Abstract
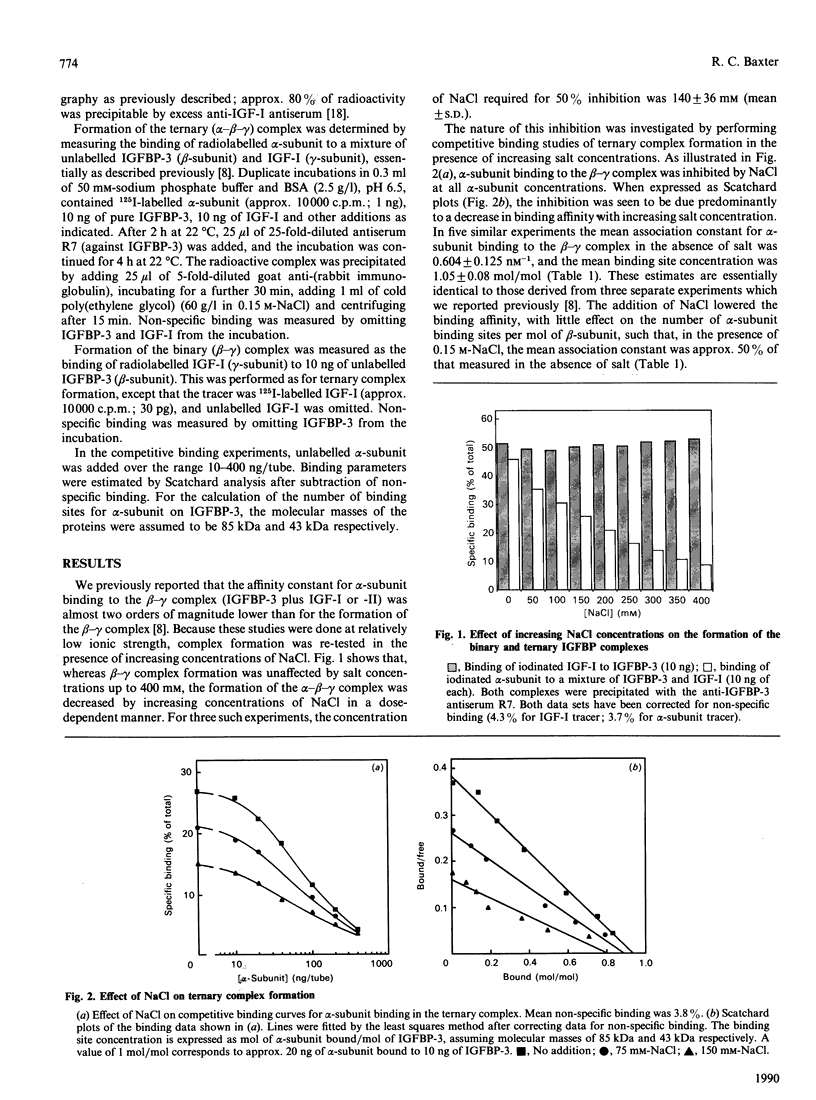
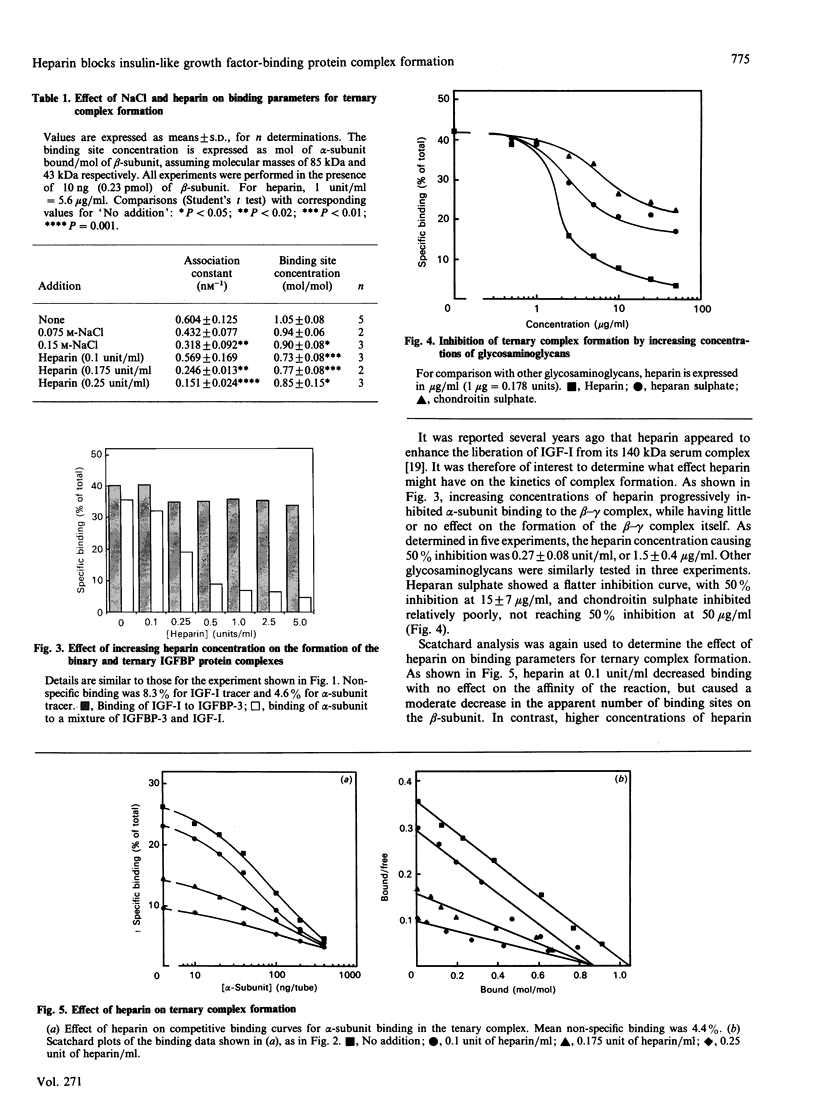
The 140 kDa insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein complex in human serum consists of three subunits: an acid-labile, non-IGF-binding glycoprotein (alpha-subunit), an IGF-binding glycoprotein known as BP-53 or IGFBP-3 (beta-subunit), and IGF-I or IGF-II (gamma-subunit). This study investigates the regulation, by salt and glycosaminoglycans, of ternary (alpha-beta-gamma) complex formation, measured by incubating radioiodinated alpha-subunit with a mixture of IGF-I and IGFBP-3 and precipitating bound radioactivity with an anti-IGFBP-3 antiserum. Increasing NaCl concentrations progressively decreased ternary complex formation without any effect on binary (beta-gamma) complex formation. In 0.15 M-NaCl, the association constant for the ternary complex was 0.318 +/- 0.092 nM-1, 100-fold lower than that for the binary complex. Glycosaminoglycans also inhibited ternary complex formation without affecting the binary complex. Heparin [50% inhibition at 0.27 +/- 0.08 units/ml (1.5 +/- 0.4 micrograms/ml)] was more potent than heparan sulphate (50% inhibition at 15 +/- 7 micrograms/ml), with chondroitin sulphate even less potent. The inhibition by heparin was due principally to a decrease in binding affinity, from 0.604 +/- 0.125 to 0.151 +/- 0.024 nM-1 in the presence of 0.25 units of heparin/ml, with a slight decrease in the number of apparent binding sites from 1.05 +/- 0.08 to 0.85 +/- 0.15 mol of alpha-subunit bound/mol of beta-subunit. Since the ternary IGF-binding protein complex cannot cross the capillary barrier, it is proposed that a decrease in the affinity of the complex, mediated by circulating or cell-associated glycosaminoglycans, may be important in the passage of IGFs and IGFBP-3 to the tissues.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar R. S., Boes M., Yorek M. Processing of insulin-like growth factors I and II by capillary and large vessel endothelial cells. Endocrinology. 1986 Mar;118(3):1072–1080. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-3-1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Brown A. S. Purification of tracer for somatomedin C radioimmunoassay by hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Clin Chem. 1982 Mar;28(3):485–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C. Characterization of the acid-labile subunit of the growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Aug;67(2):265–272. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-2-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C. Circulating levels and molecular distribution of the acid-labile (alpha) subunit of the high molecular weight insulin-like growth factor-binding protein complex. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 May;70(5):1347–1353. doi: 10.1210/jcem-70-5-1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L., Beniac V. A. High molecular weight insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex. Purification and properties of the acid-labile subunit from human serum. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11843–11848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L. Binding proteins for insulin-like growth factors in adult rat serum. Comparison with other human and rat binding proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 31;147(1):408–415. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80136-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L. Binding proteins for the insulin-like growth factors: structure, regulation and function. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1989;1(1):49–68. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(89)90041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L. Radioimmunoassay of growth hormone-dependent insulinlike growth factor binding protein in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1504–1512. doi: 10.1172/JCI112742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L. Structure of the Mr 140,000 growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex: determination by reconstitution and affinity-labeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6898–6902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C. The insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1988;91(2):229–235. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(88)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., de Mellow J. S. Measurement of insulin-like growth factor-II by radioreceptor assay using ovine placental membranes. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1986 Mar;24(3):267–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1986.tb03267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binoux M., Hossenlopp P. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) and IGF-binding proteins: comparison of human serum and lymph. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Sep;67(3):509–514. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-3-509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum W. F., Jenne E. W., Reppin F., Kietzmann K., Ranke M. B., Bierich J. R. Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I)-binding protein complex is a better mitogen than free IGF-I. Endocrinology. 1989 Aug;125(2):766–772. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-2-766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Underwood L. E., Chatelain P. G., Van Wyk J. J. Liberation of immunoreactive somatomedin-C from its binding proteins by proteolytic enzymes and heparin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Feb;56(2):384–389. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-2-384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell H. J., Enberg G., Herington A. C. Preferential association of the insulin-like growth factors I and II with metabolically inactive and active carrier-bound complexes in serum. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 1;241(3):745–750. doi: 10.1042/bj2410745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Ward A. P., Goldberg A. C., Trivedi B., Kapadia M. Characterization of somatomedin binding in human serum by ultracentrifugation and gel filtration. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Nov;55(5):916–921. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-5-916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mellow J. S., Baxter R. C. Growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein both inhibits and potentiates IGF-I-stimulated DNA synthesis in human skin fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):199–204. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80824-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlanetto R. W. The somatomedin C binding protein: evidence for a heterologous subunit structure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Jul;51(1):12–19. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-1-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall K., Brandt J., Enberg G., Fryklund L. Immunoreactive somatomedin A in human serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Feb;48(2):271–278. doi: 10.1210/jcem-48-2-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardouin S., Hossenlopp P., Segovia B., Seurin D., Portolan G., Lassarre C., Binoux M. Heterogeneity of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and relationships between structure and affinity. 1. Circulating forms in man. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):121–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L., Liu F., Rosenfeld R. G., Kemp S. F. Plasma somatomedin-binding proteins in hypopituitarism: changes during growth hormone therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Jul;53(1):100–104. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-1-100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hök M., Kjellén L., Johansson S. Cell-surface glycosaminoglycans. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:847–869. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.004215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjellén L., Oldberg A., Hök M. Cell-surface heparan sulfate. Mechanisms of proteoglycan-cell association. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10407–10413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. L., Baxter R. C. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein from human plasma. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8754–8760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norling B., Glimelius B., Wasteson A. Heparan sulfate proteoglycan of cultured cells: demonstration of a lipid- and a matrix-associated form. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Dec 31;103(4):1265–1272. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90259-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott C. D., Martin J. L., Baxter R. C. Production of insulin-like growth factor I and its binding protein by adult rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Endocrinology. 1985 Mar;116(3):1094–1101. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-3-1094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ui M., Shimonaka M., Shimasaki S., Ling N. An insulin-like growth factor-binding protein in ovarian follicular fluid blocks follicle-stimulating hormone-stimulated steroid production by ovarian granulosa cells. Endocrinology. 1989 Aug;125(2):912–916. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-2-912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton P. E., Baxter R. C., Burleigh B. D., Etherton T. D. Purification of the serum acid-stable insulin-like growth factor binding protein from the pig (Sus scrofa). Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1989;92(3):561–567. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(89)90132-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins J. R., D'Ercole A. J. Affinity-labeled plasma somatomedin-C/insulinlike growth factor I binding proteins. Evidence of growth hormone dependence and subunit structure. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1350–1358. doi: 10.1172/JCI111836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Born W., Chang J. Y., James P., Froesch E. R., Fischer J. A. Isolation and NH2-terminal amino acid sequences of rat serum carrier proteins for insulin-like growth factors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 15;156(3):1187–1194. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80758-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


