in guinea pig tissues: molecular size and rates of synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Oct 3;878(3):330–337. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90240-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semb H., Olivecrona T. Mechanisms for turnover of lipoprotein lipase in guinea pig adipocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Sep 4;921(1):104–115. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semb H., Olivecrona T. The relation between glycosylation and activity of guinea pig lipoprotein lipase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4195–4200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semb H., Peterson J., Tavernier J., Olivecrona T. Multiple effects of tumor necrosis factor on lipoprotein lipase in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8390–8394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senda M., Oka K., Brown W. V., Qasba P. K., Furuichi Y. Molecular cloning and sequence of a cDNA coding for bovine lipoprotein lipase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4369–4373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severson D. L., Lee M., Carroll R. Secretion of lipoprotein lipase from myocardial cells isolated from adult rat hearts. Mol Cell Biochem. 1988 Jan;79(1):17–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00229393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein O., Leitersdorf E., Chajek-Shaul T., Friedman G., Stein Y. Studies on lipolytic enzymes in cell culture. Monogr Atheroscler. 1986;14:124–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannier C., Ailhaud G. A continuous flow method for the study of lipoprotein lipase secretion in adipose cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Feb 12;875(2):324–333. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90183-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannier C., Ailhaud G. Biosynthesis of lipoprotein lipase in cultured mouse adipocytes. II. Processing, subunit assembly, and intracellular transport. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13206–13216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wion K. L., Kirchgessner T. G., Lusis A. J., Schotz M. C., Lawn R. M. Human lipoprotein lipase complementary DNA sequence. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1638–1641. doi: 10.1126/science.3823907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise L. S., Green H. Studies of lipoprotein lipase during the adipose conversion of 3T3 cells. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90192-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]