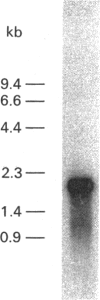
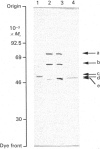
Abstract
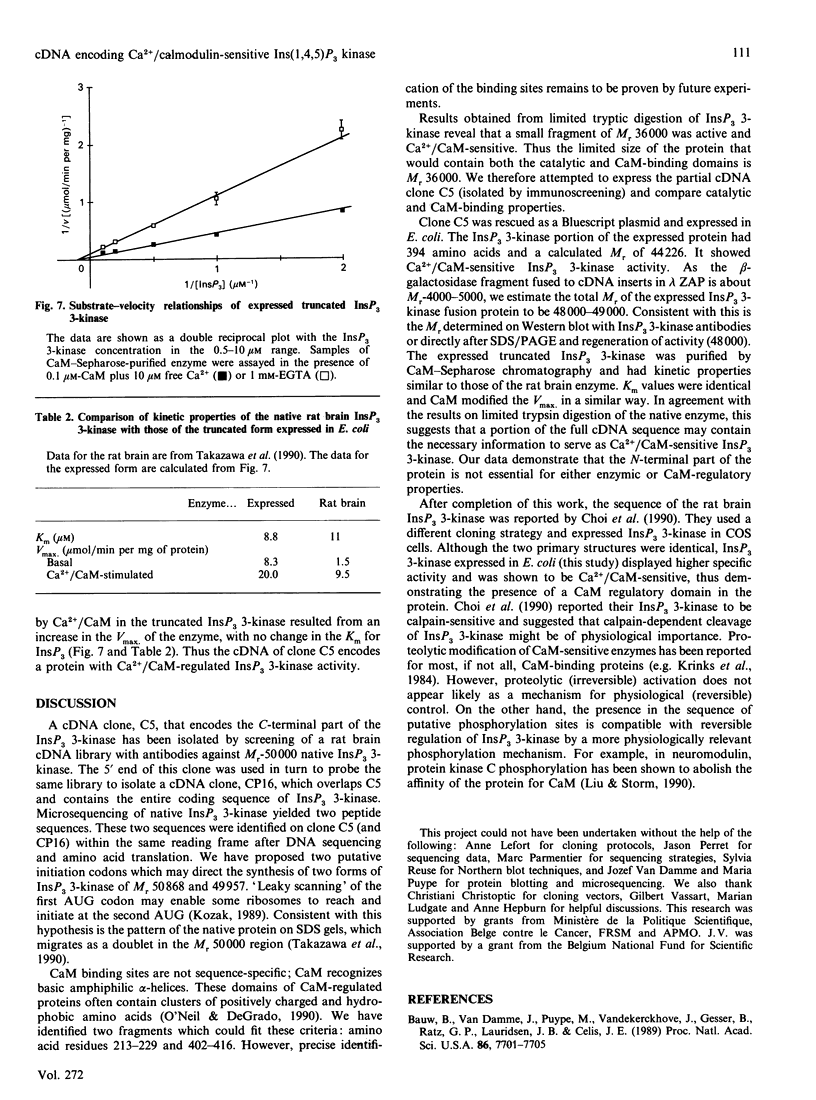
Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) 3-kinase catalyses the phosphorylation of InsP3 to inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate (InsP4). InsP3 3-kinase activity was stimulated by Ca2+ in the presence of calmodulin (CaM) and the protein was associated with two silver-stained bands which migrated with an apparent Mr of approx. 50,000 on SDS/polyacrylamide gels. Upon limited proteolysis with trypsin, the native InsP3 3-kinase was converted into polypeptides of Mr 44,000 and 36,000. Both tryptic fragments displayed InsP3 3-kinase activity that was Ca2+/CaM-sensitive. A cDNA clone, C5, that encodes the C-terminal part of the InsP3 3-kinase, was isolated by immunoscreening of a rat brain cDNA library. The 5' end of this clone was used in turn to probe the same library, yielding a clone (CP16) containing the entire coding sequence of InsP3 3-kinase. The encoding protein of 459 amino acids (calculated Mr 50,868) has several putative phosphorylation sites for cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, protein kinase C and CaM-dependent protein kinase II. When clone C5 was expressed in Escherichia coli, the truncated fusion protein showed Ca2+/CaM-sensitive InsP3 3-kinase activity. Our data demonstrate that the N-terminal part of the protein is not essential for either enzymic or CaM-regulatory properties.
