Abstract
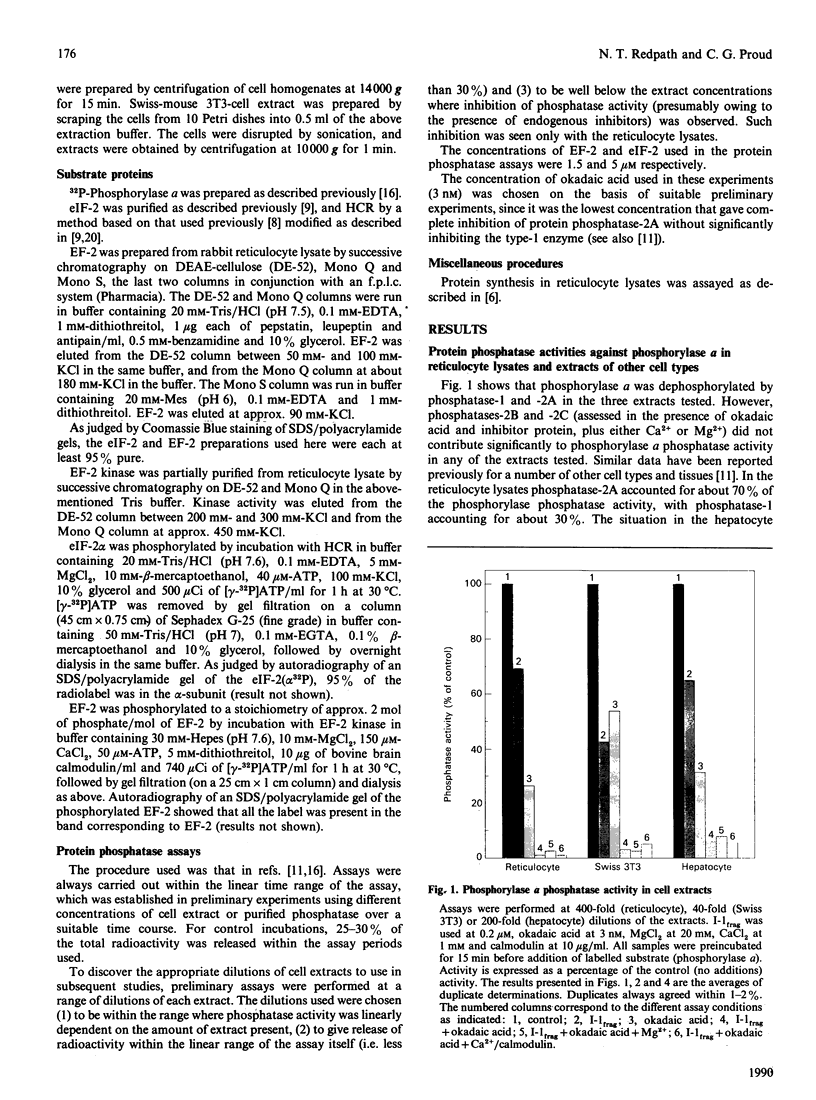
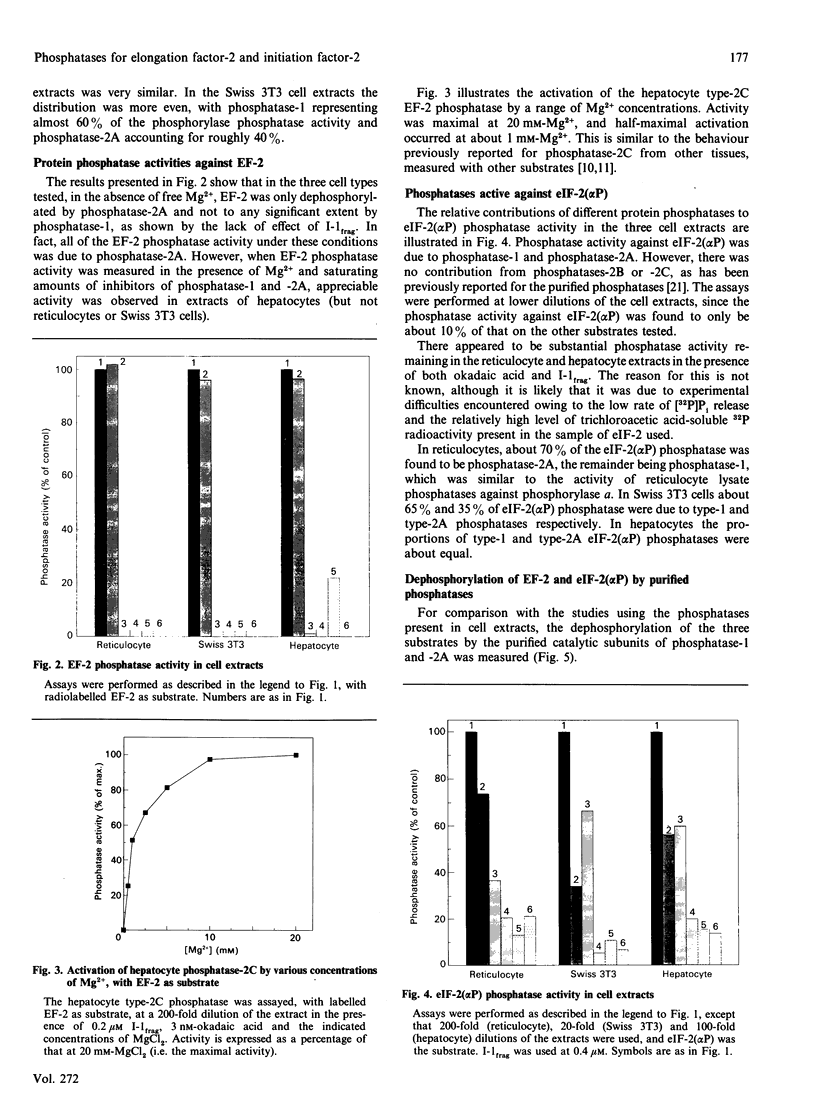
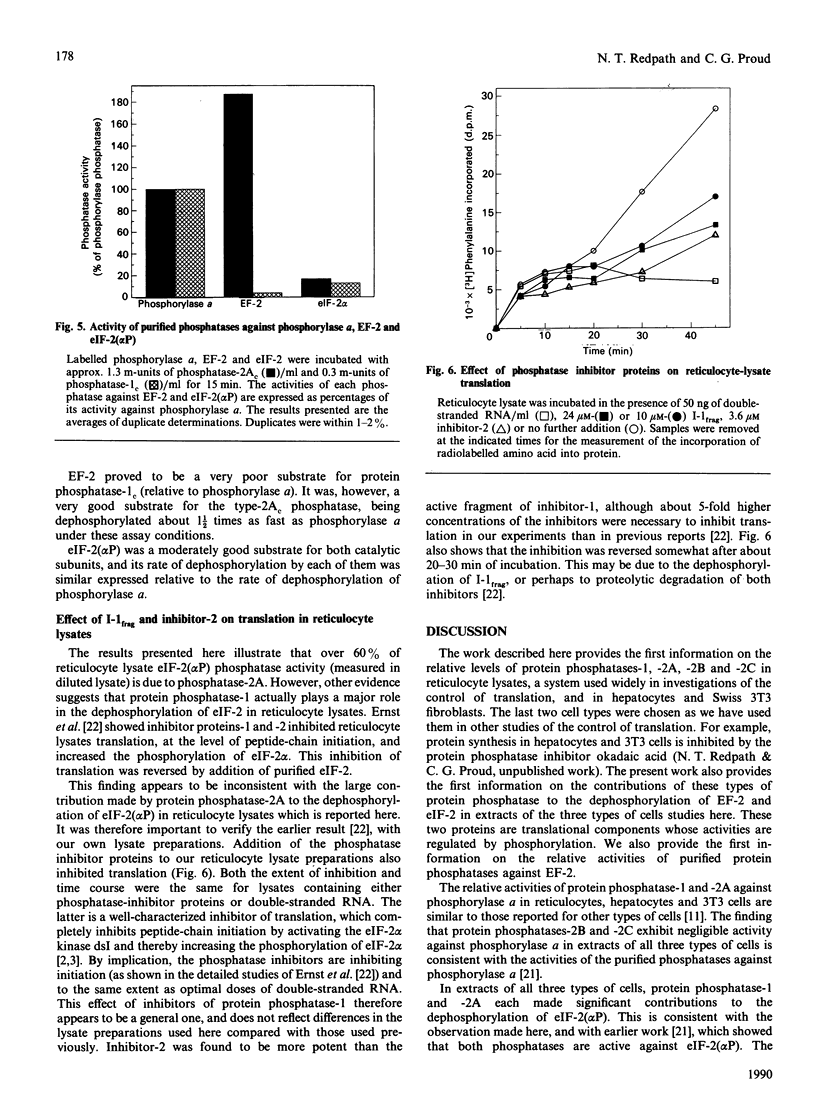
The protein phosphatases active against phosphorylase a, elongation factor-2 (EF-2) and the alpha-subunit of initiation factor-2 (eIF-2) [eIF-2(alpha P)] were studied in extracts of rabbit reticulocytes. Swiss-mouse 3T3 fibroblasts and rat hepatocytes, by use of the specific phosphatase inhibitors okadaic acid and inhibitor proteins-1 and -2. In all three extracts tested, both phosphatase-1 and phosphatase-2A contributed to overall phosphatase activity against phosphorylase and eIF-2(alpha P), but phosphatase-2B and -2C did not. In contrast, only protein phosphatase-2A was active against EF-2. Furthermore, in hepatocytes there was substantial type-2C phosphatase activity against EF-2, but not against phosphorylase or eIF-2 alpha. These findings in cell extracts were borne out by data obtained by studying the activities of purified protein phosphatase-1 and -2A against eIF-2(alpha P) and eIF-2(alpha P) was a moderately good substrate for both enzymes (relative to phosphorylase a). In contrast, EF-2 was a very poor substrate for protein phosphatase-1, but was dephosphorylated faster than phosphorylase a by protein phosphatase-2A. The implications of these findings for the control of translation and their relationships to previous work are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken A., Cohen P. Isolation and characterisation of active fragments of protein phosphatase inhibitor-1 from rabbit skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1982 Oct 4;147(1):54–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. P., McNall S. J., Krebs E. G., Fischer E. H. Stimulation of protein phosphatase activity by insulin and growth factors in 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6257–6261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. J., Colthurst D. R., Proud C. G. Structure and phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2. Casein kinase 2 and protein kinase C phosphorylate distinct but adjacent sites in the beta-subunit. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 22;968(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Alemany S., Hemmings B. A., Resink T. J., Strålfors P., Tung H. Y. Protein phosphatase-1 and protein phosphatase-2A from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1988;159:390–408. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)59039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Cohen P. T. Protein phosphatases come of age. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21435–21438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Foulkes J. G., Holmes C. F., Nimmo G. A., Tonks N. K. Protein phosphatase inhibitor-1 and inhibitor-2 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1988;159:427–437. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)59042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Klumpp S., Schelling D. L. An improved procedure for identifying and quantitating protein phosphatases in mammalian tissues. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):596–600. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80803-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. Phosphorylase kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:243–250. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99059-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colthurst D. R., Campbell D. G., Proud C. G. Structure and regulation of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF-2. Sequence of the site in the alpha subunit phosphorylated by the haem-controlled repressor and by the double-stranded RNA-activated inhibitor. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jul 15;166(2):357–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13523.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch D., Safer B. The association of eIF-2 with Met-tRNAi or eIF-2B alters the specificity of eIF-2 phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10363–10368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donella Deana A., Mac Gowan C. H., Cohen P., Marchiori F., Meyer H. E., Pinna L. A. An investigation of the substrate specificity of protein phosphatase 2C using synthetic peptide substrates; comparison with protein phosphatase 2A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Feb 19;1051(2):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90194-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Hershey J. W. Heat shock-induced translational alterations in HeLa cells. Initiation factor modifications and the inhibition of translation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11882–11889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Hershey J. W. Regulation of initiation factors during translational repression caused by serum depletion. Covalent modification. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5493–5497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst V., Levin D. H., Foulkes J. G., London I. M. Effects of skeletal muscle protein phosphatase inhibitor-2 on protein synthesis and protein phosphorylation in rabbit reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7092–7096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Hunt T., Jackson R. J. Analysis of phosphorylation of protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-2 by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Sep 1;89(2):517–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12556.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes J. G., Ernst V., Levin D. H. Separation and identification of type 1 and type 2 protein phosphatases from rabbit reticulocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1439–1443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grankowski N., Lehmusvirta D., Kramer G., Hardesty B. Partial purification and characterization of reticulocyte phosphatase with activity for phosphorylated peptide initiation factor 2. