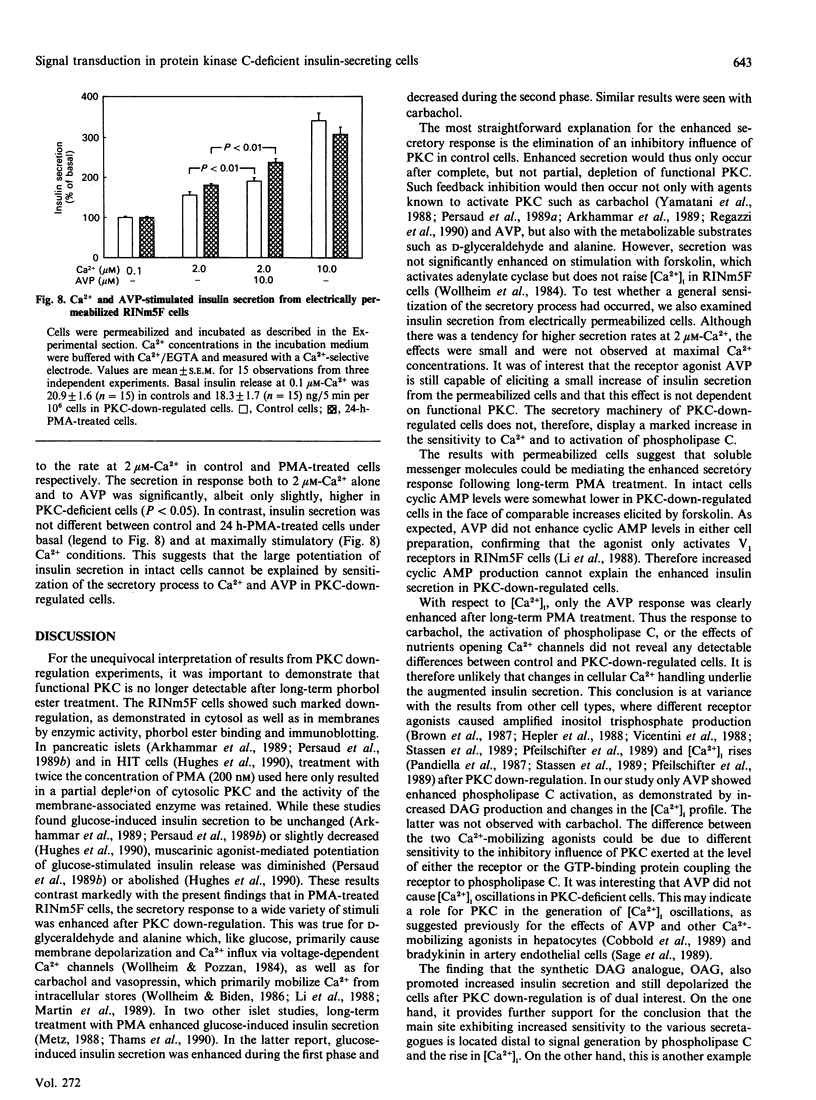
Abstract
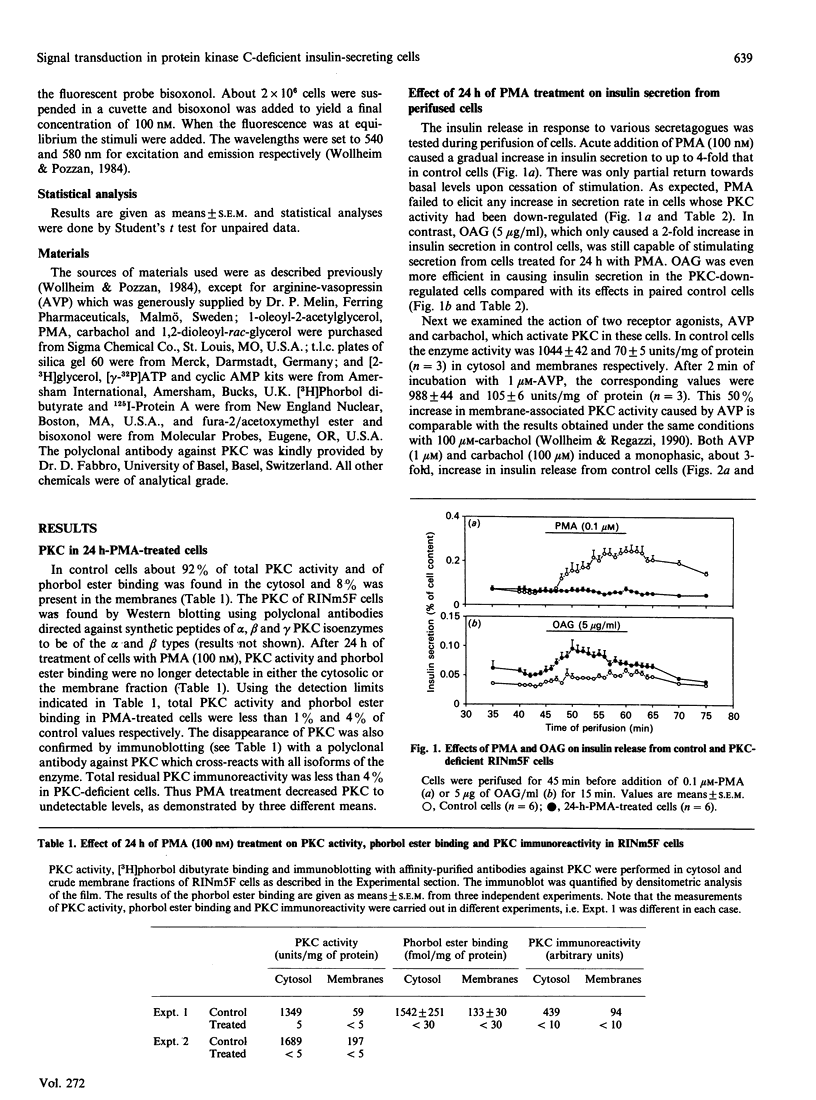
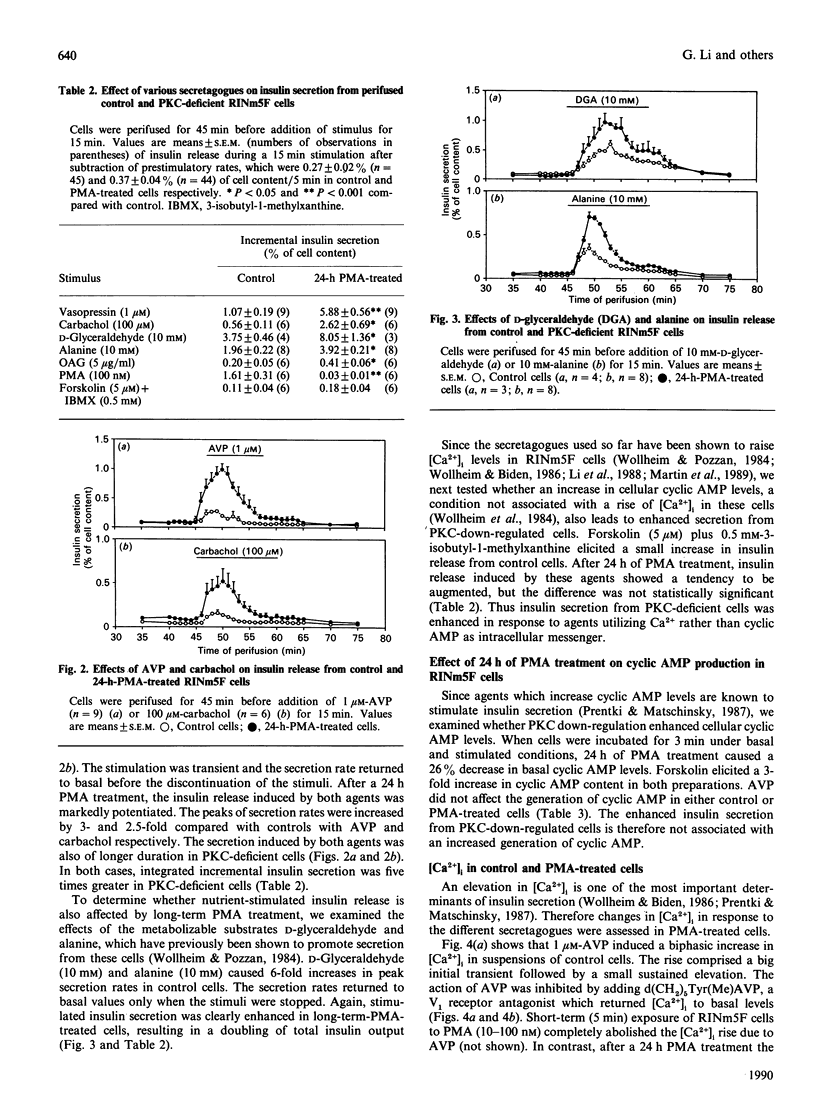
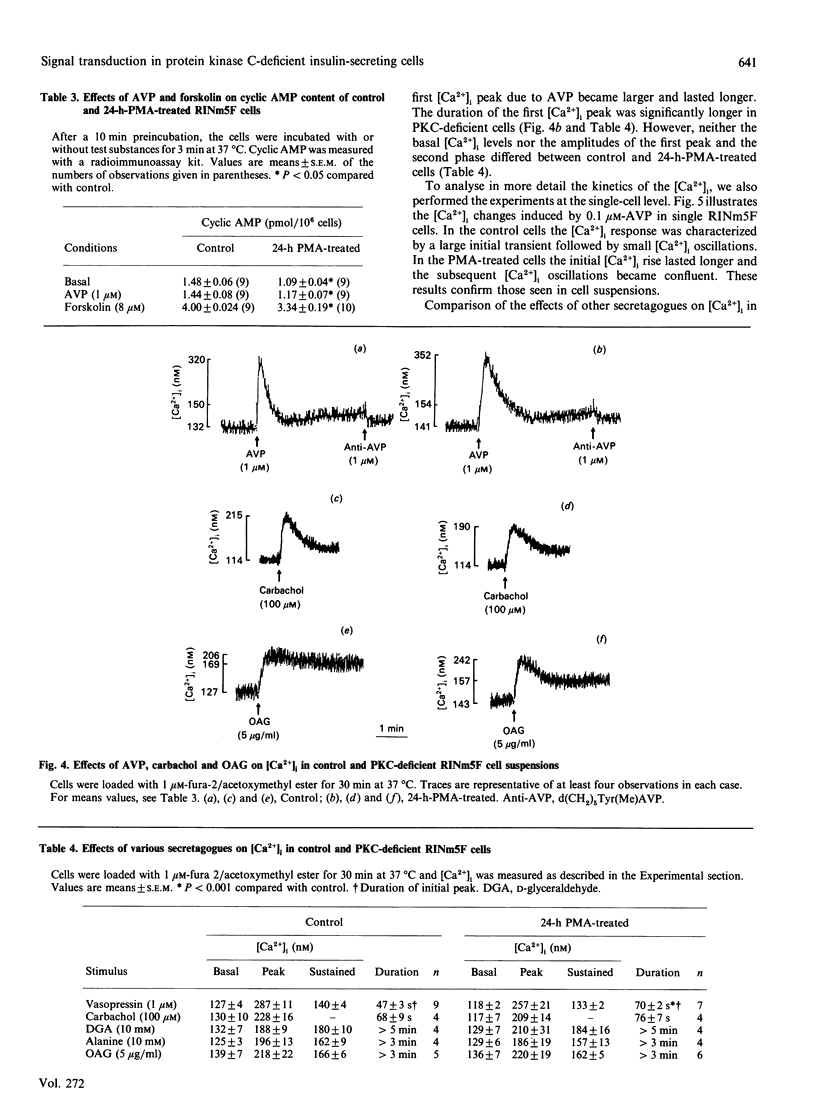
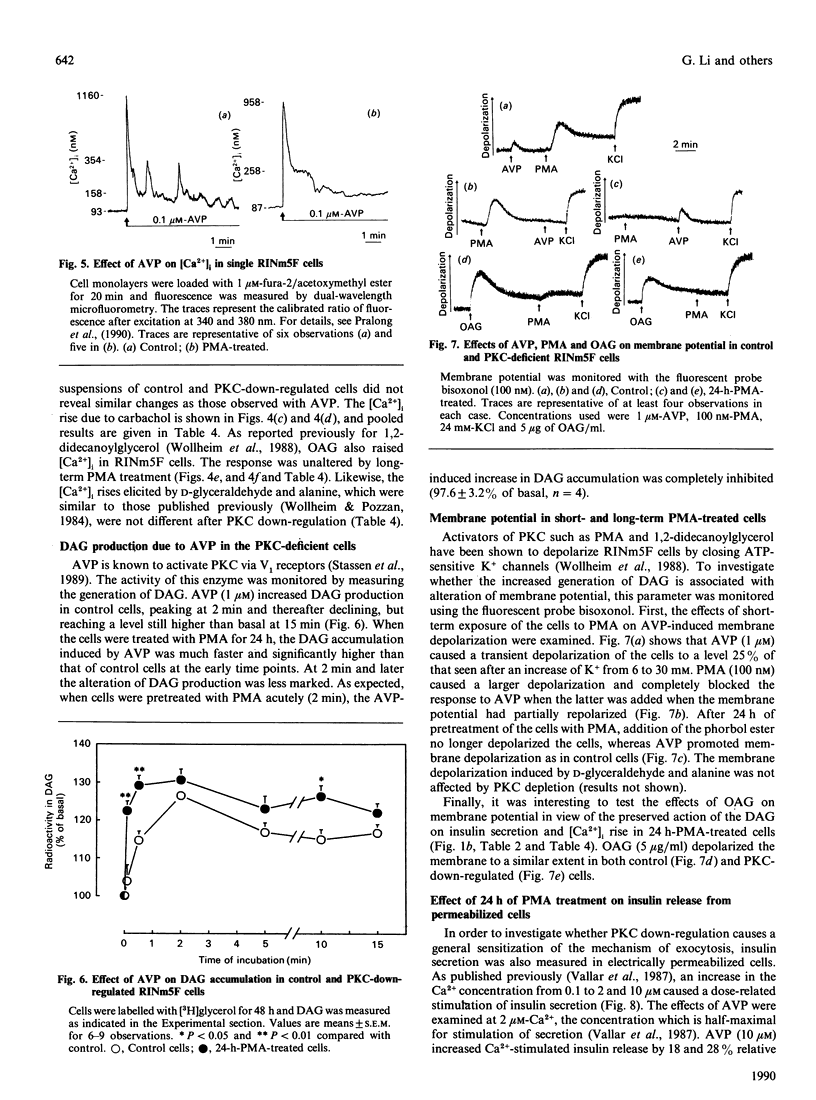
The role of protein kinase C (PKC) in stimulus recognition and insulin secretion was investigated after long-term (24 h) treatment of RINm5F cells with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA). Three methods revealed that PKC was no longer detectable, and PMA-induced insulin secretion was abolished. Such PKC-deficient cells displayed enhanced insulin secretion (2-6-fold) in response to vasopressin and carbachol (activating phospholipase C) as well as to D-glyceraldehyde and alanine (promoting membrane depolarization and voltage-gated Ca2+ influx). Insulin release stimulated by 1-oleoyl-2-acetylglycerol (OAG) was also greater in PKC-deficient cells. OAG caused membrane depolarization and raised the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i), both of which were unaffected by PKC down-regulation. Except for that caused by vasopressin, the secretagogue-induced [Ca2+]i elevations were similar in control and PKC-depleted cells. The [Ca2+]i rise evoked by vasopressin was enhanced during the early phase (observed both in cell suspensions and at the single cell level) and the stimulation of diacylglycerol production was also augmented. These findings suggest more efficient activation of phospholipase C by vasopressin after PKC depletion. Electrically permeabilized cells were used to test whether the release process is facilitated after long-term PMA treatment. PKC deficiency was associated with only slightly increased responsiveness to half-maximally (2 microM) but not to maximally stimulatory Ca2+ concentrations. At 2 microM-Ca2+ vasopressin caused secretion, which was also augmented by PMA pretreatment. The difference between intact and permeabilized cells could indicate the loss in the latter of soluble factors which mediate the enhanced secretory responses. However, changes in cyclic AMP production could not explain the difference. These results demonstrate that PKC not only exerts inhibitory influences on the coupling of receptors to phospholipase C but also interferes with more distal steps implicated in insulin secretion.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. C., Gullick W. J. Differences in phorbol-ester-induced down-regulation of protein kinase C between cell lines. