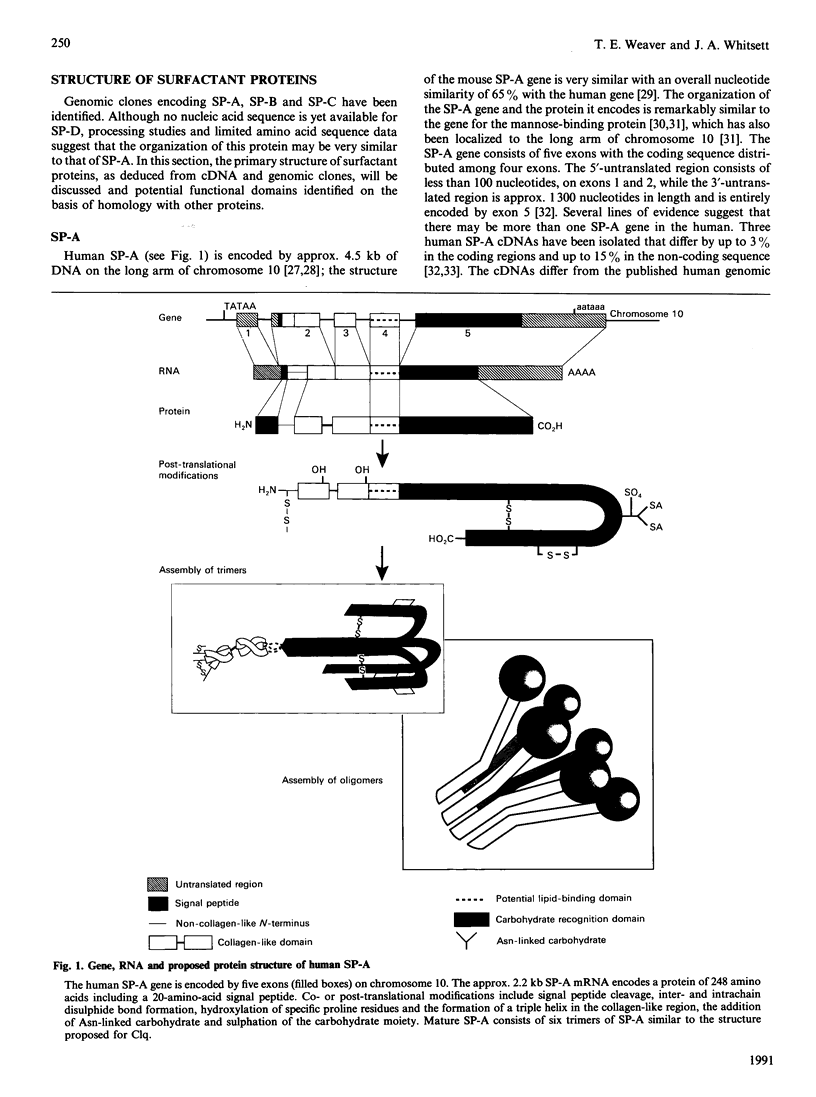
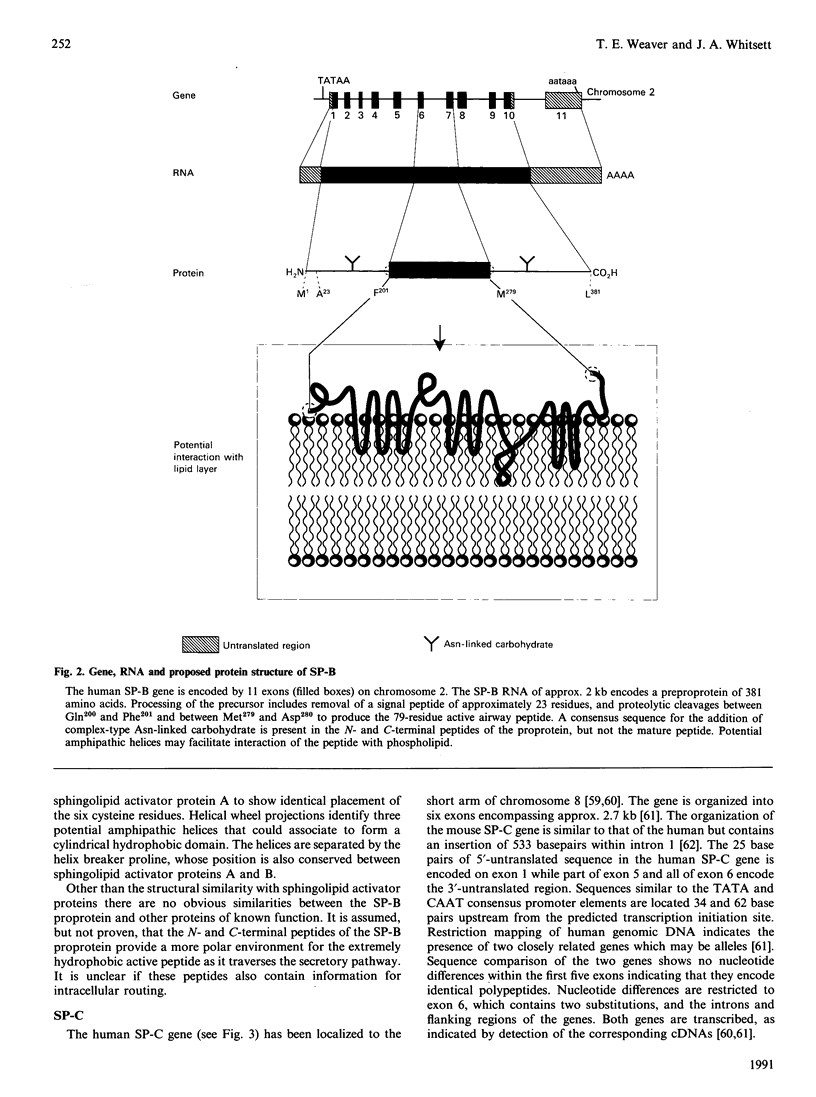
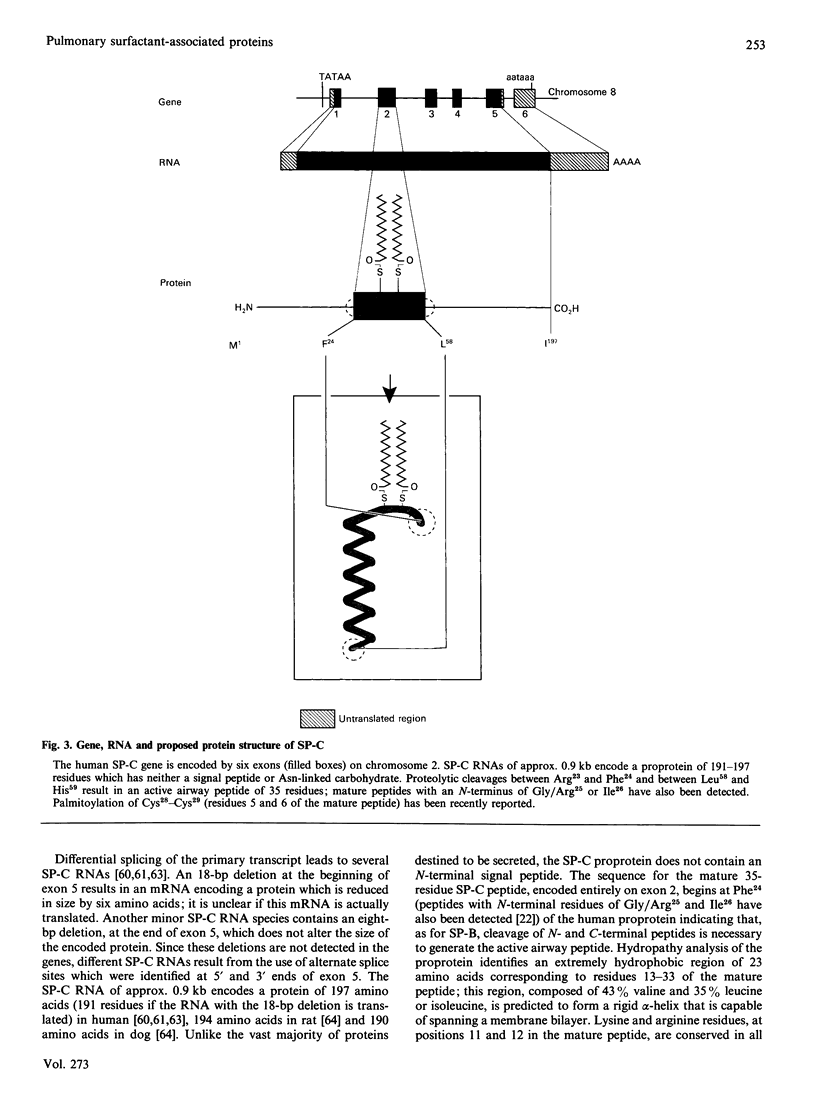
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baatz J. E., Elledge B., Whitsett J. A. Surfactant protein SP-B induces ordering at the surface of model membrane bilayers. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 17;29(28):6714–6720. doi: 10.1021/bi00480a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balis J. U., Paterson J. F., Paciga J. E., Haller E. M., Shelley S. A. Distribution and subcellular localization of surfactant-associated glycoproteins in human lung. Lab Invest. 1985 Jun;52(6):657–669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard P. L., Hawgood S., Liley H., Wellenstein G., Gonzales L. W., Benson B., Cordell B., White R. T. Regulation of pulmonary surfactant apoprotein SP 28-36 gene in fetal human lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9527–9531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard P. L. Hormonal regulation of pulmonary surfactant. Endocr Rev. 1989 May;10(2):165–181. doi: 10.1210/edrv-10-2-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard P. L., Liley H. G., Gonzales L. W., Odom M. W., Ammann A. J., Benson B., White R. T., Williams M. C. Interferon-gamma and synthesis of surfactant components by cultured human fetal lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Feb;2(2):137–143. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/2.2.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberger M. J., Lane M. D. Possible role of the Golgi apparatus in the assembly of very low density lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2390–2394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barile F. A., Guzowski D. E., Ripley C., Siddiqi Z. A., Bienkowski R. S. Ammonium chloride inhibits basal degradation of newly synthesized collagen in human fetal lung fibroblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Jan;276(1):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90018-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baritussio A., Benevento M., Pettenazzo A., Bruni R., Santucci A., Dalzoppo D., Barcaglioni P., Crepaldi G. The life cycle of a low-molecular-weight protein of surfactant (SP-C) in 3-day-old rabbits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 6;1006(1):19–25. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates S. R., Ibach P. B., Fisher A. B. Phospholipids co-isolated with rat surfactant protein C account for the apparent protein-enhanced uptake of liposomes into lung granular pneumocytes. Exp Lung Res. 1989 Sep;15(5):695–708. doi: 10.3109/01902148909062855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson B. J., Williams M. C., Sueishi K., Goerke J., Sargeant T. Role of calcium ions the structure and function of pulmonary surfactant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Mar 27;793(1):18–27. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson B., Hawgood S., Schilling J., Clements J., Damm D., Cordell B., White R. T. Structure of canine pulmonary surfactant apoprotein: cDNA and complete amino acid sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6379–6383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J. Regulation of eukaryotic transcription factors by post-translational modification. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 2;1009(2):103–109. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienkowski R. S. Intracellular degradation of newly synthesized secretory proteins. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 15;214(1):1–10. doi: 10.1042/bj2140001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggaram V., Mendelson C. R. Transcriptional regulation of the gene encoding the major surfactant protein (SP-A) in rabbit fetal lung. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19060–19065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggaram V., Qing K., Mendelson C. R. The major apoprotein of rabbit pulmonary surfactant. Elucidation of primary sequence and cyclic AMP and developmental regulation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2939–2947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggaram V., Smith M. E., Mendelson C. R. Regulation of expression of the gene encoding the major surfactant protein (SP-A) in human fetal lung in vitro. Disparate effects of glucocorticoids on transcription and on mRNA stability. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11421–11427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky-Doyle B., Leonard K. R., Reid K. B. Circular-dichroism and electron-microscopy studies of human subcomponent C1q before and after limited proteolysis by pepsin. Biochem J. 1976 Nov;159(2):279–286. doi: 10.1042/bj1590279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns G., Stroh H., Veldman G. M., Latt S. A., Floros J. The 35 kd pulmonary surfactant-associated protein is encoded on chromosome 10. Hum Genet. 1987 May;76(1):58–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00283051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle J. D. Sorting and secretory pathways in exocrine cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Feb;2(2):119–126. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/2.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chida S., Phelps D. S., Cordle C., Soll R., Floros J., Taeusch H. W. Surfactant-associated proteins in tracheal aspirates of infants with respiratory distress syndrome after surfactant therapy. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Apr;137(4):943–947. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.4.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claypool W. D., Wang D. L., Chander A., Fisher A. B. "Hydrophobic" surfactant apoproteins and augmentation of phospholipid recycling. Exp Lung Res. 1984;6(3-4):215–222. doi: 10.3109/01902148409109249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claypool W. D., Wang D. L., Chander A., Fisher A. B. An ethanol/ether soluble apoprotein from rat lung surfactant augments liposome uptake by isolated granular pneumocytes. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):677–684. doi: 10.1172/JCI111483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coalson J. J., Winter V. T., Martin H. M., King R. J. Colloidal gold immunoultrastructural localization of rat surfactant. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Feb;133(2):230–237. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.2.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curstedt T., Johansson J., Barros-Söderling J., Robertson B., Nilsson G., Westberg M., Jörnvall H. Low-molecular-mass surfactant protein type 1. The primary structure of a hydrophobic 8-kDa polypeptide with eight half-cystine residues. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Mar 15;172(3):521–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13918.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curstedt T., Johansson J., Persson P., Eklund A., Robertson B., Löwenadler B., Jörnvall H. Hydrophobic surfactant-associated polypeptides: SP-C is a lipopeptide with two palmitoylated cysteine residues, whereas SP-B lacks covalently linked fatty acyl groups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2985–2989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curstedt T., Jörnvall H., Robertson B., Bergman T., Berggren P. Two hydrophobic low-molecular-mass protein fractions of pulmonary surfactant. Characterization and biophysical activity. