Abstract
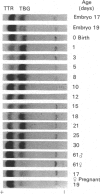
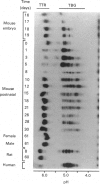
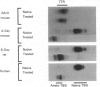
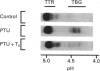
We confirm our finding of a major development-regulated thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) in the serum of the euthyroid mouse and investigate a number of its binding, structural and regulatory properties. Between 16 days foetal and 60 days postnatal life, the thyroxine (T4)- and tri-iodothyronine (T3)-binding activities of the sera show a striking ontogenic pattern: the binding is 2-3 times higher in foetuses than in mothers, then further increases after birth, reaching between 3 and 5 days maximum values which are 7-8 times higher than the adult ones. This pattern is not correlated with the ontogenesis of the acknowledged specific (transthyretin, TTR) and non-specific (albumin, alpha 1-foetoprotein) thyroid-hormone carriers of the mouse sera. PAGE studies demonstrate that the protein responsible for the elevated binding of the perinatal period is an alpha 1-globulin, with a migration similar to that of human and rat TBGs. Scatchard analysis is consistent with the notions that the T4-binding sites of TBG have high association constants, about two orders of magnitude above the T4 sites of TTR (10(9) M-1 as against 10(7) M-1) and low capacities (37 and 4 nmol/g of serum proteins in pups and adults respectively). Isoelectric focusing (i.e.f.) demonstrates that mouse TBG is a microheterogeneous protein separable, as a function of the pH gradient, in up to 10-12 isoforms, Marked shifts of the relative abundance of isoforms in the course of development are evidenced. The modulation of the TBG binding activity by non-esterified fatty acids (NEFA) and the control of its synthesis by the thyroid status are also reported. Mono- and poly-unsaturated NEFAs are strong inhibitors of the TBG, although they affect TTR less readily. On the other hand, the biosynthesis and/or secretion of TBG, but not of TTR, is under thyroid-hormone control, experimental hypothyroidism inducing a marked increase of the serum TBG. The TBG of mouse behaves as a highly significant parameter of development, pointing to a likely important function of the protein in the process of maturation. Our finding of major TBGs in both euthyroid rats and mice suggests that TBG is more widely spread than was thought until now, but difficult to detect in certain species outside definite maturation stages.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bleiberg F., Vranckx R., Wade S., Nunez E. A. A simplified method for the preparation of rat thyroxine-binding prealbumin. Factors influencing its circulating level. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Apr 29;828(3):270–277. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90308-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Huang T. S., Hurd R. E., Beredo A., Solomon D. H. A competitive ligand binding assay for measurement of thyroid hormone-binding inhibitor in serum and tissues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Apr;58(4):619–628. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-4-619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Teco G. N., Mead J. F., Huang T. S., Beredo A., Solomon D. H. Relationship between serum free fatty acids and thyroid hormone binding inhibitor in nonthyroid illnesses. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 May;60(5):980–984. doi: 10.1210/jcem-60-5-980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christeff N., Michon C., Goertz G., Hassid J., Matheron S., Girard P. M., Coulaud J. P., Nunez E. A. Abnormal free fatty acids and cortisol concentrations in the serum of AIDS patients. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1988 Jul;24(7):1179–1183. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(88)90125-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delorme J., Benassayag C., Christeff N., Vallette G., Savu L., Nunez E. Age-dependent responses of the serum non-esterified fatty acids to adrenalectomy and ovariectomy in developing rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 17;792(1):6–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90275-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dozin-van Roye B., de Nayer P. Nuclear triiodothyronine receptors in rat brain during maturation. Brain Res. 1979 Nov 30;177(3):551–554. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90471-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dussault J. H., Labrie F. Development of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis in the neonatal rat. Endocrinology. 1975 Nov;97(5):1321–1324. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-5-1321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklyn J. A., King S., Ahlquist J. A., Sheppard M. C. Effect of hypothyroidism and thyroid hormone treatment of the rat on hepatic Spot 14 and thyroxine binding prealbumin mRNAs. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1989 Sep;121(3):383–388. