Abstract
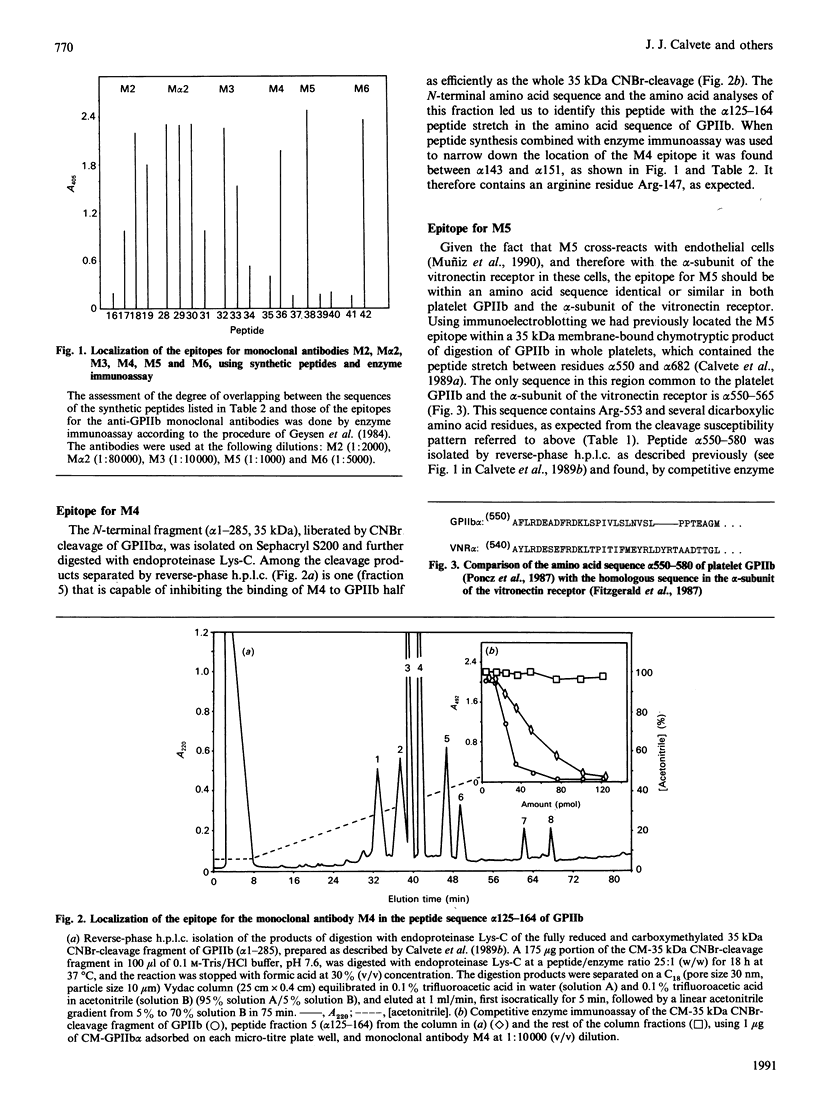
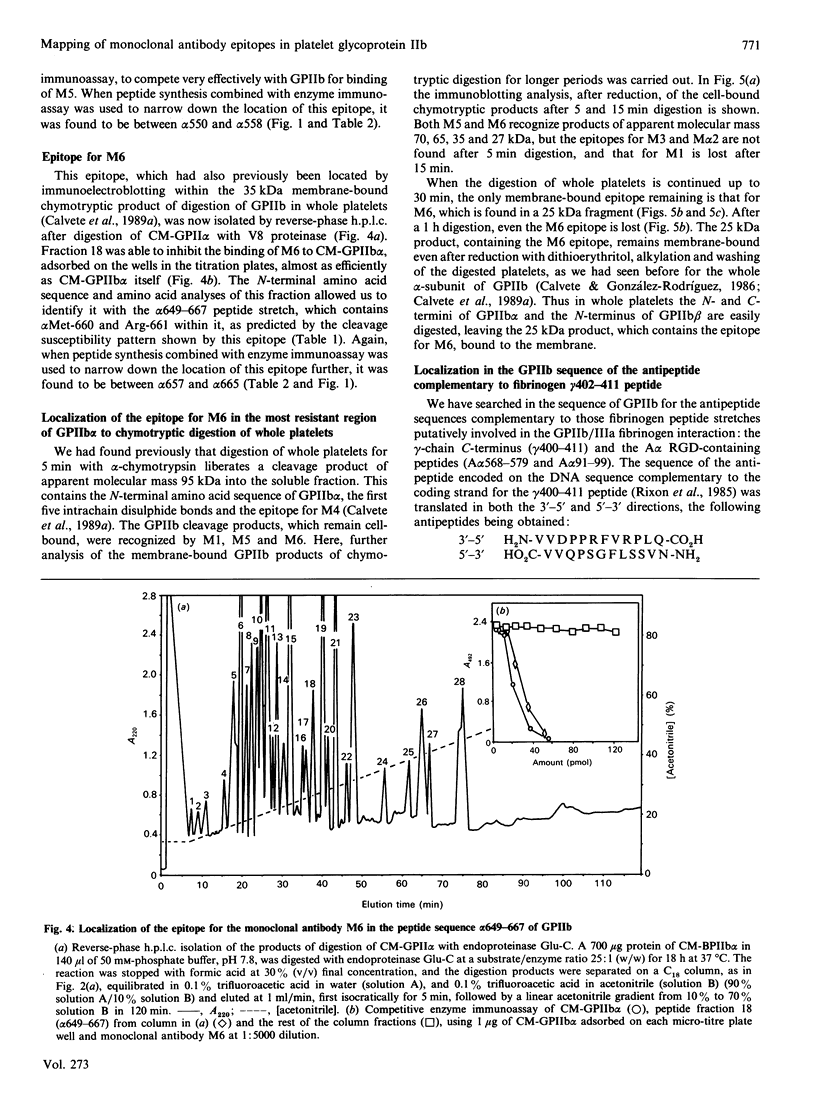
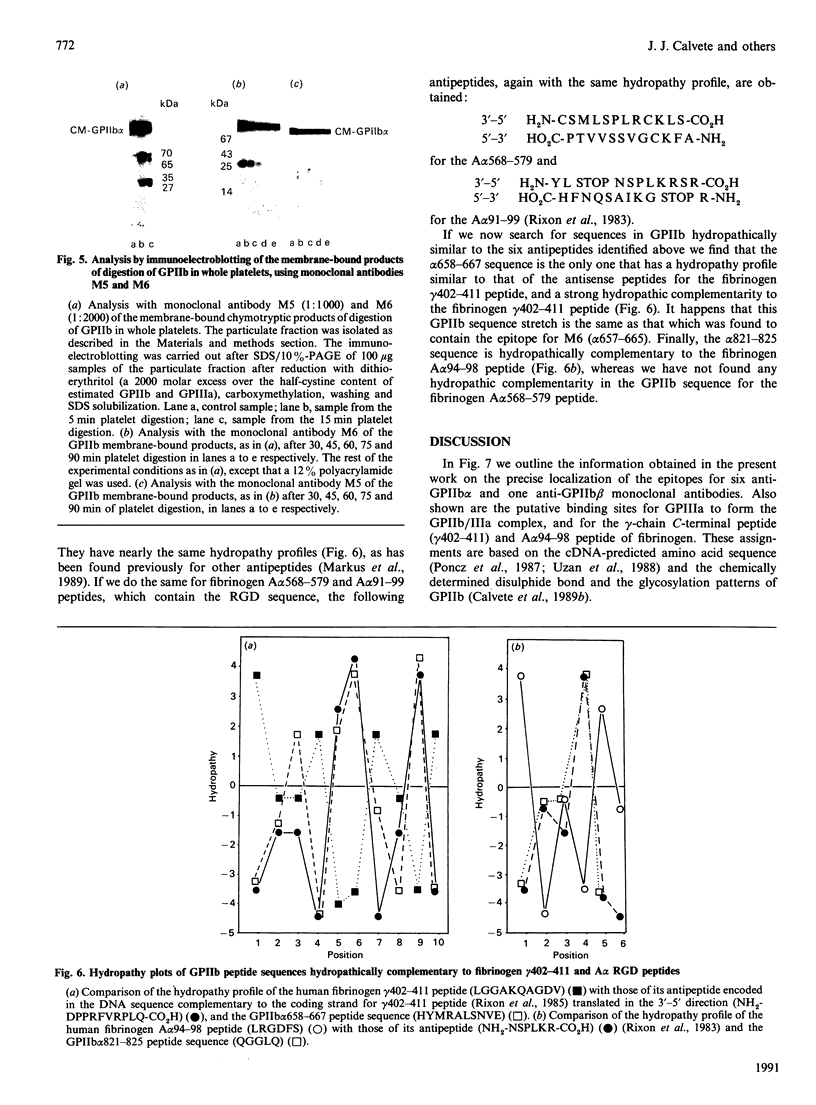
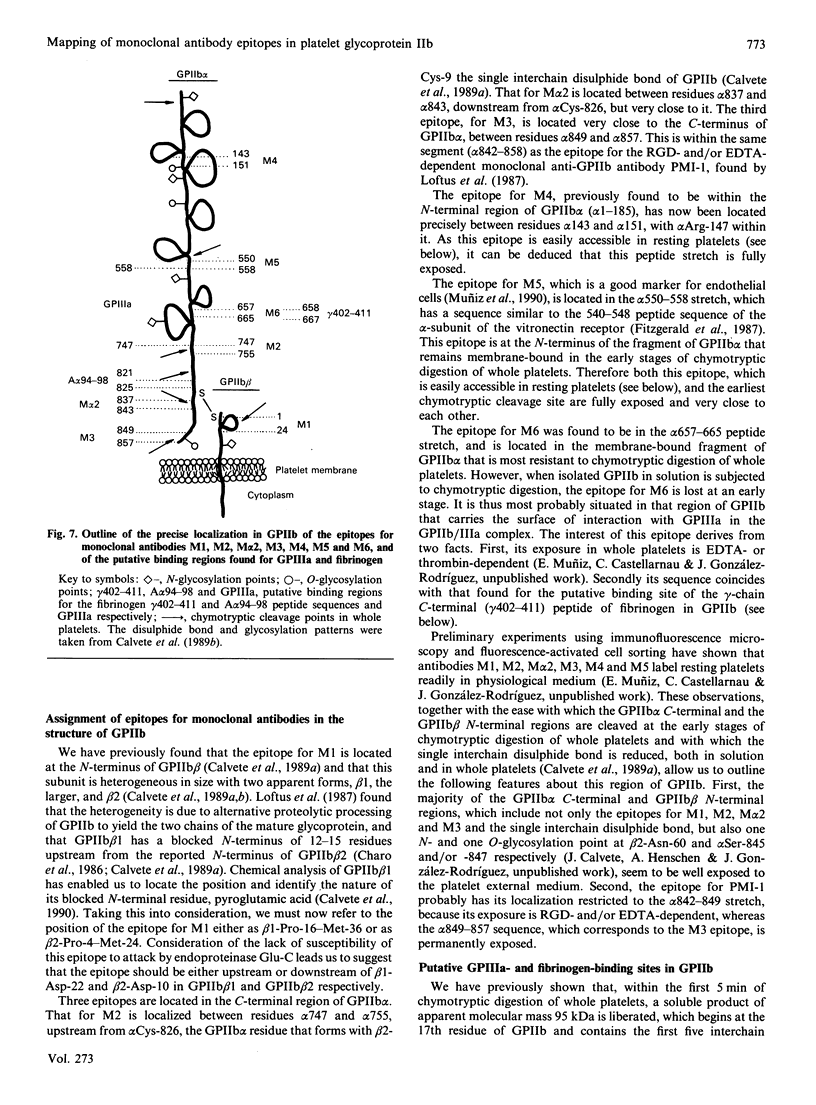
Glycoprotein IIb (GPIIb) is a major glycoprotein of the human platelet plasma membrane, which together with glycoprotein IIIa (GPIIIa) forms a Ca2(+)-dependent heterodimer, GPIIb/IIIa, which serves as the major fibrinogen receptor in activated platelets. The precise localization of the epitopes for six anti-GPIIb monoclonal antibodies (M1-M6) has been determined by a combination of enzymic and chemical cleavage procedures, peptide isolation, N-terminal sequence analysis, peptide synthesis and enzyme immunoassay. The following localizations were found: M1, beta 1-16-36, beta 2-4-24; M2, alpha 747-755; M alpha 2, alpha 837-843; M3, alpha 849-857; M4, alpha 143-151; M5, alpha 550-558; M6, alpha 657-665. Besides considerations of the degree of exposure of these epitopes, several remarkable features are readily apparent. The earliest and main chymotryptic cleavage site of GPIIb in whole platelets is between alpha cysteine-545 and alpha phenylalanine-551. The epitope for M3 was located within the same sequence (alpha 842-857) as is the epitope for PMI-1 [Loftus, Plow, Frelinger, D'Souza, Dixon, Lacy, Sorge & Ginsberg (1987) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 7114-7118] in spite of the fact that the exposure of the latter in whole platelets is EDTA-dependent whereas that in the former is not. The epitope for M5 shares full homology with the 540-548 peptide stretch of the alpha-subunit of the vitronectin receptor, and this antibody cross-reacts with endothelial cells. The M6 epitope is located in the 25 kDa membrane-bound fragment of GPIIb, which is most epitope is destroyed at an early stage of chymotrypic digestion. This suggests that this region of GPIIb, somewhere between the epitope for M5 (alpha 550-558) and the epitope for M2 (alpha 747-755), may carry the surface of interaction of GPIIb with GPIIIa in the GPIIb/IIIa heterodimer. Finally, the sequence where the epitope for M6 has been located (alpha 657-667) was the only one found to be hydropathically complementary to the gamma 402-411 peptide of fibrinogen within the amino acid sequence of both GPIIb and GPIIIa. This complementariness, the EDTA- or thrombin-dependence of the exposure of the alpha 657-665 stretch in whole platelets to M6 and the ability of this antibody to inhibit platelet aggregation led us to postulate that this peptide stretch is a putative binding site for fibrinogen in the platelet receptor.