Abstract
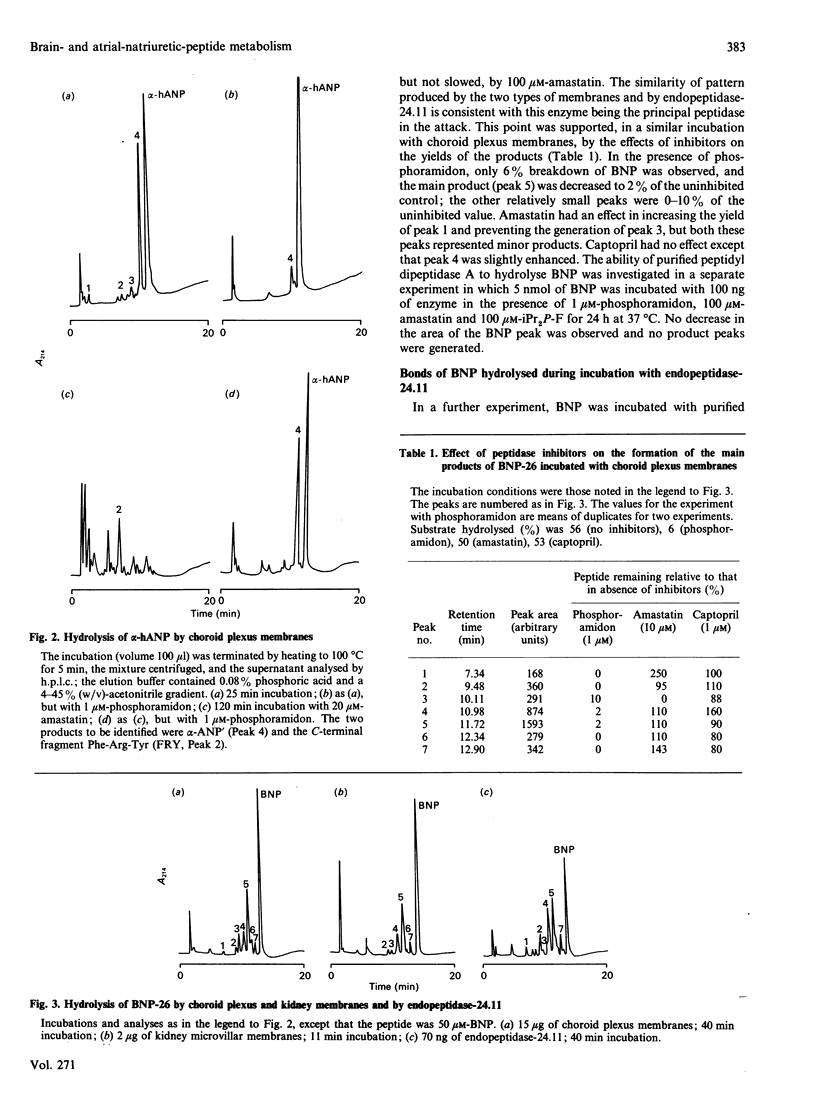
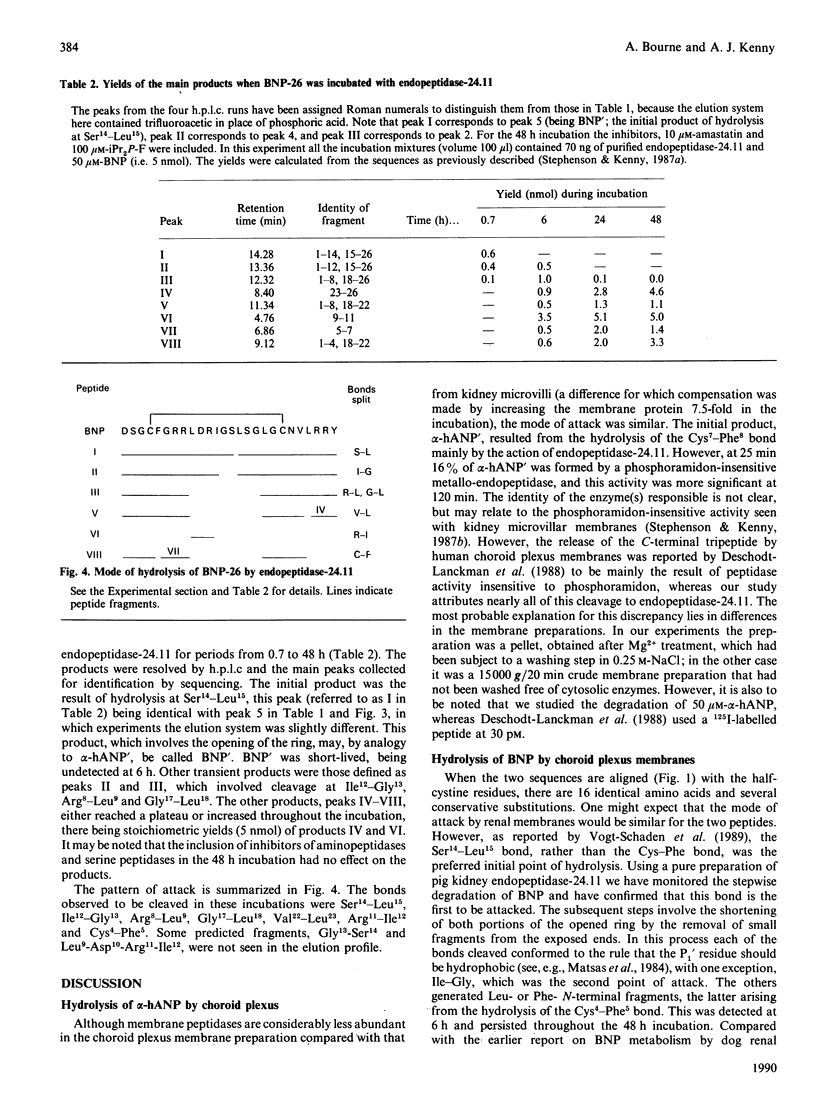
The hydrolysis of the porcine 26-residue brain natriuretic peptide (BNP-26) and its counterpart human 28-residue atrial natriuretic peptide (alpha-hANP) by pig membrane preparations and purified membrane peptidases was studied. When the two peptides were incubated with choroid plexus membranes, the products being analysed by h.p.l.c., alpha-hANP was degraded twice as fast as BNP. The h.p.l.c. profiles of alpha-hANP hydrolysis, in short incubations with choroid plexus membranes, yielded alpha hANP' as the main product, this having been previously shown to be the result of hydrolysis at the Cys7-Phe8 bond. In short incubations this cleavage was inhibited 84% by 1 microM-phosphoramidon, a specific inhibitor of endopeptidase-24.11. BNP-26 was hydrolysed by choroid plexus membranes, kidney microvillar membranes and purified endopeptidase-24.11 in a manner that yielded identical h.p.l.c. profiles. In the presence of phosphoramidon, hydrolysis by the choroid plexus membranes was 94% inhibited. Captopril had no effect and, indeed, no hydrolysis of BNP-26 by peptidyl dipeptidase A (angiotensin-converting enzyme) was observed even after prolonged incubation with the purified enzyme. The stepwise hydrolysis of BNP-26 by endopeptidase-24.11 was investigated by sequencing the peptides produced during incubation. The initial product resulted from hydrolysis at Ser14-Leu15, thereby opening the ring. This product (BNP') was short-lived; further degradation involved hydrolysis at Ile12-Gly13, Arg8-Leu9, Gly17-Leu18, Val22-Leu23, Arg11-Ile12 and Cys4-Phe5. Thus endopeptidase-24.11 is the principal enzyme in renal microvillar and choroid plexus membranes hydrolysing BNP-26 and alpha-hANP.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aburaya M., Hino J., Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Isolation and identification of rat brain natriuretic peptides in cardiac atrium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 30;163(1):226–232. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aburaya M., Minamino N., Hino J., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Distribution and molecular forms of brain natriuretic peptide in the central nervous system, heart and peripheral tissue of rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 15;165(2):880–887. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80048-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi C., Gutkowska J., Ballak M., Thibault G., Garcia R., Genest J., Cantin M. Radioautographic localization of 125I-atrial natriuretic factor binding sites in the brain. Neuroendocrinology. 1986;44(3):365–372. doi: 10.1159/000124670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth A. G., Kenny A. J. A rapid method for the preparation of microvilli from rabbit kidney. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):575–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1420575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne A., Barnes K., Taylor B. A., Turner A. J., Kenny A. J. Membrane peptidases in the pig choroid plexus and on other cell surfaces in contact with the cerebrospinal fluid. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 1;259(1):69–80. doi: 10.1042/bj2590069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull H. G., Thornberry N. A., Cordes E. H. Purification of angiotensin-converting enzyme from rabbit lung and human plasma by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2963–2972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. S., Lowe D. G., Lewis M., Hellmiss R., Chen E., Goeddel D. V. Differential activation by atrial and brain natriuretic peptides of two different receptor guanylate cyclases. Nature. 1989 Sep 7;341(6237):68–72. doi: 10.1038/341068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Shichiri M., Emori T., Marumo F., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Brain natriuretic peptide interacts with atrial natriuretic peptide receptor in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1988 Oct 10;238(2):415–418. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80523-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Nakao K., Saito Y., Yamada T., Shirakami G., Mukoyama M., Arai H., Hosoda K., Suga S., Minamino N. Radioimmunoassay for brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) detection of BNP in canine brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 16;158(1):120–128. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80186-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny A. J., Stephenson S. L. Role of endopeptidase-24.11 in the inactivation of atrial natriuretic peptide. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 9;232(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80375-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima M., Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA encoding a precursor for rat brain natriuretic peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):1420–1426. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92268-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. The metabolism of neuropeptides. The hydrolysis of peptides, including enkephalins, tachykinins and their analogues, by endopeptidase-24.11. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):433–440. doi: 10.1042/bj2230433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamino N., Aburaya M., Ueda S., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. The presence of brain natriuretic peptide of 12,000 daltons in porcine heart. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 15;155(2):740–746. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80557-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehlenschlager W. F., Baron D. A., Schomer H., Currie M. G. Atrial and brain natriuretic peptides share binding sites in the kidney and heart. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb 28;161(2-3):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90838-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saper C. B., Hurley K. M., Moga M. M., Holmes H. R., Adams S. A., Leahy K. M., Needleman P. Brain natriuretic peptides: differential localization of a new family of neuropeptides. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Jan 2;96(1):29–34. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90238-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seilhamer J. J., Arfsten A., Miller J. A., Lundquist P., Scarborough R. M., Lewicki J. A., Porter J. G. Human and canine gene homologs of porcine brain natriuretic peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 15;165(2):650–658. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakami G., Nakao K., Yamada T., Itoh H., Mori K., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Matsuo H., Imura H. Inhibitory effect of brain natriuretic peptide on central angiotensin II-stimulated pressor response in conscious rats. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Aug 15;91(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90252-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song D. L., Kohse K. P., Murad F. Brain natriuretic factor. Augmentation of cellular cyclic GMP, activation of particulate guanylate cyclase and receptor binding. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 9;232(1):125–129. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80400-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steardo L., Nathanson J. A. Brain barrier tissues: end organs for atriopeptins. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):470–473. doi: 10.1126/science.2879355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson S. L., Kenny A. J. Metabolism of neuropeptides. Hydrolysis of the angiotensins, bradykinin, substance P and oxytocin by pig kidney microvillar membranes. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):237–247. doi: 10.1042/bj2410237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson S. L., Kenny A. J. The hydrolysis of alpha-human atrial natriuretic peptide by pig kidney microvillar membranes is initiated by endopeptidase-24.11. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):183–187. doi: 10.1042/bj2430183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudoh T., Kangawa K., Minamino N., Matsuo H. A new natriuretic peptide in porcine brain. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):78–81. doi: 10.1038/332078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudoh T., Minamino N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Brain natriuretic peptide-32: N-terminal six amino acid extended form of brain natriuretic peptide identified in porcine brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 15;155(2):726–732. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80555-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda S., Minamino N., Sudoh T., Kangawa K., Matsuo H. Regional distribution of immunoreactive brain natriuretic peptide in porcine brain and spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 15;155(2):733–739. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80556-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanneste Y., Michel A., Dimaline R., Najdovski T., Deschodt-Lanckman M. Hydrolysis of alpha-human atrial natriuretic peptide in vitro by human kidney membranes and purified endopeptidase-24.11. Evidence for a novel cleavage site. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 1;254(2):531–537. doi: 10.1042/bj2540531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt-Schaden M., Gagelmann M., Hock D., Herbst F., Forssmann W. G. Degradation of porcine brain natriuretic peptide (pBNP-26) by endoprotease-24.11 from kidney cortical membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 30;161(3):1177–1183. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91366-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