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Oct 15;168(2):255–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis J. W., Laferté S., Waghorne C., Breitman M. L., Kerbel R. S. Beta 1-6 branching of Asn-linked oligosaccharides is directly associated with metastasis. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):582–585. doi: 10.1126/science.2953071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs L. G., Mason R. J., Williams M. C., Benson B. J., Sueishi K. Secretion of surfactant by primary cultures of alveolar type II cells isolated from rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Oct 14;713(1):118–127. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs L. G., Wright J. R., Hawgood S., Gonzalez R., Venstrom K., Nellenbogen J. Pulmonary surfactant and its components inhibit secretion of phosphatidylcholine from cultured rat alveolar type II cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1010–1014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drickamer K., Dordal M. S., Reynolds L. Mannose-binding proteins isolated from rat liver contain carbohydrate-recognition domains linked to collagenous tails. Complete primary structures and homology with pulmonary surfactant apoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6878–6887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drickamer K., McCreary V. Exon structure of a mannose-binding protein gene reflects its evolutionary relationship to the asialoglycoprotein receptor and nonfibrillar collagens. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2582–2589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emrie P. A., Jones C., Hofmann T., Fisher J. H. The coding sequence for the human 18,000-dalton hydrophobic pulmonary surfactant protein is located on chromosome 2 and identifies a restriction fragment length polymorphism. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Jan;14(1):105–110. doi: 10.1007/BF01535054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emrie P. A., Shannon J. M., Mason R. J., Fisher J. H. cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence for the rat hydrophobic pulmonary surfactant-associated protein, SP-B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 23;994(3):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90296-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. M., Bourbon J. R., Notter R. H., Marin L., Nogee L. M., Whitsett J. A. Relationships among surfactant fraction lipids, proteins and biophysical properties in the developing rat lung. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 1;1044(1):84–90. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(90)90222-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J. H., Emrie P. A., Drabkin H. A., Kushnik T., Gerber M., Hofmann T., Jones C. The gene encoding the hydrophobic surfactant protein SP-C is located on 8p and identifies an EcoRI RFLP. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Oct;43(4):436–441. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J. H., Emrie P. A., Shannon J., Sano K., Hattler B., Mason R. J. Rat pulmonary surfactant protein A is expressed as two differently sized mRNA species which arise from differential polyadenylation of one transcript. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Sep 7;950(3):338–345. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90130-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J. H., Kao F. T., Jones C., White R. T., Benson B. J., Mason R. J. The coding sequence for the 32,000-dalton pulmonary surfactant-associated protein A is located on chromosome 10 and identifies two separate restriction-fragment-length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Jun;40(6):503–511. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J. H., Shannon J. M., Hofmann T., Mason R. J. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence of the hydrophobic surfactant protein SP-C from rat: expression in alveolar type II cells and homology with SP-C from other species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 1;995(3):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(89)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floros J., Phelps D. S., Harding H. P., Church S., Ware J. Postnatal stimulation of rat surfactant protein A synthesis by dexamethasone. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 1):L137–L143. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.2.L137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floros J., Phelps D. S., Kourembanas S., Taeusch H. W. Primary translation products, biosynthesis, and tissue specificity of the major surfactant protein in rat. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):828–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floros J., Phelps D. S., Taeusch H. W. Biosynthesis and in vitro translation of the major surfactant-associated protein from human lung. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):495–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floros J., Steinbrink R., Jacobs K., Phelps D., Kriz R., Recny M., Sultzman L., Jones S., Taeusch H. W., Frank H. A. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for the 35-kDa pulmonary surfactant-associated protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):9029–9033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman R. B. Protein disulfide isomerase: multiple roles in the modification of nascent secretory proteins. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1069–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita Y., Kogishi K., Suzuki Y. Pulmonary damage induced in mice by a monoclonal antibody to proteins associated with pig pulmonary surfactant. Exp Lung Res. 1988;14(2):247–260. doi: 10.3109/01902148809115127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallaher K. J., Rannels D. E., Rannels S. R. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase activity in fetal rat lung: developmental effects of dexamethasone and triiodothyronine. Pediatr Res. 1989 May;25(5):530–534. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198905000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George G., Hook G. E. The pulmonary extracellular lining. Environ Health Perspect. 1984 Apr;55:227–237. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8455227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasser S. W., Korfhagen T. R., Perme C. M., Pilot-Matias T. J., Kister S. E., Whitsett J. A. Two SP-C genes encoding human pulmonary surfactant proteolipid. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10326–10331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasser S. W., Korfhagen T. R., Weaver T. E., Clark J. C., Pilot-Matias T., Meuth J., Fox J. L., Whitsett J. A. cDNA, deduced polypeptide structure and chromosomal assignment of human pulmonary surfactant proteolipid, SPL(pVal). J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):9–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasser S. W., Korfhagen T. R., Weaver T., Pilot-Matias T., Fox J. L., Whitsett J. A. cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence of human pulmonary surfactant-associated proteolipid SPL(Phe). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4007–4011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goerke J. Lung surfactant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 16;344(3-4):241–261. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(74)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales L. W., Ballard P. L., Ertsey R., Williams M. C. Glucocorticoids and thyroid hormones stimulate biochemical and morphological differentiation of human fetal lung in organ culture. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Apr;62(4):678–691. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-4-678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross I., Dynia D. W., Rooney S. A., Smart D. A., Warshaw J. B., Sissom J. F., Hoath S. B. Influence of epidermal growth factor on fetal rat lung development in vitro. Pediatr Res. 1986 May;20(5):473–477. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198605000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross I., Wilson C. M., Floros J., Dynia D. W. Initiation of fetal rat lung phospholipid and surfactant-associated protein A mRNA synthesis. Pediatr Res. 1989 Mar;25(3):239–244. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198903000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossmann G., Nilsson R., Robertson B. Scanning electron microscopy of epithelial lesions induced by artificial ventilation of the immature neonatal lung; the prophylactic effect of surfactant replacement. Eur J Pediatr. 1986 Oct;145(5):361–367. doi: 10.1007/BF00439239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haagsman H. P., Hawgood S., Sargeant T., Buckley D., White R. T., Drickamer K., Benson B. J. The major lung surfactant protein, SP 28-36, is a calcium-dependent, carbohydrate-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):13877–13880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haagsman H. P., White R. T., Schilling J., Lau K., Benson B. J., Golden J., Hawgood S., Clements J. A. Studies of the structure of lung surfactant protein SP-A. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 1):L421–L429. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.6.L421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigh R. M., Hollingsworth M., Micklewright L. A., Boyd R. D., D'Souza S. W. The effect of human urogastrone on lung phospholipids in fetal rabbits. J Dev Physiol. 1988 Oct;10(5):433–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallman M., Arjomaa P., Mizumoto M., Akino T. Surfactant proteins in the diagnosis of fetal lung maturity. I. Predictive accuracy of the 35 kD protein, the lecithin/sphingomyelin ratio, and phosphatidylglycerol. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1988 Mar;158(3 Pt 1):531–535. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(88)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood J. L. Lung surfactant. Prog Lipid Res. 1987;26(3):211–256. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(87)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawgood S., Benson B. J., Hamilton R. L., Jr Effects of a surfactant-associated protein and calcium ions on the structure and surface activity of lung surfactant lipids. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):184–190. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawgood S., Benson B. J., Schilling J., Damm D., Clements J. A., White R. T. Nucleotide and amino acid sequences of pulmonary surfactant protein SP 18 and evidence for cooperation between SP 18 and SP 28-36 in surfactant lipid adsorption. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):66–70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawgood S. Pulmonary surfactant apoproteins: a review of protein and genomic structure. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 1):L13–L22. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.2.L13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S., Dafni N., Shapiro D. L., Holm B. A., Notter R. H., Quible D. J. Hyperoxic exposure alters gene expression in the lung. Induction of the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases mRNA and other mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7092–7095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S., Shapiro D. L., Finkelstein J. N., Notter R. H., Johnston C. J., Quible D. J. Changes in gene expression in hyperoxia-induced neonatal lung injury. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 1):L107–L111. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1990.258.2.L107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagami T. Atrial natriuretic factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3043–3046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs K. A., Phelps D. S., Steinbrink R., Fisch J., Kriz R., Mitsock L., Dougherty J. P., Taeusch H. W., Floros J. Isolation of a cDNA clone encoding a high molecular weight precursor to a 6-kDa pulmonary surfactant-associated protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9808–9811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaskoll T. F., Phelps D., Taeusch H. W., Smith B. T., Slavkin H. C. Localization of pulmonary surfactant protein during mouse lung development. Dev Biol. 1984 Nov;106(1):256–261. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobe A., Ikegami M. Surfactant for the treatment of respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Nov;136(5):1256–1275. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.5.1256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson J., Curstedt T., Robertson B., Jörnvall H. Size and structure of the hydrophobic low molecular weight surfactant-associated polypeptide. Biochemistry. 1988 May 17;27(10):3544–3547. doi: 10.1021/bi00410a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson J., Jörnvall H., Eklund A., Christensen N., Robertson B., Curstedt T. Hydrophobic 3.7 kDa surfactant polypeptide: structural characterization of the human and bovine forms. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 9;232(1):61–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80386-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalina M., Socher R. Internalization of pulmonary surfactant into lamellar bodies of cultured rat pulmonary type II cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1990 Apr;38(4):483–492. doi: 10.1177/38.4.2156921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassenbrock C. K., Garcia P. D., Walter P., Kelly R. B. Heavy-chain binding protein recognizes aberrant polypeptides translocated in vitro. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):90–93. doi: 10.1038/333090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katyal S. L., Amenta J. S., Singh G., Silverman J. A. Deficient lung surfactant apoproteins in amniotic fluid with mature phospholipid profile from diabetic pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Jan 1;148(1):48–53. