Abstract
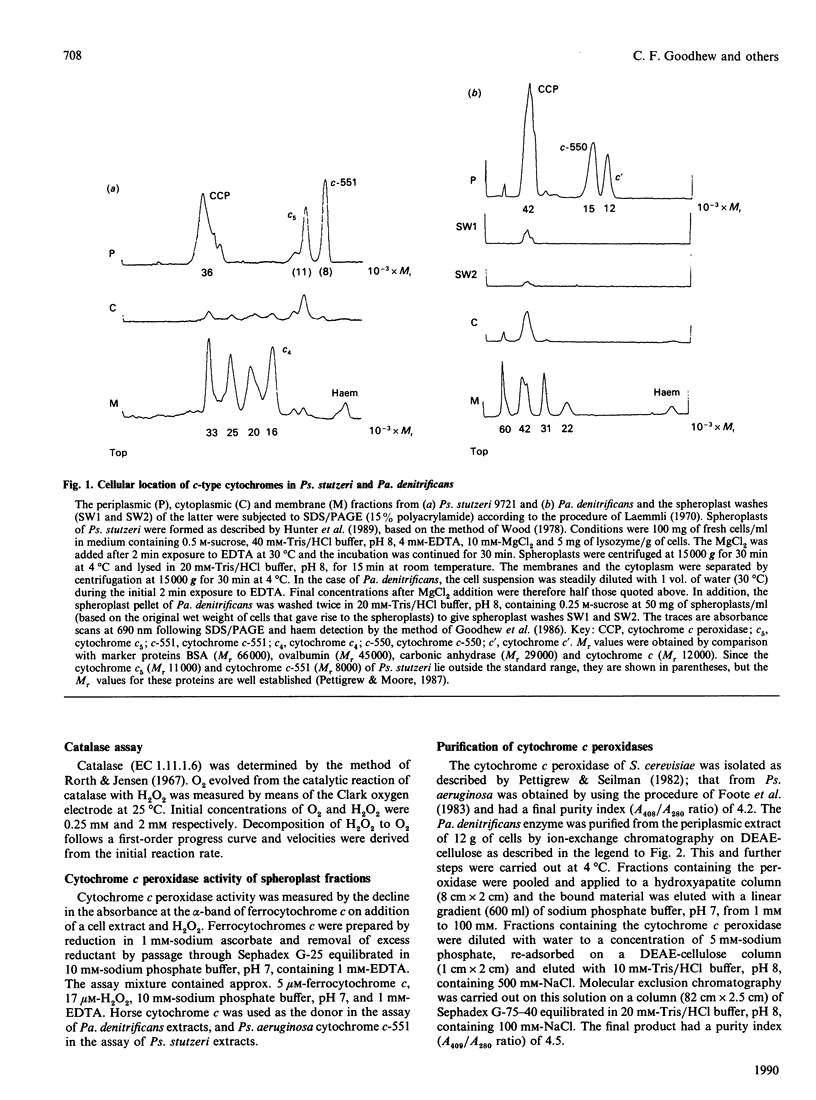
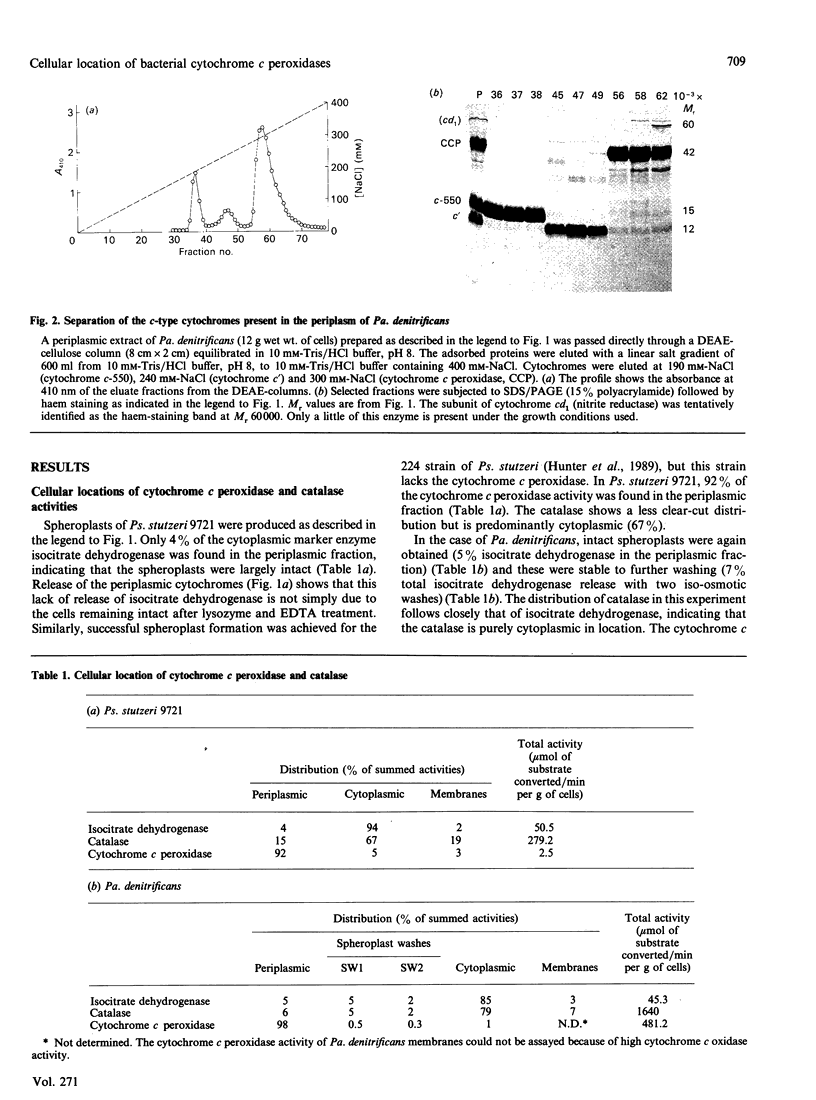
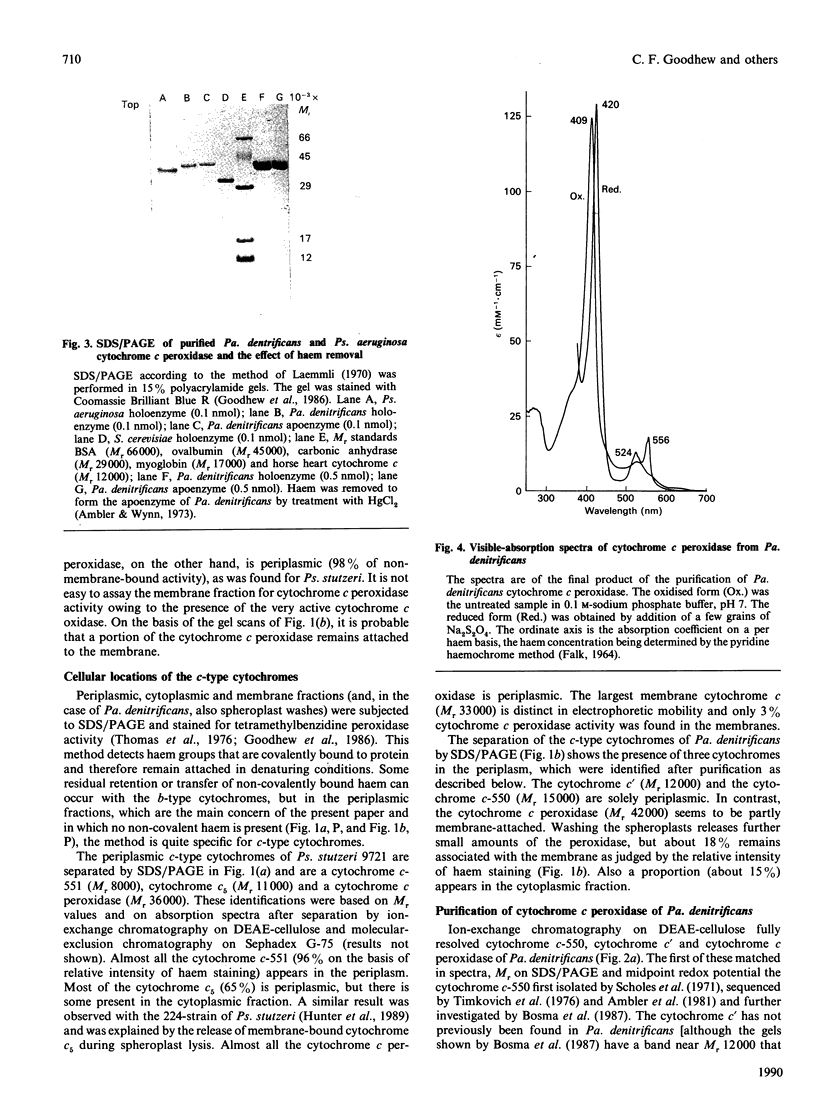
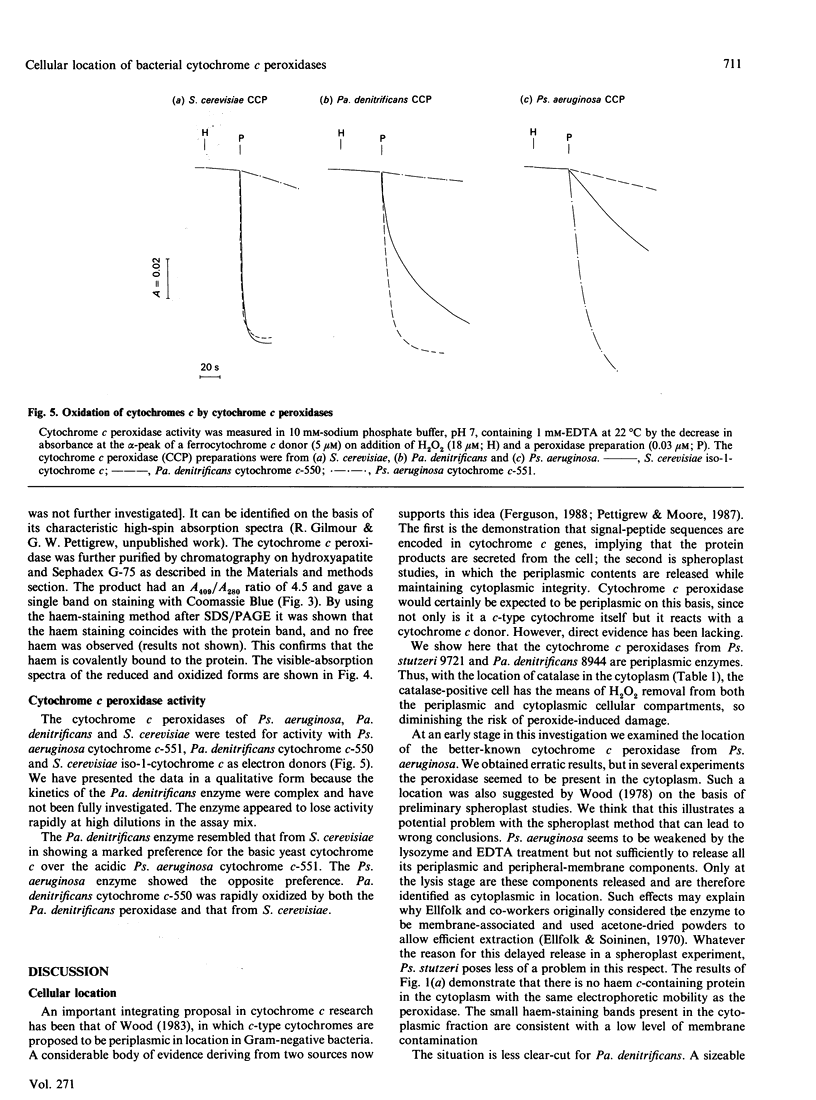
The locations of cytochrome c peroxidase and catalase activities in the two Gram-negative bacteria Pseudomonas stutzeri (N.C.I.B. 9721) and Paracoccus denitrificans (N.C.I.B. 8944) were investigated by the production of spheroplasts. In both species the cytochrome c peroxidase was predominantly periplasmic: 92% of total activity in Ps. stutzeri and 98% of nonmembrane-bound activity in Pa. denitrificans were found in this cellular compartment. In contrast, the catalase was mostly in the cytoplasmic fraction. Purification of the Pa. denitrificans cytochrome c peroxidase showed it to be the haem c-containing polypeptide of Mr 42,000 that has already been described by Bosma, Braster, Stouthamer & Van Versefeld [(1987) Eur. J. Biochem. 165, 665-670] but was not identified by them as a peroxidase. The visible-absorption spectra of the enzyme closely resemble those of cytochrome c peroxidase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa but the donor specificity is different, with the Pa. denitrificans enzyme preferring the basic mitochondrial cytochromes c to the acidic cytochromes c-551 and reacting well with the Pa. denitrificans cytochrome c-550.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler R. P., Meyer T. E., Kamen M. D., Schichman S. A., Sawyer L. A reassessment of the structure of Paracoccus cytochrome c-550. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 5;147(2):351–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90445-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P., Wynn M. The amino acid sequences of cytochromes c-551 from three species of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;131(3):485–498. doi: 10.1042/bj1310485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry E. A., Trumpower B. L. Isolation of ubiquinol oxidase from Paracoccus denitrificans and resolution into cytochrome bc1 and cytochrome c-aa3 complexes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2458–2467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma G., Braster M., Stouthamer A. H., van Verseveld H. W. Subfractionation and characterization of soluble c-type cytochromes from Paracoccus denitrificans cultured under various limiting conditions in the chemostat. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jun 15;165(3):665–670. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellfolk N., Rönnberg M., Aasa R., Andréasson L. E., Vänngård T. Properties and function of the two hemes in Pseudomonas cytochrome c peroxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb 28;743(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90413-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellfolk N., Soininen R. Pseudomonas cytochrome c peroxidase. I. Purification procedure. Acta Chem Scand. 1970;24(6):2126–2136. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.24-2126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote N., Thompson A. C., Barber D., Greenwood C. Pseudomonas cytochrome C-551 peroxidase. A purification procedure and study of CO-binding kinetics. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):701–707. doi: 10.1042/bj2090701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodhew C. F., elKurdi A. B., Pettigrew G. W. The microaerophilic respiration of Campylobacter mucosalis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Mar 30;933(1):114–123. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(88)90061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter D. J., Brown K. R., Pettigrew G. W. The role of cytochrome c4 in bacterial respiration. Cellular location and selective removal from membranes. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 15;262(1):233–240. doi: 10.1042/bj2620233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain M., Davidson V. L. Characterization of two inducible periplasmic c-type cytochromes from Paracoccus denitrificans. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8577–8580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki H., Matsubara T. Cytochrome c-557 (551) and cytochrome cd of Alcaligenes faecalis. J Biochem. 1971 May;69(5):847–857. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettigrew G. W., Seilman S. Purification and properties of a cross-linked complex between cytochrome c and cytochrome c peroxidase. Biochem J. 1982 Jan 1;201(1):9–18. doi: 10.1042/bj2010009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorth M., Jensen P. K. Determination of catalase activity by means of the Clark oxygen electrode. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 16;139(1):171–173. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rönnberg M., Ellfolk N. Heme-linked properties of Pseudomonas cytochrome c peroxidase. Evidence for non-equivalence of the hemes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 14;581(2):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90252-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rönnberg M., Kalkkinen N., Ellfolk N. The primary structure of Pseudomonas cytochrome c peroxidase. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80714-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rönnberg M., Osterlund K., Ellfolk N. Resonance Raman spectra of Pseudomonas cytochrome c peroxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 20;626(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90193-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholes P. B., McLain G., Smith L. Purification and properties of a c-type cytochrome from Micrococcus denitrificans. Biochemistry. 1971 May 25;10(11):2072–2076. doi: 10.1021/bi00787a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh J., Wharton D. C. Cytochrome c-556, a di-heme protein from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 22;292(2):391–401. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soininen R., Ellfolk N., Kalkkinen N. Pseudomonas cytochrome c peroxidase. IX. Molecular weight of the enzyme in dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Acta Chem Scand. 1973;27(3):1106–1107. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.27-1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Titani K., Ericsson L. H., Yonetani T. Primary structure of yeast cytochrome c peroxidase. II. The complete amino acid sequence. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Sep;203(2):615–629. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90219-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. E., Ryan D., Levin W. An improved staining procedure for the detection of the peroxidase activity of cytochrome P-450 on sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1976 Sep;75(1):168–176. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villalaín J., Moura I., Liu M. C., Payne W. J., LeGall J., Xavier A. V., Moura J. J. NMR and electron-paramagnetic-resonance studies of a dihaem cytochrome from Pseudomonas stutzeri (ATCC 11607) (cytochrome c peroxidase). Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 1;141(2):305–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. M. Periplasmic location of the terminal reductase in nitrite respiration. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 15;92(2):214–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80757-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. M. Why do c-type cytochromes exist? FEBS Lett. 1983 Dec 12;164(2):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80289-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]