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blalock J. E., Smith E. M. Hydropathic anti-complementarity of amino acids based on the genetic code. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 31;121(1):203–207. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90707-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bost K. L., Smith E. M., Blalock J. E. Similarity between the corticotropin (ACTH) receptor and a peptide encoded by an RNA that is complementary to ACTH mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1372–1375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brentani R. R., Ribeiro S. F., Potocnjak P., Pasqualini R., Lopes J. D., Nakaie C. R. Characterization of the cellular receptor for fibronectin through a hydropathic complementarity approach. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):364–367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvete J. J., Alvarez M. V., Rivas G., Hew C. L., Henschen A., González-Rodríguez J. Interchain and intrachain disulphide bonds in human platelet glycoprotein IIb. Localization of the epitopes for several monoclonal antibodies. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 15;261(2):551–560. doi: 10.1042/bj2610551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvete J. J., González-Rodríguez J. Isolation and biochemical characterization of the alpha- and beta-subunits of glycoprotein IIb of human platelet plasma membrane. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):155–161. doi: 10.1042/bj2400155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvete J. J., Henschen A., González-Rodríguez J. Complete localization of the intrachain disulphide bonds and the N-glycosylation points in the alpha-subunit of human platelet glycoprotein IIb. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 15;261(2):561–568. doi: 10.1042/bj2610561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvete J. J., Schäfer W., Henschen A., González-Rodríguez J. Characterization of the beta-chain N-terminus heterogeneity and the alpha-chain C-terminus of human platelet GPIIb. Posttranslational cleavage sites. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 15;272(1-2):37–40. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80443-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charo I. F., Fitzgerald L. A., Steiner B., Rall S. C., Jr, Bekeart L. S., Phillips D. R. Platelet glycoproteins IIb and IIIa: evidence for a family of immunologically and structurally related glycoproteins in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8351–8355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Souza S. E., Ginsberg M. H., Burke T. A., Lam S. C., Plow E. F. Localization of an Arg-Gly-Asp recognition site within an integrin adhesion receptor. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):91–93. doi: 10.1126/science.3262922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eirín M. T., Calvete J. J., González-Rodríguez J. New isolation procedure and further biochemical characterization of glycoproteins IIb and IIIa from human platelet plasma membrane. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):147–153. doi: 10.1042/bj2400147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elton T. S., Dion L. D., Bost K. L., Oparil S., Blalock J. E. Purification of an angiotensin II binding protein by using antibodies to a peptide encoded by angiotensin II complementary RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2518–2522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald L. A., Poncz M., Steiner B., Rall S. C., Jr, Bennett J. S., Phillips D. R. Comparison of cDNA-derived protein sequences of the human fibronectin and vitronectin receptor alpha-subunits and platelet glycoprotein IIb. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8158–8165. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Meloen R. H., Barteling S. J. Use of peptide synthesis to probe viral antigens for epitopes to a resolution of a single amino acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3998–4002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam S. C., Plow E. F., Ginsberg M. H. Platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb heavy chain forms a complex with glycoprotein IIIa that binds Arg-Gly-Asp peptides. Blood. 