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(84)80031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katyal S. L., Singh G. An enzyme-linked immunoassay of surfactant apoproteins. Its application to the study of fetal lung development in the rat. Pediatr Res. 1983 Jun;17(6):439–443. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198306000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawada H., Horiuchi T., Shannon J. M., Kuroki Y., Voelker D. R., Mason R. J. Alveolar type II cells, surfactant protein A (SP-A), and the phospholipid components of surfactant in acute silicosis in the rat. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Aug;140(2):460–470. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.2.460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Carmichael M. C., Horowitz P. M. Reassembly of lipid-protein complexes of pulmonary surfactant. Proposed mechanism of interaction. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10672–10680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Macbeth M. C. Physicochemical properties of dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine after interaction with an apolipoprotein of pulmonary surfactant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 19;557(1):86–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90092-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Martin H. Intracellular metabolism of the apoproteins of pulmonary surfactant in rat lung. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 May;48(5):812–820. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.48.5.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Martin H., Mitts D., Holmstrom F. M. Metabolism of the apoproteins in pulmonary surfactant. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1977 Apr;42(4):483–491. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1977.42.4.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Phillips M. C., Horowitz P. M., Dang S. C. Interaction between the 35 kDa apolipoprotein of pulmonary surfactant and saturated phosphatidylcholines. Effects of temperature. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Oct 24;879(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90259-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Ruch J., Gikas E. G., Platzker A. C., Creasy R. K. Appearance of paoproteins of pulmonary surfactant in human amniotic fluid. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Nov;39(5):735–741. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.39.5.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Simon D., Horowitz P. M. Aspects of secondary and quaternary structure of surfactant protein A from canine lung. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 20;1001(3):294–301. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogishi K., Kurozumi M., Fujita Y., Murayama T., Kuze F., Suzuki Y. Isolation and partial characterization of human low molecular weight protein associated with pulmonary surfactant. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jun;137(6):1426–1431. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.6.1426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korfhagen T. R., Glasser S. W., Wert S. E., Bruno M. D., Daugherty C. C., McNeish J. D., Stock J. L., Potter S. S., Whitsett J. A. Cis-acting sequences from a human surfactant protein gene confer pulmonary-specific gene expression in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6122–6126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki Y., Dempo K., Akino T. Immunohistochemical study of human pulmonary surfactant apoproteins with monoclonal antibodies. Pathologic application for hyaline membrane disease. Am J Pathol. 1986 Jul;124(1):25–33. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki Y., Mason R. J., Voelker D. R. Alveolar type II cells express a high-affinity receptor for pulmonary surfactant protein A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5566–5570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki Y., Mason R. J., Voelker D. R. Chemical modification of surfactant protein A alters high affinity binding to rat alveolar type II cells and regulation of phospholipid secretion. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17596–17602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki Y., Mason R. J., Voelker D. R. Pulmonary surfactant apoprotein A structure and modulation of surfactant secretion by rat alveolar type II cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3388–3394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki Y., Takahashi H., Fukada Y., Mikawa M., Inagawa A., Fujimoto S., Akino T. Two-site "simultaneous" immunoassay with monoclonal antibodies for the determination of surfactant apoproteins in human amniotic fluid. Pediatr Res. 1985 Oct;19(10):1017–1020. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198510000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liley H. G., Ertsey R., Gonzales L. W., Odom M. W., Hawgood S., Dobbs L. G., Ballard P. L. Synthesis of surfactant components by cultured type II cells from human lung. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jul 1;961(1):86–95. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liley H. G., Hawgood S., Wellenstein G. A., Benson B., White R. T., Ballard P. L. Surfactant protein of molecular weight 28,000-36,000 in cultured human fetal lung: cellular localization and effect of dexamethasone. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Mar;1(3):205–215. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-3-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liley H. G., White R. T., Benson B. J., Ballard P. L. Glucocorticoids both stimulate and inhibit production of pulmonary surfactant protein A in fetal human lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9096–9100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liley H. G., White R. T., Warr R. G., Benson B. J., Hawgood S., Ballard P. L. Regulation of messenger RNAs for the hydrophobic surfactant proteins in human lung. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1191–1197. doi: 10.1172/JCI114000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Bonifacino J. S., Yuan L. C., Klausner R. D. Degradation from the endoplasmic reticulum: disposing of newly synthesized proteins. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):209–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90553-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margraf L. R., Paciga J. E., Balis J. U. Surfactant-associated glycoproteins accumulate in alveolar cells and secretions during reparative stage of hyaline membrane disease. Hum Pathol. 1990 Apr;21(4):392–396. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(90)90200-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriott S. J., Brady J. N. Enhancer function in viral and cellular gene regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 17;989(2):97–110. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C. E., Cake M. H., Hartmann P. E., Cook I. F. Relationship between foetal corticosteroids, maternal progesterone and parturition in the rat. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1977 Jan;84(1):167–176. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0840167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massaro D., Clerch L., Massaro G. D. Surfactant aggregation in rat lungs: influence of temperature and ventilation. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Sep;51(3):646–653. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.51.3.646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahan M. J., Mimouni F., Miodovnik M., Hull W. M., Whitsett J. A. Surfactant associated protein (SAP-35) in amniotic fluid from diabetic and nondiabetic pregnancies. Obstet Gynecol. 1987 Jul;70(1):94–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson C. R., Chen C., Boggaram V., Zacharias C., Snyder J. M. Regulation of the synthesis of the major surfactant apoprotein in fetal rabbit lung tissue. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9938–9943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt T. A., Hallman M., Spragg R., Heldt G. P., Gilliard N. Exogenous surfactant treatments for neonatal respiratory distress syndrome and their potential role in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Drugs. 1989 Oct;38(4):591–611. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198938040-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto S., Martin B. M., Yamamoto Y., Kretz K. A., O'Brien J. S., Kishimoto Y. Saposin A: second cerebrosidase activator protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3389–3393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogee L. M., Wispe J. R. Effects of pulmonary oxygen injury on airway content of surfactant-associated protein A. Pediatr Res. 1988 Nov;24(5):568–573. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198811000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogee L. M., Wispé J. R., Clark J. C., Whitsett J. A. Increased synthesis and mRNA of surfactant protein A in oxygen-exposed rats. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1989 Aug;1(2):119–125. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/1.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notter R. H., Penney D. P., Finkelstein J. N., Shapiro D. L. Adsorption of natural lung surfactant and phospholipid extracts related to tubular myelin formation. Pediatr Res. 1986 Jan;20(1):97–101. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198601000-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notter R. H., Shapiro D. L., Ohning B., Whitsett J. A. Biophysical activity of synthetic phospholipids combined with purified lung surfactant 6000 dalton apoprotein. Chem Phys Lipids. 1987 Jun;44(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(87)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. S., Kretz K. A., Dewji N., Wenger D. A., Esch F., Fluharty A. L. Coding of two sphingolipid activator proteins (SAP-1 and SAP-2) by same genetic locus. Science. 1988 Aug 26;241(4869):1098–1101. doi: 10.1126/science.2842863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly M. A., Gazdar A. F., Clark J. C., Pilot-Matias T. J., Wert S. E., Hull W. M., Whitsett J. A. Glucocorticoids regulate surfactant protein synthesis in a pulmonary adenocarcinoma cell line. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 1):L385–L392. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.6.L385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly M. A., Gazdar A. F., Morris R. E., Whitsett J. A. Differential effects of glucocorticoid on expression of surfactant proteins in a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 30;970(2):194–204. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90179-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly M. A., Nogee L., Whitsett J. A. Requirement of the collagenous domain for carbohydrate processing and secretion of a surfactant protein, SP-A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 25;969(2):176–184. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90073-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly M. A., Weaver T. E., Pilot-Matias T. J., Sarin V. K., Gazdar A. F., Whitsett J. A. In vitro translation, post-translational processing and secretion of pulmonary surfactant protein B precursors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 10;1011(2-3):140–148. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90201-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odom M. J., Snyder J. M., Boggaram V., Mendelson C. R. Glucocorticoid regulation of the major surfactant associated protein (SP-A) and its messenger ribonucleic acid and of morphological development of human fetal lung in vitro. Endocrinology. 1988 Oct;123(4):1712–1720. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-4-1712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odom M. J., Snyder J. M., Mendelson C. R. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate analogs and beta-adrenergic agonists induce the synthesis of the major surfactant apoprotein in human fetal lung in vitro. Endocrinology. 1987 Sep;121(3):1155–1163. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-3-1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olafson R. W., Rink U., Kielland S., Yu S. H., Chung J., Harding P. G., Possmayer F. Protein sequence analysis studies on the low molecular weight hydrophobic proteins associated with bovine pulmonary surfactant. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 13;148(3):1406–1411. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80288-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paciga J. E., Shelley S. A., Paterson J. E., Knuppel R. A., Scerbo J. C., Balis J. U. Lung surfactant-associated glycoproteins and proteolipids in human amniotic fluids evaluated by dot immunobinding assays. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1988 Mar-Apr;18(2):141–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Identifying primary translation products: use of N-formylmethionyl-tRNA and prevention of NH2-terminal acetylation. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:150–157. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson A., Chang D., Crouch E. Surfactant protein D is a divalent cation-dependent carbohydrate-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5755–5760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson A., Chang D., Rust K., Moxley M., Longmore W., Crouch E. Purification and biochemical characterization of CP4 (SP-D), a collagenous surfactant-associated protein. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 25;28(15):6361–6367. doi: 10.1021/bi00441a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson A., Rust K., Chang D., Moxley M., Longmore W., Crouch E. CP4: a pneumocyte-derived collagenous surfactant-associated protein. Evidence for heterogeneity of collagenous surfactant proteins. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8576–8584. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S. R., Rothman J. E. Biosynthetic protein transport and sorting by the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:829–852. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps D. S., Floros J. Localization of surfactant protein synthesis in human lung by in situ hybridization. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Apr;137(4):939–942. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.4.