Abstract
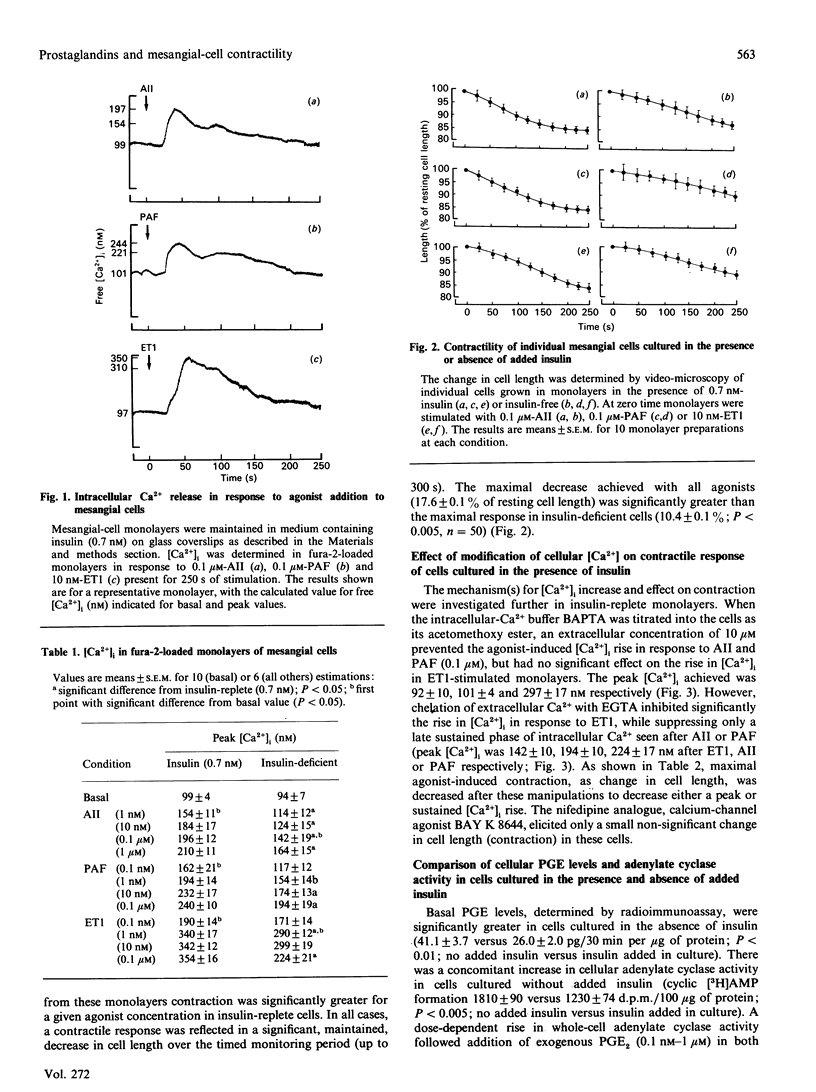
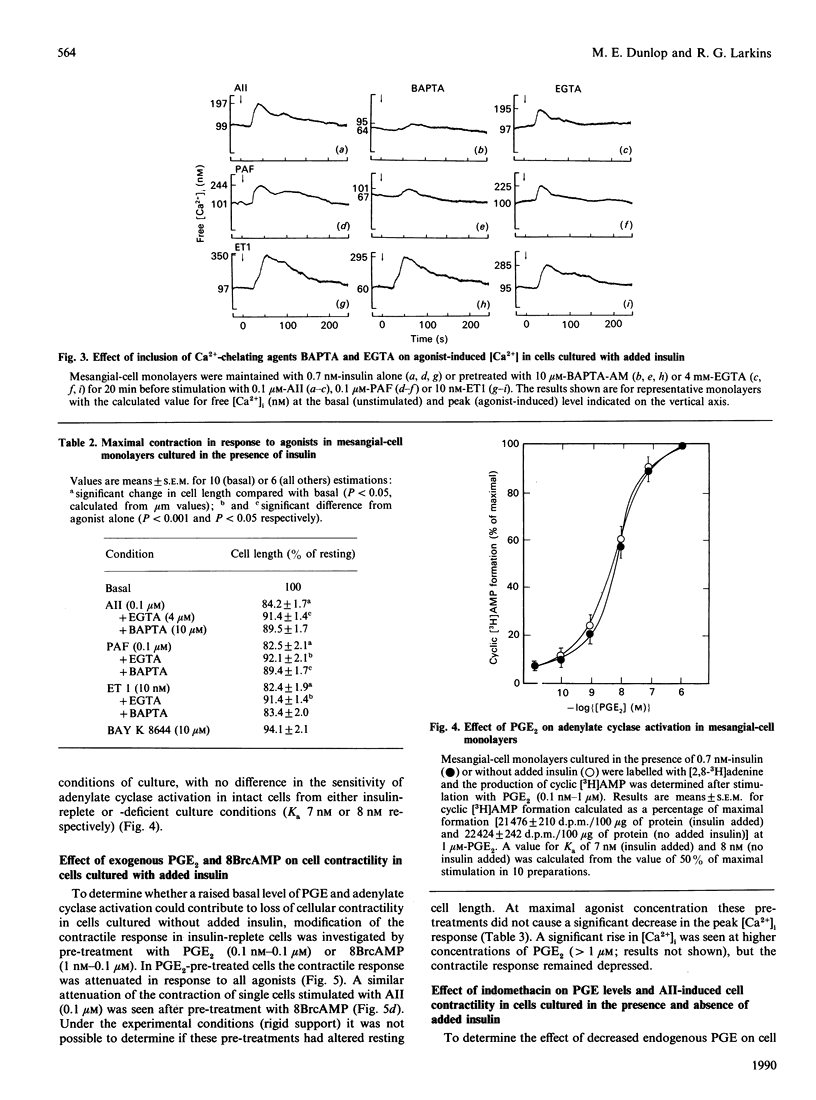
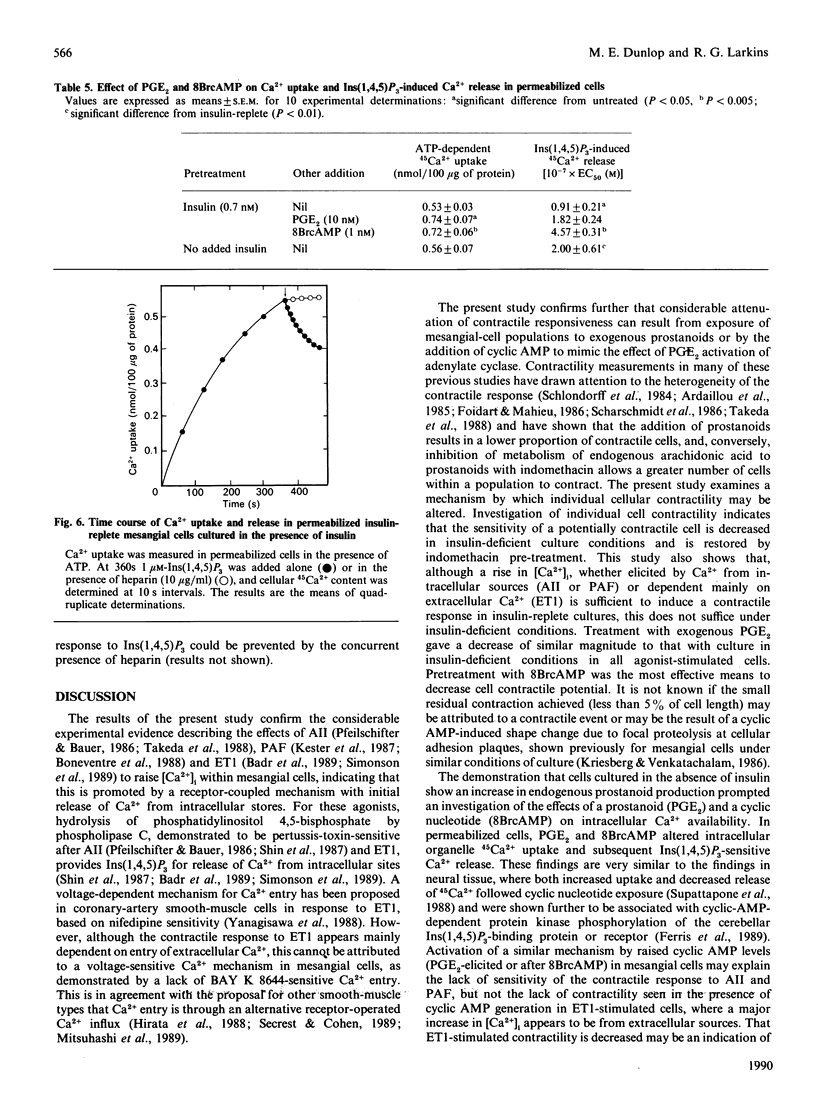
Culture of glomerular mesangial cells in the absence of insulin decreased the degree of contraction of individual cells in response to vasoconstrictive agonists, angiotensin II, platelet-activating factor and endothelin 1, as compared with cells cultured in the presence of insulin (0.7 nM). This change was associated with a decreased sensitivity of the intracellular Ca2+ response to vasoactive agents in fura-2-loaded cells and with an increase in the basal level of prostanoid [prostaglandins (PG) E1 and E2] production estimated by radioimmunoassay. Addition of exogenous PGE2 to insulin-exposed cells decreased the contractile response to that observed in insulin-deficient cells. Inclusion of 8-bromo cyclic AMP had a similar effect. In 45Ca2(+)-release studies it was shown that, in saponin-permeabilized insulin-exposed cells, preincubation with exogenous PGE2 or 8-bromo cyclic AMP decreased the sensitivity of 45Ca2+ release in response to Ins(1,4,5)P3, as demonstrated by an increase in the EC50 (concn. giving half-maximal effect) to 0.182 +/- 0.024 microM and 0.457 +/- 0.031 microM respectively, as compared with untreated permeabilized cells (EC50 0.091 +/- 0.021 microM). A similar decrease in Ins(1,4,5)P3-sensitive 45Ca2+ release was seen in permeabilized cells from insulin-free conditions of culture (EC50 0.20 +/- 0.061 microM). As altered glomerular haemodynamics are found in insulinopaenic diabetic conditions, it is proposed that a decrease in intracellular Ca2+ availability in response to vasoactive agonists and consequent decrease in mesangial-cell contractility contributes to the hyperfiltration seen in this condition.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S., Conti M. A., Hathaway D. R., Klee C. B. Phosphorylation of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase by the catalytic subunit of adenosine 3': 5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8347–8350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardaillou N., Hagege J., Nivez M. P., Ardaillou R., Schlondorff D. Vasoconstrictor-evoked prostaglandin synthesis in cultured human mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 2):F240–F246. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.2.F240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badr K. F., Murray J. J., Breyer M. D., Takahashi K., Inagami T., Harris R. C. Mesangial cell, glomerular and renal vascular responses to endothelin in the rat kidney. Elucidation of signal transduction pathways. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):336–342. doi: 10.1172/JCI113880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett R., Scharschmidt L., Ko Y. H., Schlondorff D. Comparison of glomerular and mesangial prostaglandin synthesis and glomerular contraction in two rat models of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1987 Dec;36(12):1468–1475. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.12.1468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biden T. J., Altin J. G., Karjalainen A., Bygrave F. L. Stimulation of hepatic inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate kinase activity by Ca2+-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 15;256(3):697–701. doi: 10.1042/bj2560697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre J. V., Weber P. C., Gronich J. H. PAF and PDGF increase cytosolic [Ca2+] and phospholipase activity in mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jan;254(1 Pt 2):F87–F94. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.1.F87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven P. A., Caines M. A., DeRubertis F. R. Sequential alterations in glomerular prostaglandin and thromboxane synthesis in diabetic rats: relationship to the hyperfiltration of early diabetes. Metabolism. 1987 Jan;36(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(87)90070-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven P. A., Davidson C. M., DeRubertis F. R. Increase in diacylglycerol mass in isolated glomeruli by glucose from de novo synthesis of glycerolipids. Diabetes. 1990 Jun;39(6):667–674. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.6.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven P. A., DeRubertis F. R. Protein kinase C is activated in glomeruli from streptozotocin diabetic rats. Possible mediation by glucose. J Clin Invest. 1989 May;83(5):1667–1675. doi: 10.1172/JCI114066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven P. A., Patterson M. C., DeRubertis F. R. Role of enhanced arachidonate availability through phospholipase A2 pathway in mediation of increased prostaglandin synthesis by glomeruli from diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1988 Apr;37(4):429–435. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.4.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop M. E., Larkins R. G. Effects of phosphatidic acid on islet cell phosphoinositide hydrolysis, Ca2+, and adenylate cyclase. Diabetes. 1989 Sep;38(9):1187–1192. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.9.1187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop M. E., Larkins R. G. GTP- and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced release of 45Ca2+ from a membrane store co-localized with pancreatic-islet-cell plasma membrane. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 1;253(1):67–72. doi: 10.1042/bj2530067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin L. D., Ichikawa I., Brenner B. M. Hormonal modulation of glomerular function. Am J Physiol. 1983 Feb;244(2):F95–104. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.2.F95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris C. D., Huganir R. L., Supattapone S., Snyder S. H. Purified inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor mediates calcium flux in reconstituted lipid vesicles. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):87–89. doi: 10.1038/342087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foidart J. B., Mahieu P. Glomerular mesangial cell contractility in vitro is controlled by an angiotensin-prostaglandin balance. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1986 Sep;47(1-2):163–173. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(86)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh T. K., Eis P. S., Mullaney J. M., Ebert C. L., Gill D. L. Competitive, reversible, and potent antagonism of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-activated calcium release by heparin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11075–11079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halenda S. P., Banga H. S., Zavoico G. B., Lau L. F., Feinstein M. B. Synergistic release of arachidonic acid from platelets by activators of protein kinase C and Ca2+ ionophores. Evidence for the role of protein phosphorylation in the activation of phospholipase A2 and independence from the Na+/H+ exchanger. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 5;28(18):7356–7363. doi: 10.1021/bi00444a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassid A., Pidikiti N., Gamero D. Effects of vasoactive peptides on cytosolic calcium in cultured mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Dec;251(6 Pt 2):F1018–F1028. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.6.F1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. A., Larkins R. G. Alterations in distribution of cardiac output in experimental diabetes in rats. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 2):H571–H580. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.2.H571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Yoshimi H., Takata S., Watanabe T. X., Kumagai S., Nakajima K., Sakakibara S. Cellular mechanism of action by a novel vasoconstrictor endothelin in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 15;154(3):868–875. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houslay M. D. Insulin, glucagon and the receptor-mediated control of cyclic AMP concentrations in liver. Twenty-second Colworth medal lecture. Biochem Soc Trans. 1986 Apr;14(2):183–193. doi: 10.1042/bst0140183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa I., Miele J. F., Brenner B. M. Reversal of renal cortical actions of angiotensin II by verapamil and manganese. Kidney Int. 1979 Aug;16(2):137–147. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isacke C. M., Trowbridge I. S., Hunter T. Modulation of p36 phosphorylation in human cells: studies using anti-p36 monoclonal antibodies. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2745–2751. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamm K. E., Stull J. T. The function of myosin and myosin light chain kinase phosphorylation in smooth muscle. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1985;25:593–620. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.25.040185.