Full text
PDF

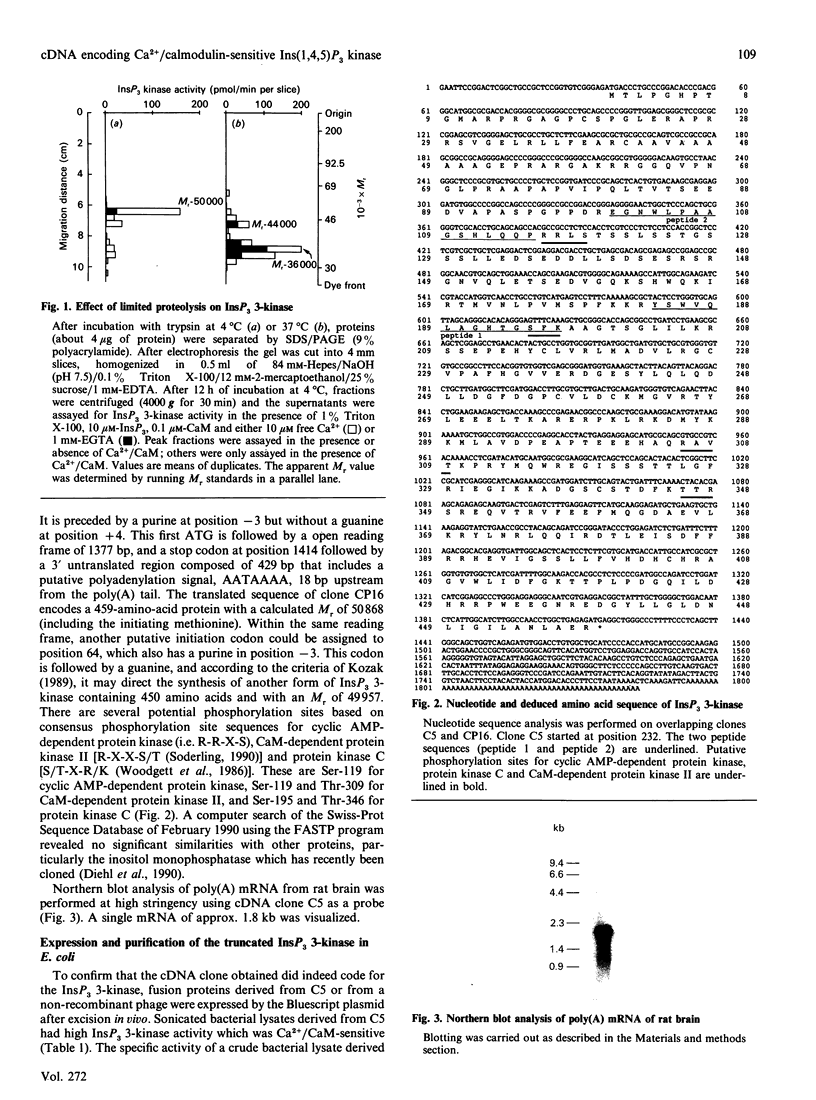
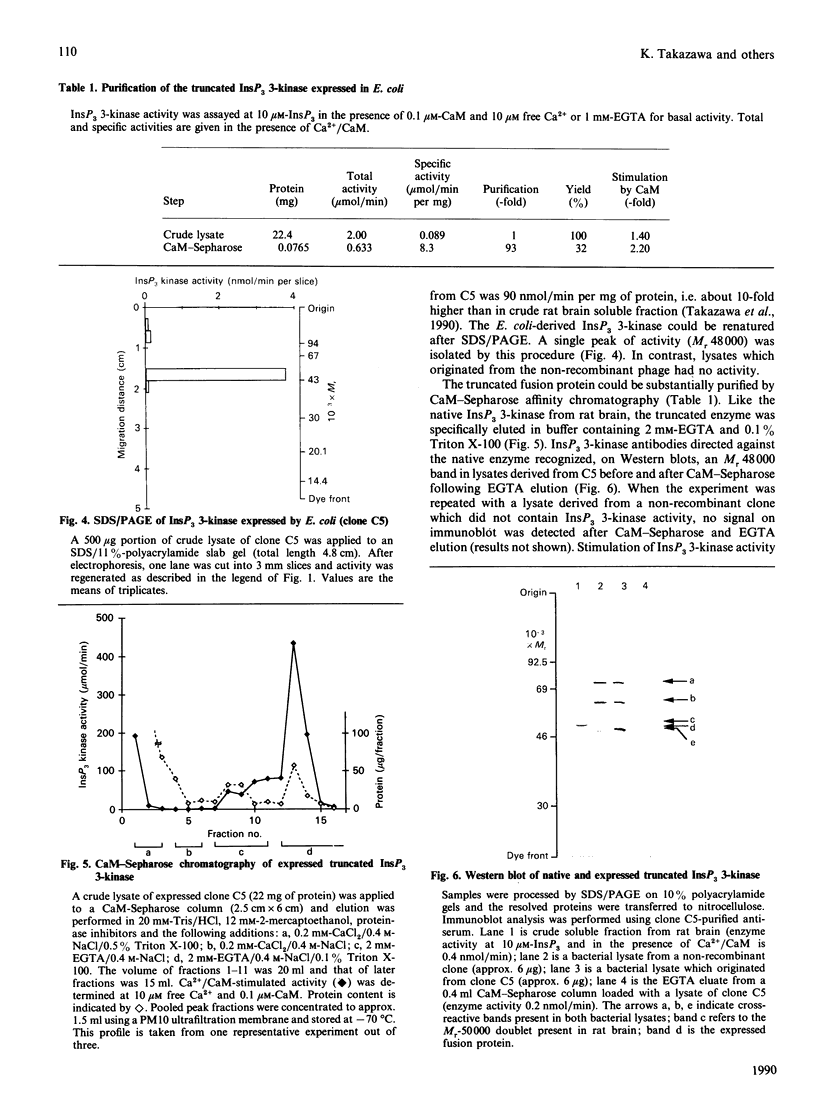

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biden T. J., Comte M., Cox J. A., Wollheim C. B. Calcium-calmodulin stimulates inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate kinase activity from insulin-secreting RINm5F cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9437–9440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi K. Y., Kim H. K., Lee S. Y., Moon K. H., Sim S. S., Kim J. W., Chung H. K., Rhee S. G. Molecular cloning and expression of a complementary DNA for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase. Science. 1990 Apr 6;248(4951):64–66. doi: 10.1126/science.2157285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl R. E., Whiting P., Potter J., Gee N., Ragan C. I., Linemeyer D., Schoepfer R., Bennett C., Dixon R. A. Cloning and expression of bovine brain inositol monophosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):5946–5949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. The inositol tris/tetrakisphosphate pathway--demonstration of Ins(1,4,5)P3 3-kinase activity in animal tissues. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):631–634. doi: 10.1038/320631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. M., Wasilenko W. J., Mattingly R. R., Weber M. J., Garrison J. C. Fibroblasts transformed with v-src show enhanced formation of an inositol tetrakisphosphate. Science. 1989 Oct 6;246(4926):121–124. doi: 10.1126/science.2506643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krinks M. H., Haiech J., Rhoads A., Klee C. B. Reversible and irreversible activation of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase: separation of the regulatory and catalytic domains by limited proteolysis. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;16:31–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. C., Storm D. R. Regulation of free calmodulin levels by neuromodulin: neuron growth and regeneration. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Mar;11(3):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90195-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manalan A. S., Klee C. B. Activation of calcineurin by limited proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4291–4295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. J., Downes C. P., Harden T. K., Michell R. H. Turkey erythrocytes possess a membrane-associated inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase that is activated by Ca2+ in the presence of calmodulin. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 1;248(2):489–493. doi: 10.1042/bj2480489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. P., Gallacher D. V., Irvine R. F., Petersen O. H. Synergism of inositol trisphosphate and tetrakisphosphate in activating Ca2+-dependent K+ channels. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):653–655. doi: 10.1038/330653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia M. A., McKeever B. M., Springer J. P., Lin T. Y., Williams H. R., Fluder E. M., Dorn C. P., Hoogsteen K. Structure of human neutrophil elastase in complex with a peptide chloromethyl ketone inhibitor at 1.84-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):7–11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil K. T., DeGrado W. F. How calmodulin binds its targets: sequence independent recognition of amphiphilic alpha-helices. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Feb;15(2):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90177-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmentier M., Lawson D. E., Vassart G. Human 27-kDa calbindin complementary DNA sequence. Evolutionary and functional implications. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):207–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13688.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Lee S. Y., Lee K. Y., Rhee S. G. Catalytic properties of inositol trisphosphate kinase: activation by Ca2+ and calmodulin. FASEB J. 1987 Nov;1(5):388–393. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.5.2824270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M., Elledge S., Sweetser D., Young R. A., Davis R. W. Lambda gt 11: gene isolation with antibody probes and other applications. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:107–128. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soderling T. R. Protein kinases. Regulation by autoinhibitory domains. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):1823–1826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takazawa K., Lemos M., Delvaux A., Lejeune C., Dumont J. E., Erneux C. Rat brain inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase. Ca2(+)-sensitivity, purification and antibody production. Biochem J. 1990 May 15;268(1):213–217. doi: 10.1042/bj2680213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takazawa K., Passareiro H., Dumont J. E., Erneux C. Ca2+/calmodulin-sensitive inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase in rat and bovine brain tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 16;153(2):632–641. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takazawa K., Passareiro H., Dumont J. E., Erneux C. Purification of bovine brain inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase. Identification of the enzyme by sodium dodecyl sulphate/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 15;261(2):483–488. doi: 10.1042/bj2610483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgett J. R., Gould K. L., Hunter T. Substrate specificity of protein kinase C. Use of synthetic peptides corresponding to physiological sites as probes for substrate recognition requirements. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):177–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Hirata M., Kuriyama H. Purification and characterization of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase from pig aortic smooth muscle. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):129–134. doi: 10.1042/bj2510129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]