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps D. S., Floros J. Proline hydroxylation alters the electrophoretic mobility of pulmonary surfactant-associated protein A. Electrophoresis. 1988 May;9(5):231–233. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150090508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phizackerley P. J., Town M. H., Newman G. E. Hydrophobic proteins of lamellated osmiophilic bodies isolated from pig lung. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 1;183(3):731–736. doi: 10.1042/bj1830731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilot-Matias T. J., Kister S. E., Fox J. L., Kropp K., Glasser S. W., Whitsett J. A. Structure and organization of the gene encoding human pulmonary surfactant proteolipid SP-B. DNA. 1989 Mar;8(2):75–86. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popliker M., Shatz A., Avivi A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Webb C. G. Onset of endogenous synthesis of epidermal growth factor in neonatal mice. Dev Biol. 1987 Jan;119(1):38–44. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Possmayer F. A proposed nomenclature for pulmonary surfactant-associated proteins. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Oct;138(4):990–998. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.4.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post M., van Golde L. M. Metabolic and developmental aspects of the pulmonary surfactant system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 9;947(2):249–286. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prockop D. J., Kivirikko K. I., Tuderman L., Guzman N. A. The biosynthesis of collagen and its disorders (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 5;301(1):13–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907053010104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rannels S. R., Gallaher K. J., Wallin R., Rannels D. E. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation of pulmonary surfactant-associated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5952–5956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Gagnon J., Frampton J. Completion of the amino acid sequences of the A and B chains of subcomponent C1q of the first component of human complement. Biochem J. 1982 Jun 1;203(3):559–569. doi: 10.1042/bj2030559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B. Proteins involved in the activation and control of the two pathways of human complement. Biochem Soc Trans. 1983 Jan;11(1):1–12. doi: 10.1042/bst0110001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid L. E., Brasnett A. H., Gilbert C. S., Porter A. C., Gewert D. R., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. A single DNA response element can confer inducibility by both alpha- and gamma-interferons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):840–844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revak S. D., Merritt T. A., Degryse E., Stefani L., Courtney M., Hallman M., Cochrane C. G. Use of human surfactant low molecular weight apoproteins in the reconstitution of surfactant biologic activity. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):826–833. doi: 10.1172/JCI113391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice W. R., Ross G. F., Singleton F. M., Dingle S., Whitsett J. A. Surfactant-associated protein inhibits phospholipid secretion from type II cells. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Aug;63(2):692–698. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.2.692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice W. R., Sarin V. K., Fox J. L., Baatz J., Wert S., Whitsett J. A. Surfactant peptides stimulate uptake of phosphatidylcholine by isolated cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 28;1006(2):237–245. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson B., Curstedt T., Grossmann G., Kobayashi T., Kokubo M., Suzuki Y. Prolonged ventilation of the premature newborn rabbit after treatment with natural or apoprotein-based artificial surfactant. Eur J Pediatr. 1988 Feb;147(2):168–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00442216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP and the induction of eukaryotic gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9063–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney S. A. Lung surfactant. Environ Health Perspect. 1984 Apr;55:205–226. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8455205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. F., Meuth J., Ohning B., Kim Y., Whitsett J. A. Purification of canine surfactant-associated glycoproteins A. Identification of a collagenase-resistant domain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 28;870(2):267–278. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90231-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross G. F., Notter R. H., Meuth J., Whitsett J. A. Phospholipid binding and biophysical activity of pulmonary surfactant-associated protein (SAP)-35 and its non-collagenous COOH-terminal domains. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14283–14291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotundo R. L., Thomas K., Porter-Jordan K., Benson R. J., Fernandez-Valle C., Fine R. E. Intracellular transport, sorting, and turnover of acetylcholinesterase. Evidence for an endoglycosidase H-sensitive form in Golgi apparatus, sarcoplasmic reticulum, and clathrin-coated vesicles and its rapid degradation by a non-lysosomal mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3146–3152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan R. M., Morris R. E., Rice W. R., Ciraolo G., Whitsett J. A. Binding and uptake of pulmonary surfactant protein (SP-A) by pulmonary type II epithelial cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 Apr;37(4):429–440. doi: 10.1177/37.4.2926121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Fisher J., Mason R. J., Kuroki Y., Schilling J., Benson B., Voelker D. Isolation and sequence of a cDNA clone for the rat pulmonary surfactant-associated protein (PSP-A). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 14;144(1):367–374. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80519-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarin V. K., Gupta S., Leung T. K., Taylor V. E., Ohning B. L., Whitsett J. A., Fox J. L. Biophysical and biological activity of a synthetic 8.7-kDa hydrophobic pulmonary surfactant protein SP-B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2633–2637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry K., Herman G. A., Day L., Deignan E., Bruns G., Morton C. C., Ezekowitz R. A. The human mannose-binding protein gene. Exon structure reveals its evolutionary relationship to a human pulmonary surfactant gene and localization to chromosome 10. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1175–1189. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellhase D. E., Emrie P. A., Fisher J. H., Shannon J. M. Ontogeny of surfactant apoproteins in the rat. Pediatr Res. 1989 Sep;26(3):167–174. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198909000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon J. M., Emrie P. A., Fisher J. H., Kuroki Y., Jennings S. D., Mason R. J. Effect of a reconstituted basement membrane on expression of surfactant apoproteins in cultured adult rat alveolar type II cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Feb;2(2):183–192. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/2.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon J. M., Mason R. J., Jennings S. D. Functional differentiation of alveolar type II epithelial cells in vitro: effects of cell shape, cell-matrix interactions and cell-cell interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 12;931(2):143–156. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90200-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelley S. A., Balis J. U., Paciga J. E., Knuppel R. A., Ruffolo E. H., Bouis P. J., Jr Surfactant "apoproteins" in human amniotic fluid: an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the prenatal assessment of lung maturity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1982 Sep 15;144(2):224–228. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(82)90632-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiffer K., Hawgood S., Düzgünes N., Goerke J. Interactions of the low molecular weight group of surfactant-associated proteins (SP 5-18) with pulmonary surfactant lipids. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2689–2695. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snead M. L., Luo W., Oliver P., Nakamura M., Don-Wheeler G., Bessem C., Bell G. I., Rall L. B., Slavkin H. C. Localization of epidermal growth factor precursor in tooth and lung during embryonic mouse development. Dev Biol. 1989 Aug;134(2):420–429. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90114-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J. M., Kwun J. E., O'Brien J. A., Rosenfeld C. R., Odom M. J. The concentration of the 35-kDa surfactant apoprotein in amniotic fluid from normal and diabetic pregnancies. Pediatr Res. 1988 Dec;24(6):728–734. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198812000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J. M., Mendelson C. R. Insulin inhibits the accumulation of the major lung surfactant apoprotein in human fetal lung explants maintained in vitro. Endocrinology. 1987 Apr;120(4):1250–1257. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-4-1250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J. M., Rodgers H. F., Nielsen H. C., O'Brien J. A. Uptake of the 35 kDa major surfactant apoprotein (SP-A) by neonatal rabbit lung tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Mar 14;1002(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahlman M. T., Orth D. N., Gray M. E. Immunocytochemical localization of epidermal growth factor in the developing human respiratory system and in acute and chronic lung disease in the neonate. Lab Invest. 1989 Apr;60(4):539–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Curstedt T., Grossmann G., Kobayashi T., Nilsson R., Nohara K., Robertson B. The role of the low-molecular weight (less than or equal to 15,000 daltons) apoproteins of pulmonary surfactant. Eur J Respir Dis. 1986 Nov;69(5):336–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Fujita Y., Kogishi K. Reconstitution of tubular myelin from synthetic lipids and proteins associated with pig pulmonary surfactant. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Jul;140(1):75–81. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Robertson B., Fujita Y., Grossmann G. Respiratory failure in mice caused by a hybridoma making antibodies to the 15 kDa surfactant apoprotein. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1988 May;32(4):283–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1988.tb02730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi A., Fujiwara T. Proteolipid in bovine lung surfactant: its role in surfactant function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):527–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Takei T., Aiba T., Masuda K., Kiuchi A., Fujiwara T. Development of synthetic lung surfactants. J Lipid Res. 1986 May;27(5):475–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Takei T., Kanazawa Y. Lung surfactants. II. Effects of fatty acids, triacylglycerols and protein on the activity of lung surfactant. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1983 Nov;31(11):4100–4109. doi: 10.1248/cpb.31.4100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenner A. J., Robinson S. L., Borchelt J., Wright J. R. Human pulmonary surfactant protein (SP-A), a protein structurally homologous to C1q, can enhance FcR- and CR1-mediated phagocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13923–13928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torday J. S., Nielsen H. C. The sex difference in fetal lung surfactant production. Exp Lung Res. 1987;12(1):1–19. doi: 10.3109/01902148709068811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Golde L. M., Batenburg J. J., Robertson B. The pulmonary surfactant system: biochemical aspects and functional significance. Physiol Rev. 1988 Apr;68(2):374–455. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1988.68.2.374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeer C. Gamma-carboxyglutamate-containing proteins and the vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 15;266(3):625–636. doi: 10.1042/bj2660625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss T., Eistetter H., Schäfer K. P., Engel J. Macromolecular organization of natural and recombinant lung surfactant protein SP 28-36. Structural homology with the complement factor C1q. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90448-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. R., Williams M. C., Benson B. Immunocytochemical localization of the major surfactant apoproteins in type II cells, Clara cells, and alveolar macrophages of rat lung. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 Sep;34(9):1137–1148. doi: 10.1177/34.9.2426341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin R., Seaton M., Martin L. F. No evidence for vitamin K-dependent carboxylation of canine surfactant apoproteins, 28-36 kDa. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 15;252(3):851–856. doi: 10.1042/bj2520851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warr R. G., Hawgood S., Buckley D. I., Crisp T. M., Schilling J., Benson B. J., Ballard P. L., Clements J. A., White R. T. Low molecular weight human pulmonary surfactant protein (SP5): isolation, characterization, and cDNA and amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7915–7919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver T. E., Hull W. M., Ross G., Whitsett J. A. In vitro acetylation of rat pulmonary surfactant-associated glycoprotein(s) A primary translation products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Feb 14;869(3):330–336. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver T. E. Pulmonary surfactant-associated proteins. Gen Pharmacol. 1988;19(3):361–368. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(88)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver T. E., Ross G., Daugherty C., Whitsett J. A. Synthesis of surfactant-associated protein, 35,000 daltons, in fetal lung. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Aug;61(2):694–700. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.2.