Abstract
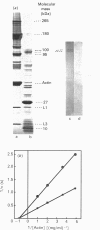
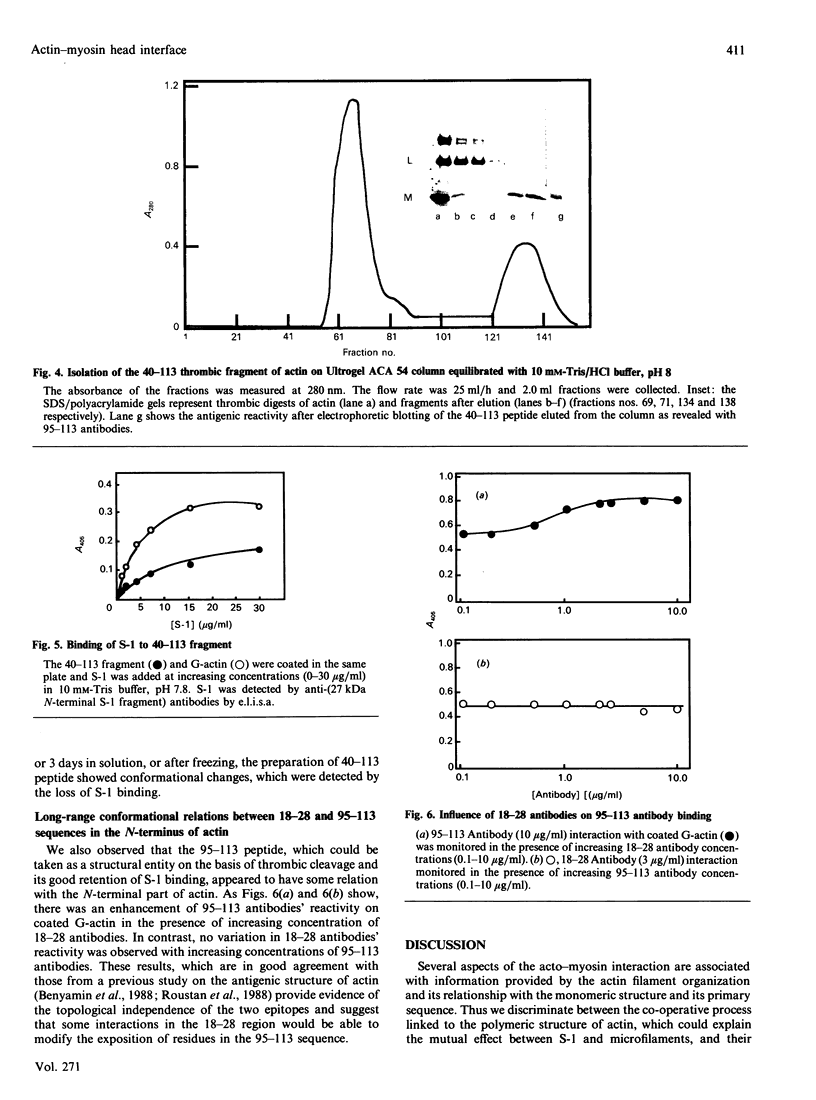
Evidence for the participation of the 1-7 and 18-28 N-terminal sequences of actin at different steps of actin-myosin interaction process is well documented in the literature. Cross-linking of the rigor complex between filamentous actin and skeletal-muscle myosin subfragment 1 was accomplished by the carboxy-group-directed zero-length protein cross-linker, 1-ethyl-3-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]carbodi-imide. After chaotropic depolymerization and thrombin digestion, which cleaves only actin, the covalent complex with Mr 100,000 was characterized by PAGE. The linkage was identified as being between myosin subfragment 1 (S-1) heavy chain and actin-(1-28)-peptide. The purified complex retained in toto its ability to combine reversibly with fresh filamentous actin, but showed a decrease in the Vmax. of actin-dependent Mg2(+)-ATPase. By using e.l.i.s.a., S-1 was observed to bind to coated monomeric actin or its 1-226 N-terminal peptide. This interaction strongly interfered with the binding of antibodies directed against the 95-113 actin sequence. Moreover, S-1 was able to bind with coated purified actin-(40-113)-peptide. Finally, antibodies directed against the 18-28 and 95-113 actin sequence, which strongly interfered with S1 binding, were unable to compete with each other. These results suggest that two topologically independent regions are involved in the actin-myosin interface: one located in the conserved 18-28 sequence and the other near residues 95-113, including the variable residue at position 89. Other experiments support the 'multisite interface model', where the two actin sites could modulate each other during S-1 interaction.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amos L. A., Huxley H. E., Holmes K. C., Goody R. S., Taylor K. A. Structural evidence that myosin heads may interact with two sites on F-actin. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):467–469. doi: 10.1038/299467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando T. Propagation of Acto-S-1 ATPase reaction-coupled conformational change in actin along the filament. J Biochem. 1989 May;105(5):818–822. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyamin Y., Roustan C., Boyer M. Anti-actin antibodies. Chemical modification allows the selective production of antibodies to the N-terminal region. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Jan 22;86(1):21–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90260-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand R., Chaussepied P., Kassab R., Boyer M., Roustan C., Benyamin Y. Cross-linking of the skeletal myosin subfragment 1 heavy chain to the N-terminal actin segment of residues 40-113. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 26;27(15):5728–5736. doi: 10.1021/bi00415a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley R. C., Trayer I. P. Affinity chromatography of immobilized actin and myosin. Biochem J. 1975 Aug;149(2):365–379. doi: 10.1042/bj1490365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer M., Feinberg J., Hue H. K., Capony J. P., Benyamin Y., Roustan C. Antigenic probes locate a serum-gelsolin-interaction site on the C-terminal part of actin. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 1;248(2):359–364. doi: 10.1042/bj2480359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer M., Roustan C., Benyamin Y. DNAse I-actin complex: an immunological study. Biosci Rep. 1985 Jan;5(1):39–46. doi: 10.1007/BF01117439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantler P. D., Gratzer W. B. Interaction of myosin with monomeric matrix-bound actin. FEBS Lett. 1973 Aug 1;34(1):10–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80691-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaussepied P., Kasprzak A. A. Isolation and characterization of the G-actin-myosin head complex. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):950–953. doi: 10.1038/342950a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaussepied P., Mornet D., Audemard E., Derancourt J., Kassab R. Abolition of ATPase activities of skeletal myosin subfragment 1 by a new selective proteolytic cleavage within the 50-kilodalton heavy chain segment. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 11;25(5):1134–1140. doi: 10.1021/bi00353a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DasGupta G., Reisler E. Antibody against the amino terminus of alpha-actin inhibits actomyosin interactions in the presence of ATP. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 20;207(4):833–836. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90249-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