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):310–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Redman R., Kaplansky D. A. Evidence that the primary effect of phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2(alpha) in rabbit reticulocyte lysate is inhibition of the release of eukaryotic initiation factor-2.GDP from 60 S ribosomal subunits. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9491–9500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Wing M., Rundquist C., Rubino M. S. Evidence that phosphorylation of eIF-2(alpha) prevents the eIF-2B-mediated dissociation of eIF-2 X GDP from the 60 S subunit of complete initiation complexes. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6899–6907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gschwendt M., Kittstein W., Mieskes G., Marks F. A type 2A protein phosphatase dephosphorylates the elongation factor 2 and is stimulated by the phorbol ester TPA in mouse epidermis in vivo. FEBS Lett. 1989 Nov 6;257(2):357–360. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81571-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Protein phosphorylation controls translation rates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20823–20826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen T. S., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 1. Classification and substrate specificities. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 2;132(2):255–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Hunt T. A novel approach to the isolation of rabbit reticulocyte haem-controlled eIF-2 alpha protein kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 18;826(4):224–228. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montine K. S., Henshaw E. C. Serum growth factors cause rapid stimulation of protein synthesis and dephosphorylation of eIF-2 in serum deprived Ehrlich cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 14;1014(3):282–288. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90224-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn A. C., Palfrey H. C. Identification of the major Mr 100,000 substrate for calmodulin-dependent protein kinase III in mammalian cells as elongation factor-2. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17299–17303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain V. M. Initiation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):625–637. doi: 10.1042/bj2350625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pato M. D., Adelstein R. S., Crouch D., Safer B., Ingebritsen T. S., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 4. Classification of two homogeneous myosin light chain phosphatases from smooth muscle as protein phosphatase-2A1 and 2C, and a homogeneous protein phosphatase from reticulocytes active on protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-2 as protein phosphatase-2A2. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 2;132(2):283–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07360.