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver T. E., Sarin V. K., Sawtell N., Hull W. M., Whitsett J. A. Identification of surfactant proteolipid SP-B in human surfactant and fetal lung. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Aug;65(2):982–987. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.2.982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver T. E., Whitsett J. A., Hull W. M., Ross G. Identification of canine pulmonary surfactant-associated glycoprotein A precursors. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Jun;58(6):2091–2095. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.58.6.2091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. T., Damm D., Miller J., Spratt K., Schilling J., Hawgood S., Benson B., Cordell B. Isolation and characterization of the human pulmonary surfactant apoprotein gene. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):361–363. doi: 10.1038/317361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Hull W., Ross G., Weaver T. Characteristics of human surfactant-associated glycoproteins A. Pediatr Res. 1985 May;19(5):501–508. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198505000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Ohning B. L., Ross G., Meuth J., Weaver T., Holm B. A., Shapiro D. L., Notter R. H. Hydrophobic surfactant-associated protein in whole lung surfactant and its importance for biophysical activity in lung surfactant extracts used for replacement therapy. Pediatr Res. 1986 May;20(5):460–467. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198605000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Pilot T., Clark J. C., Weaver T. E. Induction of surfactant protein in fetal lung. Effects of cAMP and dexamethasone on SAP-35 RNA and synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5256–5261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Ross G., Weaver T., Rice W., Dion C., Hull W. Glycosylation and secretion of surfactant-associated glycoprotein A. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15273–15279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Weaver T. E., Clark J. C., Sawtell N., Glasser S. W., Korfhagen T. R., Hull W. M. Glucocorticoid enhances surfactant proteolipid Phe and pVal synthesis and RNA in fetal lung. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15618–15623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Weaver T. E., Lieberman M. A., Clark J. C., Daugherty C. Differential effects of epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor-beta on synthesis of Mr = 35,000 surfactant-associated protein in fetal lung. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7908–7913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Weaver T., Hull W., Ross G., Dion C. Synthesis of surfactant-associated glycoprotein A by rat type II epithelial cells. Primary translation products and post-translational modification. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Apr 5;828(2):162–171. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. C., Benson B. J. Immunocytochemical localization and identification of the major surfactant protein in adult rat lung. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Feb;29(2):291–305. doi: 10.1177/29.2.7019304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. C., Hawgood S., Schenk D. B., Lewicki J., Phelps M. N., Benson B. Monoclonal antibodies to surfactant proteins SP28-36 label canine type II and nonciliated bronchiolar cells by immunofluorescence. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Feb;137(2):399–405. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.2.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintergerst E., Manz-Keinke H., Plattner H., Schlepper-Schäfer J. The interaction of a lung surfactant protein (SP-A) with macrophages is mannose dependent. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;50(2):291–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. R., Borchelt J. D., Hawgood S. Lung surfactant apoprotein SP-A (26-36 kDa) binds with high affinity to isolated alveolar type II cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5410–5414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. R., Clements J. A. Metabolism and turnover of lung surfactant. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Aug;136(2):426–444. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.2.426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. R., Wager R. E., Hamilton R. L., Huang M., Clements J. A. Uptake of lung surfactant subfractions into lamellar bodies of adult rabbit lungs. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Mar;60(3):817–825. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.3.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. R., Wager R. E., Hawgood S., Dobbs L., Clements J. A. Surfactant apoprotein Mr = 26,000-36,000 enhances uptake of liposomes by type II cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2888–2894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu J. J., Richardson C., Ford C., Spencer T., Yao L. J., Mackie G., Hammond G., Possmayer F. Isolation and characterization of the cDNA for pulmonary surfactant-associated protein-B (SP-B) in the rabbit. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 14;160(1):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91659-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Ikegami M., Jobe A. H. Effects of surfactant subfractions on preterm rabbit lung function. Pediatr Res. 1990 Jun;27(6):592–598. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199006000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. L., Wright J. R., Clements J. A. Cellular uptake and processing of surfactant lipids and apoprotein SP-A by rat lung. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Mar;66(3):1336–1342. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.3.1336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. H., Chung W., Possmayer F. Structural relationship between the two small hydrophobic apoproteins in bovine pulmonary surfactant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Sep 11;1005(1):93–96. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. H., Possmayer F. Comparative studies on the biophysical activities of the low-molecular-weight hydrophobic proteins purified from bovine pulmonary surfactant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Aug 12;961(3):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deMello D. E., Chi E. Y., Doo E., Lagunoff D. Absence of tubular myelin in lungs of infants dying with hyaline membrane disease. Am J Pathol. 1987 Apr;127(1):131–139. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deMello D. E., Phelps D. S., Patel G., Floros J., Lagunoff D. Expression of the 35kDa and low molecular weight surfactant-associated proteins in the lungs of infants dying with respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jun;134(6):1285–1293. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Baelen H., Vandoren G., de Moor P. Concentration of transcortin in the pregnant rat and its foetuses. J Endocrinol. 1977 Dec;75(3):427–431. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0750427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