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kester M., Menè P., Dubyak G. R., Dunn M. J. Elevation of cytosolic free calcium by platelet-activating factor in cultured rat mesangial cells. FASEB J. 1987 Sep;1(3):215–219. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.3.2442057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khanna N. C., Tokuda M., Waisman D. M. Phosphorylation of lipocortins in vitro by protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):547–554. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80208-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg J. I. Insulin requirement for contraction of cultured rat glomerular mesangial cells in response to angiotensin II: possible role for insulin in modulating glomerular hemodynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4190–4192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg J. I., Patel P. Y. The effects of insulin, glucose and diabetes on prostaglandin production by rat kidney glomeruli and cultured glomerular mesangial cells. Prostaglandins Leukot Med. 1983 Aug;11(4):431–442. doi: 10.1016/0262-1746(83)90097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg J. I., Venkatachalam M. A. Vasoactive agents affect mesangial cell adhesion. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):C505–C511. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.4.C505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa K., Silverblatt F. J., Klein K. L. Insulin receptors of isolated glomeruli. Int J Biochem. 1980;12(1-2):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(80)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mené P., Simonson M. S., Dunn M. J. Physiology of the mesangial cell. Physiol Rev. 1989 Oct;69(4):1347–1424. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.4.1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi T., Morris R. C., Jr, Ives H. E. Endothelin-induced increases in vascular smooth muscle Ca2+ do not depend on dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channels. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):635–639. doi: 10.1172/JCI114209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E., Andersen M. J. Increased kidney size and glomerular filtration rate in untreated juvenile diabetes: normalization by insulin-treatment. Diabetologia. 1975 Jun;11(3):221–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00422325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy V. K., Shipp J. C. Synthesis and accumulation of triglycerides in liver of diabetic rats. Effects of insulin treatment. Diabetes. 1979 May;28(5):472–478. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.5.