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 1;257(3):905–911. doi: 10.1042/bj2570905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arkhammar P., Nilsson T., Welsh M., Welsh N., Berggren P. O. Effects of protein kinase C activation on the regulation of the stimulus-secretion coupling in pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem J. 1989 Nov 15;264(1):207–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2640207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best L. A role for calcium in the breakdown of inositol phospholipids in intact and digitonin-permeabilized pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 15;238(3):773–779. doi: 10.1042/bj2380773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biden T. J., Peter-Riesch B., Schlegel W., Wollheim C. B. Ca2+-mediated generation of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate and inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate in pancreatic islets. Studies with K+, glucose, and carbamylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3567–3571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Blakeley D. M., Hamon M. H., Laurie M. S., Corps A. N. Protein kinase C-mediated negative-feedback inhibition of unstimulated and bombesin-stimulated polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in Swiss-mouse 3T3 cells. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):631–639. doi: 10.1042/bj2450631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruzzone R., Regazzi R., Wollheim C. B. Caerulein causes translocation of protein kinase C in rat acini without increasing cytosolic free Ca2+. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jul;255(1 Pt 1):G33–G39. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.255.1.G33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M. Diacylglycerol stimulates phospholipase A2 from Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 18;234(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80099-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbold P., Daly M., Dixon J., Woods N. Repetitive calcium transients in hormone-stimulated cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 1989 Feb;17(1):9–10. doi: 10.1042/bst0170009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa S. D., Fabbro D., Regazzi R., Küng W., Eppenberger U. The cytosolic phorboid receptor correlates with hormone dependency in six mammary carcinoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 17;133(2):814–822. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90977-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easom R. A., Hughes J. H., Landt M., Wolf B. A., Turk J., McDaniel M. L. Comparison of effects of phorbol esters and glucose on protein kinase C activation and insulin secretion in pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1989 Nov 15;264(1):27–33. doi: 10.1042/bj2640027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erne P., Mazurek N., Borner C., Conscience J. F., Eppenberger U., Fabbro D. Translocation of protein kinase C is not required to inhibit the antigen-induced increase of cytosolic calcium in a mast cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 27;143(1):252–259. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90658-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabbro D., Regazzi R., Costa S. D., Borner C., Eppenberger U. Protein kinase C desensitization by phorbol esters and its impact on growth of human breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 26;135(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90943-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M. C., Hermans M. P., Henquin J. C. Glucose-, calcium- and concentration-dependence of acetylcholine stimulation of insulin release and ionic fluxes in mouse islets. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 15;254(1):211–218. doi: 10.1042/bj2540211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goppelt-Strübe M., Pfannkuche H. J., Gemsa D., Resch K. The diacylglycerols dioctanoylglycerol and oleoylacetylglycerol enhance prostaglandin synthesis by inhibition of the lysophosphatide acyltransferase. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 1;247(3):773–777. doi: 10.1042/bj2470773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Earp H. S., Harden T. K. Long-term phorbol ester treatment down-regulates protein kinase C and sensitizes the phosphoinositide signaling pathway to hormone and growth factor stimulation. Evidence for a role of protein kinase C in agonist-induced desensitization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7610–7619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hii C. S., Jones P. M., Persaud S. J., Howell S. L. A re-assessment of the role of protein kinase C in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):489–493. doi: 10.1042/bj2460489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang F. L., Yoshida Y., Cunha-Melo J. R., Beaven M. A., Huang K. P. Differential down-regulation of protein kinase C isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4238–4243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. J., Chalk J. G., Ashcroft S. J. The role of cytosolic free Ca2+ and protein kinase C in acetylcholine-induced insulin release in the clonal beta-cell line, HIT-T15. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 1;267(1):227–232. doi: 10.1042/bj2670227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Kishimoto A., Nishizuka Y. The protein kinase C family: heterogeneity and its implications. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:31–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi M., Rabinovitch A., Blackard W. G., Renold A. E. Perifusion of pancreas fragments. A system for the study of dynamic aspects of insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1974 Jun;23(6):550–559. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.6.