1989 May 1;73(6):1513–1518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loftus J. C., Plow E. F., Frelinger A. L., 3rd, D'Souza S. E., Dixon D., Lacy J., Sorge J., Ginsberg M. H. Molecular cloning and chemical synthesis of a region of platelet glycoprotein IIb involved in adhesive function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7114–7118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markus G., Tritsch G. L., Parthasarathy R. A model for hydropathy-based peptide interactions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Aug 1;272(2):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEver R. P., Baenziger N. L., Majerus P. W. Isolation and quantitation of the platelet membrane glycoprotein deficient in thrombasthenia using a monoclonal hybridoma antibody. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1311–1318. doi: 10.1172/JCI109983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melero J. A., Gonzalez-Rodriguez J. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies against glycoprotein IIIa of human platelets. Their effect on platelet aggregation. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 1;141(2):421–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulchahey J. J., Neill J. D., Dion L. D., Bost K. L., Blalock J. E. Antibodies to the binding site of the receptor for luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH): generation with a synthetic decapeptide encoded by an RNA complementary to LHRH mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9714–9718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñiz-Diaz E., Castell Arnau C., Ribera A., Madoz P., Gonzalez Rodriguez J. Immunologic crossreactivity between platelet GP IIb and the vitronectin receptor alpha chain by using monoclonal anti-IIb antibodies. Blood. 1990 Jan 1;75(1):318–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasqualini R., Chamone D. F., Brentani R. R. Determination of the putative binding site for fibronectin on platelet glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex through a hydropathic complementarity approach. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14566–14570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Charo I. F., Parise L. V., Fitzgerald L. A. The platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex. Blood. 