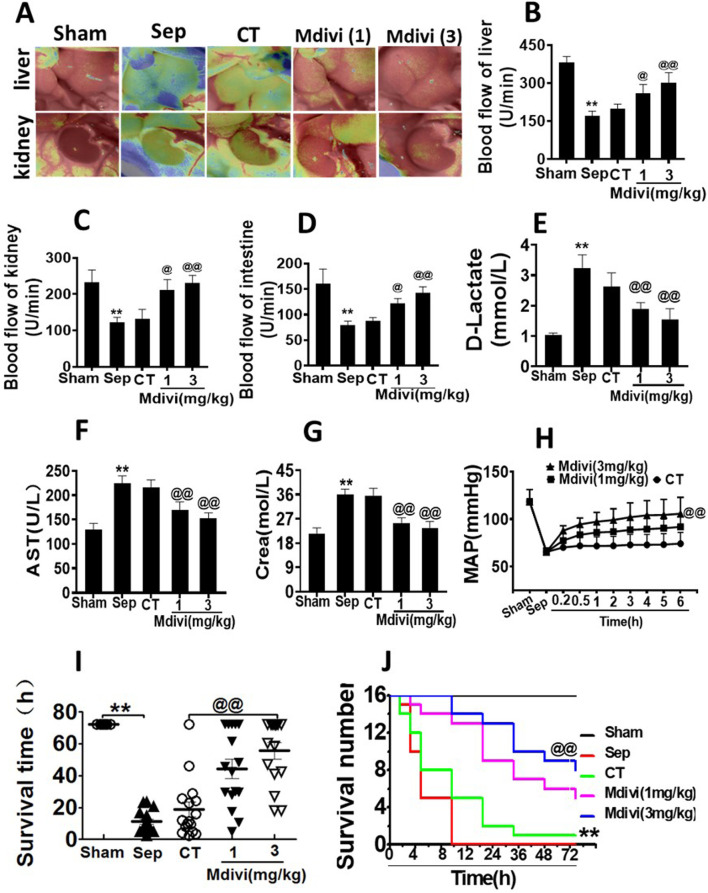
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 2 as published. Figure 2A depicts blood flow experiments. Upon comparison, we confirmed the images “Sep” and “Mdivi (1)” in the “kidney” blood flow to be identical images; specifically, the image of “Mdivi (1)” in the “kidney” blood flow was misused. The corrected Figure 2 and its caption appear below.
FIGURE 2.
Effects of Mdivi-1 on vital organ function in septic rats. (A): blood flow of liver and kidney with the Peri Cam PSI System. (B–D): blood flow of liver, kidney and intestine with laser Doppler imaging. (E): intestinal function (D-lactate). (F): aspartate aminotransferase (AST). (G): kidney function creatinine (Crea). (H): Time-lapse monitoring of mean arterial pressure after Mdivi-1 treatment. After CLP 12 h, the mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) was monitored after administration of 12 min, 30 min, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 h by femoral artery intubation. (I, J): Effects of Mdivi-1 on survival in septic rats (n = 16). Rats were randomly divided into five groups, after 6 h of treatment, blood vessels were ligated, muscle and skin layers were sutured, and the average survival time and survival rate of rats within 72 h were observed. **p < 0.01 versus Sham. @p < 0.05 and @@p < 0.01 versus conventional treatment (CT) group. Sham, the control group; Sep, sepsis; CT, conventional treatment. 1: Mdivi-1 (1 mg/kg). 3: Mdivi-1 (3 mg/kg).
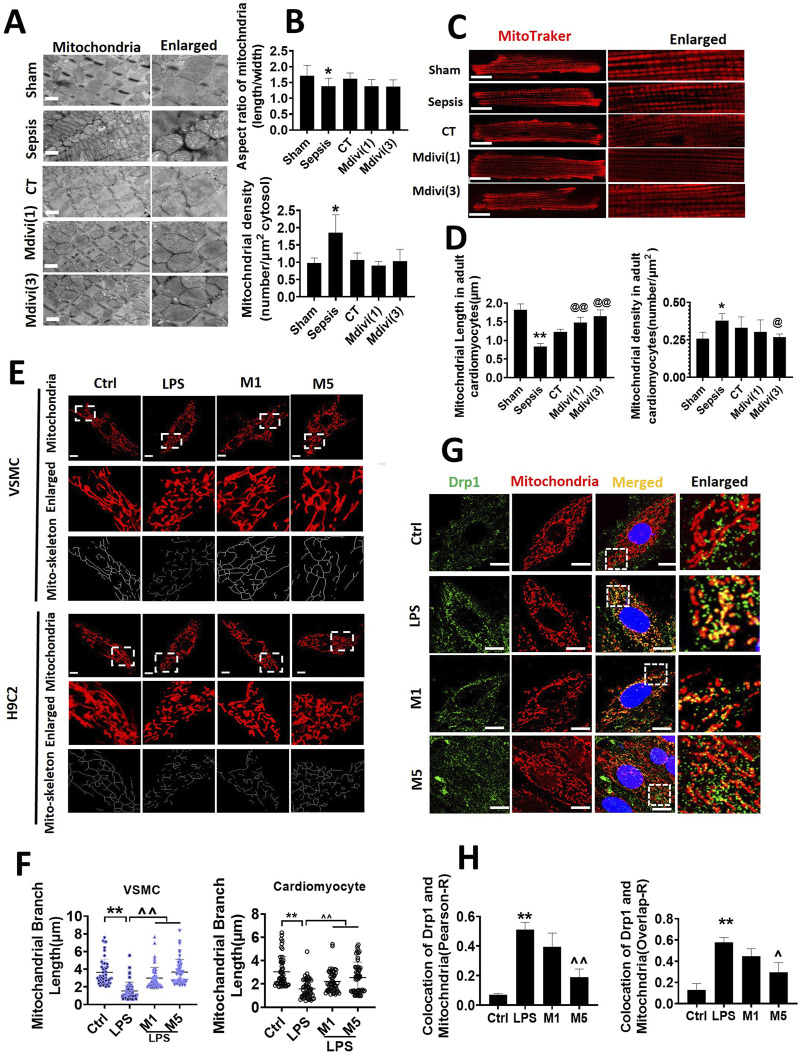
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 3 as published. Figure 3C depicts mitochondrial morphology experiments of acutely isolated cardiomyocytes. Upon comparison, we confirmed the images in “CT”and “Mdivi (1)” to be identical images; specifically, the image of “Mdivi (1)” was misused. The corrected Figure 3 and its caption appear below.
FIGURE 3.
Effects of Mdivi-1 on mitochondrial morphology in septic rats. (A, B): mitochondrial morphology of heart by transmission electron microscope (TEM) and statistical analysis (bar = 500 nm). (C, D): mitochondrial morphology of acute isolation of cardiomyocytes in vitro and statistical analysis (bar = 25 μm). (E, F): mitochondrial morphology of cardiomyocytes and vascular smooth muscle cell by laser confocal microscopy and statistical analysis (bar = 25 μm); (G, H): colocalization of mitochondria and Drp1 (bar = 25 μm). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus sham or ctrl. @p < 0.05, @@p < 0.01 versus conventional treatment (CT) group.^p < 0.05,^p < 0.01 versus LPS. Sham; the control group; Sep, sepsis; CT, conventional treatment. 1: Mdivi-1 (1 mg/kg). 3: Mdivi-1 (3 mg/kg). H9C2: cardiomyocytes. VSMC: vascular smooth muscle cell. Ctrl: control group. M1: Mdivi-1 (10 μM). M5: Mdivi-1 (50 μM).
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.