Abstract
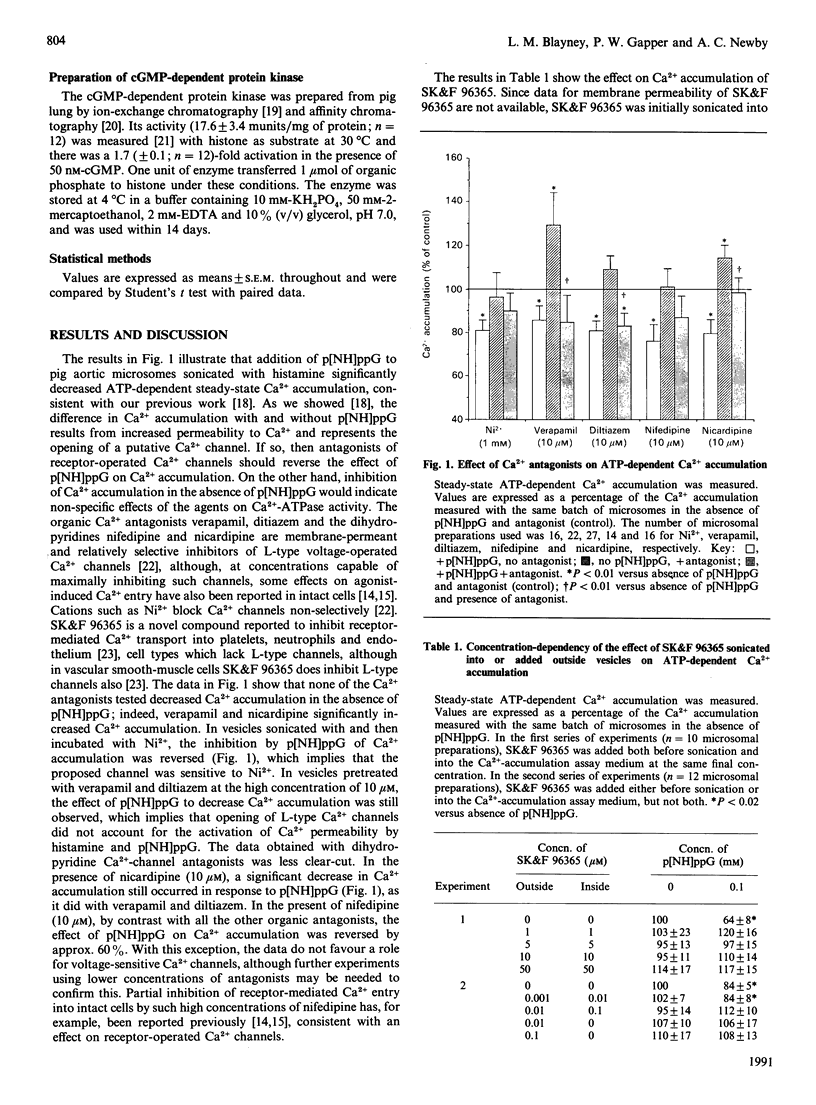
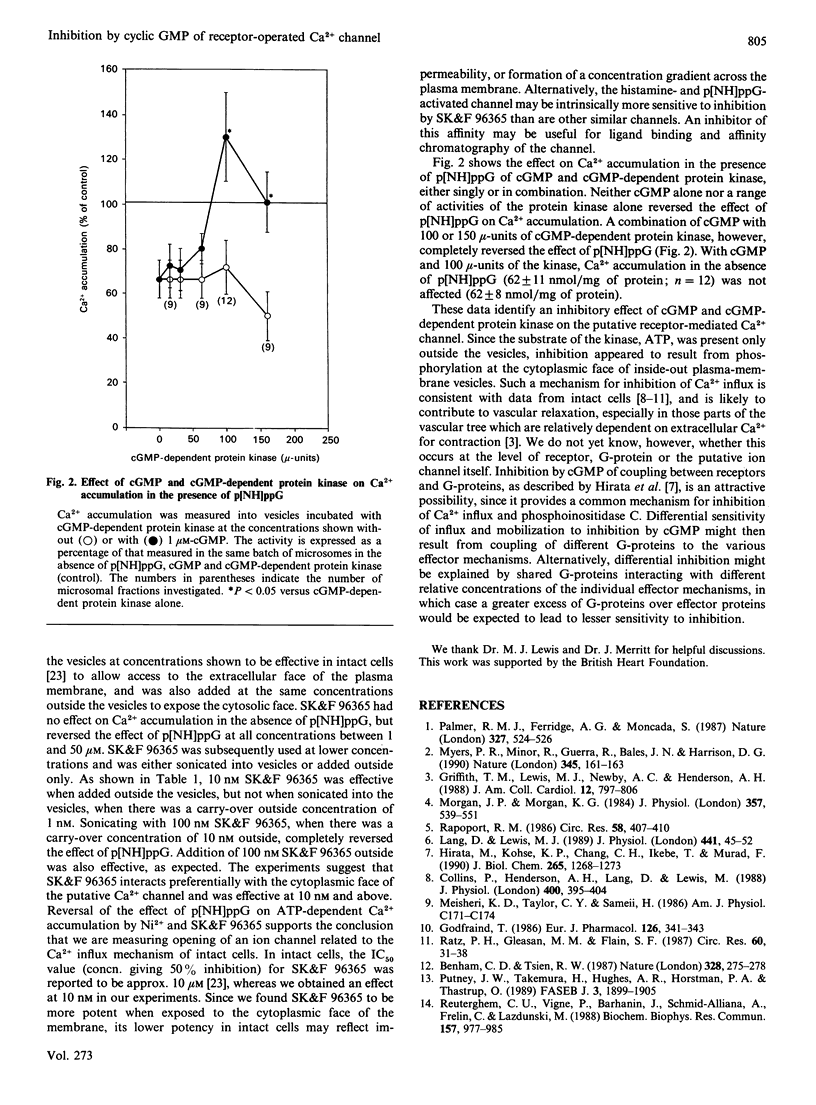
We have further characterized a putative receptor-operated Ca2+ channel that is activated by histamine and guanosine 5'-[beta gamma-imido]triphosphate. Insensitivity to verapamil, diltiazem or nicardipine, but inhibition by Ni2+ and SK&F 96365, further identify the channel with receptor-mediated Ca2+ entry in intact cells. Inhibition of the channel by cyclic-GMP-dependent protein kinase may contribute to vascular relaxation in response to nitrovasodilators.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benham C. D., Tsien R. W. A novel receptor-operated Ca2+-permeable channel activated by ATP in smooth muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):275–278. doi: 10.1038/328275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blayney L. M., Newby A. C. Histamine and a guanine nucleotide increase calcium permeability in pig aortic microsomal fractions. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 1;267(1):105–109. doi: 10.1042/bj2670105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnellie J. E., Schlichter D. J., Walter U., Greengard P. Photoaffinity labeling of a guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from vascular smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4771–4776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P., Henderson A. H., Lang D., Lewis M. J. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor and nitroprusside compared in noradrenaline- and K+-contracted rabbit and rat aortae. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:395–404. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfraind T. EDRF and cyclic GMP control gating of receptor-operated calcium channels in vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Jul 31;126(3):341–343. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith T. M., Lewis M. J., Newby A. C., Henderson A. H. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1988 Sep;12(3):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(88)90324-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata M., Kohse K. P., Chang C. H., Ikebe T., Murad F. Mechanism of cyclic GMP inhibition of inositol phosphate formation in rat aorta segments and cultured bovine aortic smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1268–1273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz L. Pharmacology of calcium channels and smooth muscle. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1986;26:225–258. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.26.040186.001301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D., Lewis M. J. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor inhibits the formation of inositol trisphosphate by rabbit aorta. J Physiol. 1989 Apr;411:45–52. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln T. M. cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:62–71. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisheri K. D., Taylor C. J., Saneii H. Synthetic atrial peptide inhibits intracellular calcium release in smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jan;250(1 Pt 1):C171–C174. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.1.C171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Armstrong W. P., Benham C. D., Hallam T. J., Jacob R., Jaxa-Chamiec A., Leigh B. K., McCarthy S. A., Moores K. E., Rink T. J. SK&F 96365, a novel inhibitor of receptor-mediated calcium entry. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 15;271(2):515–522. doi: 10.1042/bj2710515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. P., Morgan K. G. Alteration of cytoplasmic ionized calcium levels in smooth muscle by vasodilators in the ferret. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:539–551. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan R. O., Newby A. C. Nitroprusside differentially inhibits ADP-stimulated calcium influx and mobilization in human platelets. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 1;258(2):447–454. doi: 10.1042/bj2580447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers P. R., Minor R. L., Jr, Guerra R., Jr, Bates J. N., Harrison D. G. Vasorelaxant properties of the endothelium-derived relaxing factor more closely resemble S-nitrosocysteine than nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 May 10;345(6271):161–163. doi: 10.1038/345161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa K., Sano M. Partial purification and properties of guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from pig lung. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7415–7419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, Takemura H., Hughes A. R., Horstman D. A., Thastrup O. How do inositol phosphates regulate calcium signaling? FASEB J. 1989 Jun;3(8):1899–1905. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.8.2542110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate inhibition of contraction may be mediated through inhibition of phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis in rat aorta. Circ Res. 1986 Mar;58(3):407–410. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.3.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratz P. H., Gleason M. M., Flaim S. F. Simultaneous measurement of force and calcium uptake during acetylcholine-induced endothelium-dependent relaxation of rabbit thoracic aorta. Circ Res. 1987 Jan;60(1):31–38. doi: 10.1161/01.res.60.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. F., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L. Effect of a stimulant of guanylate cyclase, sin 1, on calcium movements and phospholipase C activation in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Apr 1;37(7):1263–1269. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90780-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson A. W., Stampfl A., Ashley C. C. Evidence for receptor-mediated bivalent-cation entry in A10 vascular smooth-muscle cells. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 1;267(1):277–280. doi: 10.1042/bj2670277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Renterghem C., Vigne P., Barhanin J., Schmid-Alliana A., Frelin C., Lazdunski M. Molecular mechanism of action of the vasoconstrictor peptide endothelin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 30;157(3):977–985. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80970-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


