Abstract
A bovine tropoelastin cDNA encoding exons 15-36 that includes the elastin-receptor binding site was expressed in Escherichia coli as a fusion protein with Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. After isolation of the fusion protein by affinity chromatography on Ig-Sepharose, the tropoelastin domain was separated from plasmid-pR1T2T-encoded Protein A (Protein A') by CNBr cleavage. Cell-adhesion assays demonstrated specific adhesion to the recombinant tropoelastin. Furthermore, the data indicate that interactions involving the bovine elastin receptor mediate nuchalligament fibroblast adhesion to the recombinant protein. In agreement with earlier studies of fibroblast chemotaxis to bovine tropoelastin, nuchal-ligament fibroblast adhesion demonstrated developmental regulation of the elastin receptor.
Full text
PDF


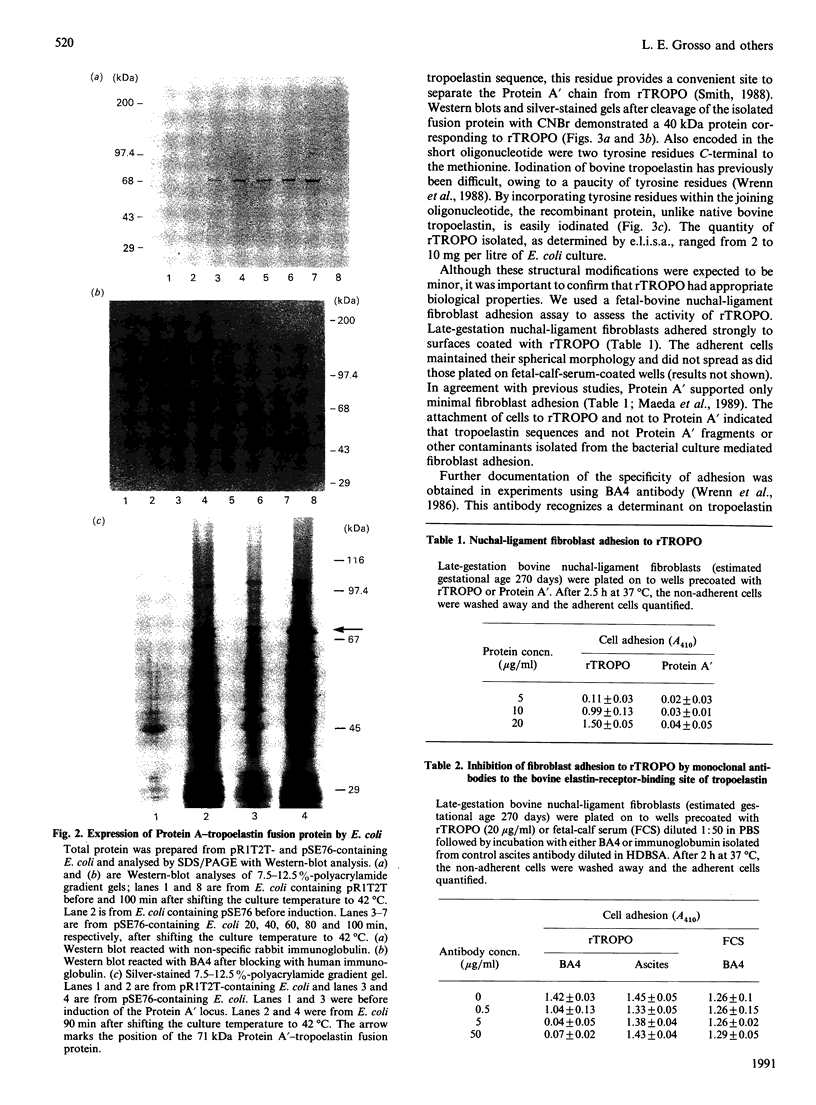
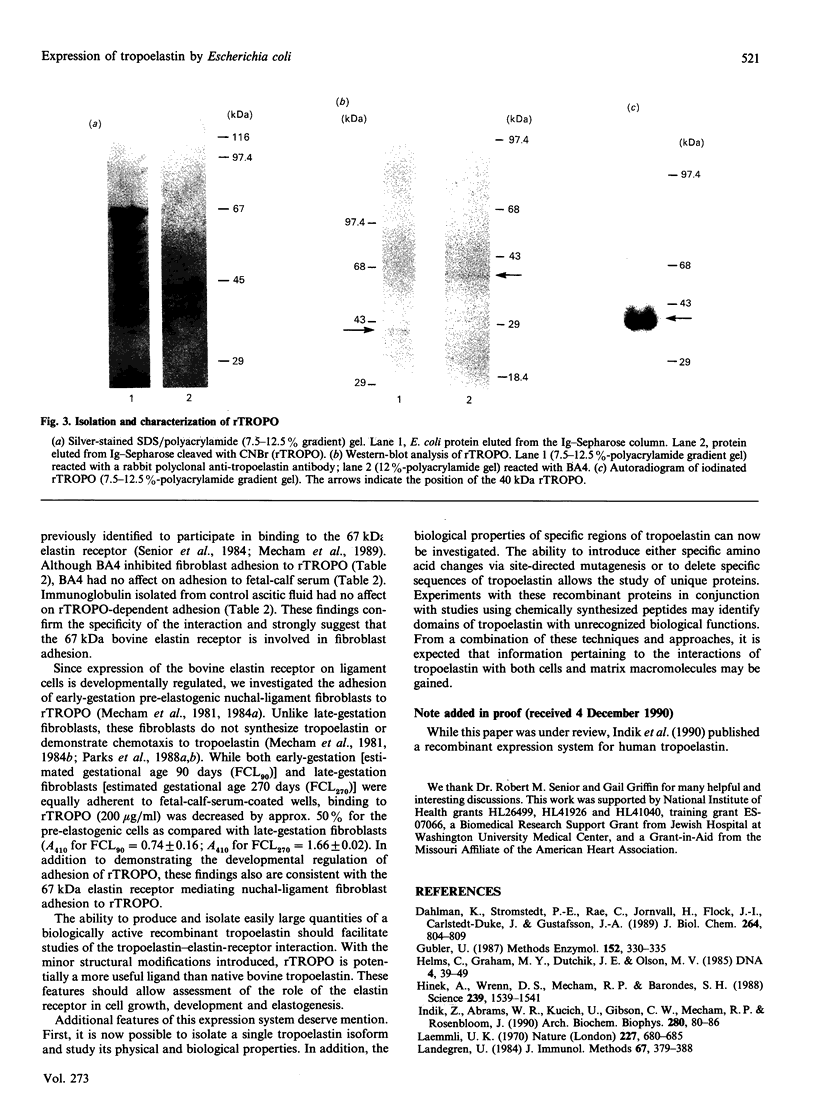

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dahlman K., Strömstedt P. E., Rae C., Jörnvall H., Flock J. I., Carlstedt-Duke J., Gustafsson J. A. High level expression in Escherichia coli of the DNA-binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor in a functional form utilizing domain-specific cleavage of a fusion protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):804–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U. Second-strand cDNA synthesis: mRNA fragments as primers. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:330–335. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms C., Graham M. Y., Dutchik J. E., Olson M. V. A new method for purifying lambda DNA from phage lysates. DNA. 1985 Feb;4(1):39–49. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinek A., Wrenn D. S., Mecham R. P., Barondes S. H. The elastin receptor: a galactoside-binding protein. Science. 1988 Mar 25;239(4847):1539–1541. doi: 10.1126/science.2832941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Indik Z., Abrams W. R., Kucich U., Gibson C. W., Mecham R. P., Rosenbloom J. Production of recombinant human tropoelastin: characterization and demonstration of immunologic and chemotactic activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Jul;280(1):80–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90521-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landegren U. Measurement of cell numbers by means of the endogenous enzyme hexosaminidase. Applications to detection of lymphokines and cell surface antigens. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Mar 16;67(2):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Oyama R., Ichihara-Tanaka K., Kimizuka F., Kato I., Titani K., Sekiguchi K. A novel cell adhesive protein engineered by insertion of the Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser tetrapeptide. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15165–15168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston F. A. The purification of eukaryotic polypeptides synthesized in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):1–12. doi: 10.1042/bj2400001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney M. M., Parkinson A. A simple, non-chromatographic procedure to purify immunoglobulins from serum and ascites fluid. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Feb 11;96(2):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90324-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecham R. P., Griffin G. L., Madaras J. G., Senior R. M. Appearance of chemotactic responsiveness to elastin peptides by developing fetal bovine ligament fibroblasts parallels the onset of elastin production. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1813–1816. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecham R. P., Hinek A., Entwistle R., Wrenn D. S., Griffin G. L., Senior R. M. Elastin binds to a multifunctional 67-kilodalton peripheral membrane protein. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3716–3722. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecham R. P., Lange G. Antigenicity of elastin: characterization of major antigenic determinants on purified insoluble elastin. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 16;21(4):669–673. doi: 10.1021/bi00533a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecham R. P., Lange G., Madaras J., Starcher B. Elastin synthesis by ligamentum nuchae fibroblasts: effects of culture conditions and extracellular matrix on elastin production. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):332–338. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecham R. P., Madaras J. G., Senior R. M. Extracellular matrix-specific induction of elastogenic differentiation and maintenance of phenotypic stability in bovine ligament fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1804–1812. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. M. Nick translation. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:91–94. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mierendorf R. C., Percy C., Young R. A. Gene isolation by screening lambda gt11 libraries with antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:458–469. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mierendorf R. C., Pfeffer D. Direct sequencing of denatured plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:556–562. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52061-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Abrahmsén L., Uhlén M. Immobilization and purification of enzymes with staphylococcal protein A gene fusion vectors. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1075–1080. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03741.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Holmgren E., Josephson S., Gatenbeck S., Philipson L., Uhlen M. Efficient secretion and purification of human insulin-like growth factor I with a gene fusion vector in Staphylococci. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1151–1162. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks W. C., Secrist H., Wu L. C., Mecham R. P. Developmental regulation of tropoelastin isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4416–4423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks W. C., Whitehouse L. A., Wu L. C., Mecham R. P. Terminal differentiation of nuchal ligament fibroblasts: characterization of synthetic properties and responsiveness to external stimuli. Dev Biol. 1988 Oct;129(2):555–564. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90400-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R. M., Griffin G. L., Mecham R. P. Chemotactic activity of elastin-derived peptides. J Clin Invest. 1980 Oct;66(4):859–862. doi: 10.1172/JCI109926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R. M., Griffin G. L., Mecham R. P. Chemotactic responses of fibroblasts to tropoelastin and elastin-derived peptides. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):614–618. doi: 10.1172/JCI110654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R. M., Griffin G. L., Mecham R. P., Wrenn D. S., Prasad K. U., Urry D. W. Val-Gly-Val-Ala-Pro-Gly, a repeating peptide in elastin, is chemotactic for fibroblasts and monocytes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):870–874. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrenn D. S., Griffin G. L., Senior R. M., Mecham R. P. Characterization of biologically active domains on elastin: identification of a monoclonal antibody to a cell recognition site. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5172–5176. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrenn D. S., Hinek A., Mecham R. P. Kinetics of receptor-mediated binding of tropoelastin to ligament fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2280–2284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrenn D. S., Parks W. C., Whitehouse L. A., Crouch E. C., Kucich U., Rosenbloom J., Mecham R. P. Identification of multiple tropoelastins secreted by bovine cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2244–2249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh H., Anderson N., Ornstein-Goldstein N., Bashir M. M., Rosenbloom J. C., Abrams W., Indik Z., Yoon K., Parks W., Mecham R. Structure of the bovine elastin gene and S1 nuclease analysis of alternative splicing of elastin mRNA in the bovine nuchal ligament. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 21;28(6):2365–2370. doi: 10.1021/bi00432a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh H., Ornstein-Goldstein N., Indik Z., Sheppard P., Anderson N., Rosenbloom J. C., Cicila G., Yoon K., Rosenbloom J. Sequence variation of bovine elastin mRNA due to alternative splicing. Coll Relat Res. 1987 Sep;7(4):235–247. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(87)80030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]