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Mikawa K., Hashimoto K., Yasuda I., Tanaka S., Tominaga M., Kuroda T., Nishizuka Y. Limited proteolysis of protein kinase C subspecies by calcium-dependent neutral protease (calpain). J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4088–4092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolesnick R. N. 1,2-Diacylglycerols but not phorbol esters stimulate sphingomyelin hydrolysis in GH3 pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):16759–16762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Dunlop M. E., Mathias P. C., Malaisse-Lagae F., Sener A. Stimulation of protein kinase C and insulin release by 1-oleoyl-2-acetyl-glycerol. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 15;149(1):23–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08887.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. C., Yule D. I., Dunne M. J., Gallacher D. V., Petersen O. H. Vasopressin directly closes ATP-sensitive potassium channels evoking membrane depolarization and an increase in the free intracellular Ca2+ concentration in insulin-secreting cells. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3595–3599. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08532.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz S. A. Perspectives in diabetes. Is protein kinase C required for physiologic insulin release? Diabetes. 1988 Jan;37(1):3–7. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.1.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandiella A., Vicentini L. M., Meldolesi J. Protein kinase C-mediated feed back inhibition of the Ca2+ response at the EGF receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 30;149(1):145–151. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91616-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persaud S. J., Jones P. M., Sugden D., Howell S. L. The role of protein kinase C in cholinergic stimulation of insulin secretion from rat islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 15;264(3):753–758. doi: 10.1042/bj2640753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persaud S. J., Jones P. M., Sugden D., Howell S. L. Translocation of protein kinase C in rat islets of Langerhans. Effects of a phorbol ester, carbachol and glucose. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):80–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80196-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter-Riesch B., Fathi M., Schlegel W., Wollheim C. B. Glucose and carbachol generate 1,2-diacylglycerols by different mechanisms in pancreatic islets. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1154–1161. doi: 10.1172/JCI113430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Findlay I. Electrophysiology of the pancreas. Physiol Rev. 1987 Jul;67(3):1054–1116. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.3.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Ochsner M., Whitebread S., De Gasparo M. Down-regulation of protein kinase C potentiates angiotensin II-stimulated polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in vascular smooth-muscle cells. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 15;262(1):285–291. doi: 10.1042/bj2620285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pralong W. F., Bartley C., Wollheim C. B. Single islet beta-cell stimulation by nutrients: relationship between pyridine nucleotides, cytosolic Ca2+ and secretion. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):53–60. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08079.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Matschinsky F. M. Ca2+, cAMP, and phospholipid-derived messengers in coupling mechanisms of insulin secretion. Physiol Rev. 1987 Oct;67(4):1185–1248. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.4.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regazzi R., Li G. D., Deshusses J., Wollheim C. B. Stimulus-response coupling in insulin-secreting HIT cells. Effects of secretagogues on cytosolic Ca2+, diacylglycerol, and protein kinase C activity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15003–15009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage S. O., Adams D. J., van Breemen C. Synchronized oscillations in cytoplasmic free calcium concentration in confluent bradykinin-stimulated bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cell monolayers. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):6–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stassen F. L., Schmidt D. B., Papadopoulos M., Sarau H. M. Prolonged incubation with phorbol esters enhanced vasopressin-induced calcium mobilization and polyphosphatidylinositol hydrolysis of vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4916–4923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thams P., Capito K., Hedeskov C. J., Kofod H. Phorbol-ester-induced down-regulation of protein kinase C in mouse pancreatic islets. Potentiation of phase 1 and inhibition of phase 2 of glucose-induced insulin secretion. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 1;265(3):777–787. doi: 10.1042/bj2650777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallar L., Biden T. J., Wollheim C. B. Guanine nucleotides induce Ca2+-independent insulin secretion from permeabilized RINm5F cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5049–5056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicentini L. M., Cervini R., Zippel R., Mantegazza P. Epidermal growth factor-induced phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Modulation by protein kinase C. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 15;228(2):346–350. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virji M. A., Steffes M. W., Estensen R. D. Phorbol myristate acetate: effect of a tumor promoter on insulin release from isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Endocrinology. 1978 Mar;102(3):706–711. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-3-706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Easom R. A., Hughes J. H., McDaniel M. L., Turk J. Secretagogue-induced diacylglycerol accumulation in isolated pancreatic islets. Mass spectrometric characterization of the fatty acyl content indicates multiple mechanisms of generation. Biochemistry. 1989 May 16;28(10):4291–4301. doi: 10.1021/bi00436a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Easom R. A., McDaniel M. L., Turk J. Diacylglycerol synthesis de novo from glucose by pancreatic islets isolated from rats and humans. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):482–490. doi: 10.1172/JCI114463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Biden T. J. Signal transduction in insulin secretion: comparison between fuel stimuli and receptor agonists. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;488:317–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb46568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Dunne M. J., Peter-Riesch B., Bruzzone R., Pozzan T., Petersen O. H. Activators of protein kinase C depolarize insulin-secreting cells by closing K+ channels. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2443–2449. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03090.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Pozzan T. Correlation between cytosolic free Ca2+ and insulin release in an insulin-secreting cell line. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2262–2267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Regazzi R. Protein kinase C in insulin releasing cells. Putative role in stimulus secretion coupling. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 1;268(2):376–380. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81289-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Ullrich S., Pozzan T. Glyceraldehyde, but not cyclic AMP-stimulated insulin release is preceded by a rise in cytosolic free Ca2+. FEBS Lett. 1984 Nov 5;177(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80972-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamatani T., Chiba T., Kadowaki S., Hishikawa R., Yamaguchi A., Inui T., Fujita T., Kawazu S. Dual action of protein kinase C activation in the regulation of insulin release by muscarinic agonist from rat insulinoma cell line (RINr). Endocrinology. 1988 Jun;122(6):2826–2832. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-6-2826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


