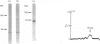Abstract
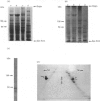
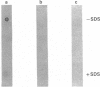
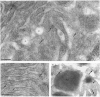
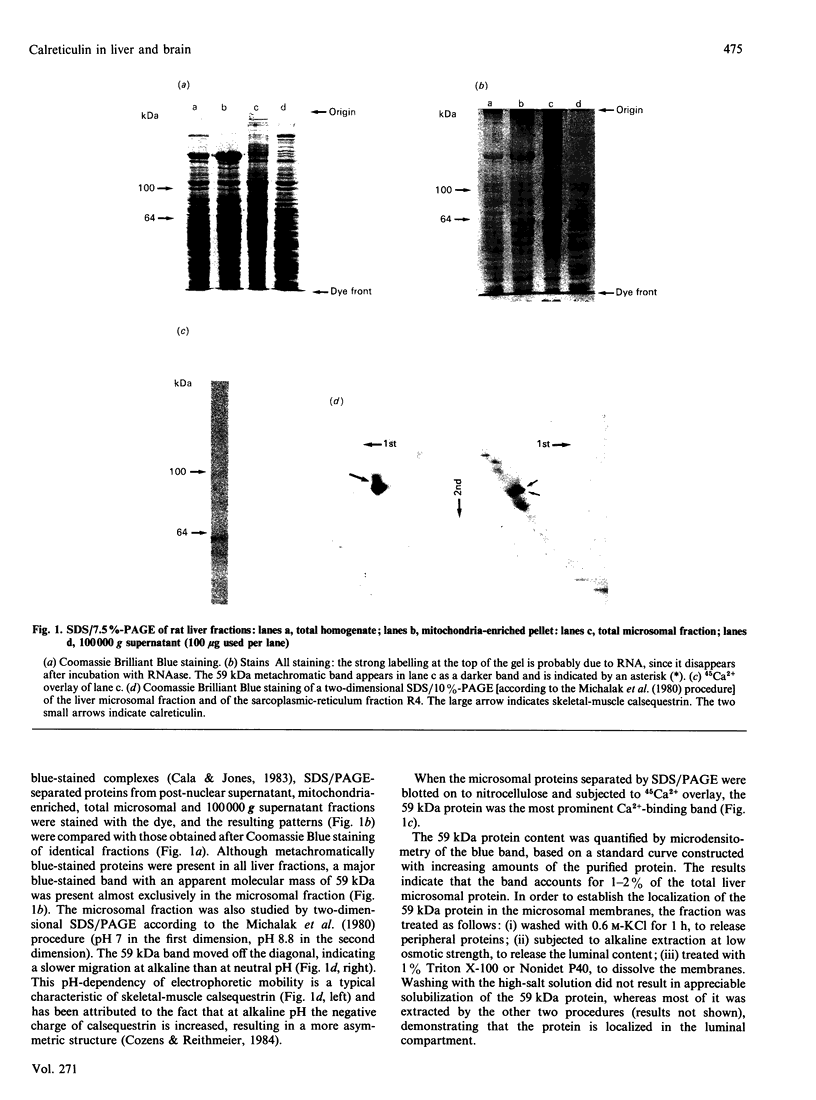
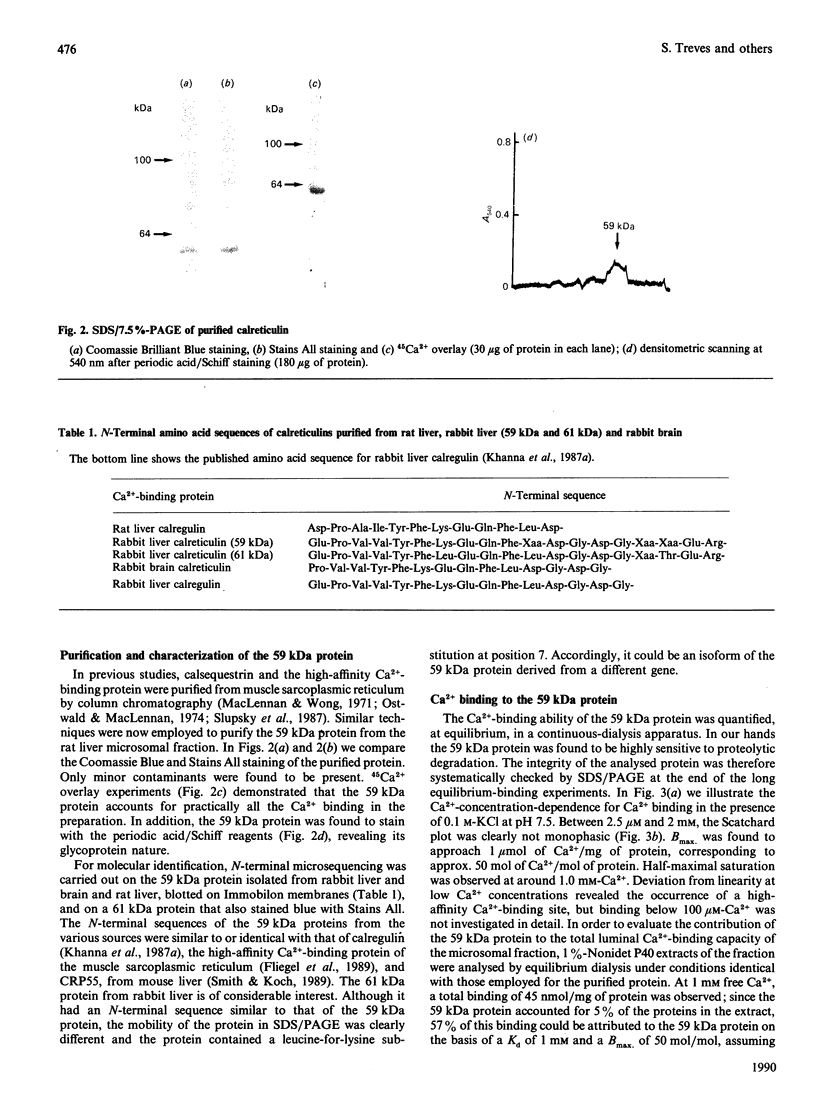
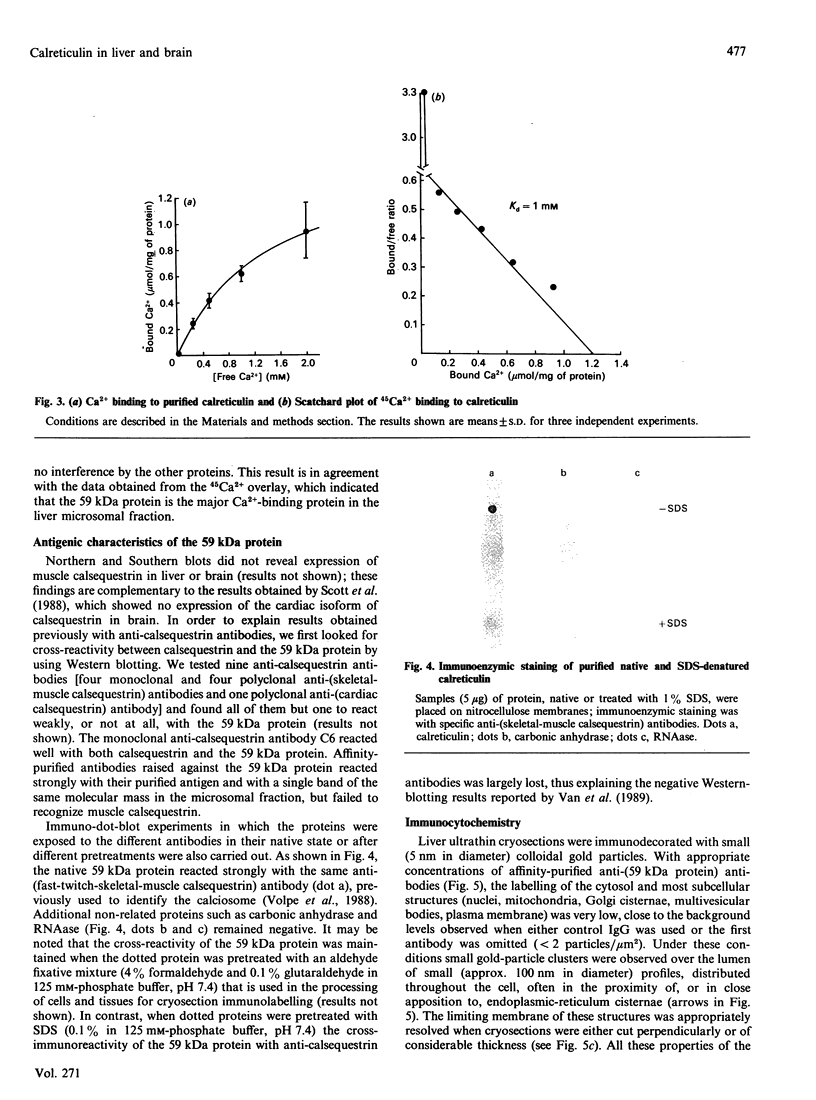
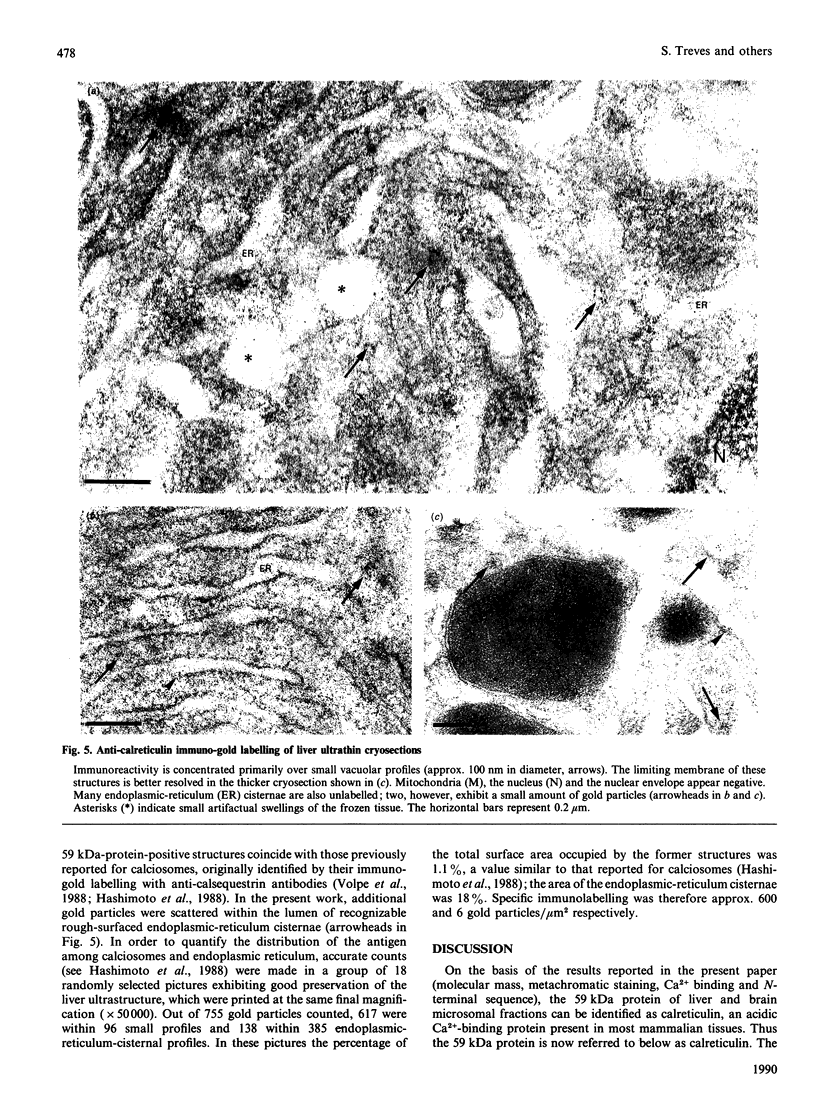
In a search for the non-muscle equivalent of calsequestrin (the low-affinity high-capacity Ca2(+)-binding protein responsible for Ca2+ storage within the terminal cisternae of the sarcoplasmic reticulum), acidic proteins were extracted from rat liver and brain microsomal preparations and purified by column chromatography. No calsequestrin was observed in these extracts, but the N-terminal amino acid sequence of the major Ca2(+)-binding protein of the liver microsomal fraction was determined and found to correspond to that of calreticulin. This protein was found to bind approx. 50 mol of Ca2+/mol of protein, with low affinity (average Kd approx. 1.0 mM). A monoclonal antibody, C6, raised against skeletal-muscle calsequestrin cross-reacted with calreticulin in SDS/PAGE immunoblots, but polyclonal antibodies reacted with native calreticulin only weakly, or not at all, after SDS denaturation. Immuno-gold decoration of liver ultrathin cryosections with affinity-purified antibodies against liver calreticulin revealed luminal labelling of vacuolar profiles indistinguishable from calciosomes, the subcellular structures previously identified by the use of anti-calsequestrin antibodies. We conclude that calreticulin is the Ca2(+)-binding protein segregated within the calciosome lumen, previously described as being calsequestrin-like. Because of its properties and intraluminal location, calreticulin might play a critical role in Ca2+ storage and release in non-muscle cells, similar to that played by calsequestrin in the muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cala S. E., Jones L. R. Rapid purification of calsequestrin from cardiac and skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles by Ca2+-dependent elution from phenyl-sepharose. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11932–11936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozens B., Reithmeier R. A. Size and shape of rabbit skeletal muscle calsequestrin. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6248–6252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damiani E., Heilmann C., Salvatori S., Margreth A. Characterization of high-capacity low-affinity calcium binding protein of liver endoplasmic reticulum: calsequestrin-like and divergent properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):973–980. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92698-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M. Calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jan;57(1):71–108. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar M. G. Progress in unraveling pathways of Golgi traffic. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:447–488. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliegel L., Burns K., MacLennan D. H., Reithmeier R. A., Michalak M. Molecular cloning of the high affinity calcium-binding protein (calreticulin) of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21522–21528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemette G., Balla T., Baukal A. J., Spät A., Catt K. J. Intracellular receptors for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in angiotensin II target tissues. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1010–1015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto S., Bruno B., Lew D. P., Pozzan T., Volpe P., Meldolesi J. Immunocytochemistry of calciosomes in liver and pancreas. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2523–2531. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensenius J. C., Andersen I., Hau J., Crone M., Koch C. Eggs: conveniently packaged antibodies. Methods for purification of yolk IgG. J Immunol Methods. 1981;46(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90333-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitany R. A., Zebrowski E. J. A high resolution PAS stain for polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller G. A., Tokuyasu K. T., Dutton A. H., Singer S. J. An improved procedure for immunoelectron microscopy: ultrathin plastic embedding of immunolabeled ultrathin frozen sections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5744–5747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khanna N. C., Tokuda M., Waisman D. M. Calregulin: purification, cellular localization, and tissue distribution. Methods Enzymol. 