Abstract
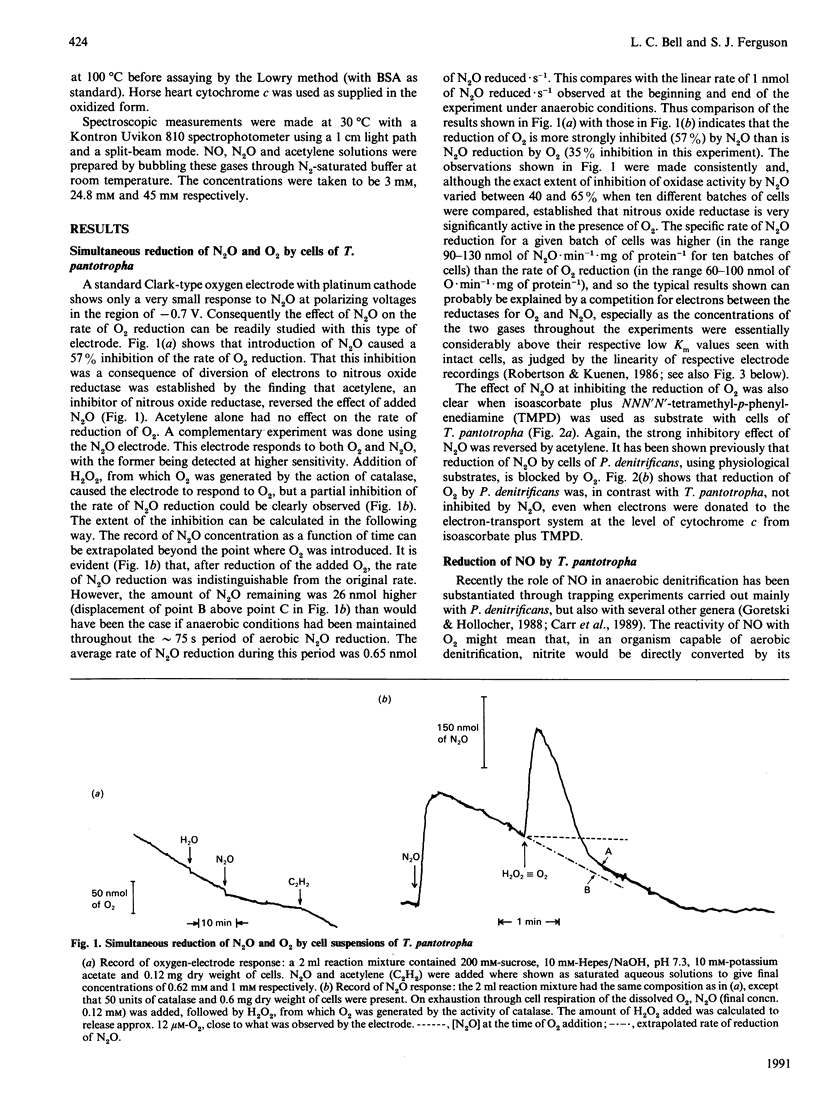
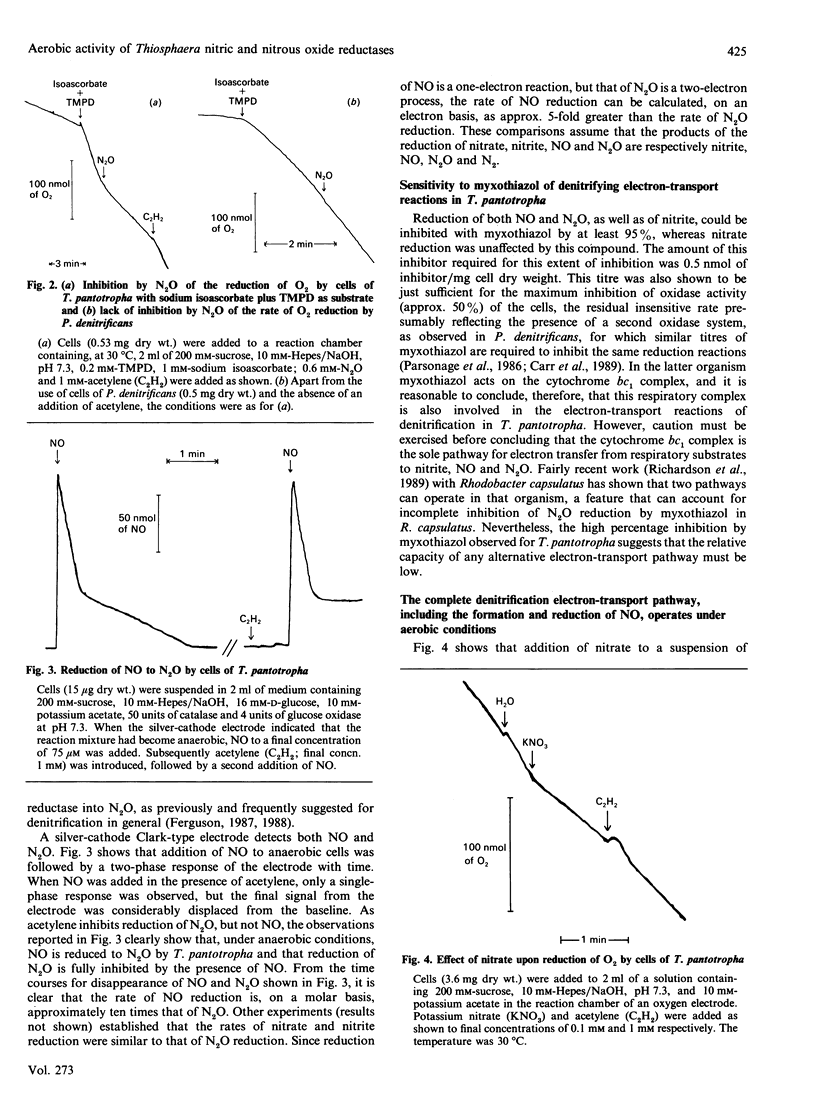
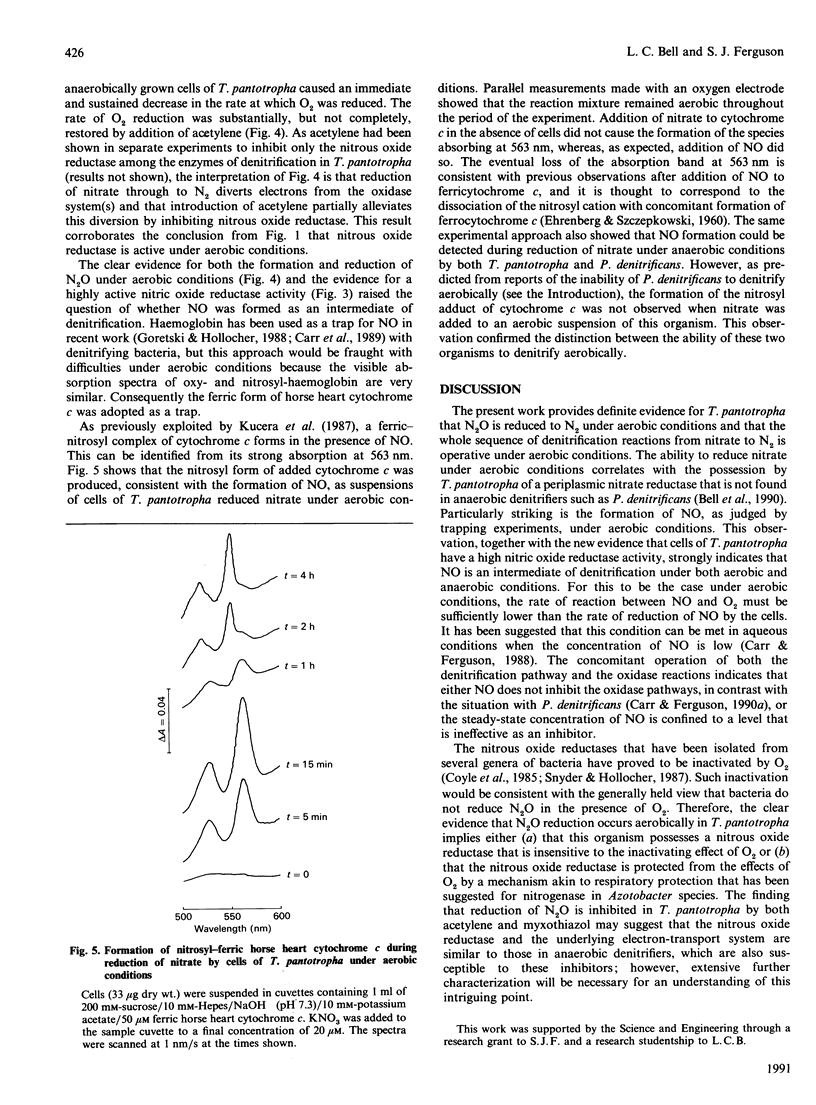
Use of Clark-type electrodes has shown that, in cells of Thiosphaera pantotropha, the nitrous oxide reductase is active in the presence of O2, and that the two gases involved (N2O, O2) are reduced simultaneously, but with mutual inhibition. Reduction of nitrate, or nitrite, to N2O under aerobic conditions involves NO as an intermediate, as judged by trapping experiments with the ferric form of extracellular horse heart cytochrome c and the demonstration that the cells possess a nitric oxide reductase activity. The overall conversion of nitrate to N2, the process of denitrification, under aerobic conditions, is thus not prevented by reaction of NO with O2 and depends upon a nitrous oxide reductase system which differs from that in other organisms by being neither directly inhibited nor inactivated by O2.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alefounder P. R., Ferguson S. J. Electron transport-linked nitrous oxide synthesis and reduction by Paracoccus denitrificans monitored with an electrode. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Feb 11;104(3):1149–1155. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91370-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell L. C., Richardson D. J., Ferguson S. J. Periplasmic and membrane-bound respiratory nitrate reductases in Thiosphaera pantotropha. The periplasmic enzyme catalyzes the first step in aerobic denitrification. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 4;265(1-2):85–87. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80889-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr G. J., Ferguson S. J. Nitric oxide formed by nitrite reductase of Paracoccus denitrificans is sufficiently stable to inhibit cytochrome oxidase activity and is reduced by its reductase under aerobic conditions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 15;1017(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90178-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr G. J., Ferguson S. J. The nitric oxide reductase of Paracoccus denitrificans. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):423–429. doi: 10.1042/bj2690423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr G. J., Page M. D., Ferguson S. J. The energy-conserving nitric-oxide-reductase system in Paracoccus denitrificans. Distinction from the nitrite reductase that catalyses synthesis of nitric oxide and evidence from trapping experiments for nitric oxide as a free intermediate during denitrification. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Feb 15;179(3):683–692. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle C. L., Zumft W. G., Kroneck P. M., Körner H., Jakob W. Nitrous oxide reductase from denitrifying Pseudomonas perfectomarina. Purification and properties of a novel multicopper enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Dec 16;153(3):459–467. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. J., Lloyd D., Boddy L. The effect of oxygen on denitrification in Paracoccus denitrificans and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Sep;135(9):2445–2451. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-9-2445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goretski J., Hollocher T. C. Trapping of nitric oxide produced during denitrification by extracellular hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2316–2323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiss B., Frunzke K., Zumft W. G. Formation of the N-N bond from nitric oxide by a membrane-bound cytochrome bc complex of nitrate-respiring (denitrifying) Pseudomonas stutzeri. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3288–3297. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3288-3297.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John P. Aerobic and anaerobic bacterial respiration monitored by electrodes. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Jan;98(1):231–238. doi: 10.1099/00221287-98-1-231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson D. J., McEwan A. G., Jackson J. B., Ferguson S. J. Electron transport pathways to nitrous oxide in Rhodobacter species. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Nov 20;185(3):659–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson L. A., Kuenen J. G. Aerobic denitrification--old wine in new bottles? Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1984;50(5-6):525–544. doi: 10.1007/BF02386224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. W., Hollocher T. C. Purification and some characteristics of nitrous oxide reductase from Paracoccus denitrificans. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6515–6525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafiriou O. C., Hanley Q. S., Snyder G. Nitric oxide and nitrous oxide production and cycling during dissimilatory nitrite reduction by Pseudomonas perfectomarina. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5694–5699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


