Abstract
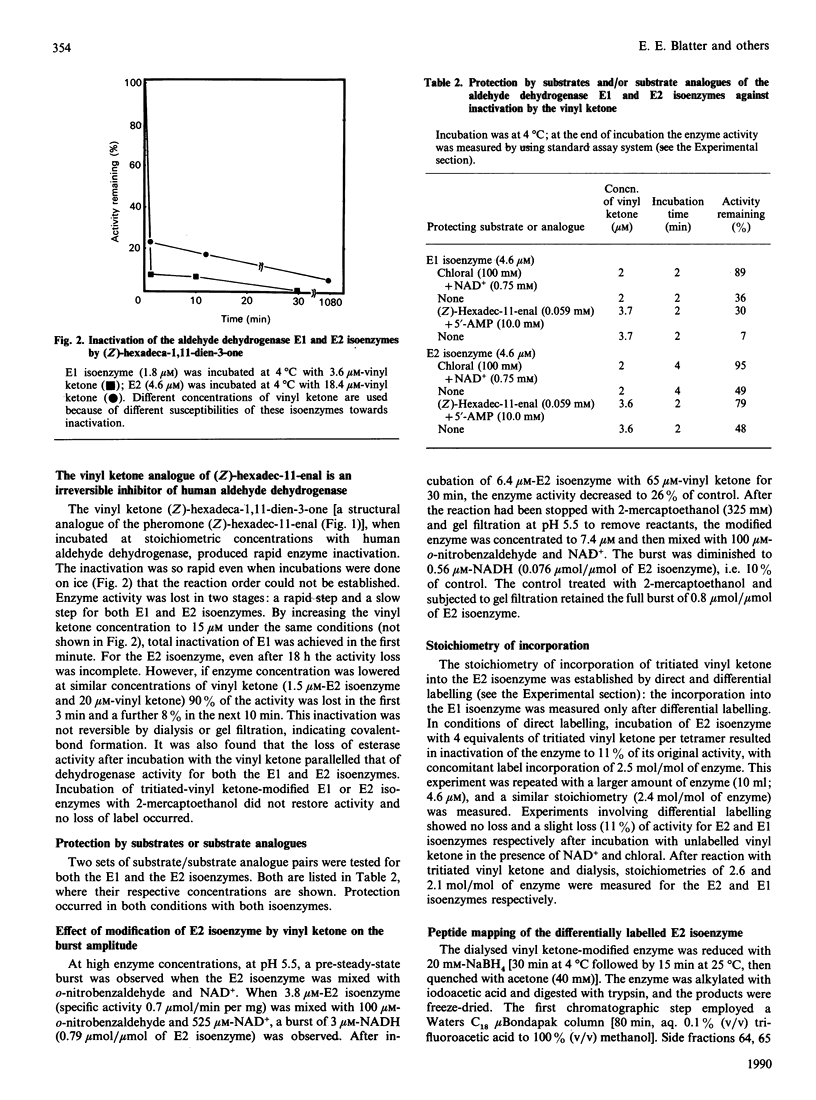
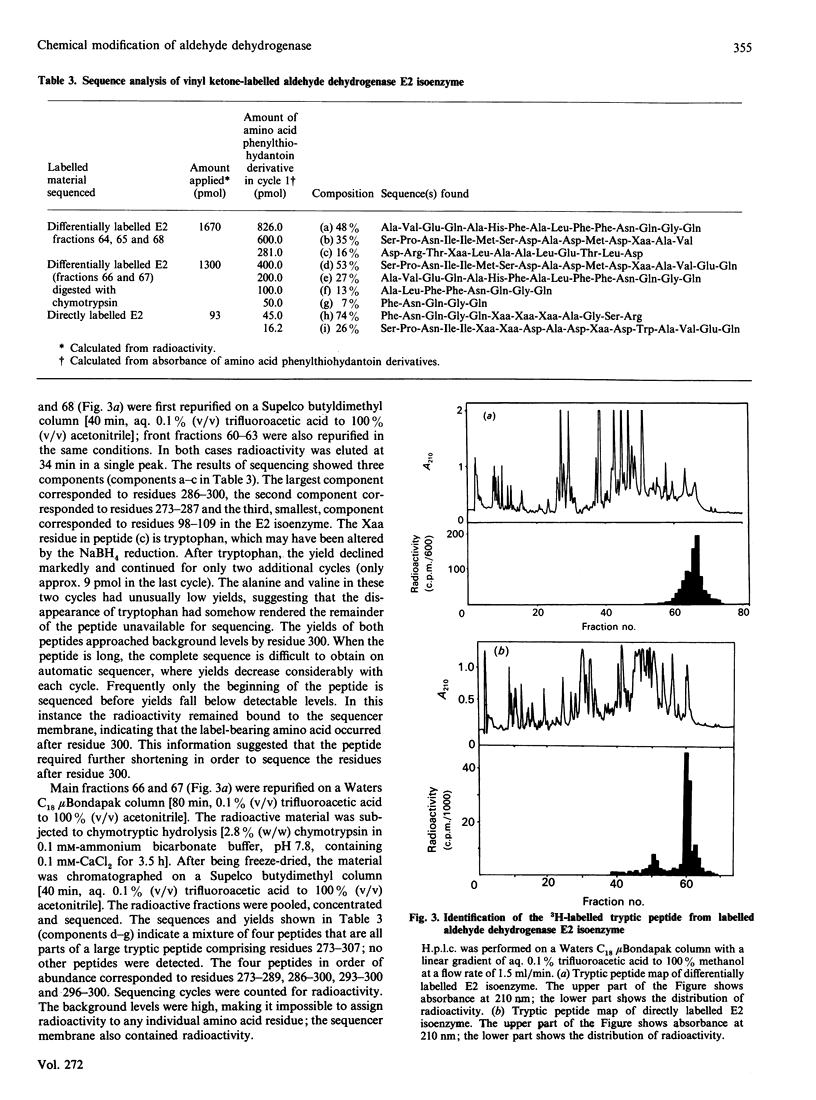
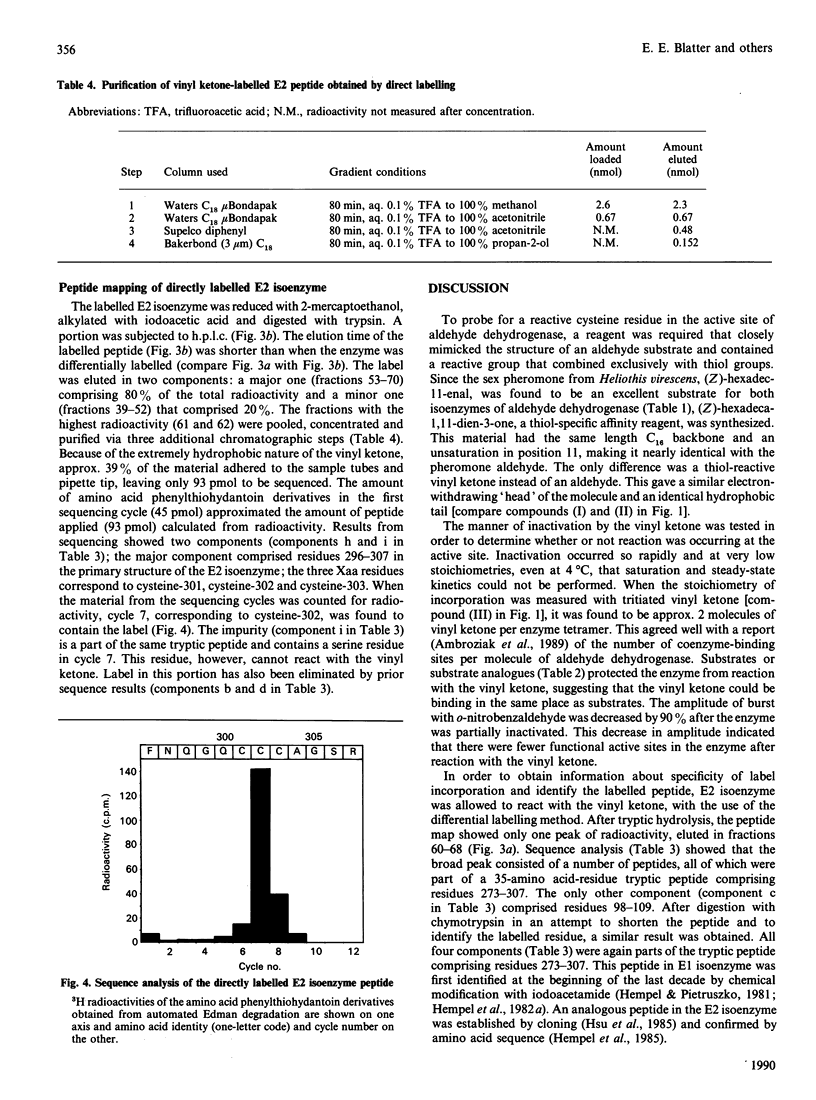
A major component of the sex pheromone from the tobacco budworm moth Heliothis virescens is a C16 straight-chain aldehyde with a single unsaturation at the eleventh position. The sex pheromones are inactivated when metabolized to their corresponding acids by insect aldehyde dehydrogenase. During this investigation it was demonstrated that the C16 aldehyde is a good substrate for human aldehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.3) isoenzymes E1 and E2 with Km and Kcat. values at pH 7.0 of 2 microM and 0.4 mumol of NADH/min per mg and of 0.6 microM and 0.24 mumol of NADH/min per mg respectively. A vinyl ketone analogue of the pheromone inhibited insect pheromone metabolism; it also inactivated human aldehyde dehydrogenase. Total inactivation of both isoenzymes was achieved at stoichiometric (equal or less than the subunit number) concentrations of vinyl ketone, incorporating 2.1-2.6 molecules/molecule of enzyme. Substrate protection was observed in the presence of the parent aldehyde and 5'-AMP. Peptide maps of tryptic digests of the E2 isoenzyme modified with 3H-labelled vinyl ketone showed that incorporation occurred into a single peptide peak. The labelled peptide of E2 isoenzyme was further purified on h.p.l.c. and sequenced. The label was incorporated into cysteine-302 in the primary structure of E2 isoenzyme, thus indicating that cysteine-302 is located in the aldehyde substrate area of the active site of aldehyde dehydrogenase. Affinity labelling of aldehyde dehydrogenase with vinyl ketones may prove to be of general utility in biochemical studies of these enzymes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abriola D. P., Fields R., Stein S., MacKerell A. D., Jr, Pietruszko R. Active site of human liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5679–5684. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abriola D. P., MacKerell A. D., Jr, Pietruszko R. Correlation of loss of activity of human aldehyde dehydrogenase with reaction of bromoacetophenone with glutamic acid-268 and cysteine-302 residues. Partial-sites reactivity of aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 15;266(1):179–187. doi: 10.1042/bj2660179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambroziak W., Kosley L. L., Pietruszko R. Human aldehyde dehydrogenase: coenzyme binding studies. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 27;28(13):5367–5373. doi: 10.1021/bi00439a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley P. D., Dunn M. F. Observation of acyl-enzyme intermediates in the sheep liver aldehyde dehydrogenase catalytic mechanism via rapid-scanning UV-visible spectroscopy. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;114:23–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson F. M. Studies on the mechanism of sheep liver cytosolic aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1985 Jan 1;225(1):159–165. doi: 10.1042/bj2250159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn T. J., Koleske A. J., Lindahl R., Pitot H. C. Phenobarbital-inducible aldehyde dehydrogenase in the rat. cDNA sequence and regulation of the mRNA by phenobarbital in responsive rats. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13057–13065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrés J., Guan K. L., Weiner H. Primary structures of rat and bovine liver mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenases deduced from cDNA sequences. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Mar 1;180(1):67–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel J. D., Pietruszko R. Selective chemical modification of human liver aldehyde dehydrogenases E1 and E2 by iodoacetamide. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10889–10896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel J. D., Reed D. M., Pietruszko R. Human aldehyde dehydrogenase: improved purification procedure and comparison of homogeneous isoenzymes E1 and E2. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1982 Summer;6(3):417–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1982.tb05001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel J., Kaiser R., Jörnvall H. Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase from human liver. Primary structure, differences in relation to the cytosolic enzyme, and functional correlations. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Nov 15;153(1):13–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel J., Pietruszko R., Fietzek P., Jörnvall H. Identification of a segment containing a reactive cysteine residue in human liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase (isoenzyme E1). Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6834–6838. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hempel J., von Bahr-Lindström H., Jörnvall H. Aldehyde dehydrogenase from human liver. Primary structure of the cytoplasmic isoenzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 15;141(1):21–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu L. C., Tani K., Fujiyoshi T., Kurachi K., Yoshida A. Cloning of cDNAs for human aldehyde dehydrogenases 1 and 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3771–3775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson J., von Bahr-Lindström H., Jeck R., Woenckhaus C., Jörnvall H. Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase from horse liver. Correlations of the same species variants for both the cytosolic and the mitochondrial forms of an enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Mar 15;172(3):527–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. E., Jr, Brennan M. D., Hempel J., Lindahl R. Cloning and complete nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA encoding a catalytically functional tumor-associated aldehyde dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1782–1786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok M., Oldenhuis R., van der Linden M. P., Meulenberg C. H., Kingma J., Witholt B. The Pseudomonas oleovorans alkBAC operon encodes two structurally related rubredoxins and an aldehyde dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5442–5451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKerell A. D., Jr, Blatter E. E., Pietruszko R. Human aldehyde dehydrogenase: kinetic identification of the isozyme for which biogenic aldehydes and acetaldehyde compete. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1986 Jun;10(3):266–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1986.tb05087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKerell A. D., Jr, MacWright R. S., Pietruszko R. Bromoacetophenone as an affinity reagent for human liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5182–5189. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett M., Gwynne D. I., Buxton F. P., Elliott R., Davies R. W., Lockington R. A., Scazzocchio C., Sealy-Lewis H. M. Cloning and characterization of the aldA gene of Aspergillus nidulans. Gene. 1987;51(2-3):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasayco M. L., Prestwich G. D. A specific affinity reagent to distinguish aldehyde dehydrogenases and oxidases. Enzymes catalyzing aldehyde oxidation in an adult moth. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3094–3101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasayco M. L., Prestwich G. D. Aldehyde-oxidizing enzymes in an adult moth: in vitro study of aldehyde metabolism in Heliothis virescens. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 May 1;278(2):444–451. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu G. C., Weiner H. Evidence for two distinct active sites on aldehyde dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1218–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu G. C., Weiner H. Identification of the cysteine residue in the active site of horse liver mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1212–1217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yun S. L., Suelter C. H. A simple method for calculating Km and V from a single enzyme reaction progress curve. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 11;480(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90315-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bahr-Lindström H., Hempel J., Jörnvall H. The cytoplasmic isoenzyme of horse liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Relationship to the corresponding human isoenzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 15;141(1):37–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bahr-Lindström H., Jeck R., Woenckhaus C., Sohn S., Hempel J., Jörnvall H. Characterization of the coenzyme binding site of liver aldehyde dehydrogenase: differential reactivity of coenzyme analogues. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 8;24(21):5847–5851. doi: 10.1021/bi00342a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