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price N. T., Nakielny S. F., Clark S. J., Proud C. G. The two forms of the beta-subunit of initiation factor-2 from reticulocyte lysates arise from proteolytic degradation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 7;1008(2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(80)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud C. G., Clemens M. J., Pain V. M. Regulation of binding of initiator tRNA to eukaryotic initiation factor eIF-2. Effects of the haem-controlled repressor on the kinetics of ternary complex formation. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 8;148(2):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80810-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redpath N. T., Proud C. G. The tumour promoter okadaic acid inhibits reticulocyte-lysate protein synthesis by increasing the net phosphorylation of elongation factor 2. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 15;262(1):69–75. doi: 10.1042/bj2620069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands A. G., Montine K. S., Henshaw E. C., Panniers R. Physiological stresses inhibit guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor in Ehrlich cells. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jul 15;175(1):93–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryazanov A. G., Davydova E. K. Mechanism of elongation factor 2 (EF-2) inactivation upon phosphorylation. Phosphorylated EF-2 is unable to catalyze translocation. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81452-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryazanov A. G., Shestakova E. A., Natapov P. G. Phosphorylation of elongation factor 2 by EF-2 kinase affects rate of translation. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):170–173. doi: 10.1038/334170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. A., Crouch D., Cohen P., Safer B. Classification of an eIF-2phosphatase as a type-2 protein phosphatase. FEBS Lett. 1980 Sep 22;119(1):16–19. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80988-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas N. S., Matts R. L., Petryshyn R., London I. M. Distribution of reversing factor in reticulocyte lysates during active protein synthesis and on inhibition by heme deprivation or double-stranded RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6998–7002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tóth B., Bollen M., Stalmans W. Acute regulation of hepatic protein phosphatases by glucagon, insulin, and glucose. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14061–14066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargas A. M., Halestrap A. P., Denton R. M. The effects of glucagon, phenylephrine and insulin on the phosphorylation of cytoplasmic, mitochondrial and membrane-bound proteins of intact liver cells from starved rats. Biochem J. 1982 Oct 15;208(1):221–229. doi: 10.1042/bj2080221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


