Abstract
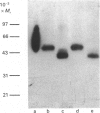
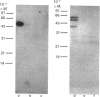
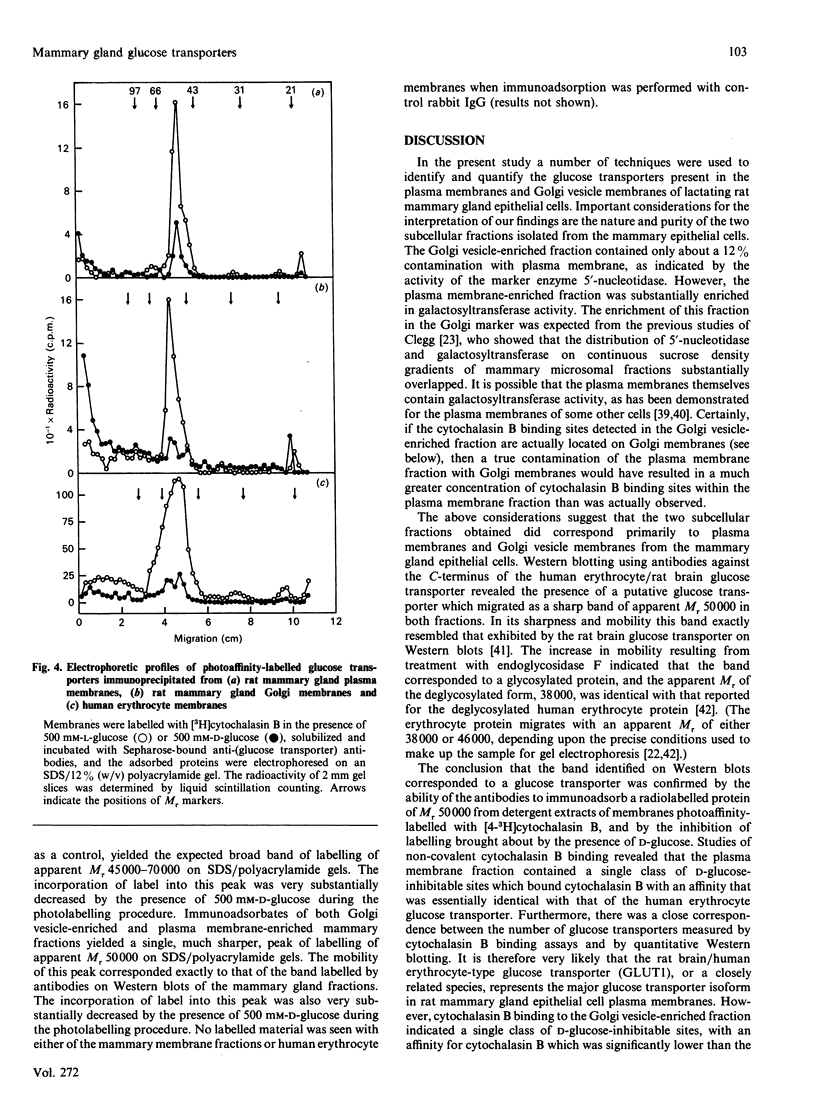
Plasma membrane- and Golgi vesicle-enriched membrane fractions were prepared from day-10 lactating rat mammary glands. Each fraction was found to contain a single set of D-glucose-inhibitable cytochalasin B-binding sites: plasma membranes and Golgi vesicles bound 20 +/- 2 and 53 +/- 4 pmol of cytochalasin/mg of membrane protein (means +/- S.E.M.), with dissociation constants of 259 +/- 47 and 520 +/- 47 nM respectively. Anti-peptide antibodies against the C-terminal region (residues 477-492) of the rat brain/human erythrocyte glucose transporter labelled a sharp band of apparent Mr 50,000 on Western blots of both fractions. Treatment with endoglycosidase F before blotting decreased the apparent Mr of this band to 38,000, indicating that it corresponded to a glycoprotein. Confirmation that this immunologically cross-reactive band was a glucose transporter was provided by the demonstration that it could be photoaffinity-labelled, in a D-glucose-sensitive fashion, with cytochalasin B. Quantitative Western blotting studies yielded values of 28 +/- 5 and 23 +/- 3 pmol of immunologically cross-reactive glucose transporters/mg of membrane protein in the plasma membrane and Golgi vesicle fractions respectively. From comparison with the concentration of cytochalasin B-binding sites, it is concluded that a protein homologous to the rat brain glucose transporter constitutes the major glucose transport species in the plasma membranes of mammary gland epithelial cells. Glucose transporters are also found in the Golgi membranes of these cells, at least half of them being similar, if not identical, to the transporters of the plasma membrane. However, their function in this location remains unclear.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod J. D., Pilch P. F. Unique cytochalasin B binding characteristics of the hepatic glucose carrier. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2222–2227. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin S. A., Baldwin J. M., Lienhard G. E. Monosaccharide transporter of the human erythrocyte. Characterization of an improved preparation. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 3;21(16):3836–3842. doi: 10.1021/bi00259a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baly D. L., Horuk R. The biology and biochemistry of the glucose transporter. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Oct 11;947(3):571–590. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J., Haspel H. C., Rosen O. M. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the rat brain glucose-transporter protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5784–5788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J. Identification of a novel gene encoding an insulin-responsive glucose transporter protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90968-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch R. Inhibition of glucose transport in the human erythrocyte by cytochalasin B. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 6;12(23):4799–4801. doi: 10.1021/bi00747a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnol A. F., Leturque A., Ferré P., Girard J. Glucose metabolism during lactation in the rat: quantitative and regulatory aspects. Am J Physiol. 1983 Oct;245(4):E351–E358. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.245.4.E351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter-Su C., Pessin J. E., Mora R., Gitomer W., Czech M. P. Photoaffinity labeling of the human erythrocyte D-glucose transporter. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5419–5425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg R. A. Lipoprotein lipase. Localization on plasma membrane fragments from lactating rat mammary tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 22;664(2):397–408. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A., Ciardelli T. L., Lienhard G. E., Boyle J. M., Whetton A. D., Baldwin S. A. Site-specific antibodies as probes of the topology and function of the human erythrocyte glucose transporter. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 15;266(3):799–808. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A., Meeran K., Cairns M. T., Baldwin S. A. Peptide-specific antibodies as probes of the orientation of the glucose transporter in the human erythrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9347–9352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbrink J., Bihler I. Membrane transport: its relation to cellular metabolic rates. Science. 1975 Jun 20;188(4194):1177–1184. doi: 10.1126/science.1096301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto H., Kayano T., Buse J. B., Edwards Y., Pilch P. F., Bell G. I., Seino S. Cloning and characterization of the major insulin-responsive glucose transporter expressed in human skeletal muscle and other insulin-responsive tissues. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7776–7779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto H., Seino S., Imura H., Seino Y., Eddy R. L., Fukushima Y., Byers M. G., Shows T. B., Bell G. I. Sequence, tissue distribution, and chromosomal localization of mRNA encoding a human glucose transporter-like protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5434–5438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDWICK D. C., LINZELL J. L., PRICE S. M. The effect of glucose and acetate on milk secretion by the perfused goat udder. Biochem J. 1961 Jul;80:37–45. doi: 10.1042/bj0800037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haspel H. C., Birnbaum M. J., Wilk E. W., Rosen O. M. Biosynthetic precursors and in vitro translation products of the glucose transporter of human hepatocarcinoma cells, human fibroblasts, and murine preadipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7219–7225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Strube M., Mueckler M. Molecular cloning and characterization of an insulin-regulatable glucose transporter. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):83–87. doi: 10.1038/338083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasanicki M. A., Cairns M. T., Davies A., Gardiner R. M., Baldwin S. A. Identification and characterization of the glucose-transport protein of the bovine blood/brain barrier. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):101–108. doi: 10.1042/bj2470101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn N. J., White A. The role of nucleoside diphosphatase in a uridine nucleotide cycle associated with lactose synthesis in rat mammary-gland Golgi apparatus. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 15;168(3):423–433. doi: 10.1042/bj1680423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavis V. R., Lee D. P., Shenolikar S. Evidence that forskolin binds to the glucose transporter of human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14571–14575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lienhard G. E., Crabb J. H., Ransome K. J. Endoglycosidase f cleaves the oligosaccharides from the glucose transporter of the human erythrocyte. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jan 25;769(2):404–410. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90324-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S., Spudich J. A. Biochemical studies on the mode of action of cytochalasin B. Cytochalasin B binding to red cell membrane in relation to glucose transport. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5778–5783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Caruso C., Baldwin S. A., Panico M., Blench I., Morris H. R., Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E., Lodish H. F. Sequence and structure of a human glucose transporter. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):941–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3839598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Isolation of an organ specific protein antigen from cell-surface membrane of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 9;154(3):540–552. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser C. G. Mechanism of the decrease in hexose transport by mouse mammary epithelial cells caused by fasting. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):149–154. doi: 10.1042/bj2490149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser C. G., Topper Y. J. Changes in the rate of carrier-mediated glucose transport by mouse mammary epithelial cells during ontogeny: hormone dependence delineated in vitro. Endocrinology. 1986 Jul;119(1):91–96. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Lentze M. J., Berger E. G. Immunocytochemical demonstration of ecto-galactosyltransferase in absorptive intestinal cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):118–125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanahan M. F. Cytochalasin B. A natural photoaffinity ligand for labeling the human erythrocyte glucose transporter. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7290–7293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaper N. L., Mann P. L., Shaper J. H. Cell surface galactosyltransferase: immunochemical localization. J Cell Biochem. 1985;28(3):229–239. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240280305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Hormonal regulation of mammalian glucose transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1059–1089. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Yver D. R., Hissin P. J., Wardzala L. J., Karnieli E., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transporters in the isolated rat adipose cells: characterization of subcellular fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 19;763(4):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Sarkar H. K., Kaback H. R., Lodish H. F. Cloning and functional expression in bacteria of a novel glucose transporter present in liver, intestine, kidney, and beta-pancreatic islet cells. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threadgold L. C., Coore H. G., Kuhn N. J. Monosaccharide transport into lactating-rat mammary acini. Biochem J. 1982 May 15;204(2):493–501. doi: 10.1042/bj2040493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threadgold L. C., Kuhn N. J. Monosaccharide transport in the mammary gland of the intact lactating rat. Biochem J. 1984 Feb 15;218(1):213–219. doi: 10.1042/bj2180213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon R. G., Finley E., Taylor E. Adenosine and the control of lipolysis in rat adipocytes during pregnancy and lactation. Biochem J. 1983 Oct 15;216(1):121–128. doi: 10.1042/bj2160121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon R. G., Flint D. J. Control of fatty acid synthesis in lactation. Proc Nutr Soc. 1983 Jun;42(2):315–331. doi: 10.1079/pns19830035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West D. W. Energy-dependent calcium sequestration activity in a Golgi apparatus fraction derived from lactating rat mammary glands. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 3;673(4):374–386. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90469-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. D., Kuhn N. J., Ward S. Permeability of lactating-rat mammary gland Golgi membranes to monosaccharides. Biochem J. 1980 Sep 15;190(3):621–624. doi: 10.1042/bj1900621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]