1987;139:36–50. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)39073-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khanna N. C., Tokuda M., Waisman D. M. Comparison of calregulins from vertebrate livers. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 15;242(1):245–251. doi: 10.1042/bj2420245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause K. H., Chou M., Thomas M. A., Sjolund R. D., Campbell K. P. Plant cells contain calsequestrin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4269–4272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause K. H., Lew P. D. Subcellular distribution of Ca2+ pumping sites in human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):107–116. doi: 10.1172/JCI113035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Wong P. T. Isolation of a calcium-sequestering protein from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1231–1235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macer D. R., Koch G. L. Identification of a set of calcium-binding proteins in reticuloplasm, the luminal content of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Sci. 1988 Sep;91(Pt 1):61–70. doi: 10.1242/jcs.91.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalak M., Campbell K. P., MacLennan D. H. Localization of the high affinity calcium binding protein and an intrinsic glycoprotein in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1317–1326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moos M., Jr, Nguyen N. Y., Liu T. Y. Reproducible high yield sequencing of proteins electrophoretically separated and transferred to an inert support. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6005–6008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. A C-terminal signal prevents secretion of luminal ER proteins. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):899–907. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberdorf J. A., Lebeche D., Head J. F., Kaminer B. Identification of a calsequestrin-like protein from sea urchin eggs. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6806–6809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostwald T. J., MacLennan D. H. Isolation of a high affinity calcium-binding protein from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):974–979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier M. F., Capponi A. M., Vallotton M. B. The inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-binding site in adrenal cortical cells is distinct from the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14078–14084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Berger E. G. Immunocytochemical localization of galactosyltransferase in HeLa cells: codistribution with thiamine pyrophosphatase in trans-Golgi cisternae. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):223–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito A., Seiler S., Chu A., Fleischer S. Preparation and morphology of sarcoplasmic reticulum terminal cisternae from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):875–885. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Ross C. A., Villa A., Supattapone S., Pozzan T., Snyder S. H., Meldolesi J. The inositol 1,4,5,-trisphosphate receptor in cerebellar Purkinje cells: quantitative immunogold labeling reveals concentration in an ER subcompartment. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):615–624. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott B. T., Simmerman H. K., Collins J. H., Nadal-Ginard B., Jones L. R. Complete amino acid sequence of canine cardiac calsequestrin deduced by cDNA cloning. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8958–8964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slupsky J. R., Ohnishi M., Carpenter M. R., Reithmeier R. A. Characterization of cardiac calsequestrin. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 6;26(20):6539–6544. doi: 10.1021/bi00394a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. J., Koch G. L. Multiple zones in the sequence of calreticulin (CRP55, calregulin, HACBP), a major calcium binding ER/SR protein. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3581–3586. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08530.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thévenod F., Dehlinger-Kremer M., Kemmer T. P., Christian A. L., Potter B. V., Schulz I. Characterization of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive (IsCaP) and -insensitive (IisCaP) nonmitochondrial Ca2+ pools in rat pancreatic acinar cells. J Membr Biol. 1989 Jul;109(2):173–186. doi: 10.1007/BF01870856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda M., Khanna N. C., Waisman D. M. Identification of bovine brain calcium binding proteins. Cell Calcium. 1987 Jun;8(3):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(87)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van P. N., Peter F., Söling H. D. Four intracisternal calcium-binding glycoproteins from rat liver microsomes with high affinity for calcium. No indication for calsequestrin-like proteins in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive calcium sequestering rat liver vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17494–17501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe P., Krause K. H., Hashimoto S., Zorzato F., Pozzan T., Meldolesi J., Lew D. P. "Calciosome," a cytoplasmic organelle: the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ store of nonmuscle cells? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1091–1095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waisman D. M., Salimath B. P., Anderson M. J. Isolation and characterization of CAB-63, a novel calcium-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1652–1660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R., Stäubli W., Gnägi H. R., Hess F. A. Correlated morphometric and biochemical studies on the liver cell. I. Morphometric model, stereologic methods, and normal morphometric data for rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):68–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagouras P., Rose J. K. Carboxy-terminal SEKDEL sequences retard but do not retain two secretory proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2633–2640. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]