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Ohara O., Teraoka H., Arita H. Group II phospholipase A2 mRNA synthesis is stimulated by two distinct mechanisms in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 12;261(1):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80663-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Bauer C. Pertussis toxin abolishes angiotensin II-induced phosphoinositide hydrolysis and prostaglandin synthesis in rat renal mesangial cells. Biochem J. 1986 May 15;236(1):289–294. doi: 10.1042/bj2360289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittner R. A., Fears R., Brindley D. N. Effects of cyclic AMP, glucocorticoids and insulin on the activities of phosphatidate phosphohydrolase, tyrosine aminotransferase and glycerol kinase in isolated rat hepatocytes in relation to the control of triacylglycerol synthesis and gluconeogenesis. Biochem J. 1985 Jan 15;225(2):455–462. doi: 10.1042/bj2250455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlondorff D., Satriano J. A., Hagege J., Perez J., Baud L. Effect of platelet-activating factor and serum-treated zymosan on prostaglandin E2 synthesis, arachidonic acid release, and contraction of cultured rat mesangial cells. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1227–1231. doi: 10.1172/JCI111309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secrest R. J., Cohen M. L. Endothelin: differential effects in vascular and nonvascular smooth muscle. Life Sci. 1989;45(15):1365–1372. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin S., Fujiwara Y., Wada A., Takama T., Orita Y., Kamada T., Tagawa K. Angiotensin II-induced increase in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in cultured rat mesangial cells: evidence by refined high performance liquid chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jan 15;142(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90452-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson M. S., Wann S., Mené P., Dubyak G. R., Kester M., Nakazato Y., Sedor J. R., Dunn M. J. Endothelin stimulates phospholipase C, Na+/H+ exchange, c-fos expression, and mitogenesis in rat mesangial cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):708–712. doi: 10.1172/JCI113935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Supattapone S., Danoff S. K., Theibert A., Joseph S. K., Steiner J., Snyder S. H. Cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of a brain inositol trisphosphate receptor decreases its release of calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8747–8750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Meyer-Lehnert H., Kim J. K., Schrier R. W. Effect of angiotensin II on Ca2+ kinetics and contraction in cultured rat glomerular mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Feb;254(2 Pt 2):F254–F266. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.2.F254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Kester M., Dunn M. J. Involvement of a pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein-coupled phospholipase A2 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated prostaglandin E2 synthesis in cultured rat mesangial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Dec 16;963(3):429–435. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90311-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