1988 Apr;71(4):831–843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncz M., Eisman R., Heidenreich R., Silver S. M., Vilaire G., Surrey S., Schwartz E., Bennett J. S. Structure of the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb. Homology to the alpha subunits of the vitronectin and fibronectin membrane receptors. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8476–8482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon M. W., Chan W. Y., Davie E. W., Chung D. W. Characterization of a complementary deoxyribonucleic acid coding for the alpha chain of human fibrinogen. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 21;22(13):3237–3244. doi: 10.1021/bi00282a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon M. W., Chung D. W., Davie E. W. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for the gamma chain of human fibrinogen. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 9;24(8):2077–2086. doi: 10.1021/bi00329a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro S. A., Lawing W. J., Jr Competition for related but nonidentical binding sites on the glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex by peptides derived from platelet adhesive proteins. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):867–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usobiaga P., Calvete J. J., Saíz J. L., Eirín M. T., González-Rodríguez J. Molecular characterization of human platelet glycoproteins IIIa and IIb and the subunits of the latter. Eur Biophys J. 1987;14(4):211–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00256354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzan G., Frachet P., Lajmanovich A., Prandini M. H., Denarier E., Duperray A., Loftus J., Ginsberg M., Plow E., Marguerie G. cDNA clones for human platelet GPIIb corresponding to mRNA from megakaryocytes and HEL cells. Evidence for an extensive homology to other Arg-Gly-Asp adhesion receptors. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):87–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon D., Karpatkin S. A monoclonal anti-platelet antibody with decreased reactivity for autoimmune thrombocytopenic platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6992–6995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



