Abstract
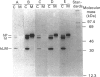
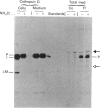
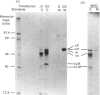
The segregation of human cathepsin D, studied in baby-hamster kidney cells (BHK) transfected with human cathepsin D cDNA and compared with that of hamster cathepsin D in the same cells, showed that, in cells that expressed human cathepsin D at a low rate, most of the enzyme remained intracellular. In contrast, when the enzyme was expressed at a high rate, most was secreted. The segregation was examined with an anti-(human cathepsin D) antibody that reacted with the human enzyme exclusively and an anti-(rat cathepsin D) antibody that reacted with both enzymes. In one protocol the cells were metabolically labelled and the two antibodies were used in sequence to precipitate the enzymes from extracts of cells and medium. High expression of the human enzyme did not interfere with the segregation of hamster cathepsin D. In another protocol the activity of cathepsin D in cells and medium was measured before and after titration with anti-(human cathepsin D) antiserum. Human cathepsin D was found predominantly in the medium, and hamster cathepsin D mainly in the cells. In the presence of 10 mM-NH4Cl the intracellular segregation of hamster cathepsin D was strongly inhibited, while the segregation of human cathepsin D was only slightly diminished. In BHK cells, at least two systems participate in the sorting of the two cathepsins, one of them being rather insensitive to NH4Cl.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conner G. E. Isolation of procathepsin D from mature cathepsin D by pepstatin affinity chromatography. Autocatalytic proteolysis of the zymogen form of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1989 Oct 15;263(2):601–604. doi: 10.1042/bj2630601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner G. E., Udey J. A., Pinto C., Sola J. Nonhuman cells correctly sort and process the human lysosomal enzyme cathepsin D. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3530–3533. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cully J., Harrach B., Hauser H., Harth N., Robenek H., Nagata S., Hasilik A. Synthesis and localization of myeloperoxidase protein in transfected BHK cells. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Feb;180(2):440–450. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong J. M., Prence E. M., Sahagian G. G. Mechanism for selective secretion of a lysosomal protease by transformed mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7377–7383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson A. H. Biosynthesis of lysosomal endopeptidases. J Cell Biochem. 1989 May;40(1):31–41. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240400104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson A. H., Blobel G. Early events in the biosynthesis of the lysosomal enzyme cathepsin D. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 10;254(23):11771–11774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust P. L., Wall D. A., Perara E., Lingappa V. R., Kornfeld S. Expression of human cathepsin D in Xenopus oocytes: phosphorylation and intracellular targeting. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):1937–1945. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gieselmann V., Hasilik A., von Figura K. Processing of human cathepsin D in lysosomes in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3215–3220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grässel S., Röling A., Hasilik A. Immunoprecipitation of labeled antigens with Eupergit C1Z. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jul;180(1):72–78. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90089-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasilik A., Neufeld E. F. Biosynthesis of lysosomal enzymes in fibroblasts. Phosphorylation of mannose residues. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4946–4950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasilik A., Neufeld E. F. Biosynthesis of lysosomal enzymes in fibroblasts. Synthesis as precursors of higher molecular weight. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4937–4945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasilik A., von Figura K., Conzelmann E., Nehrkorn H., Sandhoff K. Lysosomal enzyme precursors in human fibroblasts. Activation of cathepsin D precursor in vitro and activity of beta-hexosaminidase A precursor towards ganglioside GM2. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jul;125(2):317–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06685.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentze M., Hasilik A., von Figura K. Enhanced degradation of cathepsin D synthesized in the presence of the threonine analog beta-hydroxynorvaline. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Apr;230(1):375–382. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horst M., Hasilik A. Expression and maturation of human cathepsin D in baby-hamster kidney cells. Biochem J. 1991 Jan 15;273(Pt 2):355–361. doi: 10.1042/bj2730355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S. Trafficking of lysosomal enzymes. FASEB J. 1987 Dec;1(6):462–468. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.6.3315809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyle J. W., Nolan C. M., Oshima A., Sly W. S. Expression of human cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor cDNA in receptor-negative mouse P388D1 cells following gene transfer. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16230–16235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. J., Nathans D. Proliferin secreted by cultured cells binds to mannose 6-phosphate receptors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3521–3527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller O. T., Little L. E., Miller A. L., Lozzio C. B., Shows T. B. I-cell disease and pseudo-Hurler polydystrophy: heterozygote detection and characteristics of the altered N-acetyl-glucosamine-phosphotransferase in genetic variants. Clin Chim Acta. 1985 Aug 30;150(3):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(85)90242-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musi M., Tessitore L., Bonelli G., Kazakova O. V., Baccino F. M. Changes in rat liver immunoreactive cathepsin D after cycloheximide. Biochem Int. 1985 Feb;10(2):283–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura Y., Higaki M., Kato K. Identification of a precursor form of cathepsin D in microsomal lumen: characterization of enzymatic activation and proteolytic. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 14;148(1):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91115-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima A., Kyle J. W., Miller R. D., Hoffmann J. W., Powell P. P., Grubb J. H., Sly W. S., Tropak M., Guise K. S., Gravel R. A. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of cDNA for human beta-glucuronidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):685–689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell P. P., Kyle J. W., Miller R. D., Pantano J., Grubb J. H., Sly W. S. Rat liver beta-glucuronidase. cDNA cloning, sequence comparisons and expression of a chimeric protein in COS cells. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 1;250(2):547–555. doi: 10.1042/bj2500547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puizdar V., Turk V. Cathepsinogen D: characterization and activation to cathepsin D and inhibitory peptides. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 28;132(2):299–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochefort H., Capony F., Garcia M., Cavaillès V., Freiss G., Chambon M., Morisset M., Vignon F. Estrogen-induced lysosomal proteases secreted by breast cancer cells: a role in carcinogenesis? J Cell Biochem. 1987 Sep;35(1):17–29. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240350103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G., Kreibich G., Popov D., Kato K., Sabatini D. D. Biosynthesis of lysosomal hydrolases: their synthesis in bound polysomes and the role of co- and post-translational processing in determining their subcellular distribution. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):135–143. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C., Gieselmann V., Kreysing J., Schmidt B., Pohlmann R., Waheed A., Meyer H. E., O'Brien J. S., von Figura K. Cloning and expression of human arylsulfatase A. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1252–1259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang J., Wong R. N. Evolution in the structure and function of aspartic proteases. J Cell Biochem. 1987 Jan;33(1):53–63. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240330106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Figura K., Hasilik A. Lysosomal enzymes and their receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:167–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.001123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]