Abstract
GCDFP(gross-cystic-disease-fluid protein)-24, a progesterone-binding protein present in large amounts in cyst fluid from human breast gross cystic disease, was purified in a one-step procedure by size-exclusion h.p.l.c. Peptide fragments obtained by trypsin digestion of the intact protein were purified by reverse-phase h.p.l.c. and analysed for their amino acid composition and subjected to automated Edman degradation. A search of the National Biomedical Research Foundation Data Bank revealed that all the sequenced tryptic peptides from protein GCDFP-24 matched perfectly with regions present in the amino acid sequence determined for human apolipoprotein D. Additional data on N-terminal sequence of the unblocked proteins, carbohydrate-attachment sites, amino acid composition and molecular-mass estimations supported the identity between both molecules. On the basis of this identity a possible role of apolipoprotein D in progesterone transport is proposed.
Full text
PDF
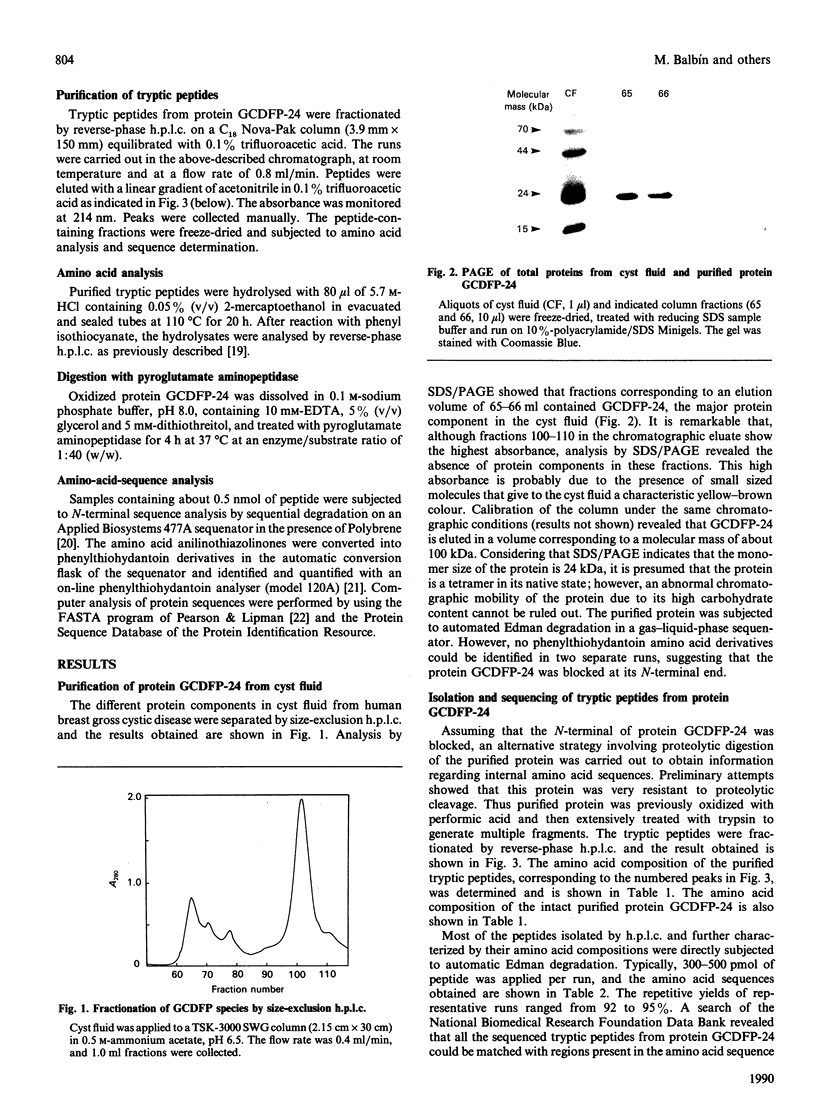
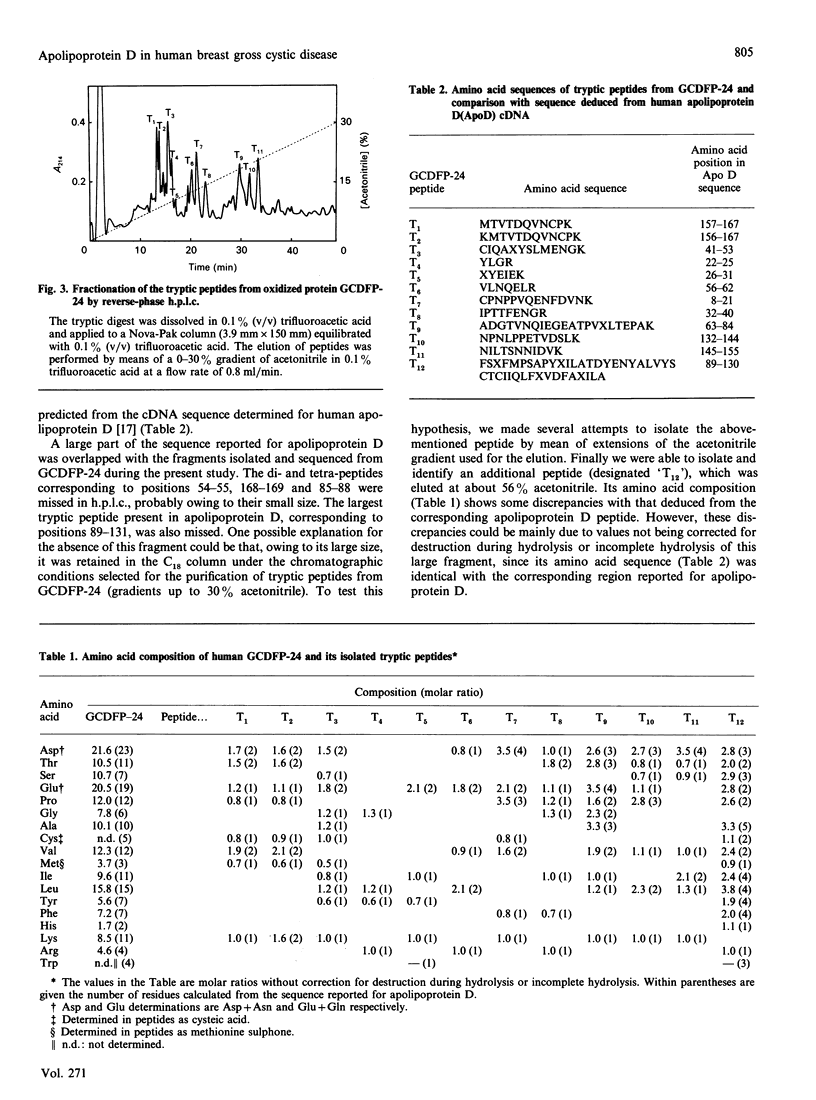


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bidlingmeyer B. A., Cohen S. A., Tarvin T. L. Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J Chromatogr. 1984 Dec 7;336(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)85133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradlow H. L., Breed C. N., Nisselbaum J., Fleisher M., Schwartz M. K. pH as a marker of breast cyst fluid biochemical type. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1987 Aug;13(4):331–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradlow H. L., Schwartz M. K., Fleisher M., Nisselbaum J. S., Boyar R., O'Connor J., Fukushima D. K. Accumulation of hormones in breast cyst fluid. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979 Nov;49(5):778–782. doi: 10.1210/jcem-49-5-778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow J. L. Apolipoprotein genetic variation and human disease. Physiol Rev. 1988 Jan;68(1):85–132. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1988.68.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collette J., Hendrick J. C., Jaspar J. M., Franchimont P. Presence of alpha-lactalbumin, epidermal growth factor, epithelial membrane antigen, and gross cystic disease fluid protein (15,000 daltons) in breast cyst fluid. Cancer Res. 1986 Jul;46(7):3728–3733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS H. H., SIMONS M., DAVIS J. B. CYSTIC DISEASE OF THE BREAST: RELATIONSHIP TO CARCINOMA. Cancer. 1964 Aug;17:957–978. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196408)17:8<957::aid-cncr2820170802>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. M., Lumsden A. B., Miller W. R. The relationship of cyst type to risk factors for breast cancer and the subsequent development of breast cancer in patients with breast cystic disease. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1985 Sep;21(9):1047–1050. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(85)90289-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., Fielding C., McLean J., Baer B., Castro G., Chen E., Comstock L., Henzel W., Kohr W., Rhee L. Cloning and expression of human apolipoprotein D cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16535–16539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escribano J., Grubb A., Méndez E. Identification of retinol as one of the protein HC chromophores. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 30;155(3):1424–1429. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godovac-Zimmermann J. The structural motif of beta-lactoglobulin and retinol-binding protein: a basic framework for binding and transport of small hydrophobic molecules? Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):64–66. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haagensen D. E., Jr, Mazoujian G., Dilley W. G., Pedersen C. E., Kister S. J., Wells S. A., Jr Breast gross cystic disease fluid analysis. I. Isolation and radioimmunoassay for a major component protein. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Feb;62(2):239–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesner L., Yu W. S., Bradlow H. L., Breed C. W., Fleisher M. Proteases in cyst fluid from human gross cyst breast disease. Cancer Res. 1988 Nov 15;48(22):6379–6383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. H., Wells R. G., Reed R. R. Isolation of an olfactory cDNA: similarity to retinol-binding protein suggests a role in olfaction. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1053–1056. doi: 10.1126/science.3493528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López Otin C., Grubb A. O., Méndez E. The complete amino acid sequence of human complex-forming glycoprotein heterogeneous in charge (protein HC) from one individual. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Feb 1;228(2):544–554. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConathy W. J., Alaupovic P. Isolation and characterization of other apolipoproteins. Methods Enzymol. 1986;128:297–310. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)28075-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConathy W. J., Alaupovic P. Studies on the isolation and partial characterization of apolipoprotein D and lipoprotein D of human plasma. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):515–520. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monson R. R., Yen S., MacMahon B. Chronic mastitis and carcinoma of the breast. Lancet. 1976 Jul 31;2(7979):224–226. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. L., Vander Zwaag R., Rogers L. W., Williams L. T., Walker W. E., Hartmann W. H. Relation between component parts of fibrocystic disease complex and breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Oct;61(4):1055–1063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlman W. H., Guériguian J. L., Sawyer M. E. A specific progesterone-binding component of human breast cyst fluid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 25;248(16):5736–5741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pervaiz S., Brew K. Homology and structure-function correlations between alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and serum retinol-binding protein and its relatives. FASEB J. 1987 Sep;1(3):209–214. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.3.3622999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pervaiz S., Brew K. Homology of beta-lactoglobulin, serum retinol-binding protein, and protein HC. Science. 1985 Apr 19;228(4697):335–337. doi: 10.1126/science.2580349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevsner J., Reed R. R., Feinstein P. G., Snyder S. H. Molecular cloning of odorant-binding protein: member of a ligand carrier family. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):336–339. doi: 10.1126/science.3388043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer L. Protein structure. One fold among many. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):659–659. doi: 10.1038/327659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmale H., Holtgreve-Grez H., Christiansen H. Possible role for salivary gland protein in taste reception indicated by homology to lipophilic-ligand carrier proteins. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):366–369. doi: 10.1038/343366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap P. L., Miller W. R., Roberts M. M., Creel R. J., Freedman B., Mirtle C. L., Pryde E. A., McClelland D. B. Protein concentrations in fluid from gross cystic disease of the breast. Clin Oncol. 1984 Mar;10(1):35–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zangerle P. F., Spyratos F., Le Doussal V., Noel G., Hacene K., Hendrick J. C., Gest J., Franchimont P. Breast cyst fluid proteins and breast cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;464:331–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb16013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]