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1210383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R. P., Birkenmeier E. H., Beamer W. G., Maltais L. J., Gordon J. I. The hypothyroid (hyt/hyt) mouse: a model system for studying the effects of thyroid hormone on developmental changes in gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5592–5596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi S., Bartalena L., Ramacciotti C., Robbins J. Polymorphism of human thyroxine-binding globulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Dec;57(6):1186–1192. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-6-1186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gärtner R., Henze R., Horn K., Pickardt C. R., Scriba P. C. Thyroxine-binding globulin: investigation of microheterogeneity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Apr;52(4):657–664. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-4-657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hervé F., Grigorova A. M., Rajkowski K., Cittanova N. Differences in the binding of thyroid hormones and indoles by rat alpha 1-fetoprotein and serum albumin. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Mar 1;122(3):609–612. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillgartner F. B., Romsos D. R. Impaired transport of thyroid hormones into livers of obese (ob/ob) mice. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jul;255(1 Pt 1):E54–E58. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.255.1.E54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. M., Young J. B., Shaw E. A. Abnormal thyroid hormone binding to serum proteins in ob/ob and db/db genetically obese mice. Endocrinology. 1985 Nov;117(5):1858–1863. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-5-1858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORNSTEIN L. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. I. BACKGROUND AND THEORY. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:321–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlman W. H., Crépy O. Steroid-protein interaction with particular reference to testosterone binding by human serum. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):182–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal H. E. A graphic method for the determination and presentation of binding parameters in a complex system. Anal Biochem. 1967 Sep;20(3):525–532. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savu L., Benassayag C., Vallette G., Christeff N., Nunez E. Mouse alpha 1-fetoprotein and albumin. A comparison of their binding properties with estrogen and fatty acid ligands. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9414–9418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savu L., Benassayag C., Vallette G., Nunez E., Jayle M. F. Purification and estrogen binding properties of mouse alpha1-fetoprotein and of two forms of the protein with different affinities for concanavalin-A. Biochimie. 1977;59(3):323–328. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(77)80149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savu L., Nunez E. A., Jayle M. F. High affinity testosterone, cortisoterone and progesterone binding activities in pregnant hamster serum. Endocrinology. 1977 Aug;101(2):369–377. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-2-369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savu L., Vranckx R., Maya M., Gripois D., Blouquit M. F., Nunez E. A. Thyroxine-binding globulin and thyroxine-binding prealbumin in hypothyroid and hyperthyroid developing rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Sep 15;992(3):379–384. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(89)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savu L., Vranckx R., Maya M., Nunez E. A. A thyroxine binding globulin (TBG)-like protein in the sera of developing and adult rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 13;148(3):1165–1173. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80255-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savu L., Vranckx R., Maya M., Nunez E. A. Binding activities of thyroxine binding globulin versus thyroxine binding prealbumin in rat sera: differential modulation by thyroid hormone ligands, oleic acid and pharmacological drugs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):919–926. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92196-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savu L., Vranckx R., Maya M., Nunez E. A. Une globuline liant la thyroxine de signification biologique majeure (thyroxine binding globulin, TBG) dans le sérum de souris: démonstration et ontogenèse. C R Acad Sci III. 1989;309(4):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasaki T., Pardridge W. M. Differential binding of thyroxine and triiodothyronine to acidic isoforms of thyroid hormone binding globulin in human serum. Biochemistry. 1988 May 17;27(10):3624–3628. doi: 10.1021/bi00410a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vranckx R., Savu L., Nunez E. A. The microheterogeneity of rat TBG. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 27;244(2):343–346. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80559-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P., Dubois J. D., Dussault J. H. Free thyroid hormone concentrations during postnatal development in the rat. Pediatr Res. 1980 Mar;14(3):247–249. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198003000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]