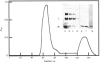
- Eisenberg E., Kielley W. W. Troponin-tropomyosin complex. Column chromatographic separation and activity of the three, active troponin components with and without tropomyosin present. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4742–4748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry G. D., Winstanley M. A., Dalgarno D. C., Scott G. M., Levine B. A., Trayer I. P. Characterization of the actin-binding site on the alkali light chain of myosin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Aug 23;830(3):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90279-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hue H. K., Benyamin Y., Roustan C. Comparative study of invertebrate actins: antigenic cross-reactivity versus sequence variability. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1989 Apr;10(2):135–142. doi: 10.1007/BF01739969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hue H. K., Labbé J. P., Harricane M. C., Cavadore J. C., Benyamin Y., Roustan C. Structural and functional variations in skeletal-muscle and scallop muscle actins. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 15;256(3):853–859. doi: 10.1042/bj2560853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Mannherz H. G., Suck D. Three-dimensional structure of the complex of actin and DNase I at 4.5 A resolution. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2113–2118. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03900.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno K. Functional, chymotryptically split actin and its interaction with myosin subfragment 1. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 16;26(12):3582–3589. doi: 10.1021/bi00386a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbé J. P., Audemard E., Bertrand R., Kassab R. Specific interactions of the alkali light chain 1 in skeletal myosin heads probed by chemical cross-linking. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 16;25(25):8325–8330. doi: 10.1021/bi00373a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marden M. C., Bohn B., Kister J., Poyart C. Effectors of hemoglobin. Separation of allosteric and affinity factors. Biophys J. 1990 Mar;57(3):397–403. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82556-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mejean C., Boyer M., Labbé J. P., Marlier L., Benyamin Y., Roustan C. Anti-actin antibodies. An immunological approach to the myosin-actin and the tropomyosin-actin interfaces. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 15;244(3):571–577. doi: 10.1042/bj2440571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L., Kalnoski M., Yunossi Z., Bulinski J. C., Reisler E. Antibodies directed against N-terminal residues on actin do not block acto-myosin binding. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 22;26(19):6064–6070. doi: 10.1021/bi00393a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan R. A., Flicker P. F. Structural relationships of actin, myosin, and tropomyosin revealed by cryo-electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):29–39. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir A. J., Levine B. A. Protein cognitive sites on the surface of actin. A proton NMR study. J Inorg Biochem. 1986 Oct-Nov;28(2-3):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0162-0134(86)80091-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. Involvement of an arginyl residue in the catalytic activity of myosin heads. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;100(2):421–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Pantel P., Bertrand R., Audemard E., Kassab R. Isolation and characterization of the trypsin-modified myosin -S1 derivatives. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jan 12;123(1):54–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muszbek L., Gladner J. A., Laki K. The fragmentation of actin by thrombin. Isolation and characterization of the split products. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Mar;167(1):99–103. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90445-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méjean C., Boyer M., Labbé J. P., Derancourt J., Benyamin Y., Roustan C. Antigenic probes locate the myosin subfragment 1 interaction site on the N-terminal part of actin. Biosci Rep. 1986 May;6(5):493–499. doi: 10.1007/BF01116141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méjean C., Hué H. K., Pons F., Roustan C., Benyamin Y. Cation binding sites on actin: a structural relationship between antigenic epitopes and cation exchange. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 15;152(1):368–375. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80723-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robin Y., Benyamin Y., Thoai N. V. Existence of homologous antigenic structures in unfolded creatine kinase and arginine kinase. FEBS Lett. 1976 Mar 15;63(1):174–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80220-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouayrenc J. F., Bertrand R., Kassab R., Walzthöny D., Bähler M., Wallimann T. Further characterization of the structural and functional properties of the cross-linked complex between F-actin and myosin S-1. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 15;146(2):391–401. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08665.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roustan C., Benyamin Y., Boyer M., Bertrand R., Audemard E., Jauregui-Adell J. Conformational changes induced by Mg2+ on actin monomers. An immunologic attempt to localize the affected region. FEBS Lett. 1985 Feb 11;181(1):119–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81125-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roustan C., Benyamin Y., Boyer M., Cavadore J. C. Structural variations in actins. A study of the immunological reactivity of the N-terminal region. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 1;233(1):193–197. doi: 10.1042/bj2330193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roustan C., Boyer M., Fattoum A., Jeanneau R., Benyamin Y., Roger M., Pradel L. A. Isolation and structural properties of a high-molecular-weight actin-binding protein (filamin-like protein) in hog thyroid gland. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec;129(1):149–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strzelecka-Golaszewska H., Sobieszek A. Activation of smooth muscle myosin by smooth and skeletal muscle actins. FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 16;134(2):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80601-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K. Identification of myosin-binding sites on the actin sequence. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 20;21(15):3654–3661. doi: 10.1021/bi00258a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K. Mapping of actin-binding sites on the heavy chain of myosin subfragment 1. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 29;22(7):1579–1585. doi: 10.1021/bi00276a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima C., Wakabayashi T. Three-dimensional image analysis of the complex of thin filaments and myosin molecules from skeletal muscle. V. Assignment of actin in the actin-tropomyosin-myosin subfragment-1 complex. J Biochem. 1985 Jan;97(1):245–263. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Taylor R. S. Separation of subfragment-1 isoenzymes from rabbit skeletal muscle myosin. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):54–56. doi: 10.1038/257054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]